移植ST公司uboot的第1步,创建配置文件、设备树、修改电源管理和sdmmc节点后,还需要进一部修改,如:网络驱动、USB OTG设备树、LCD驱动,以及编译和烧写测试。
一、在虚拟机中,使用VSCode打开my_uboot工作区
二、修改网络设备树
1、点击“arch”,然后点击“arm”,最后点击“dts”,点击“stm32mp125d-atk.dtsi”
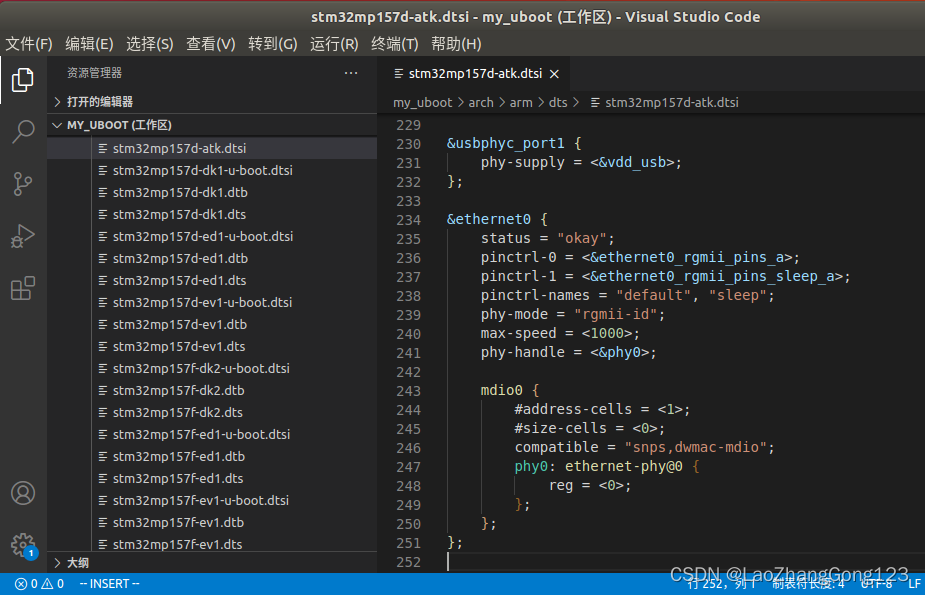
网络设备树“ethernet0节点”内容如下:
ðernet0 {
status = "okay";
pinctrl-0 = <ðernet0_rgmii_pins_a>;
pinctrl-1 = <ðernet0_rgmii_pins_sleep_a>;
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
phy-mode = "rgmii-id";
max-speed = <1000>;
phy-handle = <&phy0>;
mdio0 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
compatible = "snps,dwmac-mdio";
phy0: ethernet-phy@0 {
reg = <0>;
};
};
};
2、添加网络设备树“ethernet0节点”,见下图:
3、更新“网络驱动程序”
STM32MP157核心板V1.3的网络驱动芯片型号:YT8511,其PHY地址为0x00;
STM32MP157核心板V1.2的网络驱动芯片型号:RTL8211,其PHY地址为0x01;
网络驱动程序名字:phy.c;
网络驱动程序功能:支持YT8511和RTL8211;
正点原子的网络驱动程序路径:
程序源码→8、模块驱动源码→1、YT8511驱动源码→uboot下修改方法→phy.c
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0+
/*
* Generic PHY Management code
*
* Copyright 2011 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
* author Andy Fleming
*
* Based loosely off of Linux's PHY Lib
*/
#include <common.h>
#include <console.h>
#include <dm.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <net.h>
#include <command.h>
#include <miiphy.h>
#include <phy.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/compiler.h>
DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR;
/* Generic PHY support and helper functions */
/**
* genphy_config_advert - sanitize and advertise auto-negotiation parameters
* @phydev: target phy_device struct
*
* Description: Writes MII_ADVERTISE with the appropriate values,
* after sanitizing the values to make sure we only advertise
* what is supported. Returns < 0 on error, 0 if the PHY's advertisement
* hasn't changed, and > 0 if it has changed.
*/
static int genphy_config_advert(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
u32 advertise;
int oldadv, adv, bmsr;
int err, changed = 0;
/* Only allow advertising what this PHY supports */
phydev->advertising &= phydev->supported;
advertise = phydev->advertising;
/* Setup standard advertisement */
adv = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_ADVERTISE);
oldadv = adv;
if (adv < 0)
return adv;
adv &= ~(ADVERTISE_ALL | ADVERTISE_100BASE4 | ADVERTISE_PAUSE_CAP |
ADVERTISE_PAUSE_ASYM);
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_10baseT_Half)
adv |= ADVERTISE_10HALF;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_10baseT_Full)
adv |= ADVERTISE_10FULL;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_100baseT_Half)
adv |= ADVERTISE_100HALF;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_100baseT_Full)
adv |= ADVERTISE_100FULL;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_Pause)
adv |= ADVERTISE_PAUSE_CAP;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_Asym_Pause)
adv |= ADVERTISE_PAUSE_ASYM;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_1000baseX_Half)
adv |= ADVERTISE_1000XHALF;
if (advertise & ADVERTISED_1000baseX_Full)
adv |= ADVERTISE_1000XFULL;
if (adv != oldadv) {
err = phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_ADVERTISE, adv);
if (err < 0)
return err;
changed = 1;
}
bmsr = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMSR);
if (bmsr < 0)
return bmsr;
/* Per 802.3-2008, Section 22.2.4.2.16 Extended status all
* 1000Mbits/sec capable PHYs shall have the BMSR_ESTATEN bit set to a
* logical 1.
*/
if (!(bmsr & BMSR_ESTATEN))
return changed;
/* Configure gigabit if it's supported */
adv = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_CTRL1000);
oldadv = adv;
if (adv < 0)
return adv;
adv &= ~(ADVERTISE_1000FULL | ADVERTISE_1000HALF);
if (phydev->supported & (SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Half |
SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Full)) {
if (advertise & SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Half)
adv |= ADVERTISE_1000HALF;
if (advertise & SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Full)
adv |= ADVERTISE_1000FULL;
}
if (adv != oldadv)
changed = 1;
err = phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_CTRL1000, adv);
if (err < 0)
return err;
return changed;
}
/**
* genphy_setup_forced - configures/forces speed/duplex from @phydev
* @phydev: target phy_device struct
*
* Description: Configures MII_BMCR to force speed/duplex
* to the values in phydev. Assumes that the values are valid.
*/
static int genphy_setup_forced(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int err;
int ctl = BMCR_ANRESTART;
phydev->pause = 0;
phydev->asym_pause = 0;
if (phydev->speed == SPEED_1000)
ctl |= BMCR_SPEED1000;
else if (phydev->speed == SPEED_100)
ctl |= BMCR_SPEED100;
if (phydev->duplex == DUPLEX_FULL)
ctl |= BMCR_FULLDPLX;
err = phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMCR, ctl);
return err;
}
/**
* genphy_restart_aneg - Enable and Restart Autonegotiation
* @phydev: target phy_device struct
*/
int genphy_restart_aneg(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int ctl;
ctl = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMCR);
if (ctl < 0)
return ctl;
ctl |= (BMCR_ANENABLE | BMCR_ANRESTART);
/* Don't isolate the PHY if we're negotiating */
ctl &= ~(BMCR_ISOLATE);
ctl = phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMCR, ctl);
return ctl;
}
/**
* genphy_config_aneg - restart auto-negotiation or write BMCR
* @phydev: target phy_device struct
*
* Description: If auto-negotiation is enabled, we configure the
* advertising, and then restart auto-negotiation. If it is not
* enabled, then we write the BMCR.
