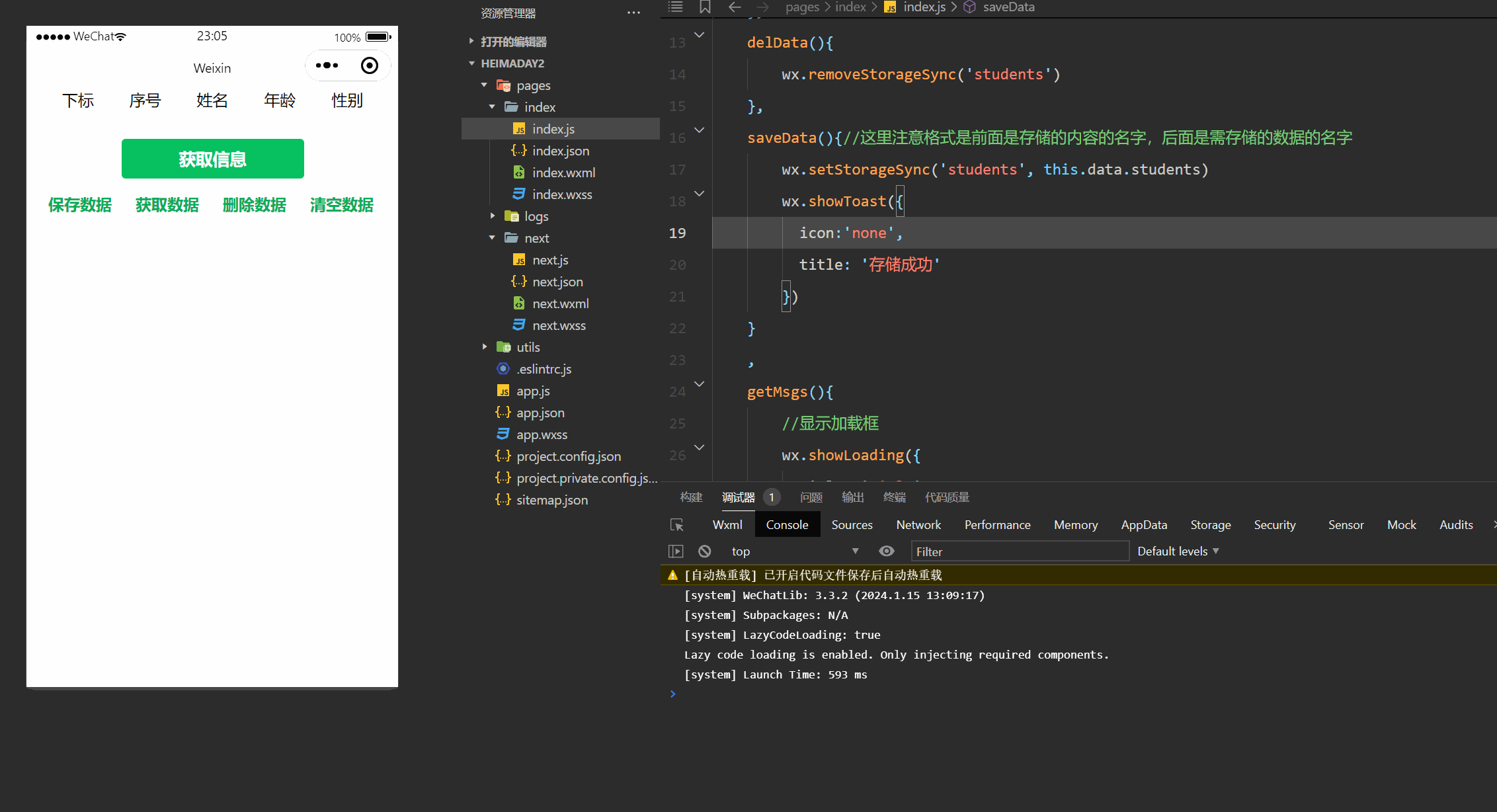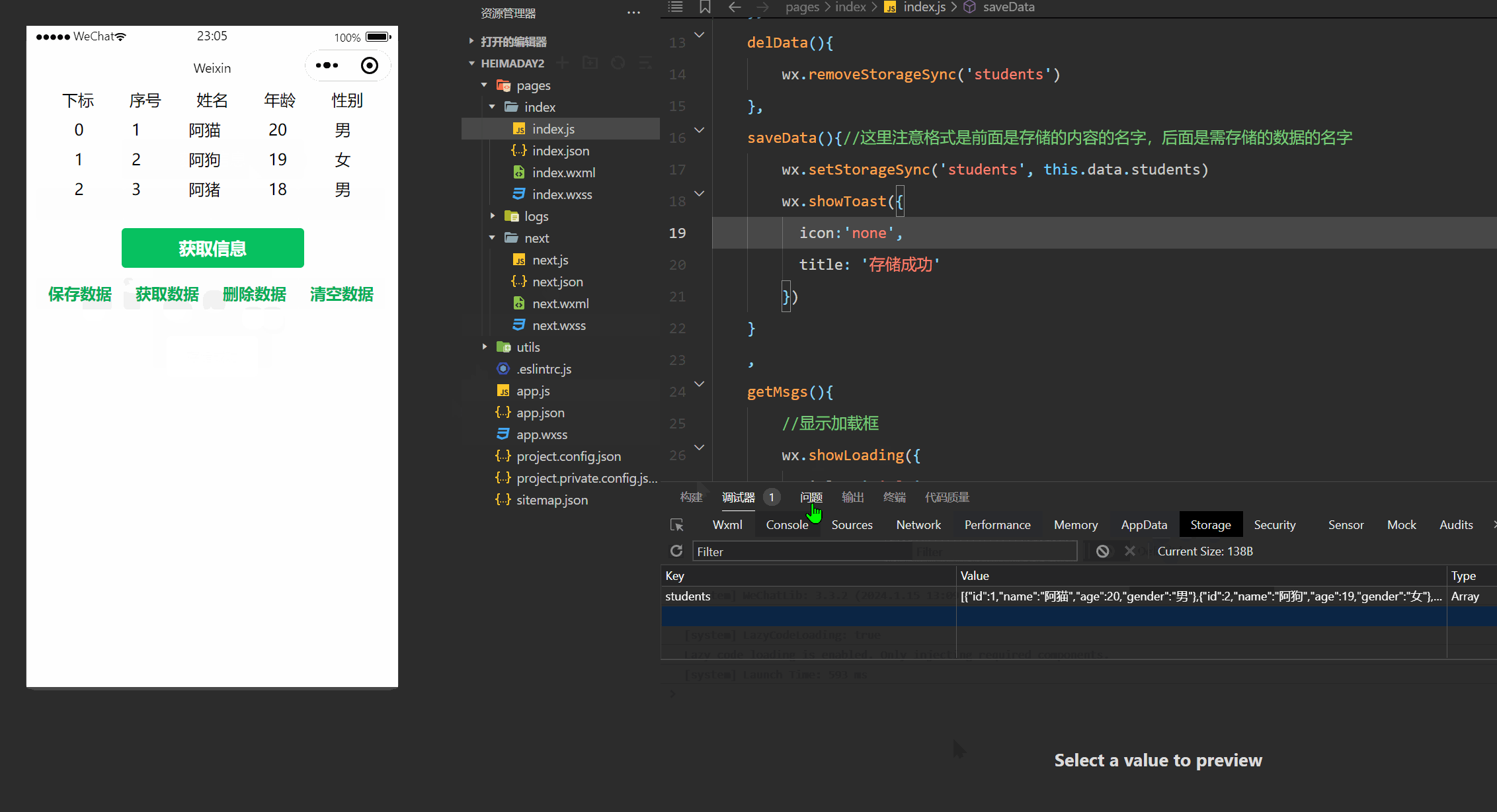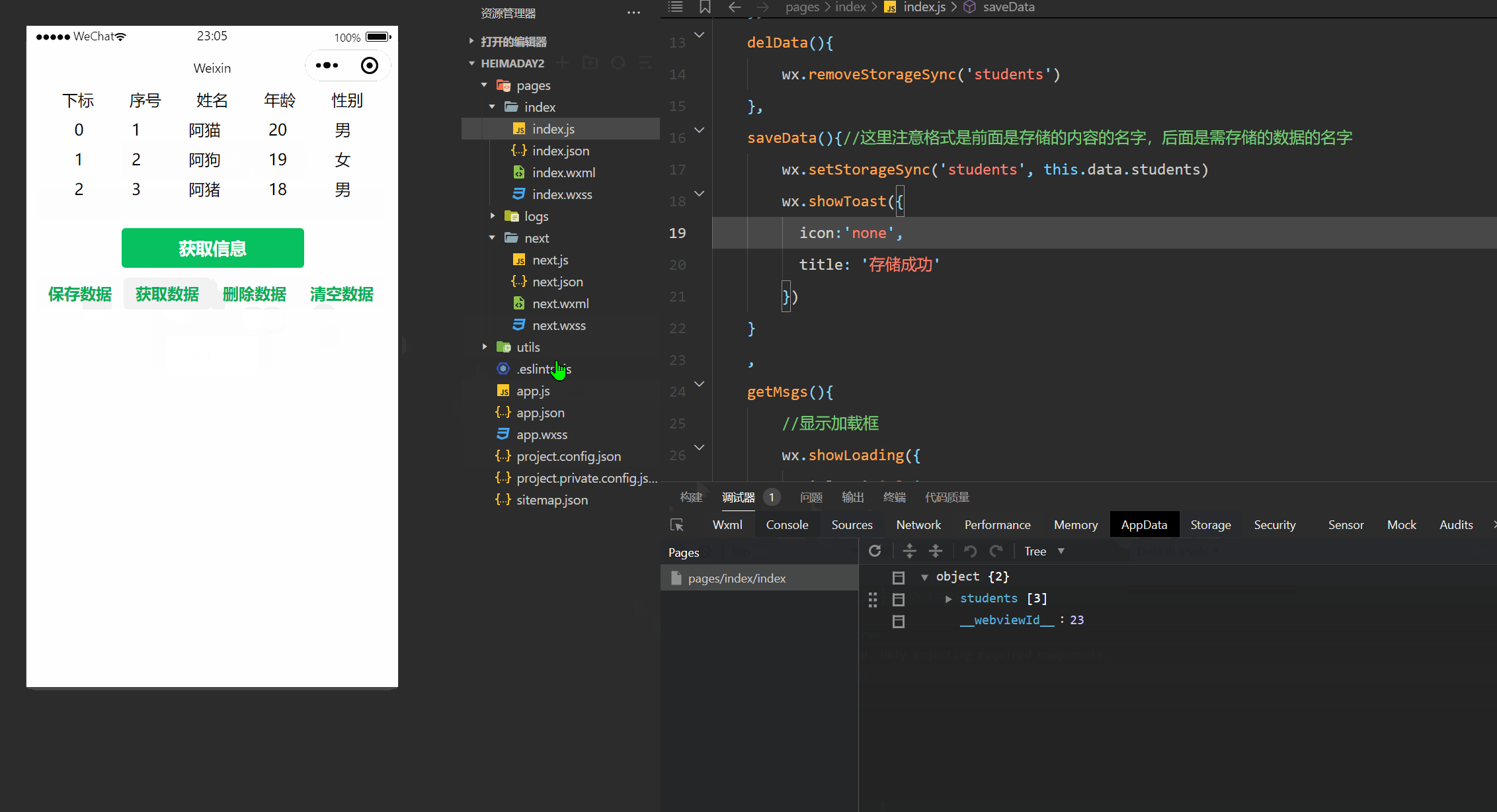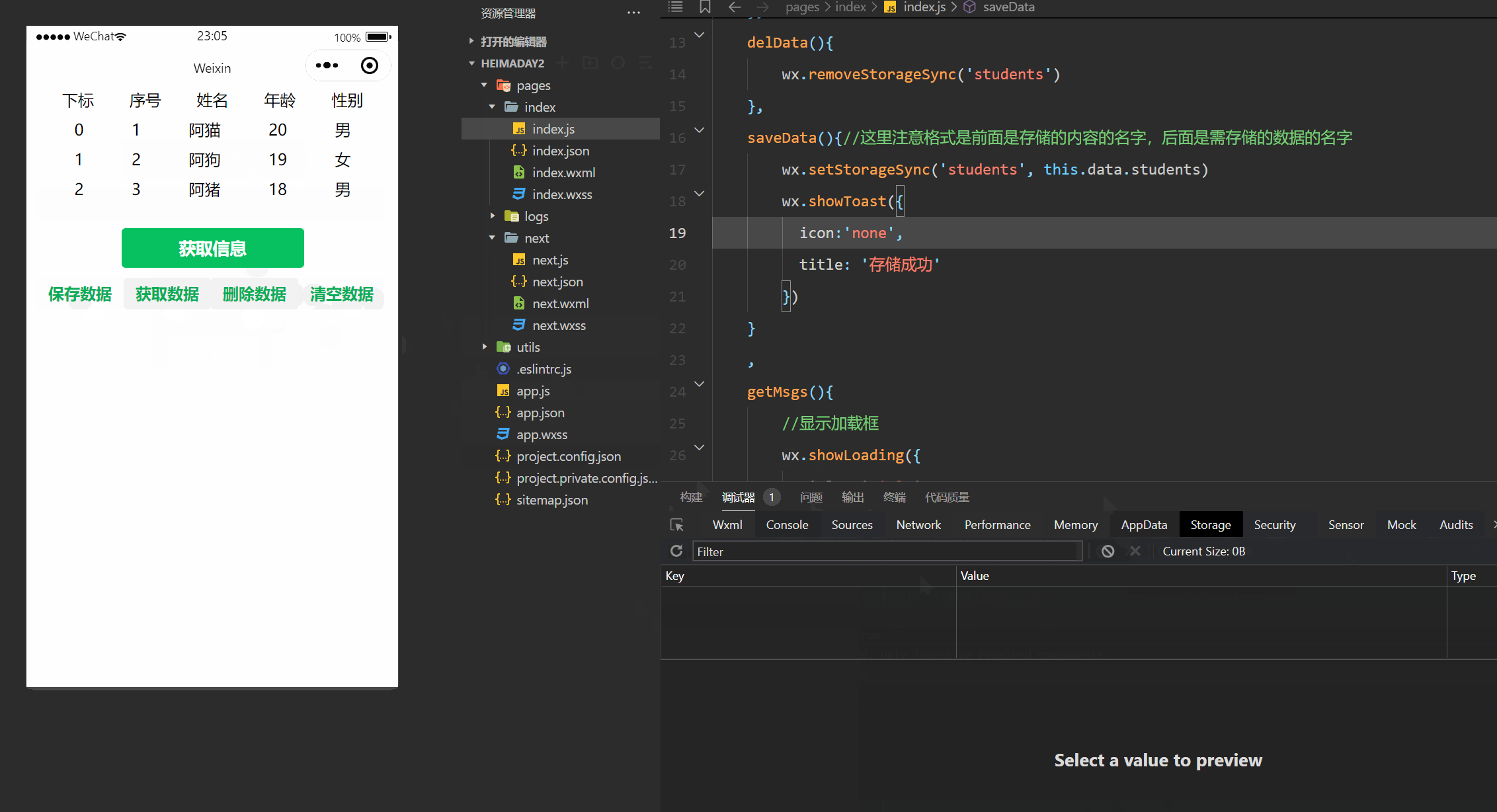
一、CentOS 6 与 CentOS 7开机流程
1.CentOS 6

1.1.打开电源首先通过内核引导开机。
1.2.开机自检,加载 BIOS 硬件信息。
1.3.MBR 记录一般是在磁盘0磁道0扇区,共512个字节。前446个字节是 BootLoder。计算机不知道我们的系统在哪里,所以需要程序进行引导,这个引导的程序就叫BootLoder。
1.4.GRUB菜单引导,选择系统。
1.5.加载内核,将菜单中选择的内核加载到内存中,启动系统。
1.6.启动系统中第一个 init 进程。(父进程)
1.7.读取 init 程序的配置文件(/etc/inittab)。
1.8.初始化系执行 /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit 程序,设置IP地址、主机名、开机自动挂载等。
