使用方式
这两个函数的使用方式其实非常简单,他们都接受一个函数``一个数组,只有在数组里面的值改变的情况下才会再次执行 effect。
差异
- useEffect 是异步执行的,而useLayoutEffect是同步执行的。
- useEffect 的执行时机是浏览器完成渲染之后,而 useLayoutEffect 的执行时机是浏览器把内容真正渲染到界面之前,和 componentDidMount 等价。
具体表现
我们用一个例子说明
import React, { useEffect, useLayoutEffect, useState } from 'react';
function App() {
const [state, setState] = useState("hello world")
useEffect(() => {
let i = 0;
while(i <= 100000000) {
i++;
};
setState("world hello");
}, []);
// useLayoutEffect(() => {
// let i = 0;
// while(i <= 100000000) {
// i++;
// };
// setState("world hello");
// }, []);
return (
<>
<div>{state}</div>
</>
);
}
export default App;
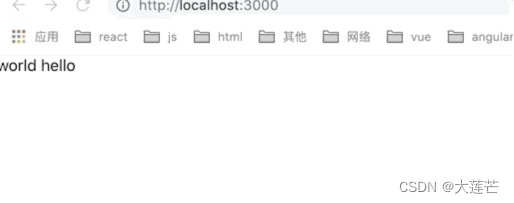
而换成 useLayoutEffect 之后闪烁现象就消失了。
·useEffect· 是渲染完之后异步执行的,所以会导致 ·hello world ·先被渲染到了屏幕上,再变成 ·world hello·,就会出现·闪烁现象·。而 useLayoutEffect是渲染之前同步执行的,所以会等它执行完再渲染上去,就避免了闪烁现象。也就是说我们最好把操作 dom 的相关操作放到 useLayouteEffect 中去,避免导致闪烁。
源码剖析
useEffect
首先找到 useEffect 调用的入口
function updateEffect(create, deps) {
{
// $FlowExpectedError - jest isn't a global, and isn't recognized outside of tests
if ('undefined' !== typeof jest) {
warnIfNotCurrentlyActingEffectsInDEV(currentlyRenderingFiber$1);
}
}
return updateEffectImpl(Update | Passive, Passive$1, create, deps);
}
调用 updateEffectImpl 时传入的 hookEffectTag 为 Passive$1 , 所以我们找一下:Passive$1。
然后我们找到是在这里传入了 Passive$1 类型来调用 useEffect 。
function commitPassiveHookEffects(finishedWork) {
if ((finishedWork.effectTag & Passive) !== NoEffect) {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case Block:
{
// TODO (#17945) We should call all passive destroy functions (for all fibers)
// before calling any create functions. The current approach only serializes
// these for a single fiber.
commitHookEffectListUnmount(Passive$1 | HasEffect, finishedWork);
commitHookEffectListMount(Passive$1 | HasEffect, finishedWork);
break;
}
}
}
}
那我们继续顺藤摸瓜找 commitPassiveHookEffects
function flushPassiveEffectsImpl() {
//...省略
while (_effect2 !== null) {
{
setCurrentFiber(_effect2);
invokeGuardedCallback(null, commitPassiveHookEffects, null, _effect2);
}
}
//...省略
}
找flushPassiveEffectsImpl
function flushPassiveEffects() {
if (pendingPassiveEffectsRenderPriority !== NoPriority) {
var priorityLevel = pendingPassiveEffectsRenderPriority > NormalPriority ? NormalPriority : pendingPassiveEffectsRenderPriority;
pendingPassiveEffectsRenderPriority = NoPriority;
return runWithPriority$1(priorityLevel, flushPassiveEffectsImpl);
}
}
再往上一层是commitBeforeMutationEffects,这里面调用flushPassiveEffects的方法是scheduleCallback,这是一个调度操作,是异步执行的。
function commitBeforeMutationEffects{
//...省略
if ((effectTag & Passive) !== NoEffect) {
// If there are passive effects, schedule a callback to flush at
// the earliest opportunity.
