文章目录
- 一、使用方式
- 1.1 特性
- 1.2 优势
- 1.3 设置
- 1.3.1 默认值
- 1.3.2 配置文件
- 1.3.3 写配置文件
- 1.3.4 监听配置文件变化
- 1.3.5 从 io.Reader 读配置
- 1.3.6 Setting Overrides
- 1.3.7 使用 Alias
- 1.3.8 环境变量
- 1.3.9 命令行 Flags
- 1.3.8.1 Flag 接口
- 1.3.9 配置中心
- 1.3.9.1 未加密
- 1.3.9.2 加密
- 1.3.9.3 监听变化
- 1.4 读取
- 1.4.1 嵌套式获取
- 1.4.2 数组下标访问
- 1.4.3 显式的 delimited key path
- 1.4.4 解析子树
- 二、源码
- 2.1 定义 Error
- 2.2 Viper struct 定义
- 2.3 构造:New 和 函数式 Options
- 2.4 Reset
- 2.5 配置中心
- 2.5.1 接口定义
- 2.5.2 添加 RemoteProvider
- 2.6 监听配置变化
- 2.7 文件设置
- 2.8 环境变量
- 2.8.1 配置
- 2.8.2 绑定
- 2.8.3 环境变量覆盖配置文件
- 2.9 搜索 key
- 2.10 Get 获取一个 key 的值
- 2.11 Unmarshal
- 2.12 BindPFlag
- 2.13 关键逻辑 find()
- 2.14 alias bieming
- 2.15 读文件
- 2.16 单测
viper 是由 spf13 作者写的,这个作者很强大,很多顶级库,
而整个代码也只有 5400 行,目的很纯粹,一直在更新,所以很适合读源码
一、使用方式
1.1 特性
viper 支持任意配置文件格式,有如下特性:
- 默认配置
- JSON, TOML, YAML, HCL, envfile
- live watching 配置文件变化
- 监听配置中心(etcd、consul)
- 读取命令行参数
- 读取 buffer
- setting explicit values(设置显式值)
1.2 优势
开发应用服务时,不希望关注异构的配置文件格式,而希望更专注业务逻辑。viper 支持如下特性:
- find, load, unmarshal 配置文件
- 支持 set default values
- 支持覆盖配置项(override values)
- 提供 alias system,可以方便地 rename parameters without breaking existing code
- 当用户提供了与默认设置相同的命令行或配置文件时,可以很容易地区分它们。
viper 优先级从高到低如下:
- 显式调用 Set()
- flag
- env
- config
- key/value store
- default
注意:viper 不区分大小写,社区对此是有争论的
1.3 设置
1.3.1 默认值
viper.SetDefault("ContentDir", "content")
viper.SetDefault("Taxonomies", map[string]string{"tag": "tags", "category": "categories"})
1.3.2 配置文件
目前,一个 viper 对象,只能读一个配置文件。但可以配置多个搜索路径。Viper 不默认任何配置搜索路径,将默认决定留给应用程序。示例如下:
viper.SetConfigName("config") // name of config file (without extension)
viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // REQUIRED if the config file does not have the extension in the name
viper.AddConfigPath("/etc/appname/") // path to look for the config file in
viper.AddConfigPath("$HOME/.appname") // call multiple times to add many search paths
viper.AddConfigPath(".") // optionally look for config in the working directory
err := viper.ReadInConfig() // Find and read the config file
if err != nil { // Handle errors reading the config file
panic(fmt.Errorf("fatal error config file: %w", err))
}
可通过如下方式处理指定的错误:
if err := viper.ReadInConfig(); err != nil {
if _, ok := err.(viper.ConfigFileNotFoundError); ok {
// Config file not found; ignore error if desired
} else {
// Config file was found but another error was produced
}
}
// Config file found and successfully parsed
1.3.3 写配置文件
有如下四个方法:
- WriteConfig - writes the current viper configuration to the predefined path, if exists. Errors if no predefined path. Will overwrite the current config file, if it exists.
- SafeWriteConfig - writes the current viper configuration to the predefined path. Errors if no predefined path. Will not overwrite the current config file, if it exists.
- WriteConfigAs - writes the current viper configuration to the given filepath. Will overwrite the given file, if it exists.
- SafeWriteConfigAs - writes the current viper configuration to the given filepath. Will not overwrite the given file, if it exists.
viper.WriteConfig() // writes current config to predefined path set by 'viper.AddConfigPath()' and 'viper.SetConfigName'
viper.SafeWriteConfig()
viper.WriteConfigAs("/path/to/my/.config")
viper.SafeWriteConfigAs("/path/to/my/.config") // will error since it has already been written
viper.SafeWriteConfigAs("/path/to/my/.other_config")
1.3.4 监听配置文件变化
监听变化,可以使进程无需重启
viper.OnConfigChange(func(e fsnotify.Event) {
fmt.Println("Config file changed:", e.Name)
})
viper.WatchConfig()
1.3.5 从 io.Reader 读配置
viper.SetConfigType("yaml")
// any approach to require this configuration into your program.
var yamlExample = []byte(`
Hacker: true
name: steve
hobbies:
- skateboarding
- snowboarding
- go
clothing:
jacket: leather
trousers: denim
age: 35
eyes : brown
beard: true
`)
viper.ReadConfig(bytes.NewBuffer(yamlExample))
viper.Get("name")
1.3.6 Setting Overrides
可能来自命令行参数,或应用逻辑
viper.Set("Verbose", true)
viper.Set("LogFile", logFile)
viper.Set("host.port", 5899) // set subset
1.3.7 使用 Alias
别名允许多个键引用单个值
viper.RegisterAlias("loud", "Verbose")
viper.Set("verbose", true) // same result as next line
viper.Set("loud", true) // same result as prior line
viper.GetBool("loud") // true
viper.GetBool("verbose") // true
1.3.8 环境变量
有如下五种方法:
AutomaticEnv()BindEnv(string...) : errorSetEnvPrefix(string)SetEnvKeyReplacer(string...) *strings.ReplacerAllowEmptyEnv(bool)
viper 处理环境变量时,不区分大小写。
Viper提供了一种机制来尝试确保ENV变量是唯一的。通过使用SetEnvPrefix,您可以告诉Viper在读取环境变量时使用前缀。BindEnv和AutomaticEnv都会使用这个前缀。
BindEnv接受一个或多个参数。第一个参数是键名称,其余参数是要绑定到该键的环境变量的名称。如果提供了多个,则它们将按指定的顺序优先。环境变量的名称区分大小写。如果未提供ENV变量名,则Viper将自动假定ENV变量匹配以下格式:前缀+“_”+全部大写的键名称。当您显式提供ENV变量名(第二个参数)时,它不会自动添加前缀。例如,如果第二个参数是“id”,Viper将查找ENV变量“ID”。
// BindEnv binds a Viper key to a ENV variable.
// ENV variables are case sensitive.
// If only a key is provided, it will use the env key matching the key, uppercased.
// If more arguments are provided, they will represent the env variable names that
// should bind to this key and will be taken in the specified order.
// EnvPrefix will be used when set when env name is not provided.
func BindEnv(input ...string) error { return v.BindEnv(input...) }
func (v *Viper) BindEnv(input ...string) error {
if len(input) == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("missing key to bind to")
}
key := strings.ToLower(input[0])
if len(input) == 1 {
v.env[key] = append(v.env[key], v.mergeWithEnvPrefix(key))
} else {
v.env[key] = append(v.env[key], input[1:]...)