*/
int genphy_config_aneg(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int result;
if (phydev->autoneg != AUTONEG_ENABLE)
return genphy_setup_forced(phydev);
result = genphy_config_advert(phydev);
if (result < 0) /* error */
return result;
if (result == 0) {
/*
* Advertisment hasn't changed, but maybe aneg was never on to
* begin with? Or maybe phy was isolated?
*/
int ctl = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMCR);
if (ctl < 0)
return ctl;
if (!(ctl & BMCR_ANENABLE) || (ctl & BMCR_ISOLATE))
result = 1; /* do restart aneg */
}
/*
* Only restart aneg if we are advertising something different
* than we were before.
*/
if (result > 0)
result = genphy_restart_aneg(phydev);
return result;
}
/***************alientek zuozhongkai add 2021/4/23****************/
#define YT8511_REG_DEBUG_ADDR_OFFSET 0x1e
#define YT8511_REG_DEBUG_DATA 0x1f
static int yt8511_rd_ext(struct phy_device *phydev, u32 regnum)
{
int val;
phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, YT8511_REG_DEBUG_ADDR_OFFSET, regnum);
val = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, YT8511_REG_DEBUG_DATA);
return val;
}
static int yt8511_wr_ext(struct phy_device *phydev, u32 regnum, u16 val)
{
int ret;
ret = phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, YT8511_REG_DEBUG_ADDR_OFFSET, regnum);
ret = phy_write(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, YT8511_REG_DEBUG_DATA, val);
return ret;
}
int yt8511_config_txdelay(struct phy_device *phydev, u8 delay)
{
int ret;
int val;
/* disable auto sleep */
val = yt8511_rd_ext(phydev, 0x27);
if (val < 0)
return val;
val &= (~BIT(15));
ret = yt8511_wr_ext(phydev, 0x27, val);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
/* enable RXC clock when no wire plug */
val = yt8511_rd_ext(phydev, 0xc);
if (val < 0)
return val;
/* ext reg 0xc b[7:4]
Tx Delay time = 150ps * N – 250ps
*/
val &= ~(0xf << delay);
val |= (0x7 << delay); //150ps * 7 - 250ps
ret = yt8511_wr_ext(phydev, 0xc, val);
return ret;
}
int yt8511_config_out_125m(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int ret;
int val;
/* disable auto sleep */
val = yt8511_rd_ext(phydev, 0x27);
if (val < 0)
return val;
val &= (~BIT(15));
ret = yt8511_wr_ext(phydev, 0x27, val);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
/* enable RXC clock when no wire plug */
val = yt8511_rd_ext(phydev, 0xc);
if (val < 0)
return val;
/* ext reg 0xc.b[2:1]
00-----25M from pll;
01---- 25M from xtl;(default)
10-----62.5M from pll;
11----125M from pll(here set to this value)
*/
val |= (3 << 1);
ret = yt8511_wr_ext(phydev, 0xc, val);
return ret;
}
/*********************end add***************************/
/**
* genphy_update_link - update link status in @phydev
* @phydev: target phy_device struct
*
* Description: Update the value in phydev->link to reflect the
* current link value. In order to do this, we need to read
* the status register twice, keeping the second value.
*/
int genphy_update_link(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
unsigned int mii_reg;
/************alientek zuozhongkai add 2021/4/23********/
unsigned int phyid1, phyid2;
phyid1 = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_PHYSID1);
phyid2 = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_PHYSID2);
if((phyid1 == 0X0) && (phyid2 == 0x10a)) {
yt8511_config_out_125m(phydev);
yt8511_config_txdelay(phydev, 4);
}
/*********************end add***************************/
/*
* Wait if the link is up, and autonegotiation is in progress
* (ie - we're capable and it's not done)
*/
mii_reg = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMSR);
/*
* If we already saw the link up, and it hasn't gone down, then
* we don't need to wait for autoneg again
*/
if (phydev->link && mii_reg & BMSR_LSTATUS)
return 0;
if ((phydev->autoneg == AUTONEG_ENABLE) &&
!(mii_reg & BMSR_ANEGCOMPLETE)) {
int i = 0;
printf("%s Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete",
phydev->dev->name);
while (!(mii_reg & BMSR_ANEGCOMPLETE)) {
/*
* Timeout reached ?
*/
if (i > PHY_ANEG_TIMEOUT) {
printf(" TIMEOUT !\n");
phydev->link = 0;
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
if (ctrlc()) {
puts("user interrupt!\n");
phydev->link = 0;
return -EINTR;
}
if ((i++ % 10) == 0)
printf(".");
mii_reg = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMSR);
mdelay(50); /* 50 ms */
}
printf(" done\n");
phydev->link = 1;
} else {
/* Read the link a second time to clear the latched state */
mii_reg = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMSR);
if (mii_reg & BMSR_LSTATUS)
phydev->link = 1;
else
phydev->link = 0;
}
return 0;
}
/*
* Generic function which updates the speed and duplex. If
* autonegotiation is enabled, it uses the AND of the link
* partner's advertised capabilities and our advertised
* capabilities. If autonegotiation is disabled, we use the
* appropriate bits in the control register.
*
* Stolen from Linux's mii.c and phy_device.c
*/
int genphy_parse_link(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int mii_reg = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMSR);
/* We're using autonegotiation */
if (phydev->autoneg == AUTONEG_ENABLE) {
u32 lpa = 0;
int gblpa = 0;
u32 estatus = 0;
/* Check for gigabit capability */
if (phydev->supported & (SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Full |
SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Half)) {
/* We want a list of states supported by
* both PHYs in the link
*/
gblpa = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_STAT1000);
if (gblpa < 0) {
debug("Could not read MII_STAT1000. ");
debug("Ignoring gigabit capability\n");
gblpa = 0;
}
gblpa &= phy_read(phydev,
MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_CTRL1000) << 2;
}
/* Set the baseline so we only have to set them
* if they're different
*/
phydev->speed = SPEED_10;
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_HALF;
/* Check the gigabit fields */
if (gblpa & (PHY_1000BTSR_1000FD | PHY_1000BTSR_1000HD)) {
phydev->speed = SPEED_1000;
if (gblpa & PHY_1000BTSR_1000FD)
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_FULL;
/* We're done! */
return 0;
}
lpa = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_ADVERTISE);
lpa &= phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_LPA);
if (lpa & (LPA_100FULL | LPA_100HALF)) {
phydev->speed = SPEED_100;
if (lpa & LPA_100FULL)
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_FULL;
} else if (lpa & LPA_10FULL) {
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_FULL;
}
/*
* Extended status may indicate that the PHY supports
* 1000BASE-T/X even though the 1000BASE-T registers
* are missing. In this case we can't tell whether the
* peer also supports it, so we only check extended
* status if the 1000BASE-T registers are actually
* missing.
