文章目录
- 1. 数据集介绍
- 2. 使用pycocotools读取数据
- 3. 验证mAP

论文:Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context
网址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1405.0312
官网:https://cocodataset.org/
1. 数据集介绍
MS COCO是一个非常大型,且常用的数据集,其中包括了目标检测、分割、图像描述等,其主要特征如下:
- Object segmentation:目标集分割
- Recognition in context:图像情景识别
- Superpixel stuff segmentation:超像素分割
- 330K image(>200K labeled):超过33万张图像,标注过的图像超过20万张
- 1.5 million object instances:150万个对象实例
- 80 object categories:80个目标类别
- 91 stuff categories:91个材料类别
- 5 captions per image:每张图像有5段情景描述
- 250000 people with keypoints:对25万个人进行了关键点标注
什么是stuff类别?
- stuff中包含没有明确边界的材料和对象
object的80类与stuff中的91类的区别在哪?
- 简单的理解就是object80类是stuff91类的子集。如果仅仅是做目标检测,基本只用object80类即可。
与PASCAL VOC对比
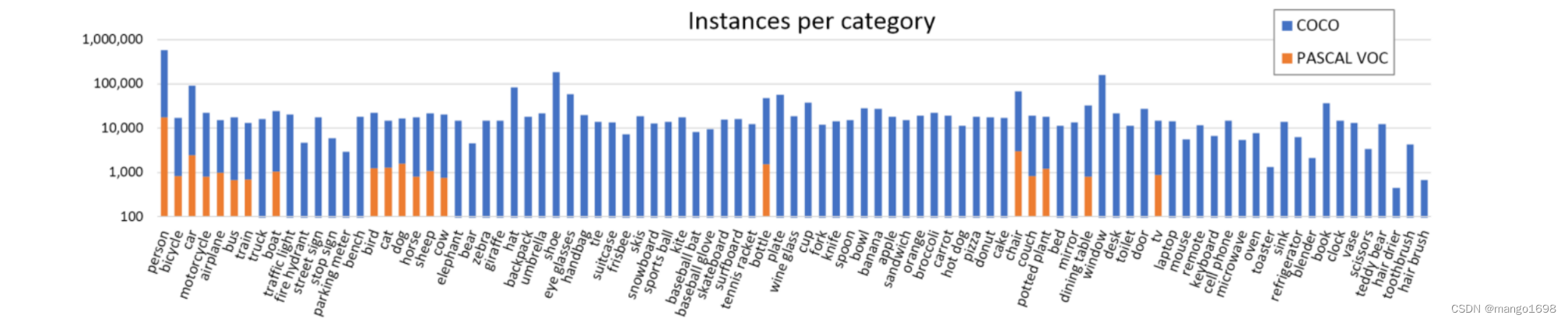
与训练效果好,但是更费时。
数据集下载
进入MS COCO官网,点击Dataset->download
对于目标检测,主要下载三个文件:
- 2017 Train images [118K/18GB]:训练过程中,使用到的所有图像文件
- 2017 Val images [5K/1GB]:验证过程中使用到的所有图像文件
- 2017 Train/Val annotations [241MB]:对于训练集和验证集的标注json文件
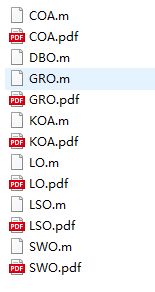
将下载好的文件都解压到同一文件夹下,可得到如下文件结构:
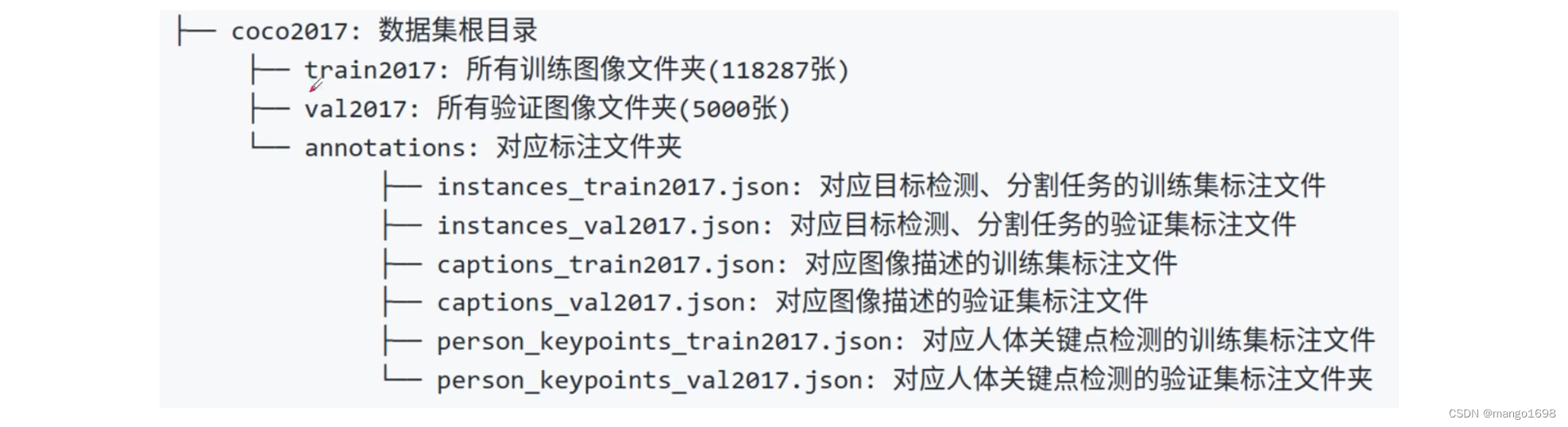
官方有给出一个关于标注文件的格式说明:https://cocodataset.org/#format-data
在instances_train2017.json中
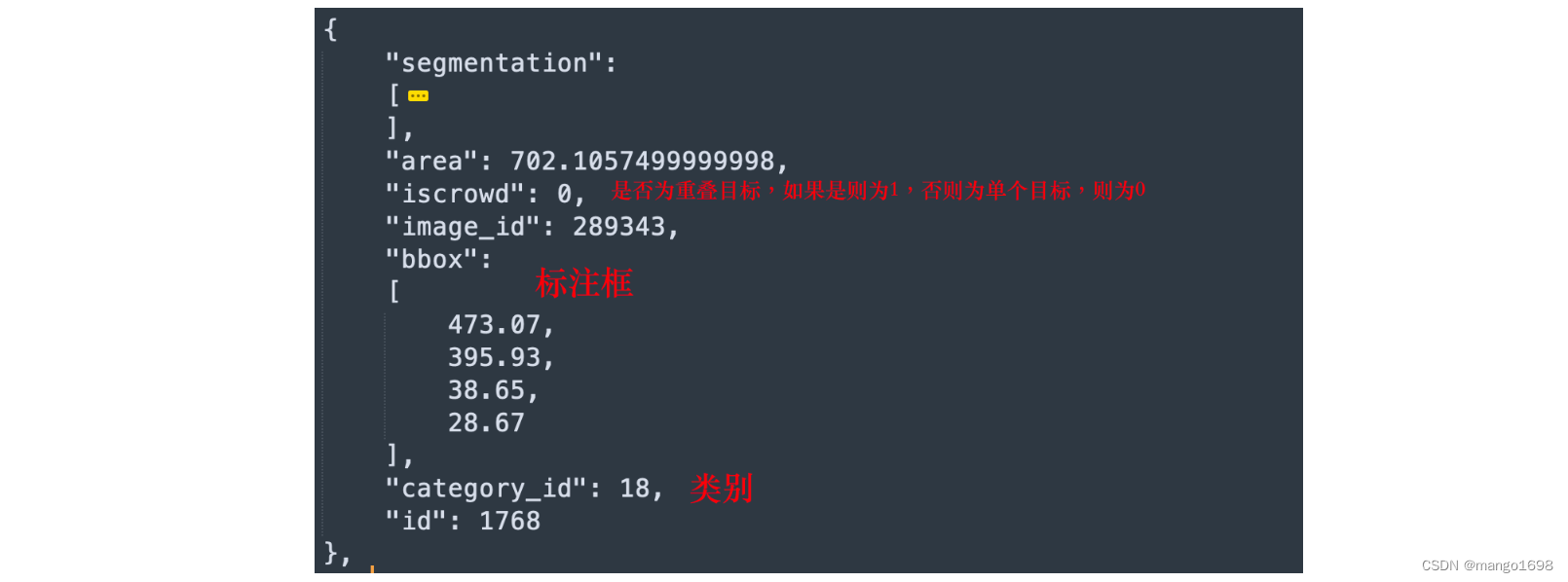
注意:这里的category_id对应的是在stuff91类中的索引。
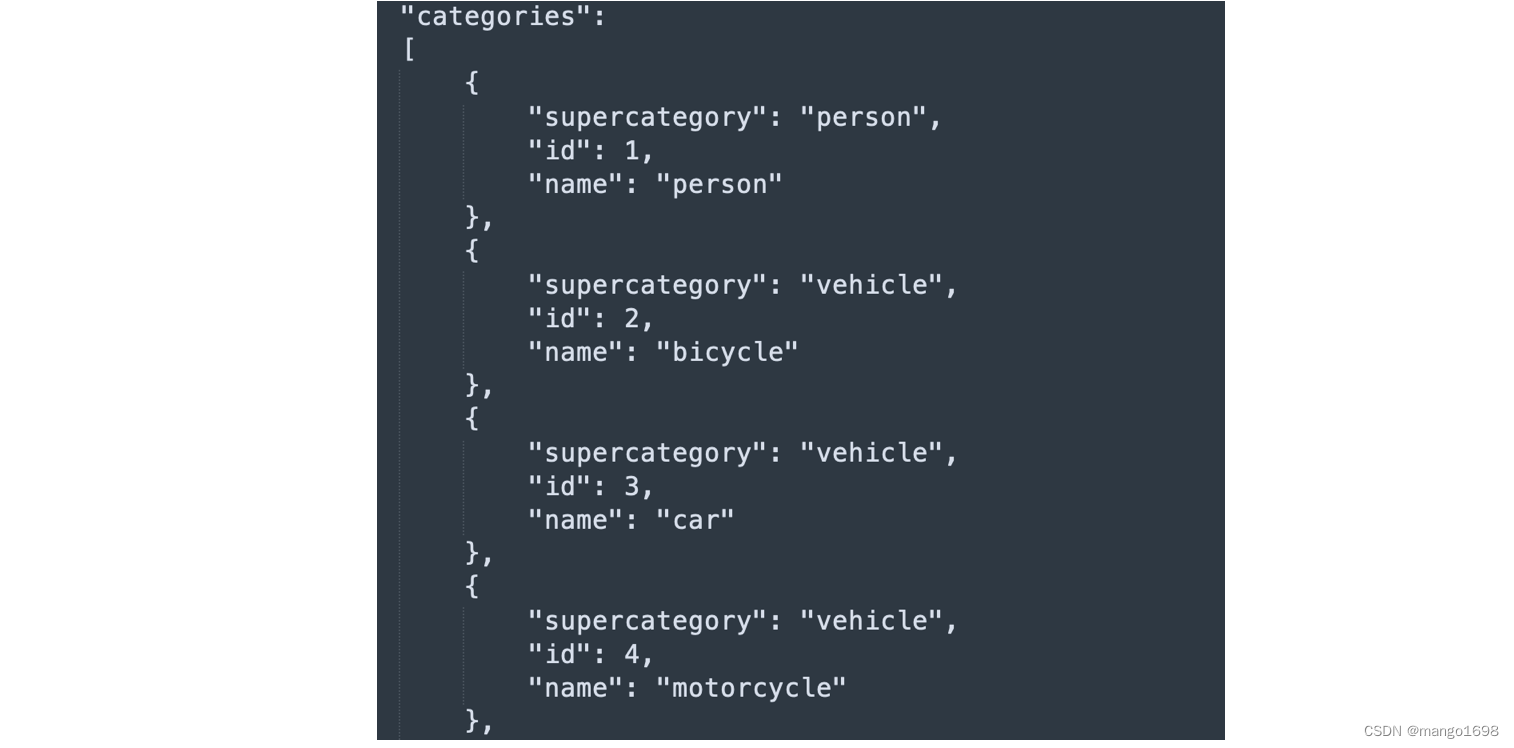
在类别中,有一个supercategory超类,为一些类别的统称。这里的id也是对应的stuff91种的索引。这里共80个类别,但是id并不是从1到80。所以,如果我们要去训练80个类别的目标检测网络的话,是需要做一个映射的,将这些类别的索引映射到1到80上。
2. 使用pycocotools读取数据
pycocotools,即python api tools of COCO。
