目录
操作字符串
查询字符串
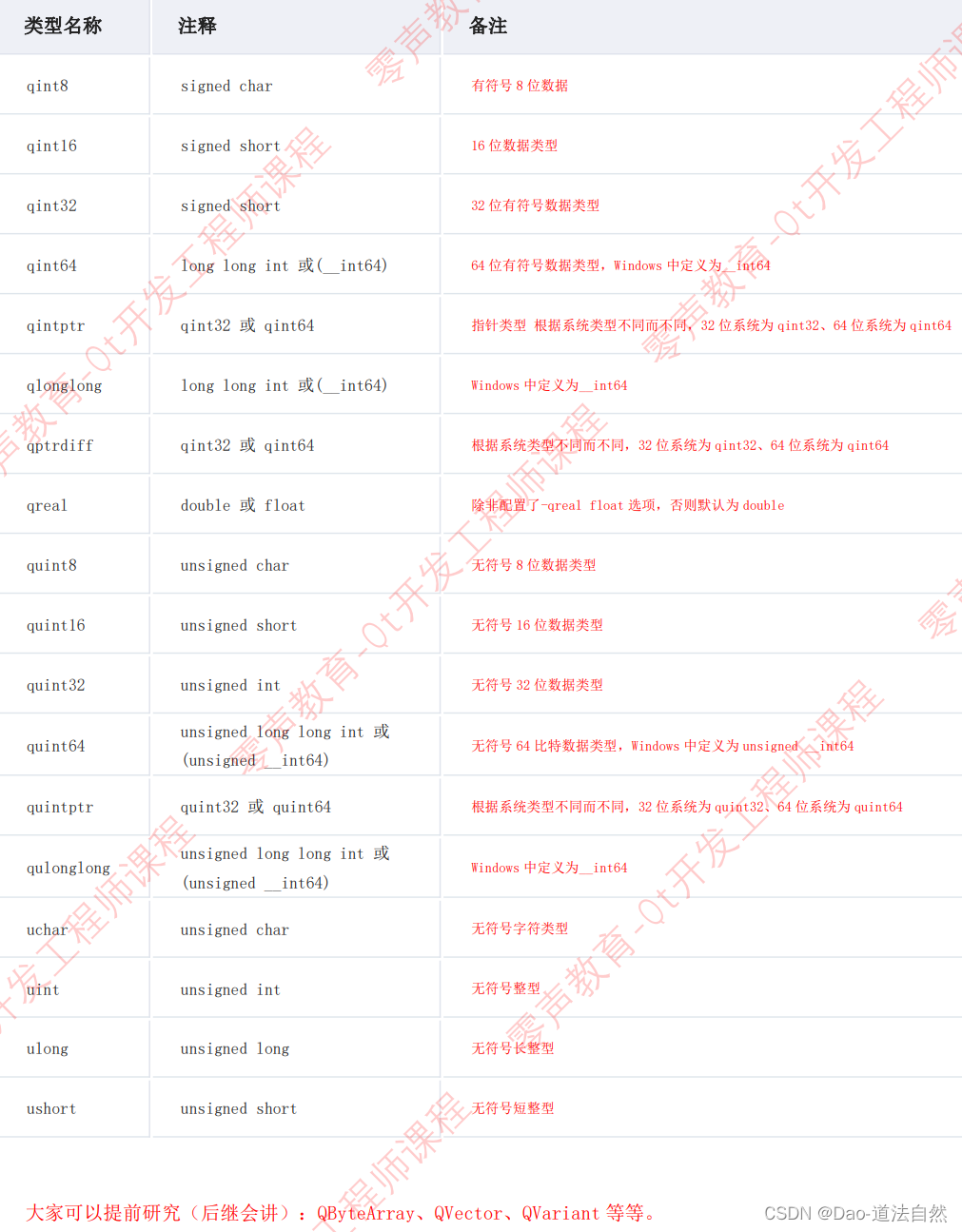
Qt 常见数据类型
操作字符串
创建一个控制台项目
(1)QString提供一个二元的 “+” 操作符,主要用于组合两个字符串。QString str1 = "Hello World' 传递给QString一个 const char* 类型的ASCII字符串 “Hello World” ,它被解释为一个典型的以 "\0" 结尾的C类型字符串
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
// 1.QString提供二元 “+” 操作符应用,功能一样 “+=”
QString str1 = "Hello";
str1 = str1 + "World";
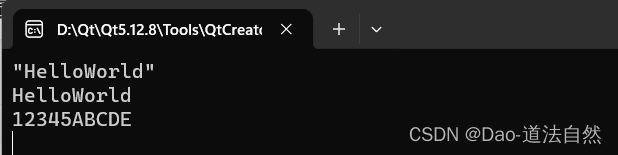
qDebug()<<str1; // 打印信息
qDebug()<<qPrintable(str1); // 去掉双引号
QString str2 = "12345";
str2+="ABCDE";
qDebug()<<qPrintable(str2);
return a.exec();
}
Qt中创建一个QCoreApplication对象的实例。
具体解释如下:
- QCoreApplication是Qt框架中的一个核心类,用于处理应用程序的事件循环和基本功能。
- a是一个QCoreApplication对象的实例,通过调用构造函数QCoreApplication(int &argc, char **argv)创建。
- argc是命令行参数的数量,通常是程序启动时通过命令行传递的参数的数量。
- argv是命令行参数的值,是一个指向字符串数组的指针,每个元素表示一个命令行参数的字符串。
通过调用exec()函数,Qt应用程序进入事件循环,开始处理用户输入、定时器事件、网络通信等各种事件,并按照信号和槽的连接关系执行相应的槽函数。
最后,通过return语句将exec()函数的返回值返回,可以在需要时获取事件循环的退出状态。
(2)QString::append() 函数具备与 “+=" 操作符同样的功能,直接在一个字符串末尾添加另一个字符串。
