tritonserver学习之一:triton使用流程
tritonserver学习之二:tritonserver编译
tritonserver学习之三:tritonserver运行流程
tritonserver学习之四:命令行解析
tritonserver学习之五:backend实现机制
1、环境准备(Ubuntu2004)
1.1 cmake安装
triton backend的编译,cmake的版本要3.17以上,从这里下载当前最新版本cmake,3.28版本:
https://githubfast.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.28.1/cmake-3.28.1.tar.gz进行环境检查:
tar zxvf cmake-3.28.1.tar.gz
cd cmake-3.28.1/
./bootstrap
你可能会遇到如下情况:

这种情况需要安装openssl:
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
安装完成后,重新执行bootstrap则运行成功。
运行make && sudo make install.
1.2 RapidJSON安装
clone代码:
git clone https://github.com/miloyip/rapidjson.git最近github抽风,如果clone不下来就用如下命令:
git clone https://githubfast.com/miloyip/rapidjson.gitcd rapidjson
mkdir build
cd build
make && make install2、c++ 自定义backend
2.1 自定义backend编译
c++自定义backend,上一篇文章:tritonserver学习之五:backend实现机制,有介绍,需要实现7个api,我们以backend代码库的recommended.cc为例,在调试过程中,我是复制了,路径如下:backend/examples/backends/liupeng,稍作改动加一些打印帮助理解:
// Copyright 2021, NVIDIA CORPORATION & AFFILIATES. All rights reserved.
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
// are met:
// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
// documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
// * Neither the name of NVIDIA CORPORATION nor the names of its
// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
// from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS ``AS IS'' AND ANY
// EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
// IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
// PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR
// CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
// EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
// PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
// PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY
// OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
#include "triton/backend/backend_common.h"
#include "triton/backend/backend_input_collector.h"
#include "triton/backend/backend_model.h"
#include "triton/backend/backend_model_instance.h"
#include "triton/backend/backend_output_responder.h"
#include "triton/core/tritonbackend.h"
namespace triton { namespace backend { namespace recommended {
//
// Backend that demonstrates the TRITONBACKEND API. This backend works
// for any model that has 1 input with any datatype and any shape and
// 1 output with the same shape and datatype as the input. The backend
// supports both batching and non-batching models.
//
// For each batch of requests, the backend returns the input tensor
// value in the output tensor.
//
/
extern "C" {
// Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_Initialize when a backend is loaded into
// Triton to allow the backend to create and initialize any state that
// is intended to be shared across all models and model instances that
// use the backend. The backend should also verify version
// compatibility with Triton in this function.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_Initialize(TRITONBACKEND_Backend* backend)
{
const char* cname;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_BackendName(backend, &cname));
std::string name(cname);
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("TRITONBACKEND_Initialize: ") + name).c_str());
// Check the backend API version that Triton supports vs. what this
// backend was compiled against. Make sure that the Triton major
// version is the same and the minor version is >= what this backend
// uses.
uint32_t api_version_major, api_version_minor;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_ApiVersion(&api_version_major, &api_version_minor));
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("Triton TRITONBACKEND API version: ") +
std::to_string(api_version_major) + "." +
std::to_string(api_version_minor))
.c_str());
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("'") + name + "' TRITONBACKEND API version: " +
std::to_string(TRITONBACKEND_API_VERSION_MAJOR) + "." +
std::to_string(TRITONBACKEND_API_VERSION_MINOR))
.c_str());
if ((api_version_major != TRITONBACKEND_API_VERSION_MAJOR) ||
(api_version_minor < TRITONBACKEND_API_VERSION_MINOR)) {
return TRITONSERVER_ErrorNew(
TRITONSERVER_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED,
"triton backend API version does not support this backend");
}
// The backend configuration may contain information needed by the
// backend, such as tritonserver command-line arguments. This
// backend doesn't use any such configuration but for this example
// print whatever is available.
TRITONSERVER_Message* backend_config_message;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_BackendConfig(backend, &backend_config_message));
const char* buffer;
size_t byte_size;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONSERVER_MessageSerializeToJson(
backend_config_message, &buffer, &byte_size));
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("backend configuration:\n") + buffer).c_str());
// This backend does not require any "global" state but as an
// example create a string to demonstrate.
std::string* state = new std::string("backend state");
RETURN_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_BackendSetState(backend, reinterpret_cast<void*>(state)));
return nullptr; // success
}
// Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_Finalize when a backend is no longer
// needed.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_Finalize(TRITONBACKEND_Backend* backend)
{
// Delete the "global" state associated with the backend.
void* vstate;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_BackendState(backend, &vstate));
std::string* state = reinterpret_cast<std::string*>(vstate);
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("TRITONBACKEND_Finalize: state is '") + *state + "'")
.c_str());
delete state;
return nullptr; // success
}
} // extern "C"
/
//
// ModelState
//
// State associated with a model that is using this backend. An object
// of this class is created and associated with each
// TRITONBACKEND_Model. ModelState is derived from BackendModel class
// provided in the backend utilities that provides many common
// functions.
//
class ModelState : public BackendModel {
public:
static TRITONSERVER_Error* Create(
TRITONBACKEND_Model* triton_model, ModelState** state);
virtual ~ModelState() = default;
// Name of the input and output tensor
const std::string& InputTensorName() const { return input_name_; }
const std::string& OutputTensorName() const { return output_name_; }
// Datatype of the input and output tensor
TRITONSERVER_DataType TensorDataType() const { return datatype_; }
// Shape of the input and output tensor as given in the model
// configuration file. This shape will not include the batch
// dimension (if the model has one).
const std::vector<int64_t>& TensorNonBatchShape() const { return nb_shape_; }
// Shape of the input and output tensor, including the batch
// dimension (if the model has one). This method cannot be called
// until the model is completely loaded and initialized, including
// all instances of the model. In practice, this means that backend
// should only call it in TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceExecute.