*/
if ((mii_reg & BMSR_ESTATEN) && !(mii_reg & BMSR_ERCAP))
estatus = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE,
MII_ESTATUS);
if (estatus & (ESTATUS_1000_XFULL | ESTATUS_1000_XHALF |
ESTATUS_1000_TFULL | ESTATUS_1000_THALF)) {
phydev->speed = SPEED_1000;
if (estatus & (ESTATUS_1000_XFULL | ESTATUS_1000_TFULL))
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_FULL;
}
} else {
u32 bmcr = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMCR);
phydev->speed = SPEED_10;
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_HALF;
if (bmcr & BMCR_FULLDPLX)
phydev->duplex = DUPLEX_FULL;
if (bmcr & BMCR_SPEED1000)
phydev->speed = SPEED_1000;
else if (bmcr & BMCR_SPEED100)
phydev->speed = SPEED_100;
}
return 0;
}
int genphy_config(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int val;
u32 features;
features = (SUPPORTED_TP | SUPPORTED_MII
| SUPPORTED_AUI | SUPPORTED_FIBRE |
SUPPORTED_BNC);
/* Do we support autonegotiation? */
val = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_BMSR);
if (val < 0)
return val;
if (val & BMSR_ANEGCAPABLE)
features |= SUPPORTED_Autoneg;
if (val & BMSR_100FULL)
features |= SUPPORTED_100baseT_Full;
if (val & BMSR_100HALF)
features |= SUPPORTED_100baseT_Half;
if (val & BMSR_10FULL)
features |= SUPPORTED_10baseT_Full;
if (val & BMSR_10HALF)
features |= SUPPORTED_10baseT_Half;
if (val & BMSR_ESTATEN) {
val = phy_read(phydev, MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, MII_ESTATUS);
if (val < 0)
return val;
if (val & ESTATUS_1000_TFULL)
features |= SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Full;
if (val & ESTATUS_1000_THALF)
features |= SUPPORTED_1000baseT_Half;
if (val & ESTATUS_1000_XFULL)
features |= SUPPORTED_1000baseX_Full;
if (val & ESTATUS_1000_XHALF)
features |= SUPPORTED_1000baseX_Half;
}
phydev->supported &= features;
phydev->advertising &= features;
genphy_config_aneg(phydev);
return 0;
}
int genphy_startup(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int ret;
ret = genphy_update_link(phydev);
if (ret)
return ret;
return genphy_parse_link(phydev);
}
int genphy_shutdown(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
return 0;
}
static struct phy_driver genphy_driver = {
.uid = 0xffffffff,
.mask = 0xffffffff,
.name = "Generic PHY",
.features = PHY_GBIT_FEATURES | SUPPORTED_MII |
SUPPORTED_AUI | SUPPORTED_FIBRE |
SUPPORTED_BNC,
.config = genphy_config,
.startup = genphy_startup,
.shutdown = genphy_shutdown,
};
int genphy_init(void)
{
return phy_register(&genphy_driver);
}
static LIST_HEAD(phy_drivers);
int phy_init(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_NEEDS_MANUAL_RELOC
/*
* The pointers inside phy_drivers also needs to be updated incase of
* manual reloc, without which these points to some invalid
* pre reloc address and leads to invalid accesses, hangs.
*/
struct list_head *head = &phy_drivers;
head->next = (void *)head->next + gd->reloc_off;
head->prev = (void *)head->prev + gd->reloc_off;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_B53_SWITCH
phy_b53_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MV88E61XX_SWITCH
phy_mv88e61xx_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_AQUANTIA
phy_aquantia_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_ATHEROS
phy_atheros_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_BROADCOM
phy_broadcom_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_CORTINA
phy_cortina_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_DAVICOM
phy_davicom_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_ET1011C
phy_et1011c_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_LXT
phy_lxt_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_MARVELL
phy_marvell_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_MICREL_KSZ8XXX
phy_micrel_ksz8xxx_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_MICREL_KSZ90X1
phy_micrel_ksz90x1_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_MESON_GXL
phy_meson_gxl_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_NATSEMI
phy_natsemi_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_REALTEK
phy_realtek_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_SMSC
phy_smsc_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_TERANETICS
phy_teranetics_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_TI
phy_ti_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_VITESSE
phy_vitesse_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_XILINX
phy_xilinx_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_MSCC
phy_mscc_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_FIXED
phy_fixed_init();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_XILINX_GMII2RGMII
phy_xilinx_gmii2rgmii_init();
#endif
genphy_init();
return 0;
}
int phy_register(struct phy_driver *drv)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&drv->list);
list_add_tail(&drv->list, &phy_drivers);
#ifdef CONFIG_NEEDS_MANUAL_RELOC
if (drv->probe)
drv->probe += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->config)
drv->config += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->startup)
drv->startup += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->shutdown)
drv->shutdown += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->readext)
drv->readext += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->writeext)
drv->writeext += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->read_mmd)
drv->read_mmd += gd->reloc_off;
if (drv->write_mmd)
drv->write_mmd += gd->reloc_off;
#endif
return 0;
}
int phy_set_supported(struct phy_device *phydev, u32 max_speed)
{
/* The default values for phydev->supported are provided by the PHY
* driver "features" member, we want to reset to sane defaults first
* before supporting higher speeds.
*/
phydev->supported &= PHY_DEFAULT_FEATURES;
switch (max_speed) {
default:
return -ENOTSUPP;
case SPEED_1000:
phydev->supported |= PHY_1000BT_FEATURES;
/* fall through */
case SPEED_100:
phydev->supported |= PHY_100BT_FEATURES;
/* fall through */
case SPEED_10:
phydev->supported |= PHY_10BT_FEATURES;
}
return 0;
}
static int phy_probe(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int err = 0;
phydev->advertising = phydev->drv->features;
phydev->supported = phydev->drv->features;
phydev->mmds = phydev->drv->mmds;
if (phydev->drv->probe)
err = phydev->drv->probe(phydev);
return err;
}
static struct phy_driver *generic_for_interface(phy_interface_t interface)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_PHYLIB_10G
if (is_10g_interface(interface))
return &gen10g_driver;
#endif
return &genphy_driver;
}
static struct phy_driver *get_phy_driver(struct phy_device *phydev,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
struct list_head *entry;
int phy_id = phydev->phy_id;
struct phy_driver *drv = NULL;
list_for_each(entry, &phy_drivers) {
drv = list_entry(entry, struct phy_driver, list);
if ((drv->uid & drv->mask) == (phy_id & drv->mask))
return drv;
}
/* If we made it here, there's no driver for this PHY */
return generic_for_interface(interface);
}
static struct phy_device *phy_device_create(struct mii_dev *bus, int addr,
u32 phy_id, bool is_c45,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
struct phy_device *dev;
/*
* We allocate the device, and initialize the
* default values
*/
dev = malloc(sizeof(*dev));
if (!dev) {
printf("Failed to allocate PHY device for %s:%d\n",
bus->name, addr);
return NULL;
}
memset(dev, 0, sizeof(*dev));
dev->duplex = -1;
dev->link = 0;
dev->interface = interface;
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_ETH
dev->node = ofnode_null();
#endif
dev->autoneg = AUTONEG_ENABLE;
dev->addr = addr;
dev->phy_id = phy_id;
dev->is_c45 = is_c45;
dev->bus = bus;
dev->drv = get_phy_driver(dev, interface);
if (phy_probe(dev)) {
printf("%s, PHY probe failed\n", __func__);
return NULL;
}
if (addr >= 0 && addr < PHY_MAX_ADDR)
bus->phymap[addr] = dev;
return dev;
}
/**
* get_phy_id - reads the specified addr for its ID.
* @bus: the target MII bus
* @addr: PHY address on the MII bus
* @phy_id: where to store the ID retrieved.
*
* Description: Reads the ID registers of the PHY at @addr on the
* @bus, stores it in @phy_id and returns zero on success.