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
// 2.QString::append()函数
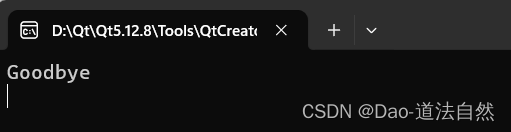
QString str1 = "Good";
QString str2 = "bye";
str1.append(str2); // str1 = "Good bye"
qDebug()<<qPrintable(str1);
return a.exec();
}
(3)组合字符串:QString::sprintf(),其实它跟 C++ 库当中 sprintf() 函数一样
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
// 3.QString::sprintf()函数
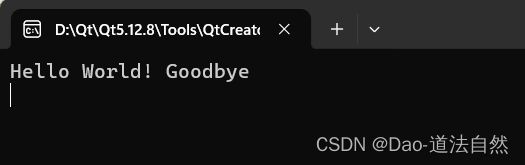
QString strtemp;
strtemp.sprintf("%s %s","Hello World!","Goodbye");
qDebug()<<qPrintable(strtemp);
return a.exec();
}
(4)字符串组合方式 QString::arg() 函数,该函数的重载可以处理多种数据类型。因为它类型齐全,同时支持 Unicode,可以改变 %n 参数顺序。
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
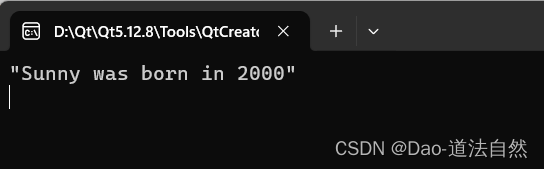
QString strTemp;
strTemp=QString("%1 was born in %2").arg("Sunny").arg(2000);
qDebug()<<strTemp;
return a.exec();
}
查询字符串
(1)函数 QString::startsWith() 判断一个字符串是否以某个字符串开头。Qt::CaseInsensitive 代表大小写不敏感;Qt::CaseSensitive 表示大小写敏感。对应关系函数 QString::endsWith().