TRITONSERVER_Error* TensorShape(std::vector<int64_t>& shape);
// Validate that this model is supported by this backend.
TRITONSERVER_Error* ValidateModelConfig();
private:
ModelState(TRITONBACKEND_Model* triton_model);
std::string input_name_;
std::string output_name_;
TRITONSERVER_DataType datatype_;
bool shape_initialized_;
std::vector<int64_t> nb_shape_;
std::vector<int64_t> shape_;
};
ModelState::ModelState(TRITONBACKEND_Model* triton_model)
: BackendModel(triton_model), shape_initialized_(false)
{
// Validate that the model's configuration matches what is supported
// by this backend.
THROW_IF_BACKEND_MODEL_ERROR(ValidateModelConfig());
}
TRITONSERVER_Error*
ModelState::Create(TRITONBACKEND_Model* triton_model, ModelState** state)
{
try {
*state = new ModelState(triton_model);
}
catch (const BackendModelException& ex) {
RETURN_ERROR_IF_TRUE(
ex.err_ == nullptr, TRITONSERVER_ERROR_INTERNAL,
std::string("unexpected nullptr in BackendModelException"));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(ex.err_);
}
return nullptr; // success
}
TRITONSERVER_Error*
ModelState::TensorShape(std::vector<int64_t>& shape)
{
// This backend supports models that batch along the first dimension
// and those that don't batch. For non-batch models the output shape
// will be the shape from the model configuration. For batch models
// the output shape will be the shape from the model configuration
// prepended with [ -1 ] to represent the batch dimension. The
// backend "responder" utility used below will set the appropriate
// batch dimension value for each response. The shape needs to be
// initialized lazily because the SupportsFirstDimBatching function
// cannot be used until the model is completely loaded.
if (!shape_initialized_) {
bool supports_first_dim_batching;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(SupportsFirstDimBatching(&supports_first_dim_batching));
if (supports_first_dim_batching) {
shape_.push_back(-1);
}
shape_.insert(shape_.end(), nb_shape_.begin(), nb_shape_.end());
shape_initialized_ = true;
}
shape = shape_;
return nullptr; // success
}
TRITONSERVER_Error*
ModelState::ValidateModelConfig()
{
// If verbose logging is enabled, dump the model's configuration as
// JSON into the console output.
if (TRITONSERVER_LogIsEnabled(TRITONSERVER_LOG_VERBOSE)) {
common::TritonJson::WriteBuffer buffer;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(ModelConfig().PrettyWrite(&buffer));
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_VERBOSE,
(std::string("model configuration:\n") + buffer.Contents()).c_str());
}
// ModelConfig is the model configuration as a TritonJson
// object. Use the TritonJson utilities to parse the JSON and
// determine if the configuration is supported by this backend.
common::TritonJson::Value inputs, outputs;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(ModelConfig().MemberAsArray("input", &inputs));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(ModelConfig().MemberAsArray("output", &outputs));
// The model must have exactly 1 input and 1 output.
RETURN_ERROR_IF_FALSE(
inputs.ArraySize() == 1, TRITONSERVER_ERROR_INVALID_ARG,
std::string("model configuration must have 1 input"));
RETURN_ERROR_IF_FALSE(
outputs.ArraySize() == 1, TRITONSERVER_ERROR_INVALID_ARG,
std::string("model configuration must have 1 output"));
common::TritonJson::Value input, output;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(inputs.IndexAsObject(0, &input));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(outputs.IndexAsObject(0, &output));
// Record the input and output name in the model state.
const char* input_name;
size_t input_name_len;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(input.MemberAsString("name", &input_name, &input_name_len));
input_name_ = std::string(input_name);
const char* output_name;
size_t output_name_len;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(
output.MemberAsString("name", &output_name, &output_name_len));
output_name_ = std::string(output_name);
// Input and output must have same datatype
std::string input_dtype, output_dtype;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(input.MemberAsString("data_type", &input_dtype));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(output.MemberAsString("data_type", &output_dtype));
RETURN_ERROR_IF_FALSE(
input_dtype == output_dtype, TRITONSERVER_ERROR_INVALID_ARG,
std::string("expected input and output datatype to match, got ") +
input_dtype + " and " + output_dtype);
datatype_ = ModelConfigDataTypeToTritonServerDataType(input_dtype);
// Input and output must have same shape. Reshape is not supported
// on either input or output so flag an error is the model
// configuration uses it.
triton::common::TritonJson::Value reshape;
RETURN_ERROR_IF_TRUE(
input.Find("reshape", &reshape), TRITONSERVER_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED,
std::string("reshape not supported for input tensor"));
RETURN_ERROR_IF_TRUE(
output.Find("reshape", &reshape), TRITONSERVER_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED,
std::string("reshape not supported for output tensor"));
std::vector<int64_t> input_shape, output_shape;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(backend::ParseShape(input, "dims", &input_shape));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(backend::ParseShape(output, "dims", &output_shape));
RETURN_ERROR_IF_FALSE(
input_shape == output_shape, TRITONSERVER_ERROR_INVALID_ARG,
std::string("expected input and output shape to match, got ") +
backend::ShapeToString(input_shape) + " and " +
backend::ShapeToString(output_shape));
nb_shape_ = input_shape;
return nullptr; // success
}
extern "C" {
// Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_ModelInitialize when a model is loaded
// to allow the backend to create any state associated with the model,
// and to also examine the model configuration to determine if the
// configuration is suitable for the backend. Any errors reported by
// this function will prevent the model from loading.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInitialize(TRITONBACKEND_Model* model)
{
// Create a ModelState object and associate it with the
// TRITONBACKEND_Model. If anything goes wrong with initialization
// of the model state then an error is returned and Triton will fail
// to load the model.