*/
int __weak get_phy_id(struct mii_dev *bus, int addr, int devad, u32 *phy_id)
{
int phy_reg;
/*
* Grab the bits from PHYIR1, and put them
* in the upper half
*/
phy_reg = bus->read(bus, addr, devad, MII_PHYSID1);
if (phy_reg < 0)
return -EIO;
*phy_id = (phy_reg & 0xffff) << 16;
/* Grab the bits from PHYIR2, and put them in the lower half */
phy_reg = bus->read(bus, addr, devad, MII_PHYSID2);
if (phy_reg < 0)
return -EIO;
*phy_id |= (phy_reg & 0xffff);
return 0;
}
static struct phy_device *create_phy_by_mask(struct mii_dev *bus,
uint phy_mask, int devad,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
u32 phy_id = 0xffffffff;
bool is_c45;
while (phy_mask) {
int addr = ffs(phy_mask) - 1;
int r = get_phy_id(bus, addr, devad, &phy_id);
/*
* If the PHY ID is flat 0 we ignore it. There are C45 PHYs
* that return all 0s for C22 reads (like Aquantia AQR112) and
* there are C22 PHYs that return all 0s for C45 reads (like
* Atheros AR8035).
*/
if (r == 0 && phy_id == 0)
goto next;
/* If the PHY ID is mostly f's, we didn't find anything */
if (r == 0 && (phy_id & 0x1fffffff) != 0x1fffffff) {
is_c45 = (devad == MDIO_DEVAD_NONE) ? false : true;
return phy_device_create(bus, addr, phy_id, is_c45,
interface);
}
next:
phy_mask &= ~(1 << addr);
}
return NULL;
}
static struct phy_device *search_for_existing_phy(struct mii_dev *bus,
uint phy_mask,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
/* If we have one, return the existing device, with new interface */
while (phy_mask) {
int addr = ffs(phy_mask) - 1;
if (bus->phymap[addr]) {
bus->phymap[addr]->interface = interface;
return bus->phymap[addr];
}
phy_mask &= ~(1 << addr);
}
return NULL;
}
static struct phy_device *get_phy_device_by_mask(struct mii_dev *bus,
uint phy_mask,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
int i;
struct phy_device *phydev;
phydev = search_for_existing_phy(bus, phy_mask, interface);
if (phydev)
return phydev;
/* Try Standard (ie Clause 22) access */
/* Otherwise we have to try Clause 45 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
phydev = create_phy_by_mask(bus, phy_mask,
i ? i : MDIO_DEVAD_NONE, interface);
if (IS_ERR(phydev))
return NULL;
if (phydev)
return phydev;
}
debug("\n%s PHY: ", bus->name);
while (phy_mask) {
int addr = ffs(phy_mask) - 1;
debug("%d ", addr);
phy_mask &= ~(1 << addr);
}
debug("not found\n");
return NULL;
}
/**
* get_phy_device - reads the specified PHY device and returns its
* @phy_device struct
* @bus: the target MII bus
* @addr: PHY address on the MII bus
*
* Description: Reads the ID registers of the PHY at @addr on the
* @bus, then allocates and returns the phy_device to represent it.
*/
static struct phy_device *get_phy_device(struct mii_dev *bus, int addr,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
return get_phy_device_by_mask(bus, 1 << addr, interface);
}
int phy_reset(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int reg;
int timeout = 500;
int devad = MDIO_DEVAD_NONE;
if (phydev->flags & PHY_FLAG_BROKEN_RESET)
return 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_PHYLIB_10G
/* If it's 10G, we need to issue reset through one of the MMDs */
if (is_10g_interface(phydev->interface)) {
if (!phydev->mmds)
gen10g_discover_mmds(phydev);
devad = ffs(phydev->mmds) - 1;
}
#endif
if (phy_write(phydev, devad, MII_BMCR, BMCR_RESET) < 0) {
debug("PHY reset failed\n");
return -1;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_RESET_DELAY
udelay(CONFIG_PHY_RESET_DELAY); /* Intel LXT971A needs this */
#endif
/*
* Poll the control register for the reset bit to go to 0 (it is
* auto-clearing). This should happen within 0.5 seconds per the
* IEEE spec.
*/
reg = phy_read(phydev, devad, MII_BMCR);
while ((reg & BMCR_RESET) && timeout--) {
reg = phy_read(phydev, devad, MII_BMCR);
if (reg < 0) {
debug("PHY status read failed\n");
return -1;
}
udelay(1000);
}
if (reg & BMCR_RESET) {
puts("PHY reset timed out\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int miiphy_reset(const char *devname, unsigned char addr)
{
struct mii_dev *bus = miiphy_get_dev_by_name(devname);
struct phy_device *phydev;
/*
* miiphy_reset was only used on standard PHYs, so we'll fake it here.
* If later code tries to connect with the right interface, this will
* be corrected by get_phy_device in phy_connect()
*/
phydev = get_phy_device(bus, addr, PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_MII);
return phy_reset(phydev);
}
struct phy_device *phy_find_by_mask(struct mii_dev *bus, uint phy_mask,
phy_interface_t interface)
{
/* Reset the bus */
if (bus->reset) {
bus->reset(bus);
/* Wait 15ms to make sure the PHY has come out of hard reset */
mdelay(15);
}
return get_phy_device_by_mask(bus, phy_mask, interface);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_ETH
void phy_connect_dev(struct phy_device *phydev, struct udevice *dev)
#else
void phy_connect_dev(struct phy_device *phydev, struct eth_device *dev)
#endif
{
/* Soft Reset the PHY */
phy_reset(phydev);
if (phydev->dev && phydev->dev != dev) {
printf("%s:%d is connected to %s. Reconnecting to %s\n",
phydev->bus->name, phydev->addr,
phydev->dev->name, dev->name);
}
phydev->dev = dev;
debug("%s connected to %s\n", dev->name, phydev->drv->name);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_XILINX_GMII2RGMII
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_ETH
static struct phy_device *phy_connect_gmii2rgmii(struct mii_dev *bus,
struct udevice *dev,
phy_interface_t interface)
#else
static struct phy_device *phy_connect_gmii2rgmii(struct mii_dev *bus,
struct eth_device *dev,
phy_interface_t interface)
#endif
{
struct phy_device *phydev = NULL;
int sn = dev_of_offset(dev);
int off;
while (sn > 0) {
off = fdt_node_offset_by_compatible(gd->fdt_blob, sn,
"xlnx,gmii-to-rgmii-1.0");
if (off > 0) {
phydev = phy_device_create(bus, off,
PHY_GMII2RGMII_ID, false,
interface);
break;
}
if (off == -FDT_ERR_NOTFOUND)
sn = fdt_first_subnode(gd->fdt_blob, sn);
else
printf("%s: Error finding compat string:%d\n",
__func__, off);
}
return phydev;
}
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_FIXED
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_ETH
static struct phy_device *phy_connect_fixed(struct mii_dev *bus,
struct udevice *dev,
phy_interface_t interface)
#else
static struct phy_device *phy_connect_fixed(struct mii_dev *bus,
struct eth_device *dev,
phy_interface_t interface)
#endif
{
struct phy_device *phydev = NULL;
int sn;
const char *name;
sn = fdt_first_subnode(gd->fdt_blob, dev_of_offset(dev));
while (sn > 0) {
name = fdt_get_name(gd->fdt_blob, sn, NULL);
if (name && strcmp(name, "fixed-link") == 0) {
phydev = phy_device_create(bus, sn, PHY_FIXED_ID, false,
interface);
break;
}
sn = fdt_next_subnode(gd->fdt_blob, sn);
}
return phydev;
}
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_ETH
struct phy_device *phy_connect(struct mii_dev *bus, int addr,
struct udevice *dev,
phy_interface_t interface)
#else
struct phy_device *phy_connect(struct mii_dev *bus, int addr,
struct eth_device *dev,
phy_interface_t interface)
#endif
{
struct phy_device *phydev = NULL;
uint mask = (addr >= 0) ? (1 << addr) : 0xffffffff;
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_FIXED
phydev = phy_connect_fixed(bus, dev, interface);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PHY_XILINX_GMII2RGMII
if (!phydev)
phydev = phy_connect_gmii2rgmii(bus, dev, interface);
#endif
if (!phydev)
phydev = phy_find_by_mask(bus, mask, interface);
/***********zuozhongkai add 2021/4/23****************/
if (!phydev) /* 如果还没有获取到phy_device,尝试YT8511 */
{
addr = 0;
mask = (addr >= 0) ? (1 << addr) : 0xffffffff;
phydev = phy_find_by_mask(bus, mask, interface);
}
/******************end add****************************/
if (phydev)
phy_connect_dev(phydev, dev);
else
printf("Could not get PHY for %s: addr %d\n", bus->name, addr);
return phydev;
}
/*
* Start the PHY. Returns 0 on success, or a negative error code.
