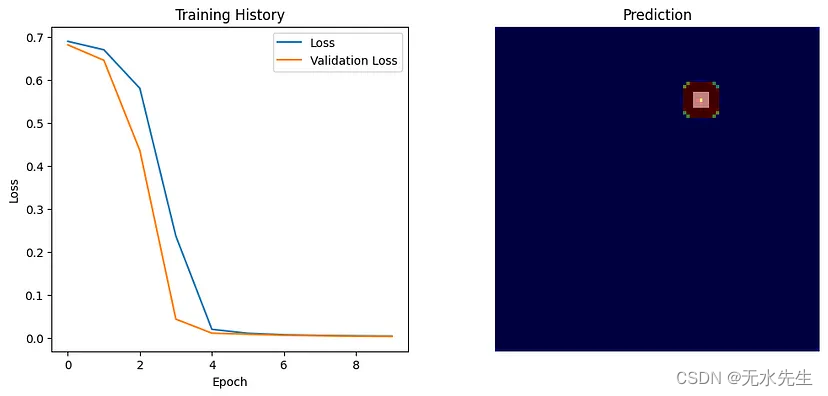
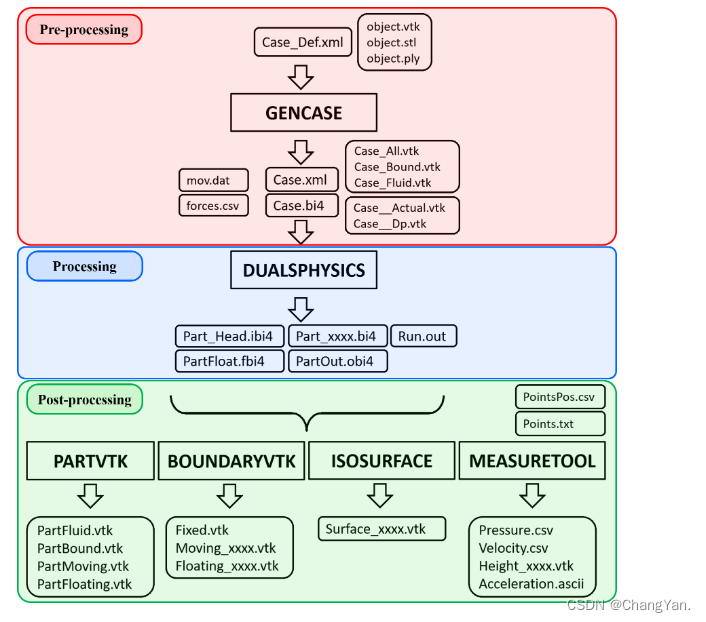
* 491.递增子序列

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>>result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer>path = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
//Arrays.sort(nums);
used = new boolean[nums.length];
backTracking(nums, 0, used);
return result;
}
public void backTracking(int[] nums, int startIndex, boolean[] used){
if(path.size() >= 2){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
if(startIndex >= nums.length) return;
HashSet<Integer>set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = startIndex ; i < nums.length ; i++){
if(set.contains(nums[i] ) == true){
continue;
}
if(!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.getLast()){
continue;
}
set.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
backTracking(nums, i+1, used);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}思路:与子集问题类似,但是不能进行排序,因为需要挑出递增数列。进行树层去重和树枝去重,树枝去重需要比较path的最后一个和当前要加入的大小
* 46.全排列

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();// 用来存放符合条件结果
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0){
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums){
if (path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (used[i]){
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}思路:全排列问题相对简单,就是进行树枝去重,i每次从0开始,只要used[i] == true,就跳过。
// 解法2:通过判断path中是否存在数字,排除已经选择的数字
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return result;
backtrack(nums, path);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer> path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
for (int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果path中已有,则跳过
if (path.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}解法二:通过判断path是否存在数字,排除已经选择的数字。
* 47.全排列 II

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer>path = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used ;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(used, false);
backTracking(nums, used);
return result;
}
public void backTracking(int[] nums, boolean[] used){
if(path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++){
if(used[i] == true){
continue;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && used[i-1] == false){
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
backTracking(nums, used);
used[i] = false;
path.removeLast();
}
}
}思路:在全排列的基础上增加了树层去重,先对nums数组进行排序,然后根据used进行树层去重,并且和全排列一样进行树枝去重。


![[AIGC 大数据基础] 浅谈hdfs](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/19fb698dcd7bf051b8d1a057ce063c81.jpeg)