ModelState* model_state;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(ModelState::Create(model, &model_state));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_ModelSetState(model, reinterpret_cast<void*>(model_state)));
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
"============TRITONBACKEND_ModelInitialize============");
return nullptr; // success
}
// Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_ModelFinalize when a model is no longer
// needed. The backend should cleanup any state associated with the
// model. This function will not be called until all model instances
// of the model have been finalized.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_ModelFinalize(TRITONBACKEND_Model* model)
{
void* vstate;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ModelState(model, &vstate));
ModelState* model_state = reinterpret_cast<ModelState*>(vstate);
delete model_state;
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
"============TRITONBACKEND_ModelFinalize============");
return nullptr; // success
}
} // extern "C"
/
//
// ModelInstanceState
//
// State associated with a model instance. An object of this class is
// created and associated with each
// TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance. ModelInstanceState is derived from
// BackendModelInstance class provided in the backend utilities that
// provides many common functions.
//
class ModelInstanceState : public BackendModelInstance {
public:
static TRITONSERVER_Error* Create(
ModelState* model_state,
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance* triton_model_instance,
ModelInstanceState** state);
virtual ~ModelInstanceState() = default;
// Get the state of the model that corresponds to this instance.
ModelState* StateForModel() const { return model_state_; }
private:
ModelInstanceState(
ModelState* model_state,
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance* triton_model_instance)
: BackendModelInstance(model_state, triton_model_instance),
model_state_(model_state)
{
}
ModelState* model_state_;
};
TRITONSERVER_Error*
ModelInstanceState::Create(
ModelState* model_state, TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance* triton_model_instance,
ModelInstanceState** state)
{
try {
*state = new ModelInstanceState(model_state, triton_model_instance);
}
catch (const BackendModelInstanceException& ex) {
RETURN_ERROR_IF_TRUE(
ex.err_ == nullptr, TRITONSERVER_ERROR_INTERNAL,
std::string("unexpected nullptr in BackendModelInstanceException"));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(ex.err_);
}
return nullptr; // success
}
extern "C" {
// Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceInitialize when a model
// instance is created to allow the backend to initialize any state
// associated with the instance.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceInitialize(TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance* instance)
{
// Get the model state associated with this instance's model.
TRITONBACKEND_Model* model;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceModel(instance, &model));
void* vmodelstate;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ModelState(model, &vmodelstate));
ModelState* model_state = reinterpret_cast<ModelState*>(vmodelstate);
// Create a ModelInstanceState object and associate it with the
// TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance.
ModelInstanceState* instance_state;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(
ModelInstanceState::Create(model_state, instance, &instance_state));
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceSetState(
instance, reinterpret_cast<void*>(instance_state)));
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
"============TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceInitialize============");
return nullptr; // success
}
// Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceFinalize when a model
// instance is no longer needed. The backend should cleanup any state
// associated with the model instance.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceFinalize(TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance* instance)
{
void* vstate;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceState(instance, &vstate));
ModelInstanceState* instance_state =
reinterpret_cast<ModelInstanceState*>(vstate);
delete instance_state;
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
"============TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceFinalize============");
return nullptr; // success
}
} // extern "C"
/
extern "C" {
// When Triton calls TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceExecute it is required
// that a backend create a response for each request in the batch. A
// response may be the output tensors required for that request or may
// be an error that is returned in the response.
//
TRITONSERVER_Error*
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceExecute(
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstance* instance, TRITONBACKEND_Request** requests,
const uint32_t request_count)
{
// Collect various timestamps during the execution of this batch or
// requests. These values are reported below before returning from
// the function.
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
"============TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceExecute============");
uint64_t exec_start_ns = 0;
SET_TIMESTAMP(exec_start_ns);
// Triton will not call this function simultaneously for the same
// 'instance'. But since this backend could be used by multiple
// instances from multiple models the implementation needs to handle
// multiple calls to this function at the same time (with different
// 'instance' objects). Best practice for a high-performance
// implementation is to avoid introducing mutex/lock and instead use
// only function-local and model-instance-specific state.
ModelInstanceState* instance_state;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceState(
instance, reinterpret_cast<void**>(&instance_state)));
ModelState* model_state = instance_state->StateForModel();
// 'responses' is initialized as a parallel array to 'requests',
// with one TRITONBACKEND_Response object for each
// TRITONBACKEND_Request object. If something goes wrong while
// creating these response objects, the backend simply returns an
// error from TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceExecute, indicating to
// Triton that this backend did not create or send any responses and
// so it is up to Triton to create and send an appropriate error
// response for each request. RETURN_IF_ERROR is one of several
// useful macros for error handling that can be found in
// backend_common.h.
std::vector<TRITONBACKEND_Response*> responses;
responses.reserve(request_count);
for (uint32_t r = 0; r < request_count; ++r) {
TRITONBACKEND_Request* request = requests[r];
TRITONBACKEND_Response* response;
RETURN_IF_ERROR(TRITONBACKEND_ResponseNew(&response, request));
responses.push_back(response);
}
// At this point, the backend takes ownership of 'requests', which
// means that it is responsible for sending a response for every
// request. From here, even if something goes wrong in processing,
// the backend must return 'nullptr' from this function to indicate
// success. Any errors and failures must be communicated via the
// response objects.
