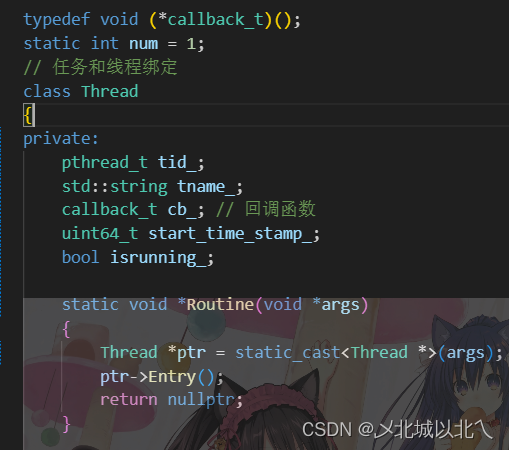
一 MyThread.hpp
#pragma once
#include<pthread.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string>
#include<ctime>
typedef void (*callback_t)();
static int num = 1;
//任务和线程绑定
class Thread
{
static void* Routine(void *args)
{
Thread* ptr = static_cast<Thread*>(args);
ptr->Entry();
return nullptr;
}
public:
Thread(callback_t cb)
:cb_(cb),tname_(""),start_time_stamp_(0),isrunning_(false)
{}
~Thread()
{}
void Run()
{
tname_ = "thread-" + std::to_string(num);
start_time_stamp_ = time(nullptr);
isrunning_ = true;
pthread_create(&tid_,nullptr,Routine,this);
}
void Join()
{
pthread_join(tid_,nullptr);
isrunning_ = false;
}
void Entry()
{
cb_();
}
bool Isrunning()
{
return isrunning_;
}
std::string Name()
{
return tname_;
}
uint64_t StartTimeStamp()
{
return start_time_stamp_;
}
private:
pthread_t tid_;
std::string tname_;
callback_t cb_;//回调函数
uint64_t start_time_stamp_;
bool isrunning_;
};二 测试
#include "MyThread.hpp"
#include <vector>
void task()
{
while (1)
{
std::cout << "I am a task" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
std::vector<Thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
threads.push_back(Thread(task));
}
for (auto &t : threads)
{
t.Run();
}
for (auto &t : threads)
{
t.Join();
}
}
// int main()
// {
// Thread t1(task);
// std::cout << "name:" << t1.Name() << " time:" << t1.StartTimeStamp()
// << " isrun?? " << t1.Isrunning() << std::endl;
// t1.Run();
// std::cout << "name:" << t1.Name() << " time:" << t1.StartTimeStamp()
// << " isrun?? " << t1.Isrunning() << std::endl;
// t1.Join();
// }

![[疑难杂症2024-001] java多线程运行时遇到java.util.ConcurrentModificationException的解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d6435d6ed7e34a679d35d068216c7da4.png#pic_center)