*/
int phy_startup(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
if (phydev->drv->startup)
return phydev->drv->startup(phydev);
return 0;
}
__weak int board_phy_config(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
if (phydev->drv->config)
return phydev->drv->config(phydev);
return 0;
}
int phy_config(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
/* Invoke an optional board-specific helper */
return board_phy_config(phydev);
}
int phy_shutdown(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
if (phydev->drv->shutdown)
phydev->drv->shutdown(phydev);
return 0;
}
int phy_get_interface_by_name(const char *str)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_COUNT; i++) {
if (!strcmp(str, phy_interface_strings[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}使用phy.c文件替换掉“my_uboot/drivers/net/phy/phy.c”。
直接给定YT8511的地址为0x00,不受设备树控制,如下:
/***********zuozhongkai add 2021/4/23****************/
if (!phydev) /* 如果还没有获取到phy_device,尝试YT8511 */
{
addr = 0;
mask = (addr >= 0) ? (1 << addr) : 0xffffffff;
phydev = phy_find_by_mask(bus, mask, interface);
}
/******************end add****************************/
注意:
添加完网络设备树“ethernet0节点”后,我们需要编译,烧录,然后测试。
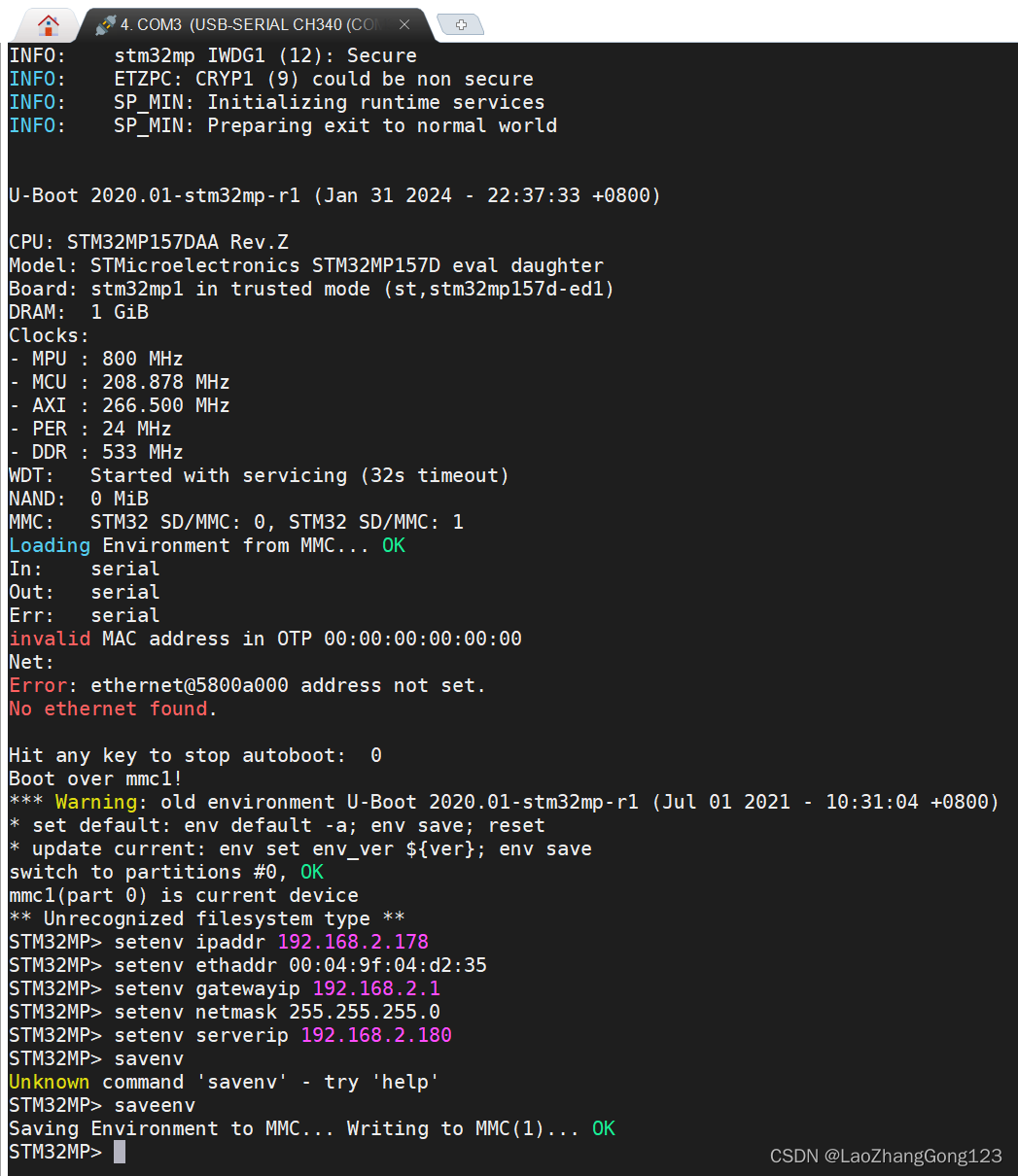
4、使用串口设置“网络地址环境变量”,如下:
setenv ipaddr 192.168.2.178 //开发板“IP地址”
setenv ethaddr 00:04:9f:04:d2:35 //开发板网卡“MAC地址”,48位
setenv gatewayip 192.168.2.1 //开发板默认网关
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0 //开发板子网掩码
setenv serverip 192.168.2.180 //服务器地址,也就是“Ubuntu地址”
saveenv