//
// To simplify error handling, the backend utilities manage
// 'responses' in a specific way and it is recommended that backends
// follow this same pattern. When an error is detected in the
// processing of a request, an appropriate error response is sent
// and the corresponding TRITONBACKEND_Response object within
// 'responses' is set to nullptr to indicate that the
// request/response has already been handled and no further processing
// should be performed for that request. Even if all responses fail,
// the backend still allows execution to flow to the end of the
// function so that statistics are correctly reported by the calls
// to TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceReportStatistics and
// TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceReportBatchStatistics.
// RESPOND_AND_SET_NULL_IF_ERROR, and
// RESPOND_ALL_AND_SET_NULL_IF_ERROR are macros from
// backend_common.h that assist in this management of response
// objects.
// The backend could iterate over the 'requests' and process each
// one separately. But for performance reasons it is usually
// preferred to create batched input tensors that are processed
// simultaneously. This is especially true for devices like GPUs
// that are capable of exploiting the large amount parallelism
// exposed by larger data sets.
//
// The backend utilities provide a "collector" to facilitate this
// batching process. The 'collector's ProcessTensor function will
// combine a tensor's value from each request in the batch into a
// single contiguous buffer. The buffer can be provided by the
// backend or 'collector' can create and manage it. In this backend,
// there is not a specific buffer into which the batch should be
// created, so use ProcessTensor arguments that cause collector to
// manage it. ProcessTensor does NOT support TRITONSERVER_TYPE_BYTES
// data type.
BackendInputCollector collector(
requests, request_count, &responses, model_state->TritonMemoryManager(),
false /* pinned_enabled */, nullptr /* stream*/);
// To instruct ProcessTensor to "gather" the entire batch of input
// tensors into a single contiguous buffer in CPU memory, set the
// "allowed input types" to be the CPU ones (see tritonserver.h in
// the triton-inference-server/core repo for allowed memory types).
std::vector<std::pair<TRITONSERVER_MemoryType, int64_t>> allowed_input_types =
{{TRITONSERVER_MEMORY_CPU_PINNED, 0}, {TRITONSERVER_MEMORY_CPU, 0}};
const char* input_buffer;
size_t input_buffer_byte_size;
TRITONSERVER_MemoryType input_buffer_memory_type;
int64_t input_buffer_memory_type_id;
RESPOND_ALL_AND_SET_NULL_IF_ERROR(
responses, request_count,
collector.ProcessTensor(
model_state->InputTensorName().c_str(), nullptr /* existing_buffer */,
0 /* existing_buffer_byte_size */, allowed_input_types, &input_buffer,
&input_buffer_byte_size, &input_buffer_memory_type,
&input_buffer_memory_type_id));
// Finalize the collector. If 'true' is returned, 'input_buffer'
// will not be valid until the backend synchronizes the CUDA
// stream or event that was used when creating the collector. For
// this backend, GPU is not supported and so no CUDA sync should
// be needed; so if 'true' is returned simply log an error.
const bool need_cuda_input_sync = collector.Finalize();
if (need_cuda_input_sync) {
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_ERROR,
"'recommended' backend: unexpected CUDA sync required by collector");
}
// 'input_buffer' contains the batched input tensor. The backend can
// implement whatever logic is necessary to produce the output
// tensor. This backend simply logs the input tensor value and then
// returns the input tensor value in the output tensor so no actual
// computation is needed.
uint64_t compute_start_ns = 0;
SET_TIMESTAMP(compute_start_ns);
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("model ") + model_state->Name() + ": requests in batch " +
std::to_string(request_count))
.c_str());
std::string tstr;
IGNORE_ERROR(BufferAsTypedString(
tstr, input_buffer, input_buffer_byte_size,
model_state->TensorDataType()));
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_INFO,
(std::string("batched " + model_state->InputTensorName() + " value: ") +
tstr)
.c_str());
const char* output_buffer = input_buffer;
TRITONSERVER_MemoryType output_buffer_memory_type = input_buffer_memory_type;
int64_t output_buffer_memory_type_id = input_buffer_memory_type_id;
uint64_t compute_end_ns = 0;
SET_TIMESTAMP(compute_end_ns);
bool supports_first_dim_batching;
RESPOND_ALL_AND_SET_NULL_IF_ERROR(
responses, request_count,
model_state->SupportsFirstDimBatching(&supports_first_dim_batching));
std::vector<int64_t> tensor_shape;
RESPOND_ALL_AND_SET_NULL_IF_ERROR(
responses, request_count, model_state->TensorShape(tensor_shape));
// Because the output tensor values are concatenated into a single
// contiguous 'output_buffer', the backend must "scatter" them out
// to the individual response output tensors. The backend utilities
// provide a "responder" to facilitate this scattering process.
// BackendOutputResponder does NOT support TRITONSERVER_TYPE_BYTES
// data type.
// The 'responders's ProcessTensor function will copy the portion of
// 'output_buffer' corresponding to each request's output into the
// response for that request.
