Netty基础入门——NIO【1】
1 NIO
1.1 三大组件
1.1.1 Channel && Buffer
- Channle
channel类似于stream,是读写数据的双向通道,而stream要么是输入要么是输出
常见channel:
* FileChannel
* DatagramChannel
* SocketChannel
* ServerSocketChannel
- Buffer
用来缓冲读写数据
常见Buffer:
* ByteBuffer
* ShortBuffer
* IntBuffer
* LongBuffer
* FloatBuffer
* DoubleBuffer
* CharBuffer
1.1.2 Selector
服务器设计演变过程:
①多线程版设计
- 内存占用高
- 线程上下文切换成本高
- 只适合连接数少的场景
②线程池版
- 阻塞模式下,线程仅能处理一个 socket 连接
- 仅适合短连接场景
③selector版
selector 的作用就是配合一个线程来管理多个 channel,获取这些 channel 上发生的事件,这些 channel 工作在非阻塞模式下,不会让线程吊死在一个 channel 上。适合连接数特别多,但流量低的场景(low traffic)
调用 selector 的 select() 会阻塞直到 channel 发生了读写就绪事件,这些事件发生,select 方法就会返回这些事件交给 thread 来处理
1.2 ByteBuffer
使用FileChannel来读取文件内容
@Slf4j
public class ChannelDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//twr写法
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("data.txt", "rw")) {
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);//缓冲区大小
do{
//channel读,向buffer写入
int len = channel.read(buffer);;
log.debug("读到字节数:{}", len);
if(len == -1){
break;
}
//切换buffer读模式
buffer.flip();
while(buffer.hasRemaining()){
log.debug("{}", (char)buffer.get());
}
//切换buffer写模式
buffer.clear();
}while (true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.2.1 ByteBuffer使用步骤
- 向buffer写入数据,例如:channel.read(buffer)
文件获取channel - 通过channel向buffer写入
- 调用flip()切换至读模式
- 从buffer读取数据,例如:buffer.get()
- 调用clear()或compact()切换至写模式
- 重复步骤1-4
1.2.2 ByteBuffer结构
- capacity
- position
- limit
- 初始状态
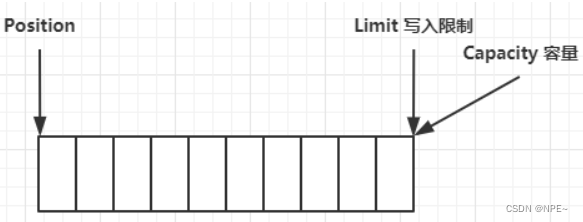
- 写入4个字节后
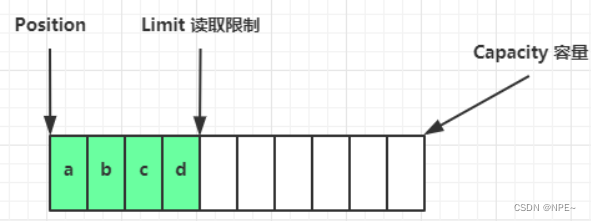
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量
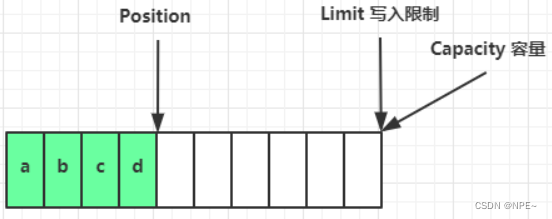
- flip动作发生,切换读写
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制
