stack和queue基本使用
- stack
- queue
- priority_queue
- stack和queue容器底层的默认容器:deque
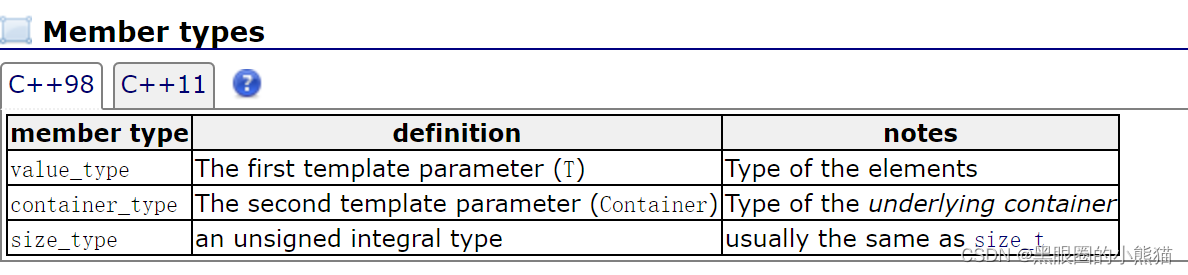
stack
stack是一种容器适配器(容器适配器可以将一种接口转为用户需要的另一种接口,如将vector、list的接口封装转成用户需要的stack的接口),在STL中stack并没有被划分到容器的行列,数据进出方式为后进先出,只能从容器的一端插入和删除数据,如果不进行指定,其底层容器默认是deque。
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> > class stack;
其基本使用也比较简单:
1.构造空栈:
explicit stack (const container_type& ctnr = container_type());
2.取栈顶元素:
value_type& top();
const value_type& top() const;
3.将元素压入栈中:
void push (const value_type& val);
4.将元素从栈中弹出:
void pop();
5.检测栈是否为空:
bool empty() const;
6.返回栈中元素个数:
size_type size() const;
7.交换两个栈
void swap (stack& x) noexcept(/*see below*/);
//Exchanges the contents of the container adaptor (*this) by those of x.
//This member function calls the non-member function swap (unqualified) to swap the underlying containers.
//The noexcept specifier matches the swap operation on the underlying container.
//将容器适配器 (*this) 的内容交换为 x 的内容。
//此成员函数调用非成员函数 swap (unqualified) 来交换基础容器。
//noexcept 说明符与基础容器上的交换操作匹配。
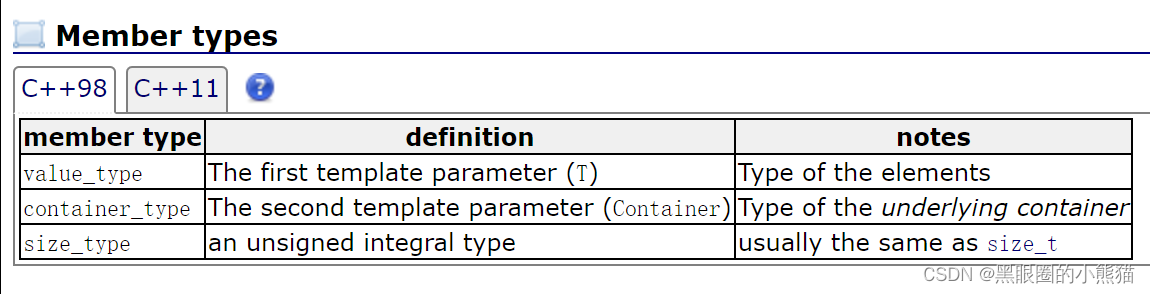
queue
queue也是一种容器适配器,在STL中也没有被划分到容器的行列,数据进出方式为先进先出,从容器的一端插入数据,在另一端提取数据。如果不进行指定,其底层容器默认也是deque。
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> > class queue;
其使用也较为简单:
1.构造空队列:
explicit queue (const container_type& ctnr = container_type());
2.返回队头元素的引用:
value_type& front();
const value_type& front() const;
3.返回队尾元素的引用:
value_type& back();
const value_type& back() const;
4.在队尾将元素入列:
void push (const value_type& val);
5.队头元素出列;
void pop();
6.检验队列是否为空:
bool empty() const;
7.返回队列元素个数:
size_type size() const;
8.交换两个队列:
void swap (queue& x) noexcept(/*see below*/);
//Exchanges the contents of the container adaptor (*this) by those of x.
//This member function calls the non-member function swap (unqualified) to swap the underlying containers.
//The noexcept specifier matches the swap operation on the underlying container.