1.9.根据运行级别串行启动服务。
1.10.运行 mingetty ,显示登录界面。
2.CentOS 7

1.1.加载内核之前部分与 CentOS 6 大致相同
1.2.启动系统父进程 systemd
1.3.读取运行级别 /etc/systemd/system/default.target
1.4.初始化系统 /usr/lib/systemd/system
1.5.运行 /usr/lib/systemd/system/getty.target加载 login 界面
3.启动流程区别
Centos7和Centos7开启流程差不多,只是启动的父进程与加载的文件不同。
二、运行级别
| System V init运行级别 | Systemd目标名称 | 作用 |
| 0 | runlevel0.target,poweroff.target | 关机 |
| 1 | runlevel1.target,rescue.target | 单用户模式 |
| 2 | runlevel2.target,multi-user.target | |
| 3 | runlevel3.target,multi-user.target | 多用户文本界面 |
| 4 | runlevel4.target,multi-user.target | |
| 5 | runlevel5.target,graphical.target | 多用户图像界面 |
| 6 | runlevel6.target,reboot.target | 重启 |
相关命令
#查看当前运行级别
~]# systemctl get-default
#修改系统下次启动时的运行级别
~]# systemctl set-default multi-user.target三、systemd 使用方法
~]# systemctl disabled httpd.service 取消开机自启
~]# systemctl enable httpd.service 开机自启服务
~]# systemctl restart httpd.service 重启服务
~]# systemctl status httpd.service 查看服务状态
~]# systemctl start httpd.service 启动服务
~]# systemctl stop httpd.service 关闭服务四、服务状态
| 状态 | 描述 |
| loaded | 服务单元的配置文件已经被处理 |
| active(running) | 服务持续运行 |
| active(exited) | 服务成功完成一次的配置 |
| active(waiting) | 服务已经运行但在等待某个事件 |
| inactive | 服务没有在运行 |
| enabled | 服务设定为开机自启动 |
| disabled | 服务设定为开机不启动 |
| static | 服务开机不启动,但可以被其他服务调用启动 |
五、单用户模式
PS:超级权限且必须面对实体硬件,不支持远程操作
忘记 root 密码进入单用户模式修改 root 密码
重启系统并出现引导界面时,按照提示按"e"键进入内核编辑模式

找到 linux16 的行,默认为 ro 系统只读,我们需要将权限修改为 rw 读写

随后在UTF-8 后加 enforcieng=0 init=/bin/bash,按下ctrl+x来运行修改过的内核程序
 修改密码后重新加载系统
修改密码后重新加载系统