}
return nil
}
在使用ENV变量时需要注意的一件重要事情是,每次访问时都会读取值。在调用BindEnv时,Viper不固定该值。
AutomaticEnv是一个强大的助手,特别是与SetEnvPrefix结合使用时。当调用时,Viper将在任何时候发出viper.Get请求时检查环境变量。它将适用以下规则。它将检查一个环境变量,该变量的名称与升级后的键相匹配,如果设置了,则使用EnvPrefix作为前缀。
SetEnvKeyReplacer允许您在一定程度上使用strings.Replacer对象重写环境密钥。如果您希望在Get()调用中使用-或其他名称,但又希望您的环境变量使用_分隔符,则此功能非常有用。在viper_test.go中可以找到使用它的示例。
或者,您也可以将EnvKeyReplacer与NewWithOptions工厂函数配合使用。与SetEnvKeyReplacer不同,它接受一个StringReplacer接口,允许您编写自定义的字符串替换逻辑。
默认情况下,空环境变量被认为是未设置的,并将回退到下一个配置源。若要将空环境变量视为集合,请使用AllowEmptyEnv方法。
示例如下:
SetEnvPrefix("spf") // will be uppercased automatically
BindEnv("id")
os.Setenv("SPF_ID", "13") // typically done outside of the app
id := Get("id") // 13
1.3.9 命令行 Flags
与BindEnv一样,该值不是在调用绑定方法时设置,而是在访问绑定方法时设置。这意味着您可以随时进行绑定,即使在init()函数中也是如此。
serverCmd.Flags().Int("port", 1138, "Port to run Application server on")
viper.BindPFlag("port", serverCmd.Flags().Lookup("port"))
您还可以绑定一组现有的p标志(pflag.FlagSet):
pflag.Int("flagname", 1234, "help message for flagname")
pflag.Parse()
viper.BindPFlags(pflag.CommandLine)
i := viper.GetInt("flagname") // retrieve values from viper instead of pflag
PFLAG包可以通过导入这些标志来处理为FLAG包定义的标志。这是通过调用由名为AddGoFlagSet()的PFLAG包提供的便利函数来实现的。
package main
import (
"flag"
"github.com/spf13/pflag"
)
func main() {
// using standard library "flag" package
flag.Int("flagname", 1234, "help message for flagname")
pflag.CommandLine.AddGoFlagSet(flag.CommandLine)
pflag.Parse()
viper.BindPFlags(pflag.CommandLine)
i := viper.GetInt("flagname") // retrieve value from viper
// ...
}
1.3.8.1 Flag 接口
Viper provides two Go interfaces to bind other flag systems if you don’t use Pflags.
FlagValue represents a single flag. This is a very simple example on how to implement this interface:
type myFlag struct {}
func (f myFlag) HasChanged() bool { return false }
func (f myFlag) Name() string { return "my-flag-name" }
func (f myFlag) ValueString() string { return "my-flag-value" }
func (f myFlag) ValueType() string { return "string" }
Once your flag implements this interface, you can simply tell Viper to bind it:
viper.BindFlagValue("my-flag-name", myFlag{})
FlagValueSet represents a group of flags. This is a very simple example on how to implement this interface:
type myFlagSet struct {
flags []myFlag
}
func (f myFlagSet) VisitAll(fn func(FlagValue)) {
for _, flag := range flags {
fn(flag)
}
}
Once your flag set implements this interface, you can simply tell Viper to bind it:
fSet := myFlagSet{
flags: []myFlag{myFlag{}, myFlag{}},
}
viper.BindFlagValues("my-flags", fSet)
1.3.9 配置中心
viper 使用crypt从 K/V 存储检索配置,这意味着您可以存储加密的配置值,如果您拥有正确的GPG密钥环,则会自动解密它们。加密是可选的。
crypt有一个命令行助手,您可以使用它将配置放入您的K/V存储中。crypt默认是 http://127.0.0.1:4001 的 etcd。
下文以 etcd 为例
1.3.9.1 未加密
viper.AddRemoteProvider("etcd3", "http://127.0.0.1:4001", "/config/hugo.json")
viper.SetConfigType("json") // because there is no file extension in a stream of bytes, supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
1.3.9.2 加密
viper.AddSecureRemoteProvider("etcd","http://127.0.0.1:4001", "/config/hugo.json", "/etc/secrets/mykeyring.gpg")
viper.SetConfigType("json")
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
1.3.9.3 监听变化
// alternatively, you can create a new viper instance.
var runtime_viper = viper.New()
runtime_viper.AddRemoteProvider("etcd", "http://127.0.0.1:4001", "/config/hugo.yml")
runtime_viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // because there is no file extension in a stream of bytes, supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
// read from remote config the first time.
err := runtime_viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
// unmarshal config
runtime_viper.Unmarshal(&runtime_conf)
// open a goroutine to watch remote changes forever
go func(){
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 5) // delay after each request
// currently, only tested with etcd support
err := runtime_viper.WatchRemoteConfig()
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("unable to read remote config: %v", err)
continue
}
// unmarshal new config into our runtime config struct. you can also use channel
// to implement a signal to notify the system of the changes
runtime_viper.Unmarshal(&runtime_conf)
}
}()
1.4 读取
Get(key string) any
GetBool(key string) bool
GetFloat64(key string) float64
GetInt(key string) int
GetIntSlice(key string) []int
GetString(key string) string
GetStringMap(key string) map[string]any
GetStringMapString(key string) map[string]string
GetStringSlice(key string) []string
GetTime(key string) time.Time
GetDuration(key string) time.Duration
IsSet(key string) bool
AllSettings() map[string]any
One important thing to recognize is that each Get function will return a zero value if it’s not found. To check if a given key exists, the IsSet() method has been provided.