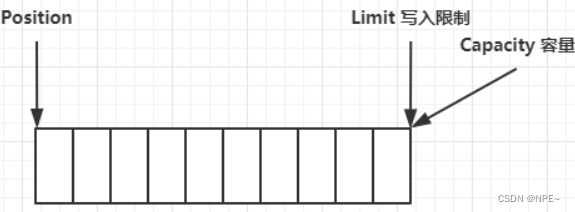
- clear动作发生后
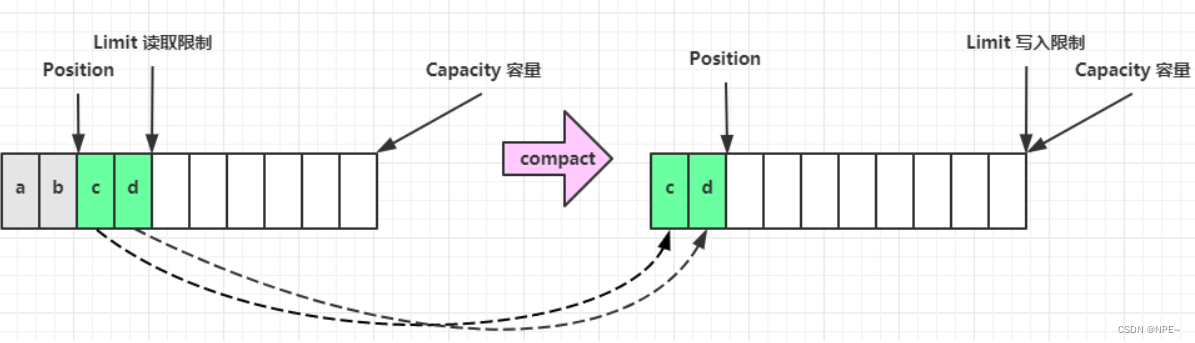
- compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式
1.2.3 ByteBuffer常见方法
- allocate为ByteBuffer分配空间,其他buffer类也有该方法
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
- 向buffer写数据
- channel的read【从channel读取到然后向buffer写】
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
- buffer自己的put方法
buf.put((byte)127);
- 从buffer读取数据
- 调用 channel 的 write 方法【从buf读,向channel写】
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
- 调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
byte b = buf.get();
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
* 可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
* 或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
1.2.4 调试工具类
1.2.5 mark、字符与ByteBuffer互转、批量读写
- mark 和 reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
注意
rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
- 字符与ByteBuffer互转
字符转ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");
ByteBuffer buffer2 = Charset.forName("utf-8").encode("你好");
ByteBuffer转字符
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
String s = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(byteBuffer).toString();
//hello
System.out.println(s);
- 批量操作byteBuffer
少搬运一次,速度更快
1. Scattering Reads(分散读取)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//test.txt文件内容:onetwothree
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("test.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
//向ByteBuffer中批量写入
ByteBuffer a = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer c = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{a,b,c});
a.flip();
b.flip();