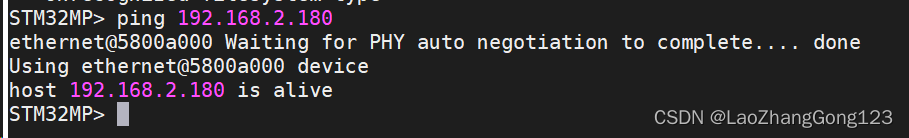
5、测试开发板网络连接
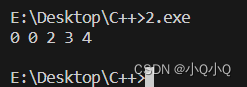
使用网线将STM32MP157开发板上的网络接口与电脑或者路由器连接起来,保证该开发板和电脑在同一个网段内,然后通过ping命令来测试一下网络连接,上电后,等串口出现“STM32MP>”,再输入“ping 192.168.2.180”,如下:
STM32MP> ping 192.168.2.180
三、修改“stm32mp125d-atk.dtsi”中的USB OTG设备树
1、点击“arch”,然后点击“arm”,最后点击“dts”,点击“stm32mp125d-atk.dtsi”
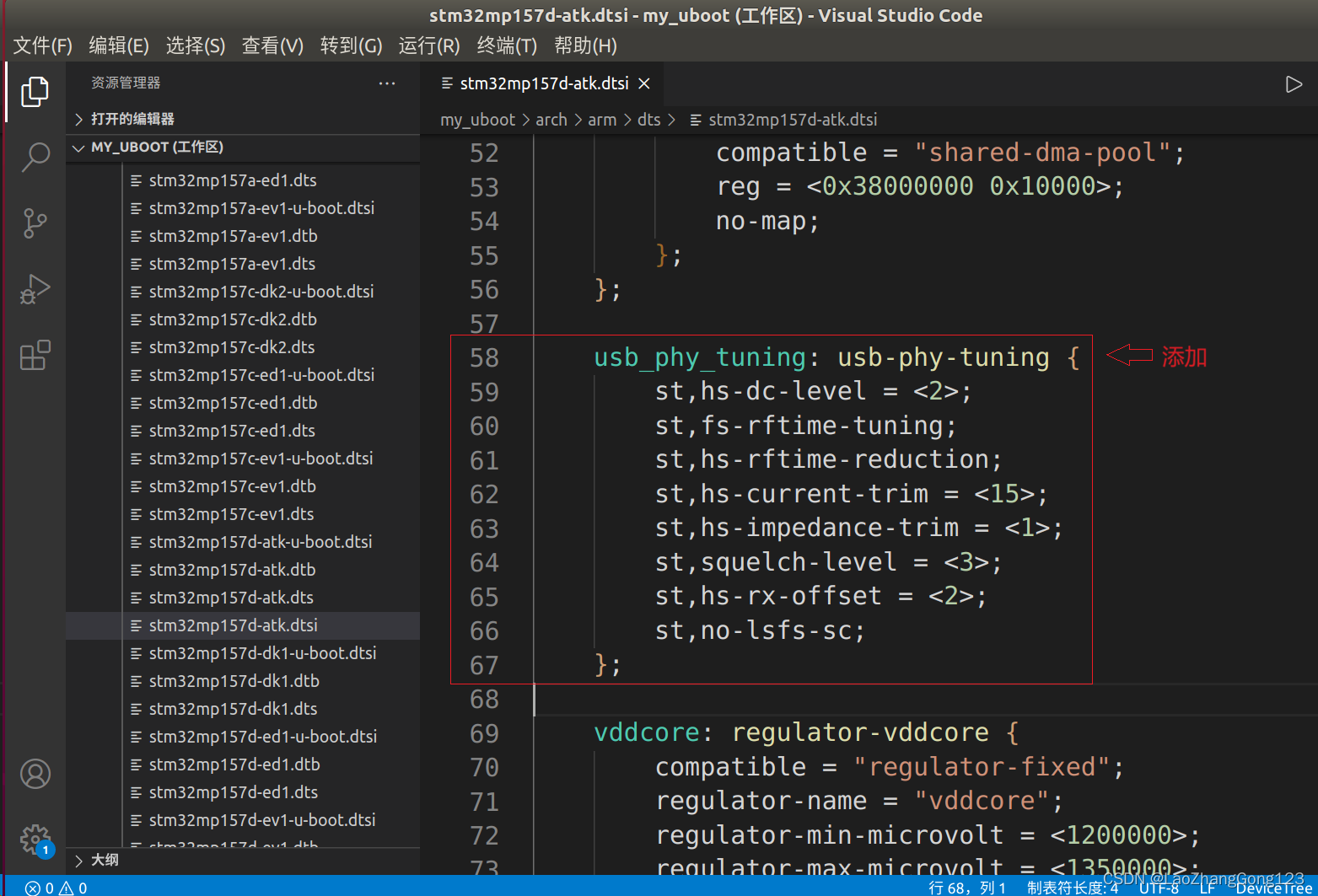
2、添加“usb_phy_tuning”子节点
usb_phy_tuning: usb-phy-tuning {
st,hs-dc-level = <2>;
st,fs-rftime-tuning;
st,hs-rftime-reduction;
st,hs-current-trim = <15>;
st,hs-impedance-trim = <1>;
st,squelch-level = <3>;
st,hs-rx-offset = <2>;
st,no-lsfs-sc;
};
见下图:
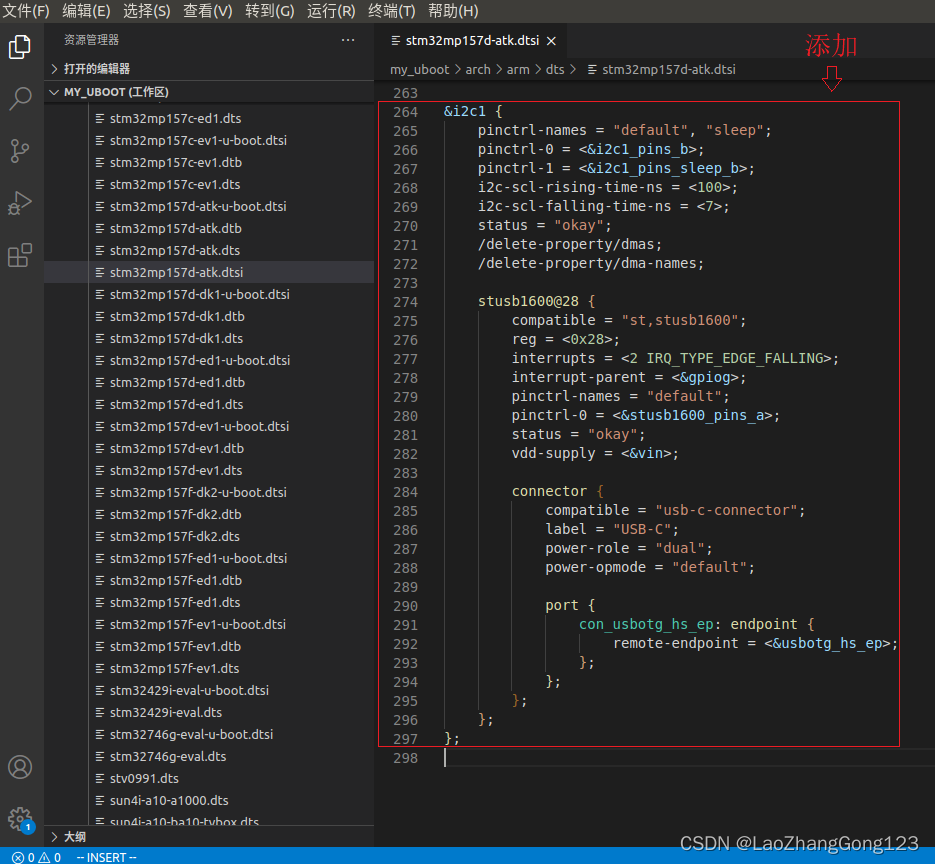
3、添加“i2c1”子节点
由于正点原子STM32MP157开发板上的“USB OTG接口类型”为 Type-C,使用的芯片是STUSB1600,它有一个I2C接口,连接到STM32MP157芯片的i2c1接口,因此,需要在设备树中添加“i2c1子节点”。
“i2c1节点”内容如下:
&i2c1 {
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&i2c1_pins_b>;
pinctrl-1 = <&i2c1_pins_sleep_b>;
i2c-scl-rising-time-ns = <100>;
i2c-scl-falling-time-ns = <7>;
status = "okay";
/delete-property/dmas;
/delete-property/dma-names;
stusb1600@28 {
compatible = "st,stusb1600";
reg = <0x28>;
interrupts = <2 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_FALLING>;
interrupt-parent = <&gpiog>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&stusb1600_pins_a>;
status = "okay";
vdd-supply = <&vin>;
connector {
compatible = "usb-c-connector";
label = "USB-C";
power-role = "dual";
power-opmode = "default";
port {
con_usbotg_hs_ep: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&usbotg_hs_ep>;
