FT2232调试记录
- (1)获取当前连接的FTDI设备通道个数:
- (2)获取当前连接的设备通道的信息:
- (3)配置SPI的通道:
- (4)如何设置GPIO:
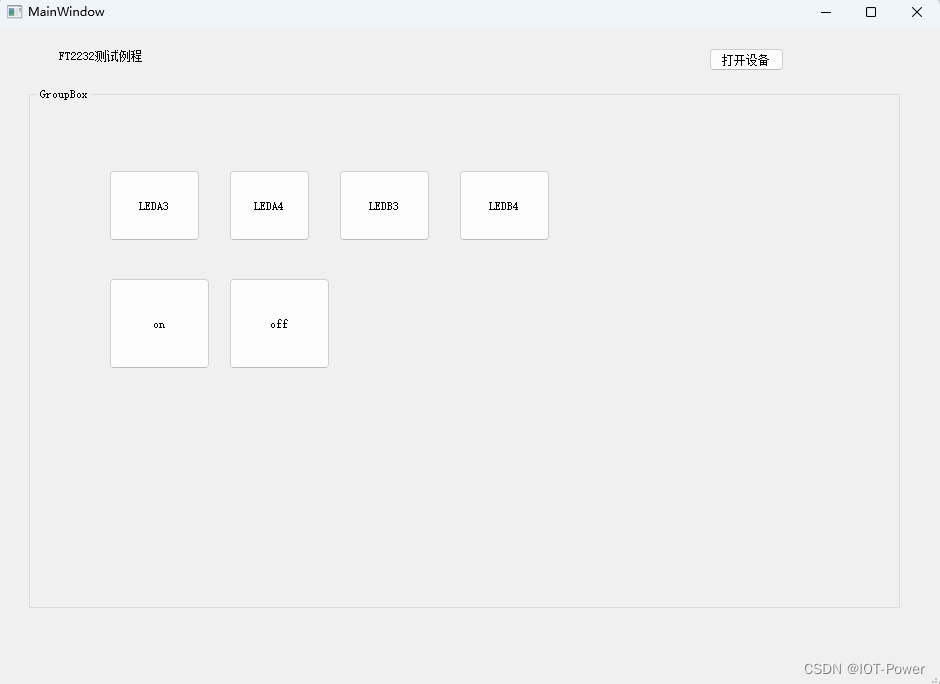
- (5)DEMO测试:
#参考文档:
(1)包含了FT2xxx和IIC SPI的操作手册。
相关文档:https://ftdichip.com/document/programming-guides/
(2)包含了MPSSE和MCU主机总线仿真模式的命令处理器。
AN108:Command Processor for MPSSE and MCU Host Bus Emulation Modes.
(3)相关博客:FT2232H编程流程分析
(1)获取当前连接的FTDI设备通道个数:
status = SPI_GetNumChannels((DWORD *)&channels);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
qDebug("Number of available SPI channels = %d\n",channels);
(2)获取当前连接的设备通道的信息:
FT2232 有两个通道,使用SPI_GetChannelInfo 获取通道信息。
FT_DEVICE_LIST_INFO_NODE devList[2];
status = SPI_GetChannelInfo(0,&devList[0]);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
printf("Information on channel number %d:\n",0);
/* print the dev info */
qDebug(" Flags=0x%x\n",devList[0].Flags);
qDebug(" Type=0x%x\n",devList[0].Type);
qDebug(" ID=0x%x\n",devList[0].ID);
qDebug(" LocId=0x%x\n",devList[0].LocId);
qDebug(" SerialNumber=%s\n",devList[0].SerialNumber);
qDebug(" Description=%s\n",devList[0].Description);
qDebug(" ftHandle=0x%x\n",devList[0].ftHandle);/*is 0 unless open*/
status = SPI_GetChannelInfo(1,&devList[1]);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
printf("Information on channel number %d:\n",1);
/* print the dev info */
qDebug(" Flags=0x%x\n",devList[1].Flags);
qDebug(" Type=0x%x\n",devList[1].Type);
qDebug(" ID=0x%x\n",devList[1].ID);
qDebug(" LocId=0x%x\n",devList[1].LocId);
qDebug(" SerialNumber=%s\n",devList[1].SerialNumber);
qDebug(" Description=%s\n",devList[1].Description);
qDebug(" ftHandle=0x%x\n",devList[1].ftHandle);/*is 0 unless open*/
Information on channel number 0:
Flags=0x2
Type=0x6
ID=0x4036010
LocId=0x231
SerialNumber=A
Description=Dual RS232-HS A
ftHandle=0x0
status ok!
Information on channel number 1:
Flags=0x2
Type=0x6
ID=0x4036010
LocId=0x232
SerialNumber=B
Description=Dual RS232-HS B
ftHandle=0x0
(3)配置SPI的通道:
如下举例为SPI操作通道 A (0):
uint32_t channels;
channelConf.ClockRate = 5000;
channelConf.LatencyTimer= 255;
channelConf.configOptions = SPI_CONFIG_OPTION_MODE0 | SPI_CONFIG_OPTION_CS_DBUS3;
channelConf.Pin = 0x00000000;/*FinalVal-FinalDir-InitVal-InitDir (for dir 0=in, 1=out)*/
status = SPI_GetNumChannels((DWORD *)&channels);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
qDebug("Number of available SPI channels = %d\n",channels);
/* Open the first available channel */
status = SPI_OpenChannel(0,&ftHandle[0]);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
qDebug("\nhandle=0x%x status=0x%x\n",ftHandle[0],status);
status = SPI_InitChannel(ftHandle[0],&channelConf);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
********
status = SPI_CloseChannel(ftHandle[0]);
(4)如何设置GPIO:
方式一:
libmpsse 库中提供的接口,FT_WriteGPIO,只能支持ACBUS(BCBUS) 即高字节操作。
FT_STATUS FT_WriteGPIO(FT_HANDLE handle, uint8 dir, uint8 value)
dir: 0 out 1 in
value:0 low 1 high
FT_STATUS FT_ReadGPIO(FT_HANDLE handle, uint8 *value)
控制引脚:AC3 AC4 BC3 BC4
FT2232H有两个MPSSE通道,每个通道带有两个8位端口:
即ADBUS和ACBUS,BDBUS和BCBUS.