BackendOutputResponder responder(
requests, request_count, &responses, model_state->TritonMemoryManager(),
supports_first_dim_batching, false /* pinned_enabled */,
nullptr /* stream*/);
responder.ProcessTensor(
model_state->OutputTensorName().c_str(), model_state->TensorDataType(),
tensor_shape, output_buffer, output_buffer_memory_type,
output_buffer_memory_type_id);
// Finalize the responder. If 'true' is returned, the output
// tensors' data will not be valid until the backend synchronizes
// the CUDA stream or event that was used when creating the
// responder. For this backend, GPU is not supported and so no CUDA
// sync should be needed; so if 'true' is returned simply log an
// error.
const bool need_cuda_output_sync = responder.Finalize();
if (need_cuda_output_sync) {
LOG_MESSAGE(
TRITONSERVER_LOG_ERROR,
"'recommended' backend: unexpected CUDA sync required by responder");
}
// Send all the responses that haven't already been sent because of
// an earlier error.
for (auto& response : responses) {
if (response != nullptr) {
LOG_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_ResponseSend(
response, TRITONSERVER_RESPONSE_COMPLETE_FINAL, nullptr),
"failed to send response");
}
}
uint64_t exec_end_ns = 0;
SET_TIMESTAMP(exec_end_ns);
#ifdef TRITON_ENABLE_STATS
// For batch statistics need to know the total batch size of the
// requests. This is not necessarily just the number of requests,
// because if the model supports batching then any request can be a
// batched request itself.
size_t total_batch_size = 0;
if (!supports_first_dim_batching) {
total_batch_size = request_count;
} else {
for (uint32_t r = 0; r < request_count; ++r) {
auto& request = requests[r];
TRITONBACKEND_Input* input = nullptr;
LOG_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_RequestInputByIndex(request, 0 /* index */, &input),
"failed getting request input");
if (input != nullptr) {
const int64_t* shape = nullptr;
LOG_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_InputProperties(
input, nullptr, nullptr, &shape, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr),
"failed getting input properties");
if (shape != nullptr) {
total_batch_size += shape[0];
}
}
}
}
#else