viper.GetString("logfile") // case-insensitive Setting & Getting
if viper.GetBool("verbose") {
fmt.Println("verbose enabled")
}
1.4.1 嵌套式获取
{
"host": {
"address": "localhost",
"port": 5799
},
"datastore": {
"metric": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3099
},
"warehouse": {
"host": "198.0.0.1",
"port": 2112
}
}
}
GetString("datastore.metric.host") // (returns "127.0.0.1")
1.4.2 数组下标访问
Viper可以通过在路径中使用数字来访问数组索引。例如:
{
"host": {
"address": "localhost",
"ports": [
5799,
6029
]
},
"datastore": {
"metric": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3099
},
"warehouse": {
"host": "198.0.0.1",
"port": 2112
}
}
}
GetInt("host.ports.1") // returns 6029
1.4.3 显式的 delimited key path
如果有显式的 delimited key path,它的优先级最高
{
"datastore.metric.host": "0.0.0.0",
"host": {
"address": "localhost",
"port": 5799
},
"datastore": {
"metric": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3099
},
"warehouse": {
"host": "198.0.0.1",
"port": 2112
}
}
}
GetString("datastore.metric.host") // returns "0.0.0.0"
1.4.4 解析子树
在开发可重用模块时,提取配置的子集并将其传递给模块通常很有用。通过这种方式,可以使用不同的配置多次实例化模块。
例如,应用程序可能会将多个不同的缓存存储用于不同的目的:
cache:
cache1:
max-items: 100
item-size: 64
cache2:
max-items: 200
item-size: 80
cache1Config := viper.Sub("cache.cache1")
if cache1Config == nil { // Sub returns nil if the key cannot be found
panic("cache configuration not found")
}
cache1 := NewCache(cache1Config)
func NewCache(v *Viper) *Cache {
return &Cache{
MaxItems: v.GetInt("max-items"),
ItemSize: v.GetInt("item-size"),
}
}
二、源码
viper.go 有 1500 行,.viper_test.go 有 2100 行,主要是这两个文件
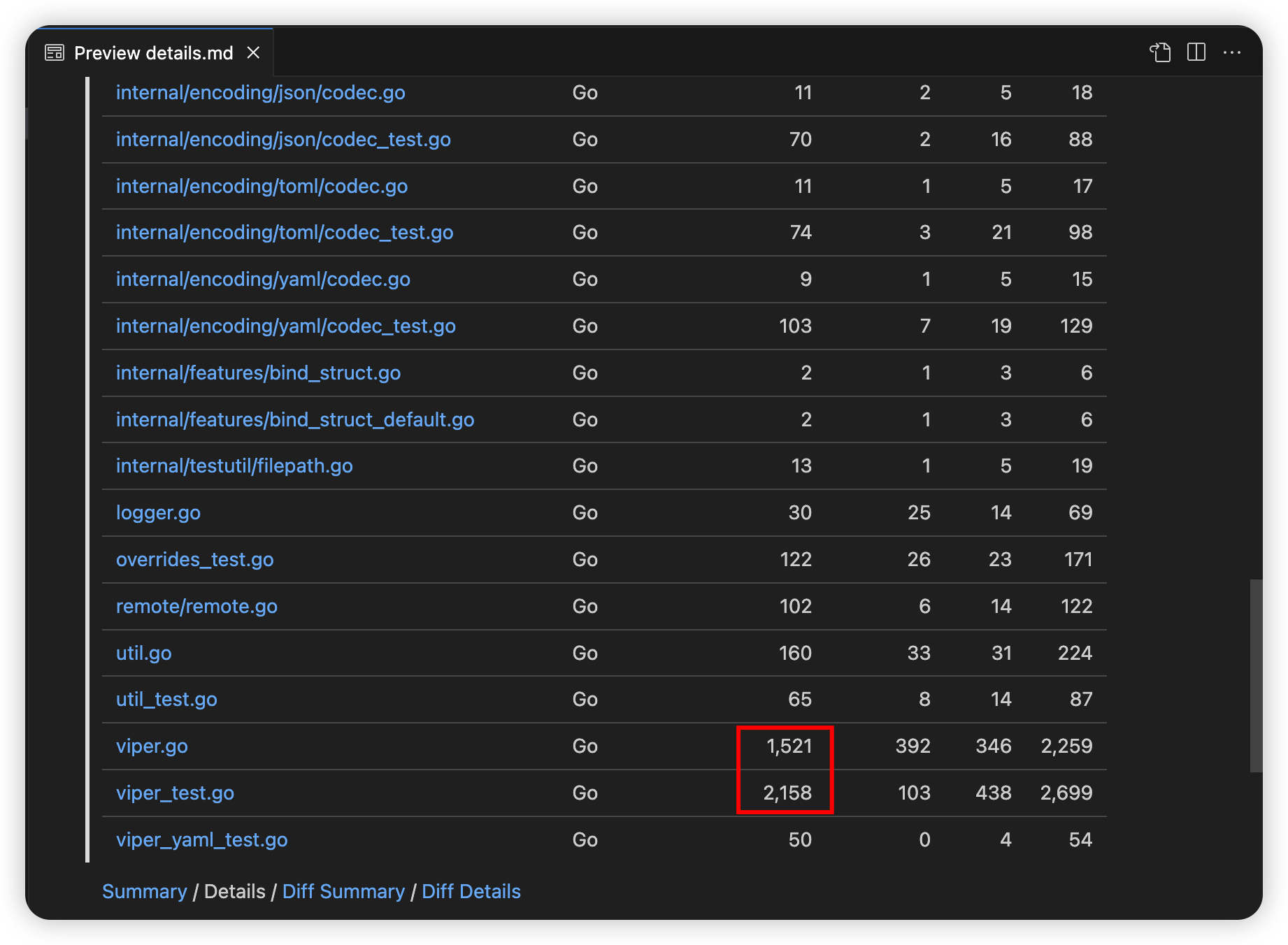
viper.go 引用了如下库
"github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify" // 监听文件系统通知 9k
"github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure" // 通过 struct tag, 从 map[string]interface{} 解析到 struct 7k
slog "github.com/sagikazarmark/slog-shim" // 日志 已被合入 go 1.21
"github.com/spf13/afero" // 文件系统抽象 5k
"github.com/spf13/cast" // 类型强转 3k
"github.com/spf13/pflag" // 命令行参数 2k
首先实例化一个 package 级别的对象,并在 package 的 init() 方法实例化它:
var v *Viper
func init() {
v = New()
}
2.1 定义 Error
然后定义了 6 种 Error()
// 1. 因为要存序列化的 err, 所以定义为 struct
// ConfigMarshalError happens when failing to marshal the configuration.
type ConfigMarshalError struct {
err error
}
// 2. 不支持的配置类型, 直接返回 配置类型 string 即可
// UnsupportedConfigError denotes encountering an unsupported
// configuration filetype.
type UnsupportedConfigError string
// 3. 不支持的远端配置类型, 当前只支持 etcd 和 consul
// UnsupportedRemoteProviderError denotes encountering an unsupported remote
// provider. Currently only etcd and Consul are supported.
type UnsupportedRemoteProviderError string
// 4. 从配置中心拉配置,的错误(配置中心内部的错误,或网络)
// RemoteConfigError denotes encountering an error while trying to
// pull the configuration from the remote provider.
type RemoteConfigError string
// 5. 文件不存在,最常见的错误,包含文件名和路径
// ConfigFileNotFoundError denotes failing to find configuration file.
type ConfigFileNotFoundError struct {
name, locations string
}
// 6. 配置文件已经存在,因为 viper 支持回写配置文件时,是否覆盖的选项
// ConfigFileAlreadyExistsError denotes failure to write new configuration file.
type ConfigFileAlreadyExistsError string
2.2 Viper struct 定义
定义顶层的 Viper struct:
// Viper is a prioritized configuration registry. It
// maintains a set of configuration sources, fetches
// values to populate those, and provides them according
// to the source's priority.
// The priority of the sources is the following:
// 1. overrides
// 2. flags
// 3. env. variables
// 4. config file
// 5. key/value store
// 6. defaults
//
// For example, if values from the following sources were loaded:
//
// Defaults : {
// "secret": "",
// "user": "default",
// "endpoint": "https://localhost"
// }
// Config : {
// "user": "root"
// "secret": "defaultsecret"
// }
// Env : {
// "secret": "somesecretkey"
// }
//
// The resulting config will have the following values:
//
// {
// "secret": "somesecretkey",
// "user": "root",
// "endpoint": "https://localhost"
// }
//
// Note: Vipers are not safe for concurrent Get() and Set() operations.
type Viper struct {
// 嵌套层级的分隔符,默认是 .
// Delimiter that separates a list of keys
// used to access a nested value in one go
keyDelim string
// 支持多个文件搜索路径
// A set of paths to look for the config file in
configPaths []string
// 用作者自己的库,而不是 golang 官方的 os 包,读文件
// The filesystem to read config from.
fs afero.Fs
// 支持多个配置中心搜索路径
// A set of remote providers to search for the configuration
remoteProviders []*defaultRemoteProvider
// Name of file to look for inside the path
configName string // 文件名
configFile string // TODO
configType string // 文件格式,如 JSON
configPermissions os.FileMode // 文件的 chmod 权限
envPrefix string // 环境变量前缀
// ini 格式的特殊选项
// Specific commands for ini parsing
iniLoadOptions ini.LoadOptions
automaticEnvApplied bool // 是否自动应用环境变量
envKeyReplacer StringReplacer // 环境变量单词的分隔符,默认是 _
allowEmptyEnv bool // 是否允许空环境变量
parents []string // TODO
config map[string]any // 最终的配置
override map[string]any // 覆盖的配置
defaults map[string]any // 默认的配置
kvstore map[string]any // 远端配置中心的配置
pflags map[string]FlagValue // 命令行参数
env map[string][]string // 环境变量
aliases map[string]string // 别名
typeByDefValue bool // TODO
onConfigChange func(fsnotify.Event) // 监听配置文件的回调函数
logger *slog.Logger // 日志接口, 兼容老 slog 和 go 1.21 的 slog
// TODO: should probably be protected with a mutex
encoderRegistry *encoding.EncoderRegistry // 编码工厂
decoderRegistry *encoding.DecoderRegistry // 解码工厂
}
2.3 构造:New 和 函数式 Options
实例化的方法如下:
// New returns an initialized Viper instance.