COCO是一个大型的图像数据集,用于目标检测、分割、人的关键点检测、素材分割和标题生成。这个包提供了Matlab、Python和LuaAPI,这些api有助于在COCO中加载、解析和可视化注释。Matlab和PythonAPI是完整的,LuaAPI只提供基本功能。
安装pycocotools
pip install pycocotools
使用pycocotools
import os.path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
json_file = "/Volumes/zt/dataset/MS COCO2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
img_path = "/Volumes/zt/dataset/MS COCO2017/val2017"
# 加载coco json文件
coco = COCO(annotation_file=json_file)
# 获取json文件中所有图像的索引 并且进行排序
ids = list(sorted(coco.imgs.keys()))
print("number of images: {}".format(len(ids)))
# 获取所有coco类别标签
coco_classes = dict([(v["id"],v["name"]) for k,v in coco.cats.items()])
# 遍历前3张图像
for img_id in ids[:3]:
# 获取对应图像id的所有标注目标的索引 annotations idx信息
ann_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id)
# 根据标注目标的索引 annotations idx信息获取所有标注信息
targets = coco.loadAnns(ann_ids)
# 获取图像文件名称
img_name = coco.loadImgs(img_id)[0]['file_name']
# 读取图像 转为RGB格式
img = Image.open(os.path.join(img_path,img_name)).convert("RGB")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 画出标注框
for target in targets:
x,y,w,h = target["bbox"]
x1,y1,x2,y2 = x,y,int(x+w),int(y+h)
draw.rectangle((x1,y1,x2,y2),width=3,outline="red")
font = ImageFont.truetype('/System/Library/Fonts/Times.ttc', 24)
draw.text((x1,y1),coco_classes[target["category_id"]],fill="red",font=font)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
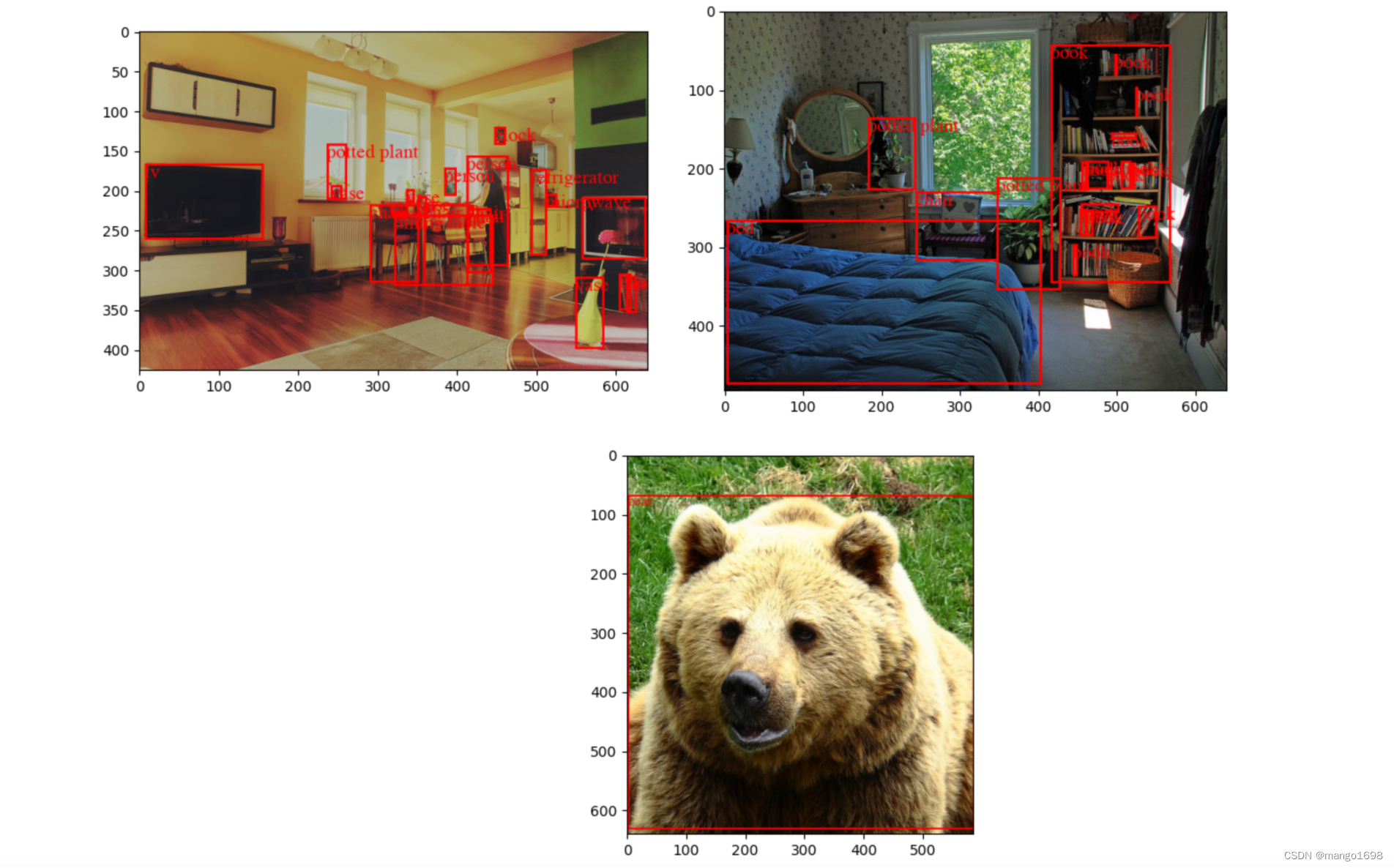
结果:

3. 验证mAP
首先要弄清楚cocoapi指定的数据格式(训练网络预测的结果),在官网的Evaluate下拉框中选择Results Format,可以看到每种任务的指定数据格式要求。