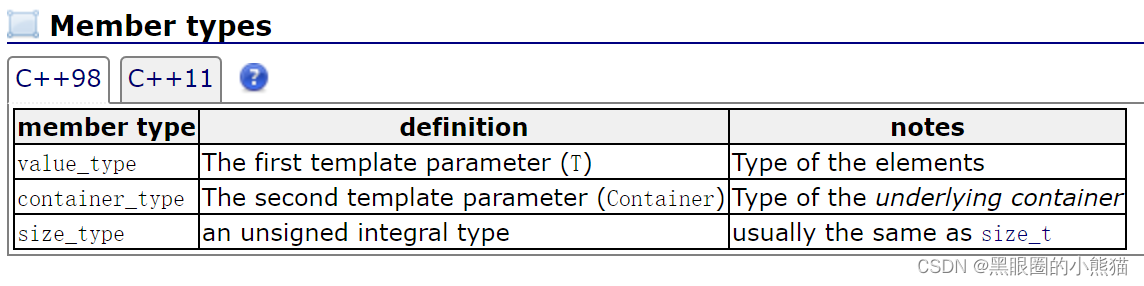
priority_queue
在头文件<queue> 中,除queue外,还有一个容器适配器:priority_queue,这是一个优先级队列,可以将其当作堆来看待,其底层容器默认是vector(因为该容器其实是一个堆,所以其底层容器必须要可以用下标[ ]进行访问)。
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>,class Compare = less<typename Container::value_type> > class priority_queue;
//typename Container::value_type可以当成T看待
其用法依旧很简单:
1.构造空的优先级队列:
explicit priority_queue (const Compare& comp = Compare(),
const Container& ctnr = Container());
2.使用迭代器构造队列:
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue (InputIterator first, InputIterator last,const Compare& comp = Compare(),const Container& ctnr = Container());
3.返回优先级队列中最大元素/最小元素(默认是最大元素),即返回堆顶元素:
const value_type& top() const;
4.在优先级队列中插入元素:
void push (const value_type& val);
5.删除优先级队列中最大元素/最小元素(默认是最大元素),即删除堆顶元素:
void pop();
6.检验优先级队列是否为空:
bool empty() const;
7.返回优先级队列元素个数;
size_type size() const;
8.交换两个优先级队列;
void swap (priority_queue& x) noexcept (/*see below*/);
//Exchanges the contents of the container adaptor by those of x, swapping both the underlying container value and their comparison function using the corresponding swap non-member functions (unqualified).
//This member function has a noexcept specifier that matches the combined noexcept of the swap operations on the underlying container and the comparison functions.
stack和queue容器底层的默认容器:deque
deque是由一小段一小段的连续空间构成的,其结构大致如下:
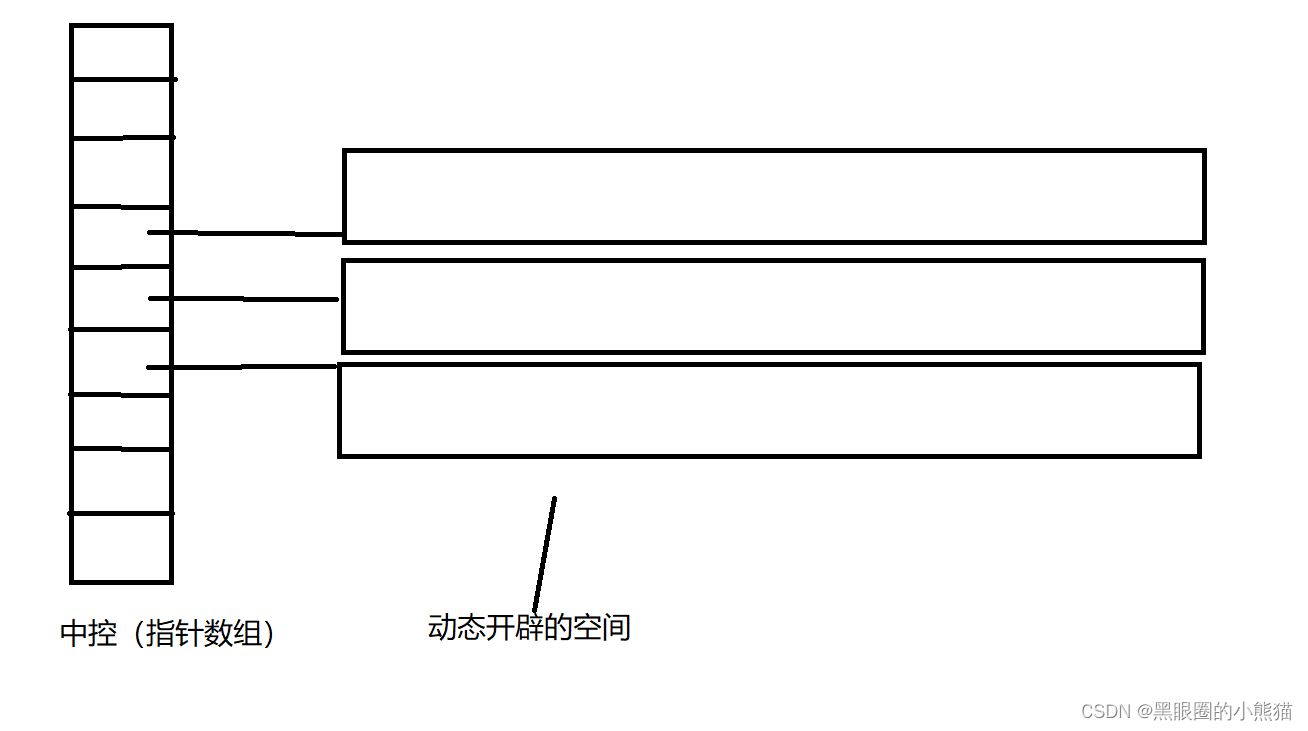
中控即指针数组从中间位置开始使用,以保证其头插头删尾删的高效性,但该结构却导致了下标访问的高效性与中间元素插入删除的高效性之间是互斥的:如果为每个指针开辟的空间大小都是相同的,那么如果需要进行下标访问时,只要简单的计算就行了,其效率可以保证,但删除和插入中间元素其效率确实极低的;如果为每个指针开辟的空间大小不同(即可以进行缩容扩容),虽然保证了中间元素删除插入的高效性,但其进行下标访问的效率就会极大下降。
总之,deque在头部插入和删除元素的效率是比vector高的,其空间利用率也比list高,其缺陷也非常明显,在遍历和中间元素插入删除效率非常低。
而stack和queue选择deque作为底层容器的原因是因为stack和queue不需要进行遍历,而且只对首尾元素进行操作,完全符合deque的优点且避开了其缺点。