func New() *Viper {
v := new(Viper)
v.keyDelim = "."
v.configName = "config"
v.configPermissions = os.FileMode(0o644)
v.fs = afero.NewOsFs()
v.config = make(map[string]any)
v.parents = []string{}
v.override = make(map[string]any)
v.defaults = make(map[string]any)
v.kvstore = make(map[string]any)
v.pflags = make(map[string]FlagValue)
v.env = make(map[string][]string)
v.aliases = make(map[string]string)
v.typeByDefValue = false
v.logger = slog.New(&discardHandler{})
v.resetEncoding() // 向工厂注册 yaml,json,toml,hcl,ini,java properties,dotenv
return v
}
函数式编程,配置 option:
// 这里两篇文章是很好的设计理念,通过函数式的 Option,便于扩展,便于用户使用
// Option configures Viper using the functional options paradigm popularized by Rob Pike and Dave Cheney.
// If you're unfamiliar with this style,
// see https://commandcenter.blogspot.com/2014/01/self-referential-functions-and-design.html and
// https://dave.cheney.net/2014/10/17/functional-options-for-friendly-apis.
type Option interface { // 定义一个接口
apply(v *Viper) // 其有 apply 方法,apply 方法可以传入 *Viper 参数,并改变 *Viper 的行为
}
type optionFunc func(v *Viper) // 定义一个类型
func (fn optionFunc) apply(v *Viper) { // 这个类型实现了 Option 接口
fn(v)
}
apply() 函数只被 NewWithOptions() 这一个地方调用了,其遍历并应用 opts:
// NewWithOptions creates a new Viper instance.
func NewWithOptions(opts ...Option) *Viper {
v := New()
for _, opt := range opts {
opt.apply(v)
}
v.resetEncoding()
return v
}
有 4 个地方调用了 Option interface,详细情况如下:
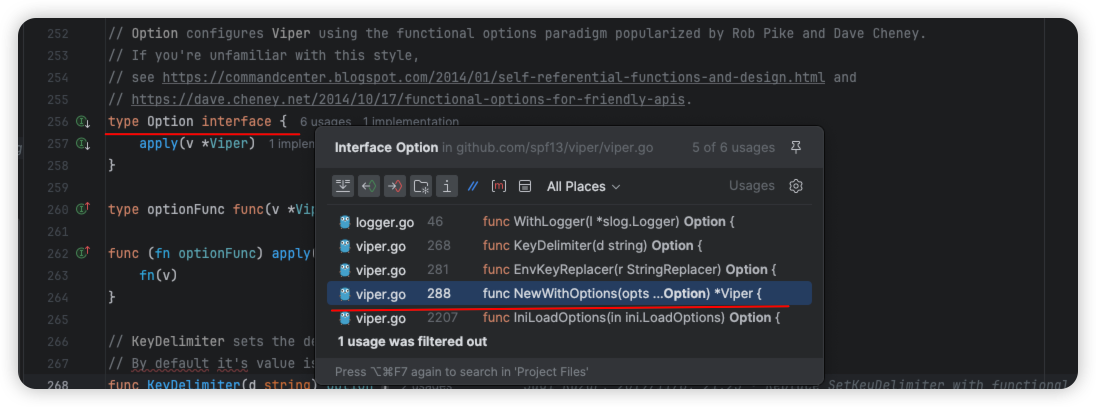
// 第一处,设置 logger
// WithLogger sets a custom logger.
func WithLogger(l *slog.Logger) Option {
return optionFunc(func(v *Viper) {
v.logger = l
})
}
// 第二处调用,设置嵌套标识符,默认是 .
// KeyDelimiter sets the delimiter used for determining key parts.
// By default it's value is ".".
func KeyDelimiter(d string) Option {
return optionFunc(func(v *Viper) {
v.keyDelim = d
})
}
// 第三处调用,设置嵌套标识符,默认是 .
// EnvKeyReplacer sets a replacer used for mapping environment variables to internal keys.
func EnvKeyReplacer(r StringReplacer) Option {
return optionFunc(func(v *Viper) {
v.envKeyReplacer = r
})
}
// 第四处调用,不太重要的 ini 类型
// IniLoadOptions sets the load options for ini parsing.
func IniLoadOptions(in ini.LoadOptions) Option {
return optionFunc(func(v *Viper) {
v.iniLoadOptions = in
})
}
2.4 Reset
Reset函数仅用于测试,单测,或应用程序的业务逻辑测试
// In the public interface for the viper package so applications
// can use it in their testing as well.
func Reset() {
v = New()
SupportedExts = []string{"json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "hcl", "tfvars", "dotenv", "env", "ini"}
SupportedRemoteProviders = []string{"etcd", "etcd3", "consul", "firestore", "nats"}
}
2.5 配置中心
2.5.1 接口定义
secretKeyring:表示密钥环的路径或位置。它指定了密钥环文件的路径或位置,用于对敏感配置数据进行加密或解密操作。密钥环通常用于保护敏感信息,如密码、API密钥等
type defaultRemoteProvider struct {
provider string // 配置中心后端的类型,可以是某个特定的服务提供商或框架,例如"consul"、"etcd"、"zookeeper"等。
endpoint string // 配置中心的地址或终端点。它指定了配置中心的网络地址或连接终端点,用于与配置中心进行通信。
path string // 配置中心中存储配置的路径。它指定了在配置中心中存储配置的位置或路径,用于定位特定的配置数据。
secretKeyring string // 密钥环的路径或位置。它指定了密钥文件的路径或位置,用于对敏感配置数据进行加密或解密操作。
}
func (rp defaultRemoteProvider) Provider() string {
return rp.provider
}
func (rp defaultRemoteProvider) Endpoint() string {
return rp.endpoint
}
func (rp defaultRemoteProvider) Path() string {
return rp.path
}
func (rp defaultRemoteProvider) SecretKeyring() string {
return rp.secretKeyring
}
// 定义了接口,虽然目前只有一个实现,但如果长年累月后,大版本升级时就对老用户很友好了
// RemoteProvider stores the configuration necessary
// to connect to a remote key/value store.
// Optional secretKeyring to unencrypt encrypted values
// can be provided.
type RemoteProvider interface {
Provider() string
Endpoint() string
Path() string
SecretKeyring() string
}
2.5.2 添加 RemoteProvider
// AddRemoteProvider adds a remote configuration source.
// Remote Providers are searched in the order they are added.
// provider is a string value: "etcd", "etcd3", "consul", "firestore" or "nats" are currently supported.
// endpoint is the url. etcd requires http://ip:port, consul requires ip:port, nats requires nats://ip:port
// path is the path in the k/v store to retrieve configuration
// To retrieve a config file called myapp.json from /configs/myapp.json
// you should set path to /configs and set config name (SetConfigName()) to
// "myapp".
func AddRemoteProvider(provider, endpoint, path string) error {
return v.AddRemoteProvider(provider, endpoint, path)
}
func (v *Viper) AddRemoteProvider(provider, endpoint, path string) error {
if !stringInSlice(provider, SupportedRemoteProviders) {
return UnsupportedRemoteProviderError(provider)
}
if provider != "" && endpoint != "" {
v.logger.Info("adding remote provider", "provider", provider, "endpoint", endpoint)
rp := &defaultRemoteProvider{
endpoint: endpoint,
provider: provider,
path: path,
}
if !v.providerPathExists(rp) {
v.remoteProviders = append(v.remoteProviders, rp)
}
}
return nil
}
// AddSecureRemoteProvider adds a remote configuration source.