其中:
【低字节】 ADBUS(BDBUS)用于同步串行通信(I2C/SPI/JTAG)
【高字节】 ACBUS(BCBUS)可以免费用作GPIO
初始化时候打开channel:
/* Open the first available channel */
status = SPI_OpenChannel(0,&ftHandle[0]);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
qDebug("\nhandle=0x%x status=0x%x\n",ftHandle[0],status);
status = SPI_InitChannel(ftHandle[0],&channelConf);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
// status = SPI_CloseChannel(ftHandle[0]);
/* Open the first available channel */
status = SPI_OpenChannel(1,&ftHandle[1]);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
qDebug("\nhandle=0x%x status=0x%x\n",ftHandle[1],status);
status = SPI_InitChannel(ftHandle[1],&channelConf);
APP_CHECK_STATUS(status);
// status = SPI_CloseChannel(ftHandle[1]);
void bsp_ft2232::bsp_ledA(enum typePinA chl, bool highlow)
{
uint8_t val=0;
FT_ReadGPIO(ftHandle[0],&val);
FT_WriteGPIO(ftHandle[0],gpio_setting[0], ( highlow ? (val|(0x1<<(chl)) ) : (val&(~(0x1<<(chl))) ) ) );
}
void bsp_ft2232::bsp_ledB(enum typePinB chl, bool highlow)
{
uint8_t val=0;
FT_ReadGPIO(ftHandle[1],&val);
FT_WriteGPIO(ftHandle[1],gpio_setting[1], ( highlow ? (val|(0x1<<(chl)) ) : (val&(~(0x1<<(chl))) ) ) );
}
方式二:
使用ftd2xx 库中提供的接口。 调用FT_Write 库。
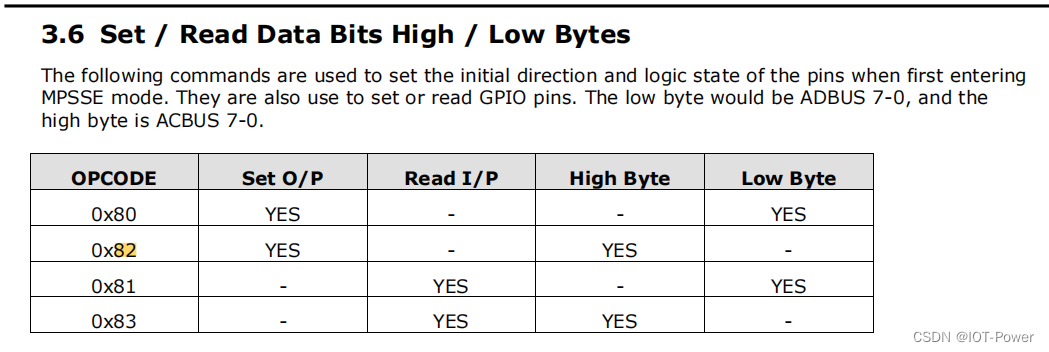
3.6.1 Set Data bits LowByte
0x80, 0xValue, 0xDirection
This will setup the direction of the first 8 lines and force a value on the bits that are set as output. A 1 in
the Direction byte will make that bit an output.
3.6.2 Set Data bits High Byte
0x82, 0xValue, 0xDirection
This will setup the direction of the high 8 lines and force a value on the bits that are set as output. A 1 in
the Direction byte will make that bit an output.
3.6.3 Read Data bits LowByte
0x81,
This will read the current state of the first 8 pins and send back 1 byte.
3.6.4 Read Data bits HighByte
0x83,
This will read the current state of the high 8 pins and send back 1 byte.
void bsp_ft2232::bsp_ledtest(bool highlow)
{
if(highlow)
{
dwNumBytesToSend = 0;
byOutputBuffer[dwNumBytesToSend++] = 0x82;
byOutputBuffer[dwNumBytesToSend++] = 0xFF;
byOutputBuffer[dwNumBytesToSend++] = 0xFF;
status = FT_Write(ftHandle[0], byOutputBuffer, dwNumBytesToSend, &dwNumBytesSent);
qDebug("on %d\r\n",dwNumBytesSent);
dwNumBytesSent=0;
dwNumBytesToSend = 0;
}else{
dwNumBytesToSend = 0;
byOutputBuffer[dwNumBytesToSend++] = 0x82;
byOutputBuffer[dwNumBytesToSend++] = 0x00;
byOutputBuffer[dwNumBytesToSend++] = 0xFF;
status = FT_Write(ftHandle[0], byOutputBuffer, dwNumBytesToSend, &dwNumBytesSent);
qDebug("off %d\r\n",dwNumBytesSent);
dwNumBytesSent=0;
dwNumBytesToSend = 0;
}
}
(5)DEMO测试: