目录
1.回文词
2.猜数字游戏的提示
3.生成元
4.环状序列
5.刽子手游戏
1.回文词
问题描述
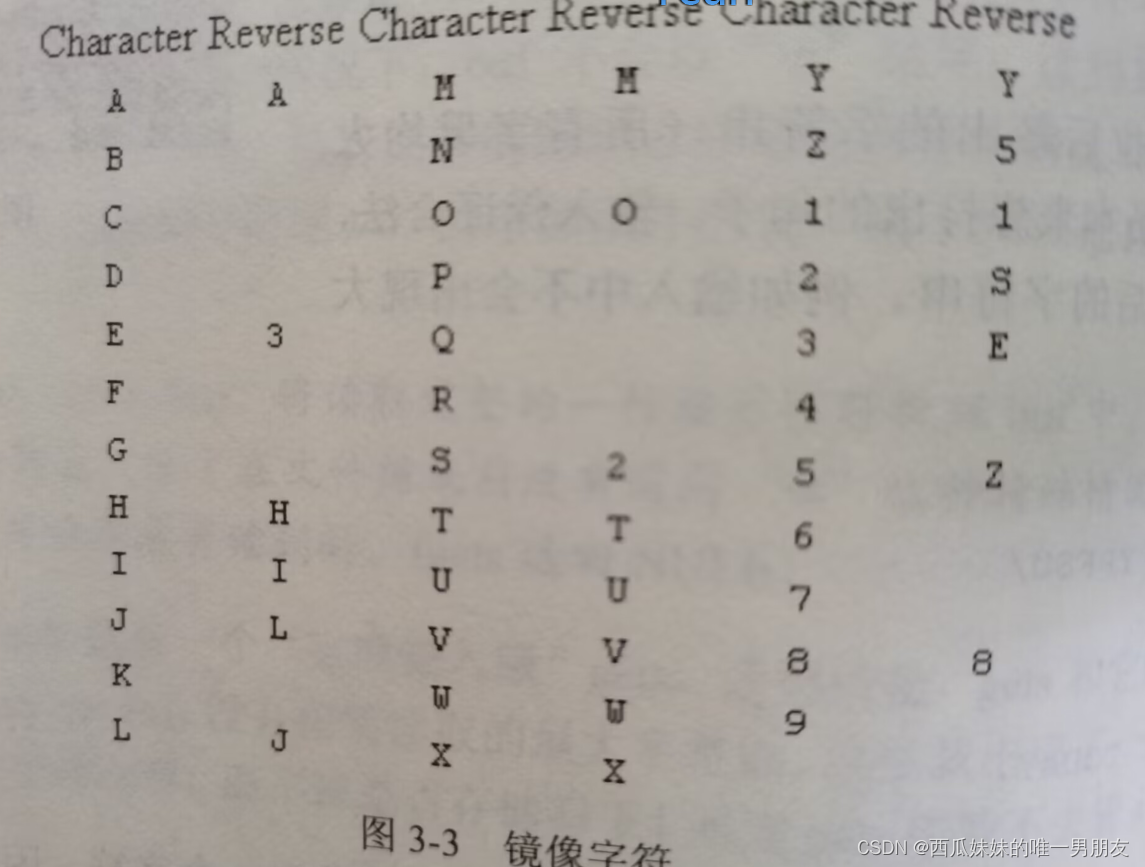
输入一个字符串,判断它是否为回文串以及镜像串。输入字符串保证不含数字0。所谓回文串,就是反转以后和原串相同,如abba和madam。所有镜像串,就是左右镜像之后和原串相同,如2S和3AIAE。注意,并不是每个字符在镜像之后都能找得到一个合法字符。本题中,每个字符的镜像如图所示(空白项表示该字符镜像后不能得到一个合法字符)。
示例代码
#include<iostream>
#include<ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
const char* rev = "A 3 HIL JM O 2TUVWXY51SE Z 8 ";
const char* msg[] = { "not a palindrome","a regular palindrome","a mirrored string","a mirrored palindrome" };
char r(char ch) {
if (isalpha(ch)) {//如果是字母
return rev[ch - 'A'];
}
return rev[ch - '0' + 25];//如果是数字
}
int main() {
char s[30];
while (scanf("%s", s) == 1) {
int len = strlen(s);
int p = 1, m = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (len + 1) / 2; i++) {
if (s[i] != s[len - 1 - i]) {//不是回文串
p = 0;
}
if (r(s[i]) != s[len - 1 - i]) {//不是镜像串
m = 0;
}
}
printf("%s -- is %s.\n\n", s, msg[m * 2 + p]);
}
return 0;
}
2.猜数字游戏的提示
问题描述
实现一个经典“猜数字”游戏。给定答案序列和用户猜的序列,统计有多少数字位置正确(A),有多少数字在两个序列都出现过但位置不对(B)。
输入包含多组数据。每组输入第一行为序列长度n,第二行是答案序列,接下来是若干猜测序列。猜测序列全0时该组数据结束。n=0时输入结束。
样例输入
4
1 3 5 5
1 1 2 3
4 3 3 5
6 5 5 1
6 1 3 5
1 3 5 5
0 0 0 0
10
1 2 2 2 4 5 6 6 6 9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5
1 2 1 3 1 5 1 6 1 9
1 2 2 5 5 5 6 6 6 7
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
样例输出
Game 1:
(1,1)
(2,0)
(1,2)
(1,2)
(4,0)
Game 2:
(2,4)
(3,2)
(5,0)
(7,0)
分析
直接统计可得A,为了求B,对于每个数字(1-9),统计二者出现的次数c1和c2,则min(c1,c2)就是该数字对B的贡献。最后要减去A的部分。
示例代码
#include<iostream>
#define maxn 1010
int main() {
int n, a[maxn], b[maxn];
int kase = 0;
while (scanf("%d", &n) == 1 && n) {//n=0时输入结束
printf("Game %d:\n", ++kase);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
for (;;) {
int A = 0, B = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
if (a[i] == b[i]) {
A++;
}
}
if (b[0] == 0) {//正常的猜测序列不会有0,所以只判断第一个数是否为0即可
break;
}
for (int d = 1; d <= 9; d++) {
int c1 = 0, c2 = 0;//统计数字d在答案序列和预测序列中各出现多少次
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] == d) {
c1++;
}
if (b[i] == d) {
c2++;
}
}
if (c1 < c2) {
B += c1;
}
else {
B += c2;
}
}
printf(" (%d,%d)\n", A, B - A);
}
}
return 0;
}
3.生成元
问题描述
如果x加上x的各个数字之和得到y,就说x是y的生成元。给出n(1<=n<=100000),求最小生成元。无解输出0.例如,n=216,121,2005时的解分别为198,0,1979。
分析
只需一次性枚举100000内的所有正整数m,标记 m加上m的各个数字之和得到的数有一个生成元是m。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#define maxn 100005
int ans[maxn];
int main() {
int T, n;
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));//全赋值为0
for (int m = 1; m < maxn; m++) {
int x = m, y = m;
while (x > 0) {