// Secure Remote Providers are searched in the order they are added.
// provider is a string value: "etcd", "etcd3", "consul", "firestore" or "nats" are currently supported.
// endpoint is the url. etcd requires http://ip:port consul requires ip:port
// secretkeyring is the filepath to your openpgp secret keyring. e.g. /etc/secrets/myring.gpg
// path is the path in the k/v store to retrieve configuration
// To retrieve a config file called myapp.json from /configs/myapp.json
// you should set path to /configs and set config name (SetConfigName()) to
// "myapp".
// Secure Remote Providers are implemented with github.com/bketelsen/crypt.
func AddSecureRemoteProvider(provider, endpoint, path, secretkeyring string) error {
return v.AddSecureRemoteProvider(provider, endpoint, path, secretkeyring)
}
func (v *Viper) AddSecureRemoteProvider(provider, endpoint, path, secretkeyring string) error {
if !stringInSlice(provider, SupportedRemoteProviders) {
return UnsupportedRemoteProviderError(provider)
}
if provider != "" && endpoint != "" {
v.logger.Info("adding remote provider", "provider", provider, "endpoint", endpoint)
rp := &defaultRemoteProvider{
endpoint: endpoint,
provider: provider,
path: path,
secretKeyring: secretkeyring,
}
if !v.providerPathExists(rp) {
v.remoteProviders = append(v.remoteProviders, rp)
}
}
return nil
}
func (v *Viper) providerPathExists(p *defaultRemoteProvider) bool {
for _, y := range v.remoteProviders {
if reflect.DeepEqual(y, p) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
2.6 监听配置变化
启动了两级 goroutine,WatchConfig() 是非阻塞的,内层 goroutine 会持续运行。PS:外层 goroutine 等待内层 goroutine 结束后,才结束自身。
// 包级方法
// OnConfigChange sets the event handler that is called when a config file changes.
func OnConfigChange(run func(in fsnotify.Event)) { v.OnConfigChange(run) }
// 实例级方法,设置回调函数,内部通过第三方库 fsnotify 实现
// OnConfigChange sets the event handler that is called when a config file changes.
func (v *Viper) OnConfigChange(run func(in fsnotify.Event)) {
v.onConfigChange = run
}
// WatchConfig starts watching a config file for changes.
func WatchConfig() { v.WatchConfig() }
// 当且仅当调此方法时,才会启动协程监听变化
// WatchConfig starts watching a config file for changes.
func (v *Viper) WatchConfig() {
initWG := sync.WaitGroup{}
initWG.Add(1)
go func() {
watcher, err := fsnotify.NewWatcher()
if err != nil {
v.logger.Error(fmt.Sprintf("failed to create watcher: %s", err))
os.Exit(1)
}
defer watcher.Close()
// we have to watch the entire directory to pick up renames/atomic saves in a cross-platform way
filename, err := v.getConfigFile()
if err != nil {
v.logger.Error(fmt.Sprintf("get config file: %s", err))
initWG.Done()
return
}
configFile := filepath.Clean(filename)
configDir, _ := filepath.Split(configFile)
realConfigFile, _ := filepath.EvalSymlinks(filename)
eventsWG := sync.WaitGroup{}
eventsWG.Add(1)
go func() {
for {
select {
case event, ok := <-watcher.Events:
if !ok { // 'Events' channel is closed
eventsWG.Done()
return
}
currentConfigFile, _ := filepath.EvalSymlinks(filename)
// we only care about the config file with the following cases:
// 1 - if the config file was modified or created
// 2 - if the real path to the config file changed (eg: k8s ConfigMap replacement)
if (filepath.Clean(event.Name) == configFile &&
(event.Has(fsnotify.Write) || event.Has(fsnotify.Create))) ||
(currentConfigFile != "" && currentConfigFile != realConfigFile) {
realConfigFile = currentConfigFile
err := v.ReadInConfig()
if err != nil {
v.logger.Error(fmt.Sprintf("read config file: %s", err))
}
if v.onConfigChange != nil {
v.onConfigChange(event)
}
} else if filepath.Clean(event.Name) == configFile && event.Has(fsnotify.Remove) {
eventsWG.Done()
return
}
case err, ok := <-watcher.Errors:
if ok { // 'Errors' channel is not closed
v.logger.Error(fmt.Sprintf("watcher error: %s", err))
}
eventsWG.Done()
return
}
}
}()
watcher.Add(configDir)
initWG.Done() // done initializing the watch in this go routine, so the parent routine can move on...
eventsWG.Wait() // now, wait for event loop to end in this go-routine...
}()
initWG.Wait() // make sure that the go routine above fully ended before returning
}
2.7 文件设置
// 直接定义配置文件全路径
// SetConfigFile explicitly defines the path, name and extension of the config file.
// Viper will use this and not check any of the config paths.
func SetConfigFile(in string) { v.SetConfigFile(in) }
func (v *Viper) SetConfigFile(in string) {
if in != "" {
v.configFile = in
}
}
// 查看真正使用的配置文件
// ConfigFileUsed returns the file used to populate the config registry.
func ConfigFileUsed() string { return v.ConfigFileUsed() }
func (v *Viper) ConfigFileUsed() string { return v.configFile }
// 添加配置文件路径(支持多个)
// AddConfigPath adds a path for Viper to search for the config file in.
// Can be called multiple times to define multiple search paths.
func AddConfigPath(in string) { v.AddConfigPath(in) }
func (v *Viper) AddConfigPath(in string) {
if in != "" {
absin := absPathify(v.logger, in) // 从这个函数的单测可看出,可以变为绝对路径,例如可把 ./sub 变为 sub
v.logger.Info("adding path to search paths", "path", absin)
if !stringInSlice(absin, v.configPaths) {
v.configPaths = append(v.configPaths, absin)
}
}
}
2.8 环境变量
2.8.1 配置
// SetEnvPrefix defines a prefix that ENVIRONMENT variables will use.
// E.g. if your prefix is "spf", the env registry will look for env
// variables that start with "SPF_".
func SetEnvPrefix(in string) { v.SetEnvPrefix(in) }
func (v *Viper) SetEnvPrefix(in string) {
if in != "" {
v.envPrefix = in
}
}
func GetEnvPrefix() string { return v.GetEnvPrefix() }
func (v *Viper) GetEnvPrefix() string {
return v.envPrefix
}
// 默认用 _ 和 前缀 拼接 字符串
func (v *Viper) mergeWithEnvPrefix(in string) string {
if v.envPrefix != "" {
return strings.ToUpper(v.envPrefix + "_" + in)
}
return strings.ToUpper(in)
}
// 默认不允许空环境变量
// AllowEmptyEnv tells Viper to consider set,
// but empty environment variables as valid values instead of falling back.
// For backward compatibility reasons this is false by default.
func AllowEmptyEnv(allowEmptyEnv bool) { v.AllowEmptyEnv(allowEmptyEnv) }
func (v *Viper) AllowEmptyEnv(allowEmptyEnv bool) {
v.allowEmptyEnv = allowEmptyEnv
}
// TODO: should getEnv logic be moved into find(). Can generalize the use of
// rewriting keys many things, Ex: Get('someKey') -> some_key
// (camel case to snake case for JSON keys perhaps)
// getEnv is a wrapper around os.Getenv which replaces characters in the original
// key. This allows env vars which have different keys than the config object
// keys.
func (v *Viper) getEnv(key string) (string, bool) {
if v.envKeyReplacer != nil {
key = v.envKeyReplacer.Replace(key) // 字符串替换
}
val, ok := os.LookupEnv(key) // 判断环境变量是否存在
return val, ok && (v.allowEmptyEnv || val != "")
}
2.8.2 绑定
// 环境变量不区分大小写,如果手动指定了,会转为全大写去找环境变量
// 可以指定多个,参数的第一项是要绑定到哪个值,后面的参数按顺序优先级读取
// BindEnv binds a Viper key to a ENV variable.
// ENV variables are case sensitive.
// If only a key is provided, it will use the env key matching the key, uppercased.
// If more arguments are provided, they will represent the env variable names that
// should bind to this key and will be taken in the specified order.
// EnvPrefix will be used when set when env name is not provided.
func BindEnv(input ...string) error { return v.BindEnv(input...) }
// 使用示例如下
func TestAllKeysWithEnv(t *testing.T) {
v := New()
// bind and define environment variables (including a nested one)
v.BindEnv("id")
v.BindEnv("foo.bar")
v.SetEnvKeyReplacer(strings.NewReplacer(".", "_"))
t.Setenv("ID", "13")
t.Setenv("FOO_BAR", "baz")
assert.ElementsMatch(t, []string{"id", "foo.bar"}, v.AllKeys())
}
// 比如之前配置文件「没有」 foo 配置项,然后通过 BindEnv() 绑定环境变量,并通过 os.SetEnv() 写入环境变量,最终可以通过 viper.Get("foo") 获取配置项。
// 因为其内部会将 foo 的环境变量绑定到 foo 的配置项上,即使之前并不存在这个配置项
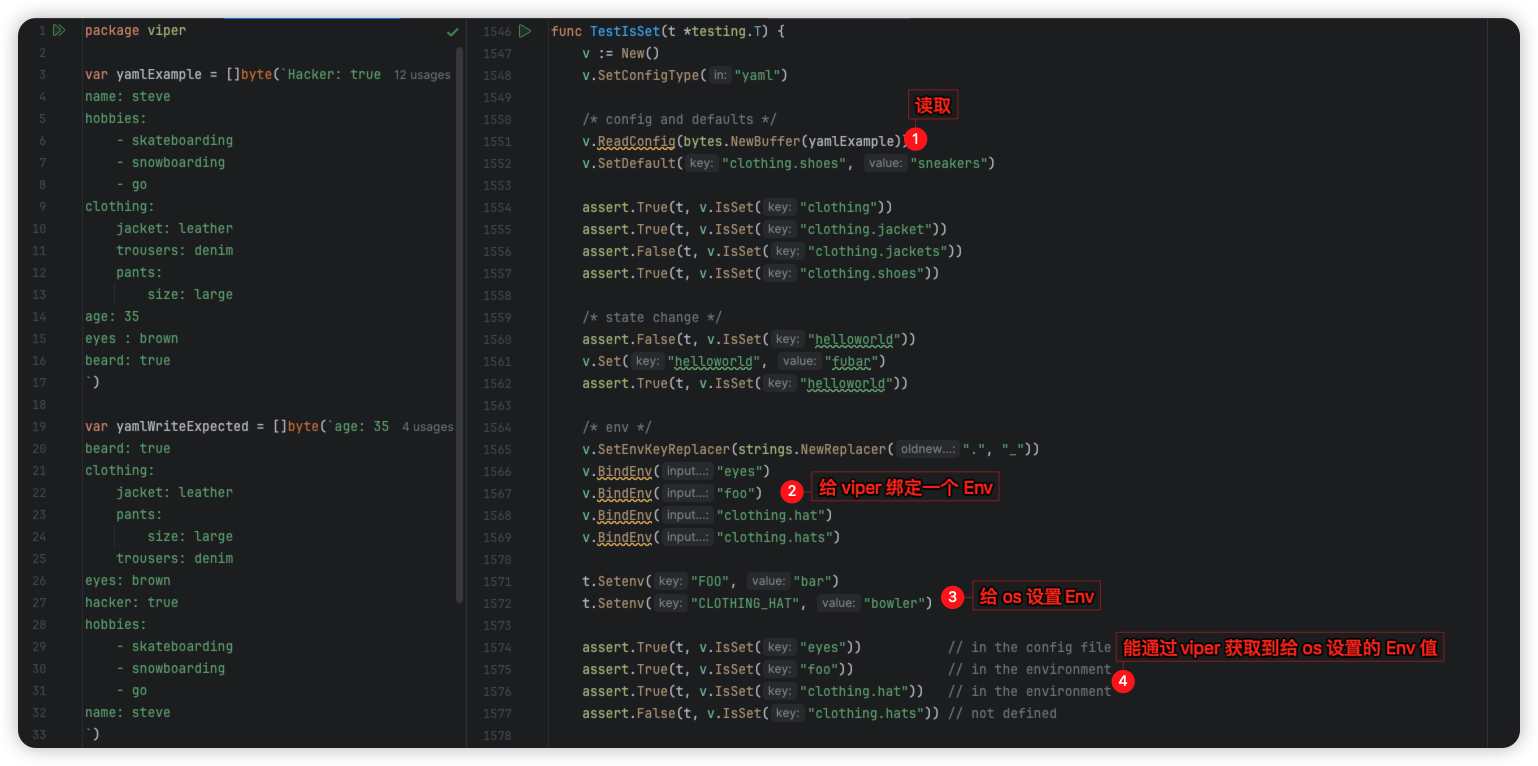
2.8.3 环境变量覆盖配置文件
设置 v.SetEnvKeyReplacer(strings.NewReplacer(“.”, “_”))
然后配置项层级之间默认以 . 作为分隔符
环境变量会将 . 转为 _ 做分隔符
找到环境变量后,会覆盖
2.9 搜索 key
// 递归方法
// searchMap recursively searches for a value for path in source map.
// Returns nil if not found.
// Note: This assumes that the path entries and map keys are lower cased.
func (v *Viper) searchMap(source map[string]any, path []string) any {
if len(path) == 0 {
return source
}
next, ok := source[path[0]]
if ok {
// Fast path
if len(path) == 1 {
return next
}
// Nested case
switch next := next.(type) {
case map[any]any:
return v.searchMap(cast.ToStringMap(next), path[1:])
case map[string]any:
// Type assertion is safe here since it is only reached
// if the type of `next` is the same as the type being asserted
return v.searchMap(next, path[1:])
default:
// got a value but nested key expected, return "nil" for not found
return nil
}
}
return nil
}
// searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes recursively searches for a value for path in source map/slice.
//
// While searchMap() considers each path element as a single map key or slice index, this
// function searches for, and prioritizes, merged path elements.
// e.g., if in the source, "foo" is defined with a sub-key "bar", and "foo.bar"
// is also defined, this latter value is returned for path ["foo", "bar"].
//
// This should be useful only at config level (other maps may not contain dots
// in their keys).