(void)exec_start_ns;
(void)exec_end_ns;
(void)compute_start_ns;
(void)compute_end_ns;
#endif // TRITON_ENABLE_STATS
// Report statistics for each request, and then release the request.
for (uint32_t r = 0; r < request_count; ++r) {
auto& request = requests[r];
#ifdef TRITON_ENABLE_STATS
LOG_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceReportStatistics(
instance_state->TritonModelInstance(), request,
(responses[r] != nullptr) /* success */, exec_start_ns,
compute_start_ns, compute_end_ns, exec_end_ns),
"failed reporting request statistics");
#endif // TRITON_ENABLE_STATS
LOG_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_RequestRelease(request, TRITONSERVER_REQUEST_RELEASE_ALL),
"failed releasing request");
}
#ifdef TRITON_ENABLE_STATS
// Report batch statistics.
LOG_IF_ERROR(
TRITONBACKEND_ModelInstanceReportBatchStatistics(
instance_state->TritonModelInstance(), total_batch_size,
exec_start_ns, compute_start_ns, compute_end_ns, exec_end_ns),
"failed reporting batch request statistics");
#endif // TRITON_ENABLE_STATS
return nullptr; // success
}
} // extern "C"
}}} // namespace triton::backend::recommended
之后执行编译:
mkdir build
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX:PATH=`pwd`/install ..
make install编译完成后,会生成动态库:

2.2 自定义backend的serve
模型的serve除了需要模型本身之外,还需要相应的配置文件,例如:
backend: "liupeng"
max_batch_size: 8
dynamic_batching {
max_queue_delay_microseconds: 5000000
}
input [
{
name: "IN0"
data_type: TYPE_INT32
dims: [ 4 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUT0"
data_type: TYPE_INT32
dims: [ 4 ]
}
]
instance_group [
{
kind: KIND_CPU
}
]
注意,backend的名称是有要求的,其名称必须为:libtriton_backendname.so红色部分。
1、配置文件准备完成后,之后按照如下目录形式放入到model_repository路径下:
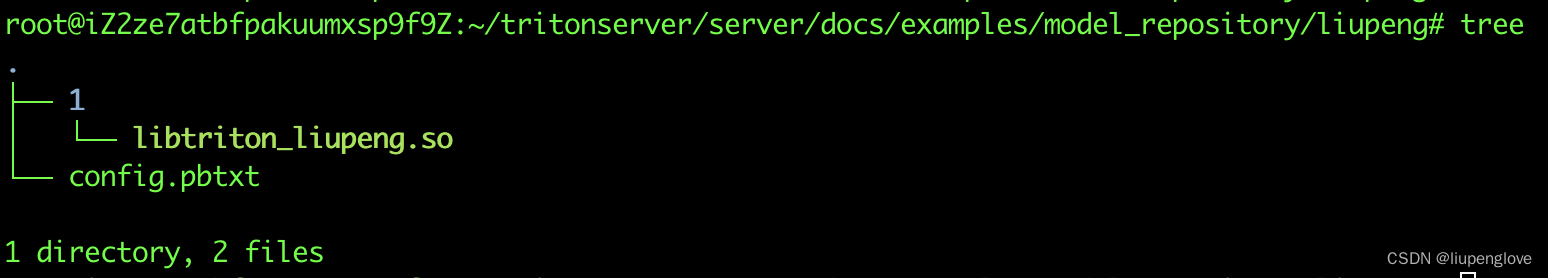
2、启动triton镜像,并将 model_repository路径映射到容器中,命令行:
docker run --rm -p8000:8000 -p8001:8001 -p8002:8002 -it -v /root/tritonserver/server/docs/examples/model_repository:/models nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:23.12-py3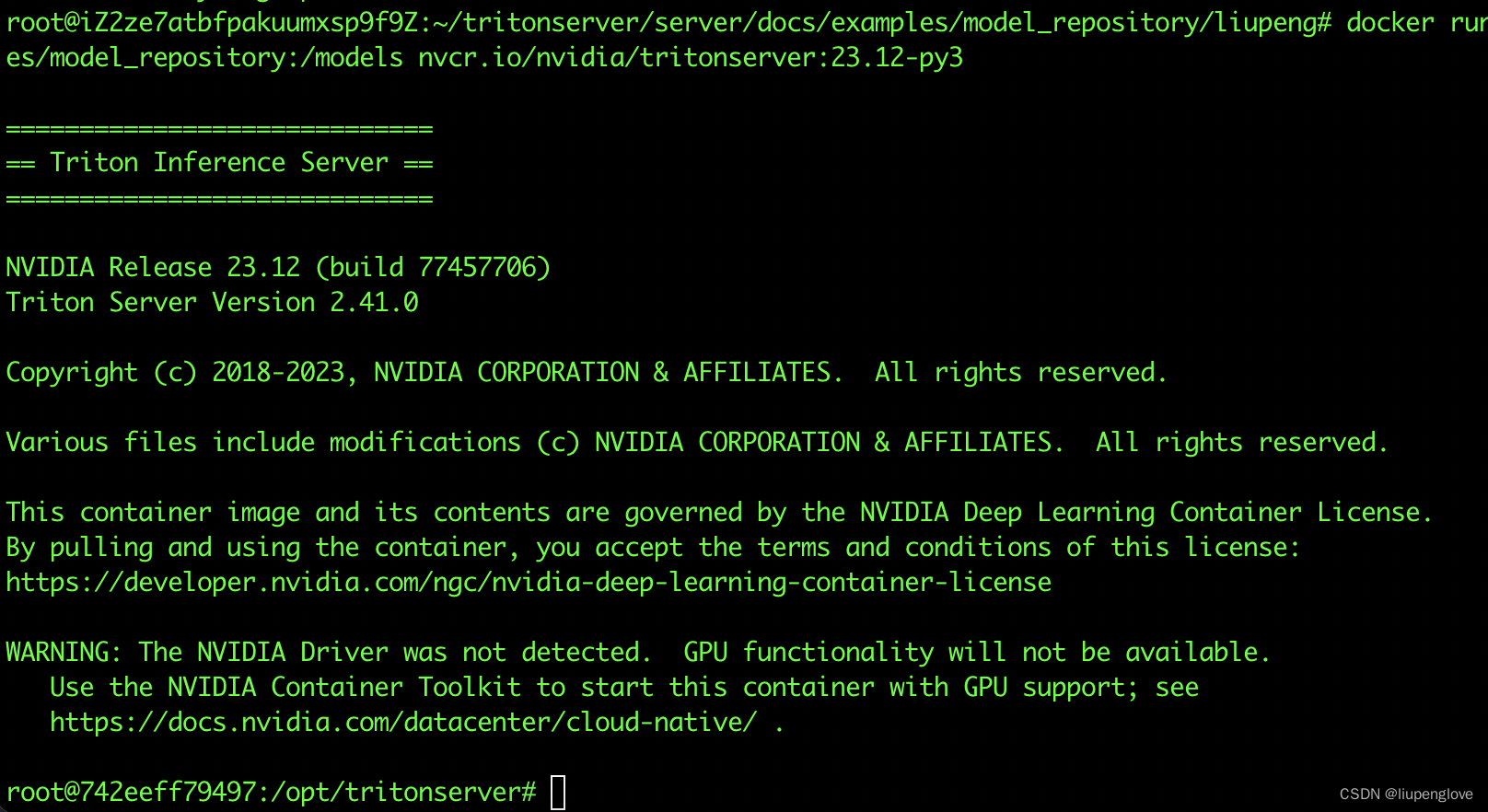
3、启动triton:
tritonserver --model-repository=/models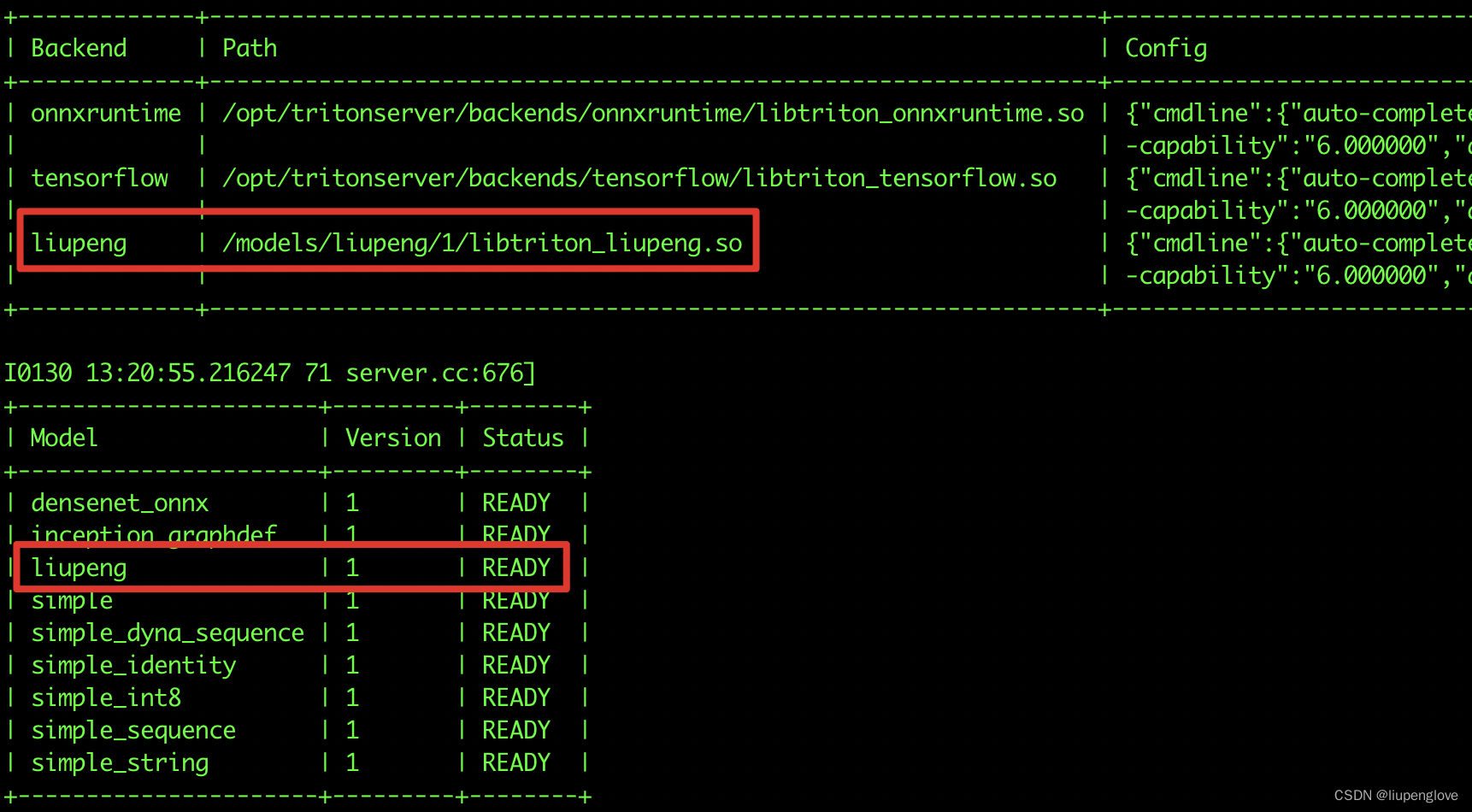
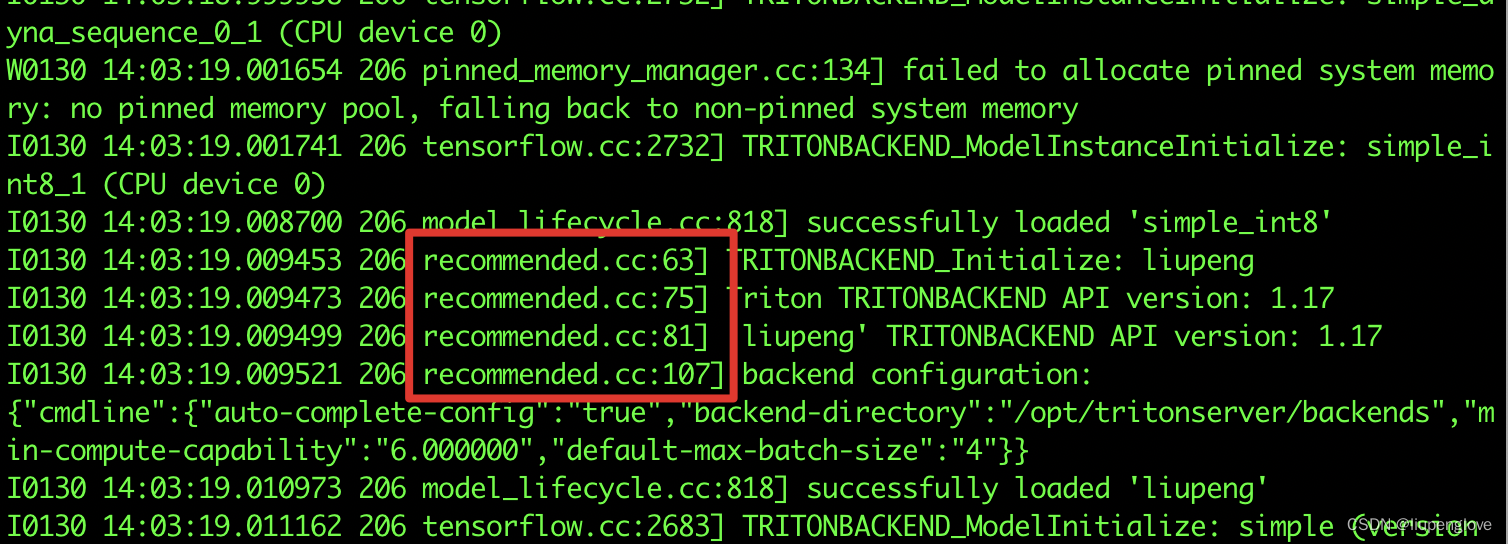
在triton启动时,会执行 TRITONBACKEND_Initialize函数,有如下打印:
3、python自定义backend
3.1 python自定义backend代码
python自定义backend相比c++简单很多,只要实现三个api即可:
def initialize(self, args)
def execute(self, requests)
def finalize(self)示例代码位于:
https://gitee.com/bd-super-sugar/python_backend/blob/main/examples/add_sub/model.py
代码如下:
# Copyright (c) 2020, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
#
# Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
# modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
# are met:
# * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
# * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
# documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
# * Neither the name of NVIDIA CORPORATION nor the names of its
# contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
# from this software without specific prior written permission.
#
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS ``AS IS'' AND ANY
# EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
# IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
# PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR
# CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
# EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
# PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
# PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY
# OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
# (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
# OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
import json
# triton_python_backend_utils is available in every Triton Python model. You
# need to use this module to create inference requests and responses. It also
# contains some utility functions for extracting information from model_config
# and converting Triton input/output types to numpy types.
import triton_python_backend_utils as pb_utils
class TritonPythonModel:
"""Your Python model must use the same class name. Every Python model
that is created must have "TritonPythonModel" as the class name.
"""
def initialize(self, args):
"""`initialize` is called only once when the model is being loaded.
Implementing `initialize` function is optional. This function allows
the model to initialize any state associated with this model.