c.flip();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
2.Gathering Writes(聚集写入)
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("test.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(6);
buffer.put("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
buffer2.put("你好".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//切换为读模式
buffer.flip();
buffer2.flip();
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{buffer, buffer2});
} catch (IOException e) {
}
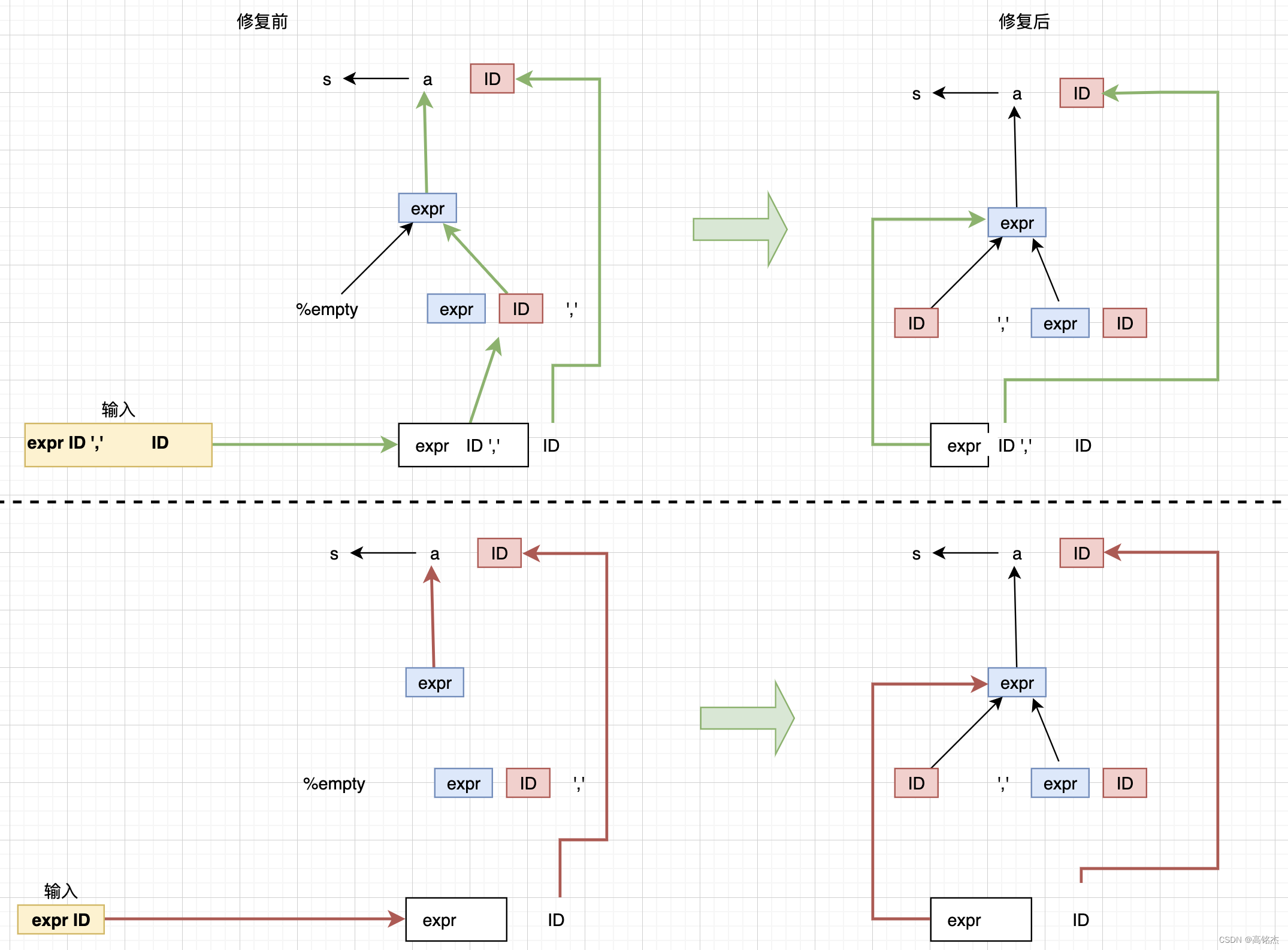
1.3 生产案例【粘包半包问题解决】
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔
但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条为
- Hello,world\n
- I’m zhangsan\n
- How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)
- Hello,world\nI’m zhangsan\nHo
- w are you?\n
现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*原本数据:
* Hello,world\n
* I'm zhangsan\n
* How are you?\n
*
* 特殊原因出现:粘包、半包问题
* Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo
* w are you?\n
*/
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you?\nhaha!\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
//处理粘包、半包问题
public static void split(ByteBuffer source){
//切换为读模式
source.flip();
//原来的长度:Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo【粘包、半包后一条数据的长度】
int oldLimit = source.limit();
//limit:byteBuffer最大范围
for(int i = 0; i < oldLimit; i++){
if(source.get(i) == '\n'){
//定义新ByteBuffer,内存利用率最大化【粘包、半包前真实数据长度】
ByteBuffer tar = ByteBuffer.allocate(i + 1 - source.position());
// 0 ~ limit【假如i为1,此时有两个数据要读,因此最大限制为2 -> i+1】
source.limit(i + 1);
tar.put(source);//从source读,向tar写
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(tar);
//还原长度,继续向下读
source.limit(oldLimit);
}
}
//没有读完的数据,压缩
source.compact();
}