//
// Note: This assumes that the path entries and map keys are lower cased.
func (v *Viper) searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes(source any, path []string) any {
if len(path) == 0 {
return source
}
// search for path prefixes, starting from the longest one
for i := len(path); i > 0; i-- {
prefixKey := strings.ToLower(strings.Join(path[0:i], v.keyDelim))
var val any
switch sourceIndexable := source.(type) {
case []any:
val = v.searchSliceWithPathPrefixes(sourceIndexable, prefixKey, i, path)
case map[string]any:
val = v.searchMapWithPathPrefixes(sourceIndexable, prefixKey, i, path)
}
if val != nil {
return val
}
}
// not found
return nil
}
// searchSliceWithPathPrefixes searches for a value for path in sourceSlice
//
// This function is part of the searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes recurring search and
// should not be called directly from functions other than searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes.
func (v *Viper) searchSliceWithPathPrefixes(
sourceSlice []any,
prefixKey string,
pathIndex int,
path []string,
) any {
// if the prefixKey is not a number or it is out of bounds of the slice
index, err := strconv.Atoi(prefixKey)
if err != nil || len(sourceSlice) <= index {
return nil
}
next := sourceSlice[index]
// Fast path
if pathIndex == len(path) {
return next
}
switch n := next.(type) {
case map[any]any:
return v.searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes(cast.ToStringMap(n), path[pathIndex:])
case map[string]any, []any:
return v.searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes(n, path[pathIndex:])
default:
// got a value but nested key expected, do nothing and look for next prefix
}
// not found
return nil
}
// searchMapWithPathPrefixes searches for a value for path in sourceMap
//
// This function is part of the searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes recurring search and
// should not be called directly from functions other than searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes.
func (v *Viper) searchMapWithPathPrefixes(
sourceMap map[string]any,
prefixKey string,
pathIndex int,
path []string,
) any {
next, ok := sourceMap[prefixKey]
if !ok {
return nil
}
// Fast path
if pathIndex == len(path) {
return next
}
// Nested case
switch n := next.(type) {
case map[any]any:
return v.searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes(cast.ToStringMap(n), path[pathIndex:])
case map[string]any, []any:
return v.searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes(n, path[pathIndex:])
default:
// got a value but nested key expected, do nothing and look for next prefix
}
// not found
return nil
}
// isPathShadowedInDeepMap makes sure the given path is not shadowed somewhere
// on its path in the map.
// e.g., if "foo.bar" has a value in the given map, it “shadows”
//
// "foo.bar.baz" in a lower-priority map
func (v *Viper) isPathShadowedInDeepMap(path []string, m map[string]any) string {
var parentVal any
for i := 1; i < len(path); i++ {
parentVal = v.searchMap(m, path[0:i])
if parentVal == nil {
// not found, no need to add more path elements
return ""
}
switch parentVal.(type) {
case map[any]any:
continue
case map[string]any:
continue
default:
// parentVal is a regular value which shadows "path"
return strings.Join(path[0:i], v.keyDelim)
}
}
return ""
}
// isPathShadowedInFlatMap makes sure the given path is not shadowed somewhere
// in a sub-path of the map.
// e.g., if "foo.bar" has a value in the given map, it “shadows”
//
// "foo.bar.baz" in a lower-priority map
func (v *Viper) isPathShadowedInFlatMap(path []string, mi any) string {
// unify input map
var m map[string]interface{}
switch miv := mi.(type) {
case map[string]string:
m = castMapStringToMapInterface(miv)
case map[string]FlagValue:
m = castMapFlagToMapInterface(miv)
default:
return ""
}
// scan paths
var parentKey string
for i := 1; i < len(path); i++ {
parentKey = strings.Join(path[0:i], v.keyDelim)
if _, ok := m[parentKey]; ok {
return parentKey
}
}
return ""
}
// isPathShadowedInAutoEnv makes sure the given path is not shadowed somewhere
// in the environment, when automatic env is on.
// e.g., if "foo.bar" has a value in the environment, it “shadows”
//
// "foo.bar.baz" in a lower-priority map
func (v *Viper) isPathShadowedInAutoEnv(path []string) string {
var parentKey string
for i := 1; i < len(path); i++ {
parentKey = strings.Join(path[0:i], v.keyDelim)
if _, ok := v.getEnv(v.mergeWithEnvPrefix(parentKey)); ok {
return parentKey
}
}
return ""
}
2.10 Get 获取一个 key 的值
// Get can retrieve any value given the key to use.
// Get is case-insensitive for a key.
// Get has the behavior of returning the value associated with the first
// place from where it is set. Viper will check in the following order:
// override, flag, env, config file, key/value store, default
//
// Get returns an interface. For a specific value use one of the Get____ methods.
func Get(key string) any { return v.Get(key) }
func (v *Viper) Get(key string) any {
lcaseKey := strings.ToLower(key)
val := v.find(lcaseKey, true)
if val == nil {
return nil
}
if v.typeByDefValue {
// TODO(bep) this branch isn't covered by a single test.
valType := val
path := strings.Split(lcaseKey, v.keyDelim)
defVal := v.searchMap(v.defaults, path)
if defVal != nil {
valType = defVal
}
switch valType.(type) {
case bool:
return cast.ToBool(val)
case string:
return cast.ToString(val)
case int32, int16, int8, int:
return cast.ToInt(val)
case uint:
return cast.ToUint(val)
case uint32:
return cast.ToUint32(val)
case uint64:
return cast.ToUint64(val)
case int64:
return cast.ToInt64(val)
case float64, float32:
return cast.ToFloat64(val)
case time.Time:
return cast.ToTime(val)
case time.Duration:
return cast.ToDuration(val)
case []string:
return cast.ToStringSlice(val)
case []int:
return cast.ToIntSlice(val)
case []time.Duration:
return cast.ToDurationSlice(val)
}
}
return val
}
2.11 Unmarshal
和官方的 Unmarshal 方法不一样,不支持 json tag,使用时需注意。因为最佳实践建议通过 GetXXX() 方法,而不是 Unmarshal 到 struct,所以推荐看官方的 Unmarshal,可跳过此方法。
// UnmarshalKey takes a single key and unmarshals it into a Struct.
func UnmarshalKey(key string, rawVal any, opts ...DecoderConfigOption) error {
// Unmarshal unmarshals the config into a Struct. Make sure that the tags
// on the fields of the structure are properly set.
func Unmarshal(rawVal any, opts ...DecoderConfigOption) error {
func (v *Viper) decodeStructKeys(input any, opts ...DecoderConfigOption) ([]string, error) {
// defaultDecoderConfig returns default mapstructure.DecoderConfig with support
// of time.Duration values & string slices.
func defaultDecoderConfig(output any, opts ...DecoderConfigOption) *mapstructure.DecoderConfig {
// decode is a wrapper around mapstructure.Decode that mimics the WeakDecode functionality.
func decode(input any, config *mapstructure.DecoderConfig) error {
// UnmarshalExact unmarshals the config into a Struct, erroring if a field is nonexistent
// in the destination struct.
func UnmarshalExact(rawVal any, opts ...DecoderConfigOption) error {
return v.UnmarshalExact(rawVal, opts...)
}
2.12 BindPFlag
// BindPFlag binds a specific key to a pflag (as used by cobra).
// Example (where serverCmd is a Cobra instance):
//
// serverCmd.Flags().Int("port", 1138, "Port to run Application server on")
// Viper.BindPFlag("port", serverCmd.Flags().Lookup("port"))
func BindPFlag(key string, flag *pflag.Flag) error { return v.BindPFlag(key, flag) }
// BindFlagValues binds a full FlagValue set to the configuration, using each flag's long
// name as the config key.
func BindFlagValues(flags FlagValueSet) error { return v.BindFlagValues(flags) }
// BindFlagValue binds a specific key to a FlagValue.
func BindFlagValue(key string, flag FlagValue) error { return v.BindFlagValue(key, flag) }
2.13 关键逻辑 find()
按优先级,赋值
// Given a key, find the value.
//
// Viper will check to see if an alias exists first.
// Viper will then check in the following order:
// flag, env, config file, key/value store.
// Lastly, if no value was found and flagDefault is true, and if the key
// corresponds to a flag, the flag's default value is returned.
//
// Note: this assumes a lower-cased key given.
func (v *Viper) find(lcaseKey string, flagDefault bool) any {
有两个地方调用了,所以 find() 的输入是全小写字母
func (v *Viper) Get(key string) any {
lcaseKey := strings.ToLower(key) // 转小写
val := v.find(lcaseKey, true)
if val == nil {return nil}
return val
}
func (v *Viper) IsSet(key string) bool {
lcaseKey := strings.ToLower(key) // 转小写
val := v.find(lcaseKey, false)
return val != nil
}
下面分析详细逻辑:
// Given a key, find the value.