Parameters
----------
args : dict
Both keys and values are strings. The dictionary keys and values are:
* model_config: A JSON string containing the model configuration
* model_instance_kind: A string containing model instance kind
* model_instance_device_id: A string containing model instance device ID
* model_repository: Model repository path
* model_version: Model version
* model_name: Model name
"""
# You must parse model_config. JSON string is not parsed here
self.model_config = model_config = json.loads(args["model_config"])
# Get OUTPUT0 configuration
output0_config = pb_utils.get_output_config_by_name(model_config, "OUTPUT0")
# Get OUTPUT1 configuration
output1_config = pb_utils.get_output_config_by_name(model_config, "OUTPUT1")
# Convert Triton types to numpy types
self.output0_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
output0_config["data_type"]
)
self.output1_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(
output1_config["data_type"]
)
def execute(self, requests):
"""`execute` MUST be implemented in every Python model. `execute`
function receives a list of pb_utils.InferenceRequest as the only
argument. This function is called when an inference request is made
for this model. Depending on the batching configuration (e.g. Dynamic
Batching) used, `requests` may contain multiple requests. Every
Python model, must create one pb_utils.InferenceResponse for every
pb_utils.InferenceRequest in `requests`. If there is an error, you can
set the error argument when creating a pb_utils.InferenceResponse
Parameters
----------
requests : list
A list of pb_utils.InferenceRequest
Returns
-------
list
A list of pb_utils.InferenceResponse. The length of this list must
be the same as `requests`
"""
output0_dtype = self.output0_dtype
output1_dtype = self.output1_dtype
responses = []
# Every Python backend must iterate over everyone of the requests
# and create a pb_utils.InferenceResponse for each of them.
for request in requests:
# Get INPUT0
in_0 = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT0")
# Get INPUT1
in_1 = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT1")
out_0, out_1 = (
in_0.as_numpy() + in_1.as_numpy(),
in_0.as_numpy() - in_1.as_numpy(),
)
# Create output tensors. You need pb_utils.Tensor
# objects to create pb_utils.InferenceResponse.
out_tensor_0 = pb_utils.Tensor("OUTPUT0", out_0.astype(output0_dtype))
out_tensor_1 = pb_utils.Tensor("OUTPUT1", out_1.astype(output1_dtype))
# Create InferenceResponse. You can set an error here in case
# there was a problem with handling this inference request.
# Below is an example of how you can set errors in inference
# response:
#
# pb_utils.InferenceResponse(
# output_tensors=..., TritonError("An error occurred"))
inference_response = pb_utils.InferenceResponse(
output_tensors=[out_tensor_0, out_tensor_1]
)
responses.append(inference_response)
# You should return a list of pb_utils.InferenceResponse. Length
# of this list must match the length of `requests` list.
return responses
def finalize(self):
"""`finalize` is called only once when the model is being unloaded.
Implementing `finalize` function is OPTIONAL. This function allows
the model to perform any necessary clean ups before exit.
"""
print("Cleaning up...")对应的配置config.pbtxt如下:
name: "liupeng_python"
backend: "python"
input [
{
name: "INPUT0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 4 ]
}
]
input [
{
name: "INPUT1"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 4 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUTPUT0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 4 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUTPUT1"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 4 ]
}
]
instance_group [{ kind: KIND_CPU }]3.2 模型的serve
模型目录组织结构如下:
 启动后,模型加载情况:
启动后,模型加载情况:

到此,python自定义backend已经加载成功。
4、执行推理
以python自定义backend为例,client端代码:
# Copyright 2020-2021, NVIDIA CORPORATION & AFFILIATES. All rights reserved.
#
# Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
# modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
# are met:
# * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
# * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
# documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
# * Neither the name of NVIDIA CORPORATION nor the names of its
# contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
# from this software without specific prior written permission.
#
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS ``AS IS'' AND ANY
# EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
# IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
# PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR
# CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
# EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
# PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
# PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY
# OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
# (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
# OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
import sys
import numpy as np
import tritonclient.http as httpclient
from tritonclient.utils import *
model_name = "liupeng_python"
shape = [4]
with httpclient.InferenceServerClient("localhost:8000") as client:
input0_data = np.random.rand(*shape).astype(np.float32)
input1_data = np.random.rand(*shape).astype(np.float32)
inputs = [
httpclient.InferInput(
"INPUT0", input0_data.shape, np_to_triton_dtype(input0_data.dtype)
),
httpclient.InferInput(
"INPUT1", input1_data.shape, np_to_triton_dtype(input1_data.dtype)
),
]
inputs[0].set_data_from_numpy(input0_data)
inputs[1].set_data_from_numpy(input1_data)
outputs = [
httpclient.InferRequestedOutput("OUTPUT0"),
httpclient.InferRequestedOutput("OUTPUT1"),
]
response = client.infer(model_name, inputs, request_id=str(1), outputs=outputs)
result = response.get_response()
output0_data = response.as_numpy("OUTPUT0")
output1_data = response.as_numpy("OUTPUT1")
print(
"INPUT0 ({}) + INPUT1 ({}) = OUTPUT0 ({})".format(
input0_data, input1_data, output0_data
)
)
print(
"INPUT0 ({}) - INPUT1 ({}) = OUTPUT1 ({})".format(
input0_data, input1_data, output1_data
)
)
if not np.allclose(input0_data + input1_data, output0_data):
print("add_sub example error: incorrect sum")
sys.exit(1)
if not np.allclose(input0_data - input1_data, output1_data):
print("add_sub example error: incorrect difference")
sys.exit(1)
print("PASS: liupeng_python")
sys.exit(0)安装好triton client依赖库后,执行该脚本,即可请求到【liupeng_python】模型上,简单期间,可以在triton的client镜像中运行。

5、欢迎关注
欢迎关注本人公众号: