线性表是最简单、最基本的一种数据结构,线性表示多个具有相同类型数据“串在一起”,每个元素有前驱(前一个元素)和后继(后一个元素)。根据不同的特性,线性表也分为数组(vector)、栈(stack)、队列(queue)、链表(list)等等。根据这些特性和数据结构可以解决不同种类的问题。
一、寄包柜(vector or map)
1.1 使用vector
vector和数组相比,vector可以改变长度,清空的时间复杂度为O(1)。
vector常用操作如下:
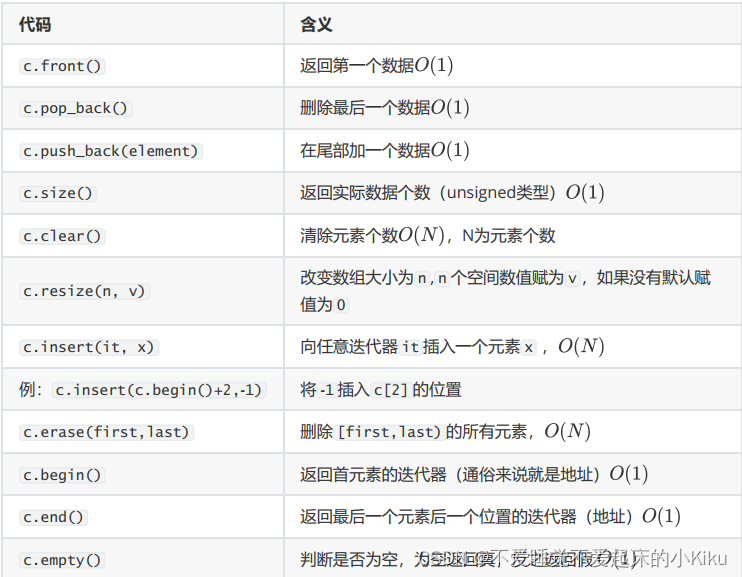
AC代码:
我们可以建立一个二维数组s[x][y]来记录第i个柜子的第j个格子中的物品。根据本题的数据范围,需要开一个大约40GB的int数组,而本题的空间限制这有125MB,显然会超空间,所以我们可以用一个vector来解决。
先设定一个可以满足大多数情况且不超内存的二维可变数组,如果实际情况所需内存超过所开范围可以使用resize函数重新为vector分配空间。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> //头文件
using namespace std;
inline int read() //快读
{
int s=0,w=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return s*w;
}
inline void write(int x) //快出
{
if(x<0)
{
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
int main() //主函数
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); //输入输出优化流
int n,q,f,x,y,z; //定义
n=read(); //输入寄包裹个数和询问次数
q=read();
vector<vector<int> > a(n+1); //定义一个可变数组,初始化,总共0-n号寄包柜
while(q--)
{
f=read(); //输入操作种类
if(f==1) //存包操作
{
x=read(); //输入
y=read();
z=read();
if(a[x].size()<y+1) a[x].resize(y+1); //如果这个寄包柜不够大,就扩大新的寄包柜,直到能装下为止
a[x][y]=z; //存包
}else{
x=read(); //输入
y=read();
write(a[x][y]); //输出下标为x,y的元素
puts(""); //换行
}
}
return 0; //结束
}使用可变长度数组vector的方法可以使得二维数组中每一行的长度不一样,从而在一定程度上减少空闲空间的产生,不过这种方法有一定局限性。
1.2 使用map
显然使用vector并不是最优写法,因为只有少量数组空间会被利用,大量空间会被浪费,这里我们可以想到使用离散化的方式来对稀疏数据进行操作,即使用map。
map常用操作如下:
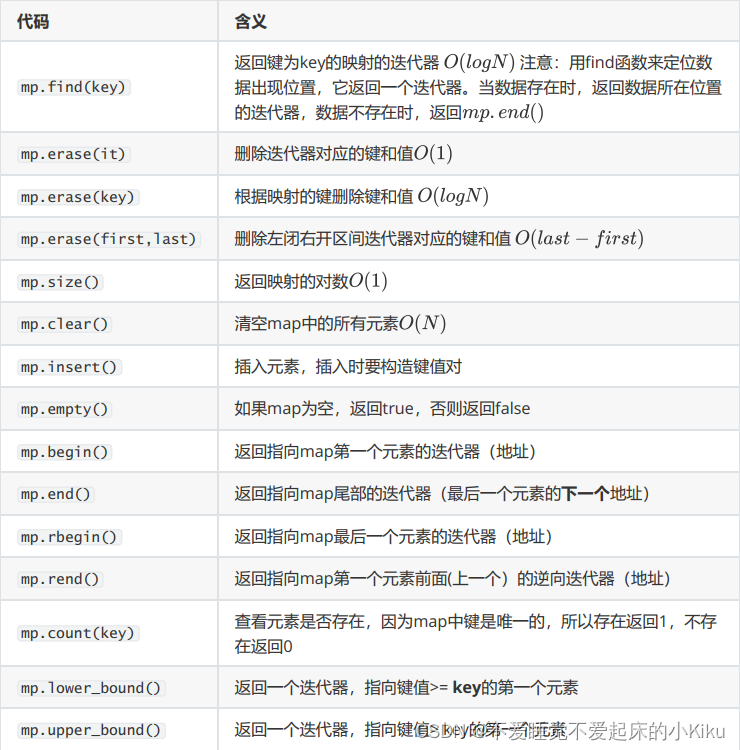
AC代码:
由于本题中有柜号和格子号二维信息,所以使用map容器嵌套pair类型变量即可,不需要开辟二维map。
使用count函数可以实现对map中键值的存在性查找。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
map<pair<long, long>, long> bag;
int main()
{
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++)
{
int type = 0;
cin >> type;
if (type == 1)
{
int x, y, k;
cin >> x >> y >> k;
bag[{x, y}] = k;
}
else if (type == 2)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (bag.count({ x,y }) != 0)
{
cout << bag[{x, y}] << endl;
}
}
}
}二、队列安排(list)
list是一种实际运用比较少的数据类型,一般可以使用vector来代替,list的优势在于可以快速的插入和删除链上元素,劣势在于只能使用迭代器进行顺序查找。
list使用方法:
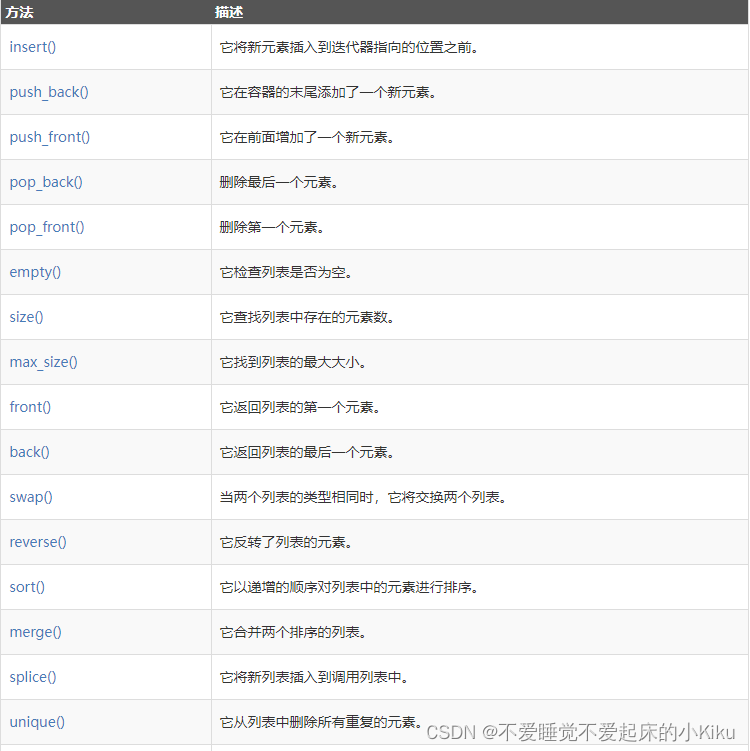
AC代码:
本题将每个同学看作一个节点,使用链表将其连接在一起。但由于list查找速度缓慢,同时随机插入节点会导致list中节点的编号混乱,为了减少遍历list查找节点浪费的时间,我们可以使用一个数组来顺序保存每一个节点的迭代器。从而实现O(1)量级的快速查找。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
using Iter = list<int>::iterator;
const int maxN = 1e5 + 5;
list<int> List;
Iter pos[maxN];
bool be[maxN] = { false };
int main()
{
int N, M;
cin >> N;
List.push_front(1);
pos[1] = List.begin();
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
int k, p;
cin >> k >> p;
if (p == 0)
{
pos[i] = List.insert(pos[k], i);
}
else
{
pos[i] = List.insert(next(pos[k]), i);
}
}
cin >> M;
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++)
{
int tmp; cin >> tmp;
if (tmp <= N && !be[tmp])
{
List.erase(pos[tmp]);
be[tmp] = true;
}
}
for (auto x : List)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
}list中的迭代器为list<int>::iterator,使用数组pos按照1~n顺序保存每个节点所在list中的位置。同时由于删除节点会耗费一定的时间,我们可以使用一个辅助数组be来保存list中每个节点的存在性,be数组与list节点一一对应。
三、验证栈序列(stack)
栈是唯一的只能从一个开口增删数据的数据结构,使用push函数向栈中压入数据,使用pop弹出数据,使用top函数查看栈顶数据。
需要注意的是如果栈为空,仍然使用top函数会异常中断,报错。
stack使用方法:
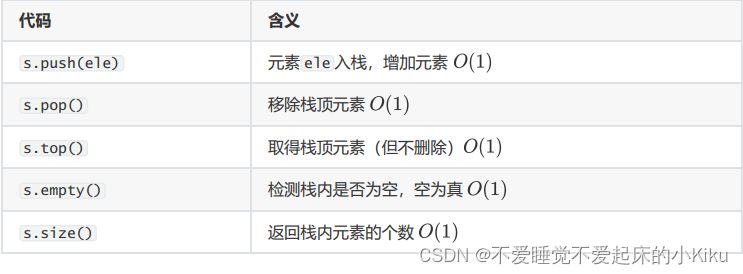
AC代码:
本题使用栈对序列进行模拟。将pushed中数据依次入栈,当栈顶数与poped序列中某数相同时,将栈顶数出栈。若操作结束后,栈中仍然有残留数据,说明poped序列无法实现。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int pushed[100005];
int poped[100005];
stack<int> stk;
int main()
{
int q; cin >> q;
for (int cnt = 1; cnt <= q; cnt++)
{
int num; cin >> num;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++)
cin >> pushed[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++)
cin >> poped[i];
int index = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++)
{
stk.push(pushed[i]);
while (stk.top() == poped[index])
{
stk.pop();
index++;
if (stk.empty())
break;
}
}
if (stk.empty()) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
while (!stk.empty())
stk.pop();
}
}本题中存在的坑在于当栈为空时,使用top函数会报错,需先用empty函数确认栈不为空后,才能使用top函数查看栈顶。
四、海港(queue)
queue(队列)为两端开口,的管道容器,一侧为入口,一侧为出口,可以实现先进先出,后进后出,无法随机增删,此外还有deque(双端队列),管道两侧均可以增删数据。
queue使用方法:
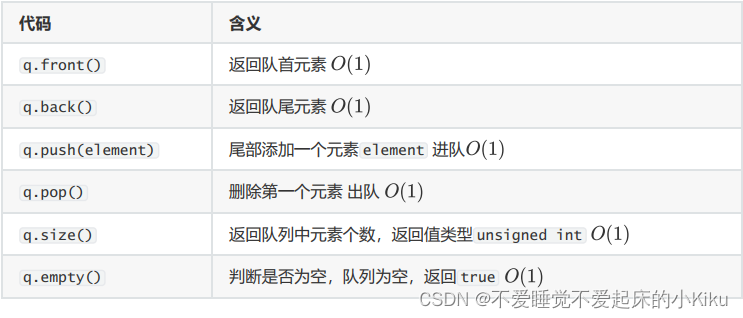
AC代码:
本题可以将node结构塞入queue队列当中,node结构中存储某个人的信息,包括下船时间和国籍,由于下船时间已经从下到大排序,所以每次淘汰下船时间超过24h的人时只需要从出口端删除信息即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int Time;
int Nation;
};
queue<node> ship;
int national[100005] = { 0 };
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int count = 0;
for (int cnt = 1; cnt <= n; cnt++)
{
int t, k;
cin >> t >> k;
while (!ship.empty())
{
if (t - ship.front().Time >= 86400)
{
national[ship.front().Nation] -= 1;
if (national[ship.front().Nation] == 0)
{
count -= 1;
}
ship.pop();
}
else
break;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
int people; cin >> people;
node tmp;
tmp.Time = t, tmp.Nation = people;
ship.push(tmp);
if (national[tmp.Nation] == 0)
count += 1;
national[tmp.Nation] += 1;
}
printf("%d\n", count);
}
}代码逻辑为:
- 先淘汰下船时间超过24h的人,用一个national数组存储每个国籍的人数,若淘汰后某个国籍人数为0,那么count减1;
- 然后对当前时间下船的人操作,若该人的到来使得某个国籍的人数从0变为1,那么count加1.
五、营业额统计(set)
set能有序地维护同一类型的元素,但相同的元素只能出现一次。
也就是说,我们将数据插入set中后,set会自动帮我们排序(相当于优先队列)。
set使用方法:

AC代码:
每次输入一个新的数x后,通过lowerbound操作找到set中大于等于x的第一个数。
- 如果这是第一个数,直接插入到set里。
- 这个数等于x,显然最小波动值为0,我们也不需要再插入一个x放到set里了。
- 这个数大于x,通过set的特性可以很轻松的找到这个数的前驱,也就是小于x的第一个数。将两个数分别减去x,对绝对值取个min就好了。此时要将x插入到set中。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
set<int> s;
set<int>::iterator r,l;
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int a; cin >> a;
s.insert(a);
int ans = a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
int tmp; cin >> tmp;
r = s.lower_bound(tmp);
if (r == s.end())
{
ans += abs(tmp - *(--r));//k的前一个数,也就是小于tmp的最大数
s.insert(tmp);
continue;
}
else if (r == s.begin())
{
ans += abs(tmp - *r);
s.insert(tmp);
continue;
}
else
{
l = --s.lower_bound(tmp);
ans += min(abs(tmp - *r), abs(tmp - *l));
s.insert(tmp);
}
}
cout << ans;
}迭代器是一种检查容器内元素并遍历元素的数据类型,通常用于对C++中各种容器内元素的访问,但不同的容器有不同的迭代器,初学者可以将迭代器理解为指针。
迭代器使用方法:
- 比较两个迭代器是否相等(==、!=)。
- 前置和后置递增运算(++、--)(无法随机访问!)。
- 读取元素的解引用运算符(*)。只能读元素,也就是解引用只能出现在赋值运算符的右边。
- 箭头运算符(->),解引用迭代器,并提取对象的成员。