//
// Viper will check to see if an alias exists first.
// Viper will then check in the following order:
// flag, env, config file, key/value store.
// Lastly, if no value was found and flagDefault is true, and if the key
// corresponds to a flag, the flag's default value is returned.
//
// Note: this assumes a lower-cased key given.
// Get 的参数是 A.B.C.D.E, 会转为全小写 a.b.c.d.e
// 输入的 lcaseKey 是 a.b.c.d.e
func (v *Viper) find(lcaseKey string, flagDefault bool) any {
var (
val any
exists bool
path = strings.Split(lcaseKey, v.keyDelim) // 按默认的分隔符 . 分隔, 即 []{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"}
nested = len(path) > 1 // 是否是嵌套层级,true
)
// 优先级1. alias
// compute the path through the nested maps to the nested value
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInDeepMap(path, castMapStringToMapInterface(v.aliases)) != "" { // 默认 v.alias 是空,因为没有别名
return nil
}
// if the requested key is an alias, then return the proper key
lcaseKey = v.realKey(lcaseKey) // 通过 alias 找到真正的 key, 通过递归做深度优先搜索
path = strings.Split(lcaseKey, v.keyDelim) // 按真正的 lcaseKey 重新计算 path
nested = len(path) > 1 // 同上
// 优先级2. 找 override 的, 应该是通过 SetXXX() 方法赋值的
// Set() override first
val = v.searchMap(v.override, path)
if val != nil {
return val
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInDeepMap(path, v.override) != "" {
return nil
}
// 优先级3. pflags
// PFlag override next
flag, exists := v.pflags[lcaseKey]
if exists && flag.HasChanged() {
switch flag.ValueType() {
case "int", "int8", "int16", "int32", "int64":
return cast.ToInt(flag.ValueString())
case "bool":
return cast.ToBool(flag.ValueString())
case "stringSlice", "stringArray":
s := strings.TrimPrefix(flag.ValueString(), "[")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "]")
res, _ := readAsCSV(s)
return res
case "intSlice":
s := strings.TrimPrefix(flag.ValueString(), "[")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "]")
res, _ := readAsCSV(s)
return cast.ToIntSlice(res)
case "durationSlice":
s := strings.TrimPrefix(flag.ValueString(), "[")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "]")
slice := strings.Split(s, ",")
return cast.ToDurationSlice(slice)
case "stringToString":
return stringToStringConv(flag.ValueString())
case "stringToInt":
return stringToIntConv(flag.ValueString())
default:
return flag.ValueString()
}
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInFlatMap(path, v.pflags) != "" {
return nil
}
// 优先级4. 环境变量
// Env override next
if v.automaticEnvApplied { // 只有设置了环境变量开关, 才会生效
envKey := strings.Join(append(v.parents, lcaseKey), ".")
// even if it hasn't been registered, if automaticEnv is used,
// check any Get request
if val, ok := v.getEnv(v.mergeWithEnvPrefix(envKey)); ok { // 如果设置了 Env 前缀的话
return val
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInAutoEnv(path) != "" {
return nil
}
}
envkeys, exists := v.env[lcaseKey]
if exists {
for _, envkey := range envkeys {
if val, ok := v.getEnv(envkey); ok { // 如果找到了环境变量,直接返回
return val
}
}
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInFlatMap(path, v.env) != "" {
return nil
}
// 优先级5. 在配置文件路径中找
// Config file next
val = v.searchIndexableWithPathPrefixes(v.config, path)
if val != nil {
return val
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInDeepMap(path, v.config) != "" {
return nil
}
// 优先级6. 在配置中心找
// K/V store next
val = v.searchMap(v.kvstore, path)
if val != nil {
return val
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInDeepMap(path, v.kvstore) != "" {
return nil
}
// 优先级7. 默认值
// Default next
val = v.searchMap(v.defaults, path)
if val != nil {
return val
}
if nested && v.isPathShadowedInDeepMap(path, v.defaults) != "" {
return nil
}
// 优先级8. flag 的默认值
if flagDefault {
// last chance: if no value is found and a flag does exist for the key,
// get the flag's default value even if the flag's value has not been set.
if flag, exists := v.pflags[lcaseKey]; exists {
switch flag.ValueType() {
case "int", "int8", "int16", "int32", "int64":
return cast.ToInt(flag.ValueString())
case "bool":
return cast.ToBool(flag.ValueString())
case "stringSlice", "stringArray":
s := strings.TrimPrefix(flag.ValueString(), "[")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "]")
res, _ := readAsCSV(s) // 逗号分隔的字符串是通过 readAsCSV()封装的
return res
case "intSlice":
s := strings.TrimPrefix(flag.ValueString(), "[")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "]")
res, _ := readAsCSV(s)
return cast.ToIntSlice(res)
case "stringToString":
return stringToStringConv(flag.ValueString())
case "stringToInt":
return stringToIntConv(flag.ValueString())
case "durationSlice":
s := strings.TrimPrefix(flag.ValueString(), "[")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "]")
slice := strings.Split(s, ",")
return cast.ToDurationSlice(slice)
default:
return flag.ValueString()
}
}
// last item, no need to check shadowing
}
// 没找到
return nil
}
2.14 alias bieming
// RegisterAlias creates an alias that provides another accessor for the same key.
// This enables one to change a name without breaking the application.
func RegisterAlias(alias, key string) { v.RegisterAlias(alias, key) }
func (v *Viper) RegisterAlias(alias, key string) {
v.registerAlias(alias, strings.ToLower(key))
}
func (v *Viper) registerAlias(alias, key string) {
alias = strings.ToLower(alias)
if alias != key && alias != v.realKey(key) {
_, exists := v.aliases[alias]
if !exists {
// if we alias something that exists in one of the maps to another
// name, we'll never be able to get that value using the original
// name, so move the config value to the new realkey.
if val, ok := v.config[alias]; ok {
delete(v.config, alias)
v.config[key] = val
}
if val, ok := v.kvstore[alias]; ok {
delete(v.kvstore, alias)
v.kvstore[key] = val
}
if val, ok := v.defaults[alias]; ok {
delete(v.defaults, alias)
v.defaults[key] = val
}
if val, ok := v.override[alias]; ok {
delete(v.override, alias)
v.override[key] = val
}
v.aliases[alias] = key
}
} else {
v.logger.Warn("creating circular reference alias", "alias", alias, "key", key, "real_key", v.realKey(key))
}
}
func (v *Viper) realKey(key string) string {
newkey, exists := v.aliases[key]
if exists {
v.logger.Debug("key is an alias", "alias", key, "to", newkey)
return v.realKey(newkey)
}
return key
}
2.15 读文件
// ReadInConfig will discover and load the configuration file from disk
// and key/value stores, searching in one of the defined paths.
func ReadInConfig() error { return v.ReadInConfig() }
// MergeInConfig merges a new configuration with an existing config.
func MergeInConfig() error { return v.MergeInConfig() }
// MergeConfig merges a new configuration with an existing config.
func MergeConfig(in io.Reader) error { return v.MergeConfig(in) }
// MergeConfigMap merges the configuration from the map given with an existing config.
// Note that the map given may be modified.
func MergeConfigMap(cfg map[string]any) error { return v.MergeConfigMap(cfg) }
// WriteConfig writes the current configuration to a file.
func WriteConfig() error { return v.WriteConfig() }
2.16 单测
看 viper_test,通过单测学使用方法,确实非常好用,比代码注释更易懂
其余的就不再看了,后续花时间看更多更新的库,和经典的服务,然后上手模仿