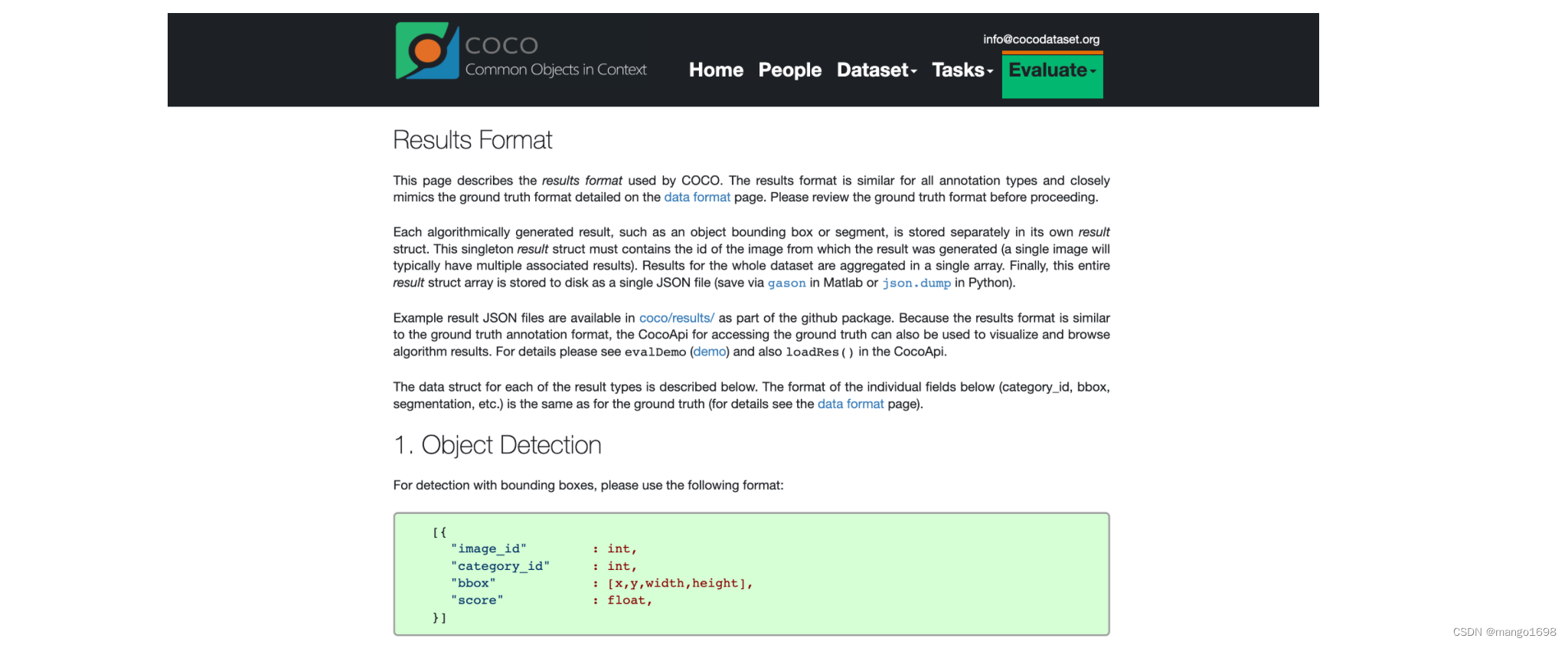
根据官方文档给的预测结果格式可以看到,我们需要以列表的形式保存结果,列表中的每个元素对应一个检测目标(每个元素都是字典类型),每个目标记录了四个信息:
image_id记录该目标所属图像的id(int类型)category_id记录预测该目标的类别索引,注意这里索引是对应stuff中91个类别的索引信息(int类型)bbox记录预测该目标的边界框信息,注意对应目标的[xmin,ymin,width,height](list[float]类型)score记录预测该目标的概率(float类型)
计算mAP,代码实现:
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval
# 载入coco2017验证集标注文件
# accumulate predictions from all iamges
coco_true = COCO(annotation_file='./instances_train2017.json')
# 载入网络在coco2017验证集上的预测结果
coco_pred = COCO(annotation_file='./predict_result.json')
coco_evaluator = COCOeval(cocoGt=coco_true, cocoDt=coco_pred,iouType='bbox')
coco_evaluator.evaluate()
coco_evaluator.accumulate()
coco_evaluator.summarize()