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
QString strTemp="How are you";
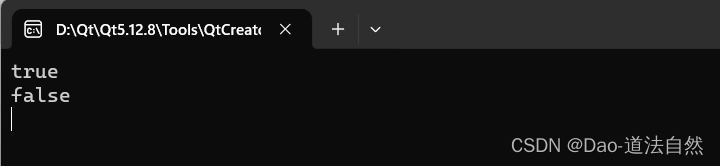
qDebug()<<strTemp.startsWith("How",Qt::CaseSensitive); // true
qDebug()<<strTemp.startsWith("are",Qt::CaseInsensitive); // false
return a.exec();
}
(2)函数QString::contains() 判断一个指定的字符串是否出现过
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
QString strTemp="How are you";
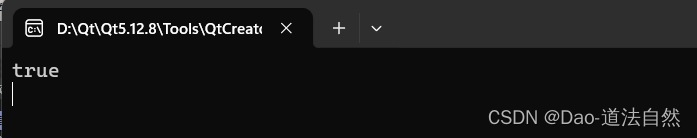
qDebug()<<strTemp.contains("How",Qt::CaseSensitive); // true
return a.exec();
}
(3)QString::toInt() 函数将字符串转换为整型数值,toDouble()/toFloat()/toLong()等等
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
QString str="25";
bool isloop; // 判断是否成功
int hex=str.toInt(&isloop,16);
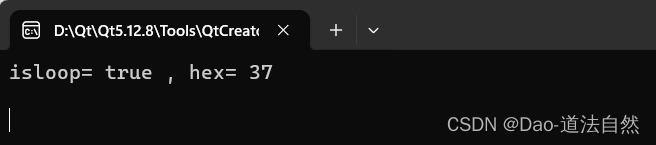
qDebug()<<"isloop="<<isloop<<","<<"hex="<<hex<<endl;
return a.exec();
}
(4)QString::compare() 函数对两个字符串进行比较
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
int a1=QString::compare("abcd","ABCD",Qt::CaseInsensitive);
int b1=QString::compare("about","Cat",Qt::CaseSensitive);
int c1=QString::compare("abcd","Cat",Qt::CaseInsensitive);
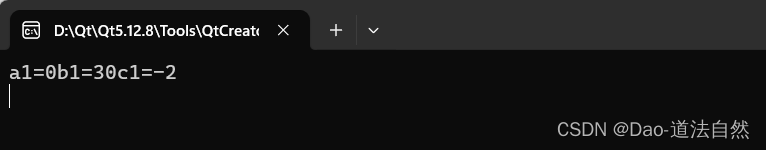
cout<<"a1="<<a1<<"b1="<<b1<<"c1="<<c1<<endl;
return a.exec();
}
(5)Qt将QString转换成ASCII
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
QString str="ABC abc";
QByteArray bytes=str.toUtf8();
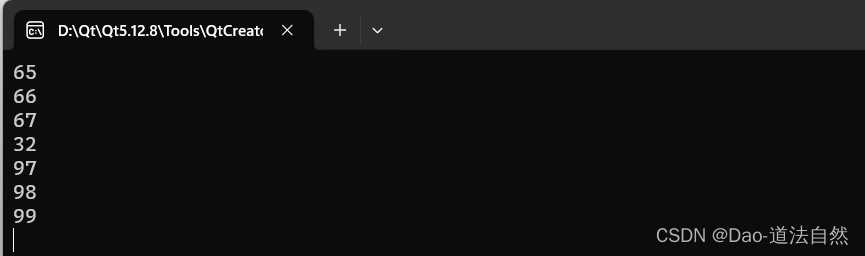
for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++)
qDebug()<<int(bytes.at(i));
return a.exec();
}
Qt 常见数据类型
注意:定义在 #include <QtGlobal>
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include <iostream>
#include <QDateTime>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
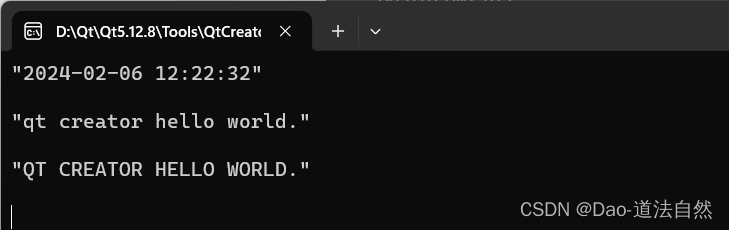
QDateTime dt;
QString strDT=dt.currentDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
qDebug()<<strDT<<endl;
QByteArray a1("Qt Creator Hello World.");
QByteArray b1=a1.toLower(); // 将字符串大写字母转小写,小写不变
qDebug()<<b1<<endl;
QByteArray c1=a1.toUpper();
qDebug()<<c1<<endl;
return a.exec();
}

![[疑难杂症2024-001] java多线程运行时遇到java.util.ConcurrentModificationException的解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d6435d6ed7e34a679d35d068216c7da4.png#pic_center)