};
};
};
};
};
见下图:
4、添加usb接口相关节点:usbh_ehci,usbotg_hs和usbphyc
注意:usbotg_hs节点是我们以前屏蔽掉的。
节点内容如下:
&usbh_ehci {
phys = <&usbphyc_port0>;
status = "okay";
};
&usbotg_hs {
phys = <&usbphyc_port1 0>;
phy-names = "usb2-phy";
usb-role-switch;
status = "okay";
port {
usbotg_hs_ep: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&con_usbotg_hs_ep>;
};
};
};
&usbphyc {
status = "okay";
};
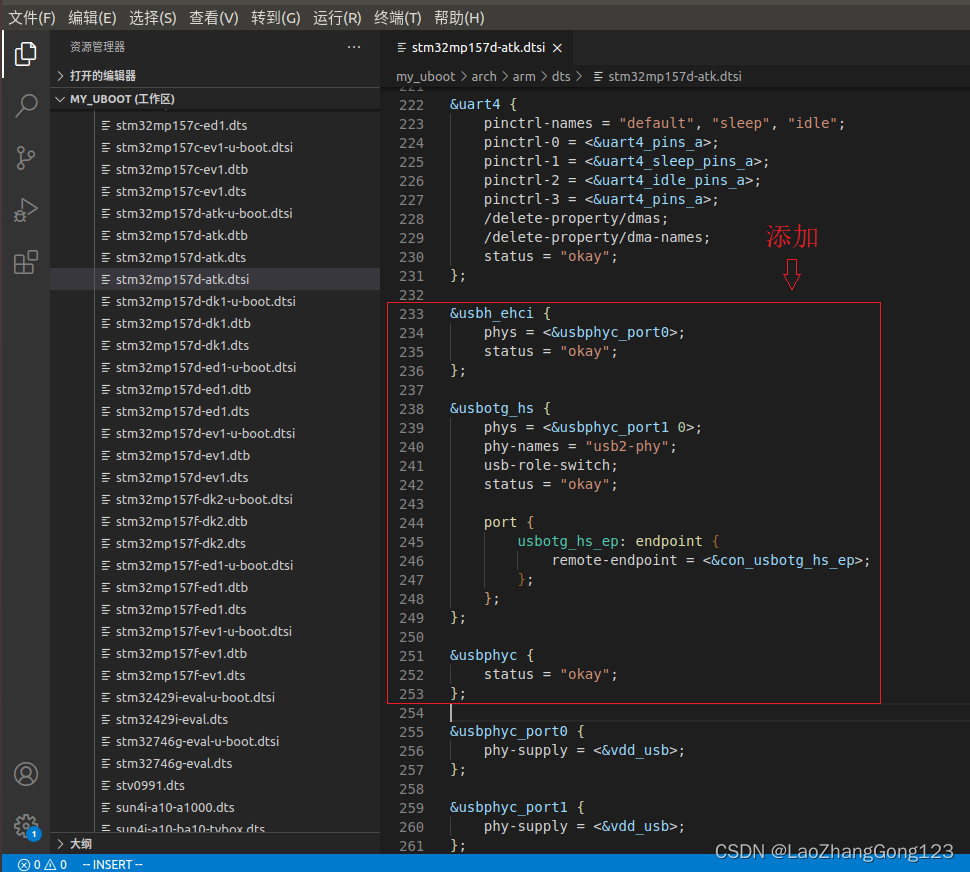
四、修改“stm32mp125d-atk-u-boot.dtsi”中的USB OTG设备树
1、点击“arch”,然后点击“arm”,最后点击“dts”,点击“stm32mp125d-atk-u-boot.dtsi”,打开该文件。
2、添加“usbotg_hs”节点。
&usbotg_hs {
u-boot,force-b-session-valid;
hnp-srp-disable;
/* TEMP: force peripheral for USB OTG */
dr_mode = "peripheral";
};
添加“usbotg_hs”节点后,见下图:
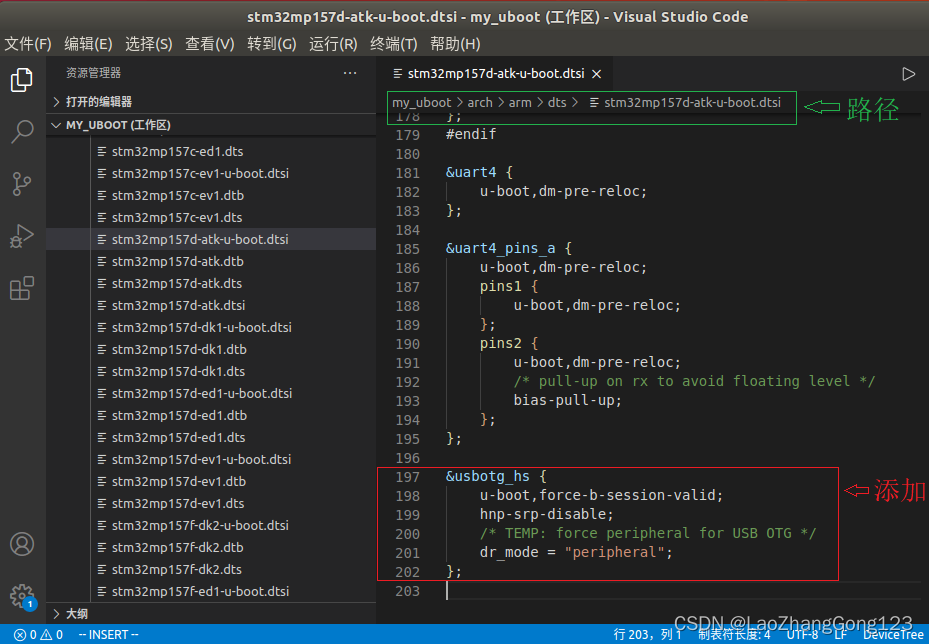
至此,USB OTG设备树修改完成了。
注意:
修改完“USB OTG设备树”后,我们需要重新编译,烧录,然后测试。
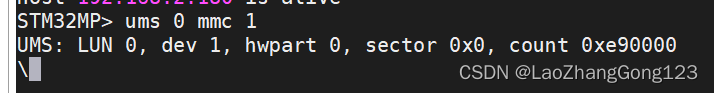
3、STM32MP157D开发板的USB OTG接口连接到电脑里,给开发板上电,等串口出现“STM32MP>”,再输入“ums 0 mmc 1”,如下:
STM32MP> ums 0 mmc 1
如果电脑上出现新的磁盘,说明USB OTG工作成功。
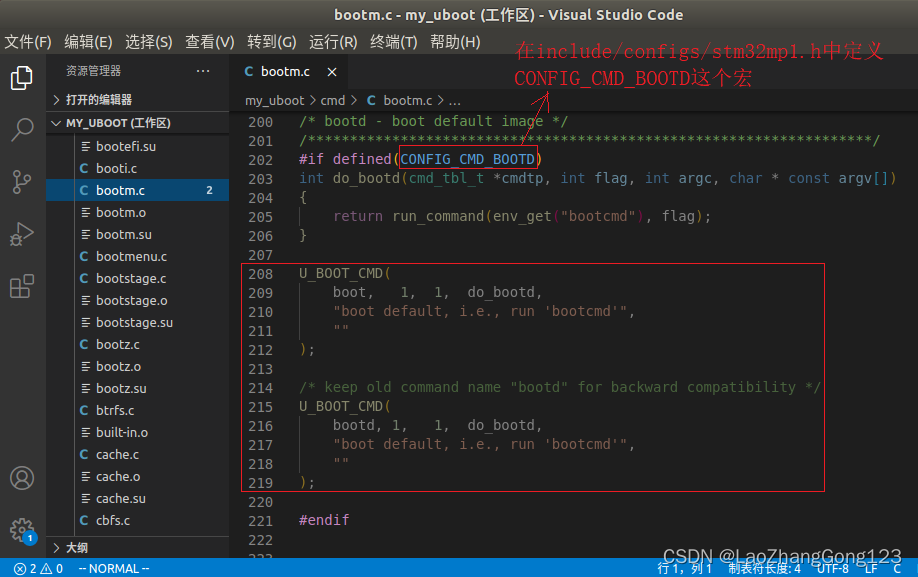
五、使能boot和bootd命令
ST公司的uboot默认没有使能boot和bootd这两个命令。这两个命令位于“my_uboot/cmd/bootm.c”文件中
1、查看“U_BOOT_CMD”,见下图:
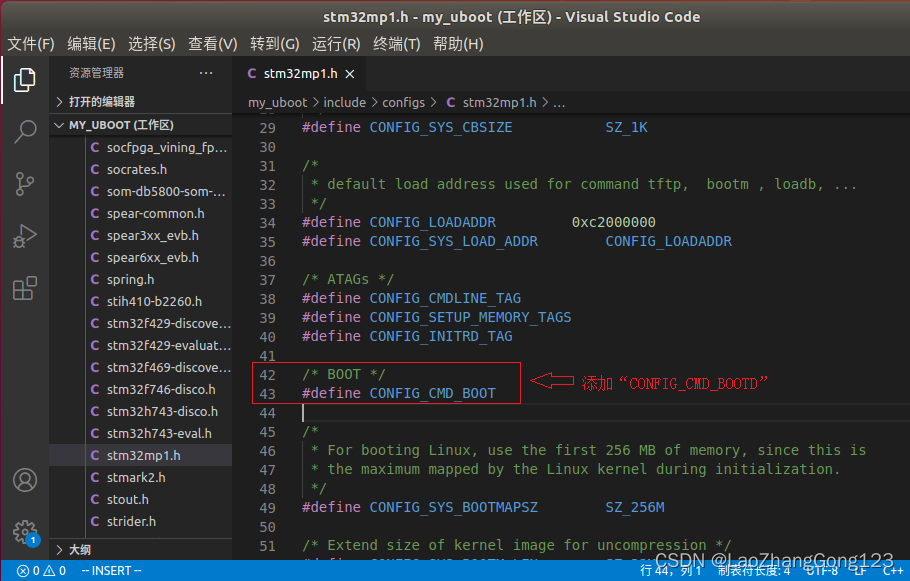
2、打开“my_boot/include/configs/stm32mp1.h”,添加“CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD”宏
/* BOOT */
#define CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD
添加“CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD”宏后,见下图:
注意:
添加“CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD”宏后,我们需要重新编译,烧录,然后测试。