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
scheduleCallback(NormalPriority, function () {
flushPassiveEffects();
return null;
});
}
}
//...省略
}
继续顺着 commitBeforeMutationEffects方法往上找的话,我们可以找到最终调用 useEffect 的地方是 commitRootImpl ,这是我们 commit 阶段会调用的一个函数,所以就是在这里面对 useEffect 进行了调度,在完成渲染工作以后去异步执行了 useEffect 。
useLayoutEffect
function updateLayoutEffect(create, deps) {
return updateEffectImpl(Update, Layout, create, deps);
}
这里传进去的 hookEffectTag 是Layout,那么我们找一下Layout。
function commitLifeCycles(finishedRoot, current, finishedWork, committedExpirationTime) {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case Block:
{
// At this point layout effects have already been destroyed (during mutation phase).
// This is done to prevent sibling component effects from interfering with each other,
// e.g. a destroy function in one component should never override a ref set
// by a create function in another component during the same commit.
commitHookEffectListMount(Layout | HasEffect, finishedWork);
return;
}
case ClassComponent:
{
var instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
if (finishedWork.effectTag & Update) {
if (current === null) {
startPhaseTimer(finishedWork, 'componentDidMount'); // We could update instance props and state here,
// but instead we rely on them being set during last render.
// TODO: revisit this when we implement resuming.
{
if (finishedWork.type === finishedWork.elementType && !didWarnAboutReassigningProps) {
if (instance.props !== finishedWork.memoizedProps) {
error('Expected %s props to match memoized props before ' + 'componentDidMount. ' + 'This might either be because of a bug in React, or because ' + 'a component reassigns its own `this.props`. ' + 'Please file an issue.', getComponentName(finishedWork.type) || 'instance');
}
if (instance.state !== finishedWork.memoizedState) {
error('Expected %s state to match memoized state before ' + 'componentDidMount. ' + 'This might either be because of a bug in React, or because ' + 'a component reassigns its own `this.props`. ' + 'Please file an issue.', getComponentName(finishedWork.type) || 'instance');
}
}
}
instance.componentDidMount();
stopPhaseTimer();
} else {
var prevProps = finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type ? current.memoizedProps : resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, current.memoizedProps);
var prevState = current.memoizedState;
startPhaseTimer(finishedWork, 'componentDidUpdate'); // We could update instance props and state here,
// but instead we rely on them being set during last render.
// TODO: revisit this when we implement resuming.
{
if (finishedWork.type === finishedWork.elementType && !didWarnAboutReassigningProps) {
if (instance.props !== finishedWork.memoizedProps) {
error('Expected %s props to match memoized props before ' + 'componentDidUpdate. ' + 'This might either be because of a bug in React, or because ' + 'a component reassigns its own `this.props`. ' + 'Please file an issue.', getComponentName(finishedWork.type) || 'instance');
}
if (instance.state !== finishedWork.memoizedState) {
error('Expected %s state to match memoized state before ' + 'componentDidUpdate. ' + 'This might either be because of a bug in React, or because ' + 'a component reassigns its own `this.props`. ' + 'Please file an issue.', getComponentName(finishedWork.type) || 'instance');
}
}
}
instance.componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate);
stopPhaseTimer();
}
}
...省略
}
而在这里我们可以看到,class 组件的 componentDidMount生命周期也是在这里被调用的,所以其实useLayoutEffect是和componentDidMount等价的。
而一直往上找最后还是会找到 commitRootImpl方法中去,同时在这个过程中并没有找到什么调度的方法,所以 useLayoutEffect会同步执行。
总结
- 优先使用 useEffect,因为它是异步执行的,不会阻塞渲染
- 会影响到渲染的操作尽量放到 useLayoutEffect中去,避免出现闪烁问题
- useLayoutEffect和componentDidMount是等价的,会同步调用,阻塞渲染
- useLayoutEffect在服务端渲染的时候使用会有一个 warning,因为它可能导致首屏实际内容和服务端渲染出来的内容不一致。




![表单验证[用户名、邮箱、密码、重复密码]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0d1c2d12530e4282aa7a0c84a24e95a8.png)