y += x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
if (ans[y] == 0 || m < ans[y]) {
ans[y] = m;
}
}
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", ans[n]);
}
return 0;
}
4.环状序列
问题描述
长度为n的环状串有n种表示法,分别为从某个位置开始顺时针得到。在这些表示法种,字典序最小的称为“最小表示”。
输入一个长度为n(n<=100)的环状DNA串(只包含A、C、G、T这四种子字符)的一种表示法,你的任务是输出该环状串的最小表示。例如,CTCC的最小表示为CCCT,CGAGTCAGCT的最小i表示为AGCTCGAGTC。
分析
字典序。所谓字典序,就是字符串在字典中的顺序。一般地,对于两个字符串,从第一个字符开始比较,当某一个位置的字符不同时,该位置字符较小的串,字典序较小(例如,abc比bcd小);如果其中一个字符串已经没有更多字符,但另一个字符串还没结束,则较短的字符串的字典序较小(例如,hi比history小)。字典序的概念可以推广到任意序列,例如,序列1,2,4,7比1,2,5小。
用变量ans表示目前为止,字典序最小串在输入串中的起始位置,然后不断更新ans。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#define maxn 105
//环状串s的表示法p是否比表示法q的字典序小
int less(const char* s, int p, int q) {
int n = strlen(s);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[(p + i) % n] != s[(q + i) % n]) {
return s[(p + i) % n] < s[(q + i) % n];
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int T;
char s[maxn];
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%s", s);
int ans = 0;
int n = strlen(s);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (less(s, i, ans)) {
ans = i;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
putchar(s[(i + ans) % n]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
5.刽子手游戏
问题描述
刽子手游戏其实是一款简单猜单词游戏。游戏规则是这样的:计算机想一个单词让你猜,你每次可以猜一个字母。如果单词里有那个字母,所有该字母会显示出来;如果没有这个字母,则计算机会在一幅“刽子手”画上填一笔。这幅画一共需要7笔就能完成,因此你最多只能错6次。注意,猜一个已经猜过的字母也算错。
在本题中,你的任务是编写一个“裁判”程序,输入单词和玩家的猜测,判断玩家赢了(You win.)、输了(You lose.)还是放弃了(You chickened out.)。每组数据包含三行,第1行时游戏编号(-1为输入结束标记),第2行是计算机想的单词,第3行是玩家的猜测。后两行保证只含小写字母。
样例输入
1
cheese
chese
2
cheese
abcdefg
3
cheese
abcdefgij
-1
样例输出
Round 1
You win.
Round 2
You chickened out.
Round 3
You lose.
示例代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#define maxn 100
int left, chance;//还需要猜left个位置,错chance次之后就会输
char s[maxn], s2[maxn];//答案是字符串s,玩家猜的字母序列是s2
int win, lose;//win=1表示已经赢了;lose=1表示已经输了
void guess(char ch) {
int bad = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++) {
if (s[i] == ch) {
left--;
s[i] = ' ';
bad = 0;
}
}
if (bad) --chance;
if (!chance) lose = 1;
if (!left) win = 1;
}
int main() {
int rnd;
while (scanf("%d%s%s", &rnd, s, s2) == 3 && rnd != -1) {
printf("Round %d\n", rnd);
win = lose = 0;//求解一组新数据之前要初始化
left = strlen(s);
chance = 7;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s2); i++) {
guess(s2[i]);//猜一个字母
if (win || lose) {//检查状态
break;
}
}
//根据结果进行输出
if (win)printf("You win.\n");
else if (lose) printf("You lose.\n");
else printf("You chickened out.\n");
}
return 0;
}