3、连接USB串口,给开发板上电,等串口出现“STM32MP>”,再输入:
“? boot”或“? bootd”,如下:
STM32MP> ? boot
STM32MP> ? bootd
见下图:
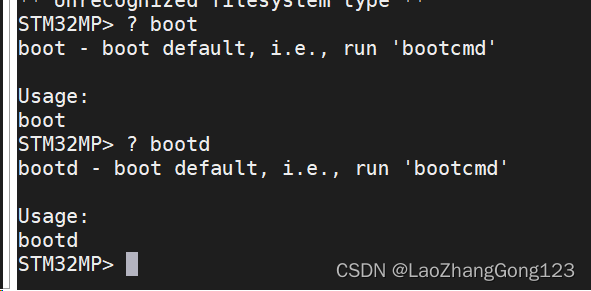
如果串口上出现上述信息,表示开发板使能了“boot”命令。
六、修改LCD驱动
1、点击“arch”,然后点击“arm”,最后点击“dts”,点击“stm32mp125d-atk.dts”
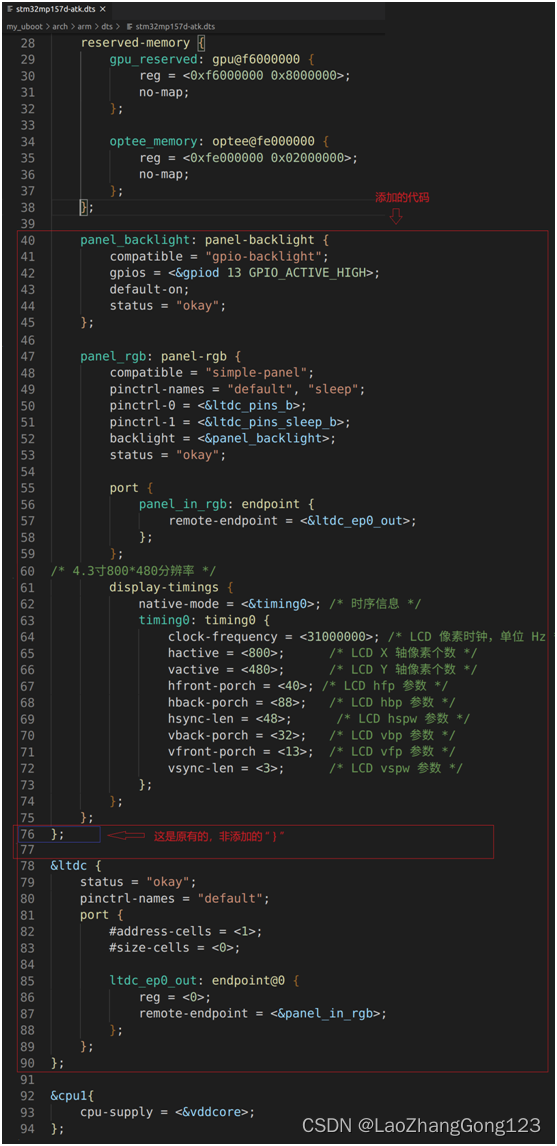
2、添加LCD背光节点“panel_backlight”,添加panel_rgb
panel_backlight: panel-backlight {
compatible = "gpio-backlight";
gpios = <&gpiod 13 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>;
default-on;
status = "okay";
};
panel_rgb: panel-rgb {
compatible = "simple-panel";
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <<dc_pins_b>;
pinctrl-1 = <<dc_pins_sleep_b>;
backlight = <&panel_backlight>;
status = "okay";
port {
panel_in_rgb: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <<dc_ep0_out>;
};
};
/* 4.3寸800*480分辨率 */
display-timings {
native-mode = <&timing0>; /* 时序信息 */
timing0: timing0 {
clock-frequency = <31000000>; /* LCD 像素时钟,单位 Hz */
hactive = <800>; /* LCD X 轴像素个数 */
vactive = <480>; /* LCD Y 轴像素个数 */
hfront-porch = <40>; /* LCD hfp 参数 */
hback-porch = <88>; /* LCD hbp 参数 */
hsync-len = <48>; /* LCD hspw 参数 */
vback-porch = <32>; /* LCD vbp 参数 */
vfront-porch = <13>; /* LCD vfp 参数 */
vsync-len = <3>; /* LCD vspw 参数 */
};
};
};
}; /*这是原有的“ } ”,非添加的*/
<dc {
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
port {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
ltdc_ep0_out: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&panel_in_rgb>;
};
};
};
至此,移植ST公司uboot的第2步,可以说实现了。 这时候,就可以烧写测试了。