本篇将给出单链表的实现,头部插入/删除,尾部插入/删除,元素查找,指定位置前插入数据,指定位置之后插入元素,删除当前元素,删除当前元素之后的元素。
在给出这些操作,先给出单链表的定义,之后还会给出一些链表的扩展。
1.什么是单链表
链表的定义为:是一种物理存储上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
以上为链表的定义,那么什么是单链表呢,就是在链表中的元素只存在数据域和指针域,指针域存放的是下一个元素的地址。即:
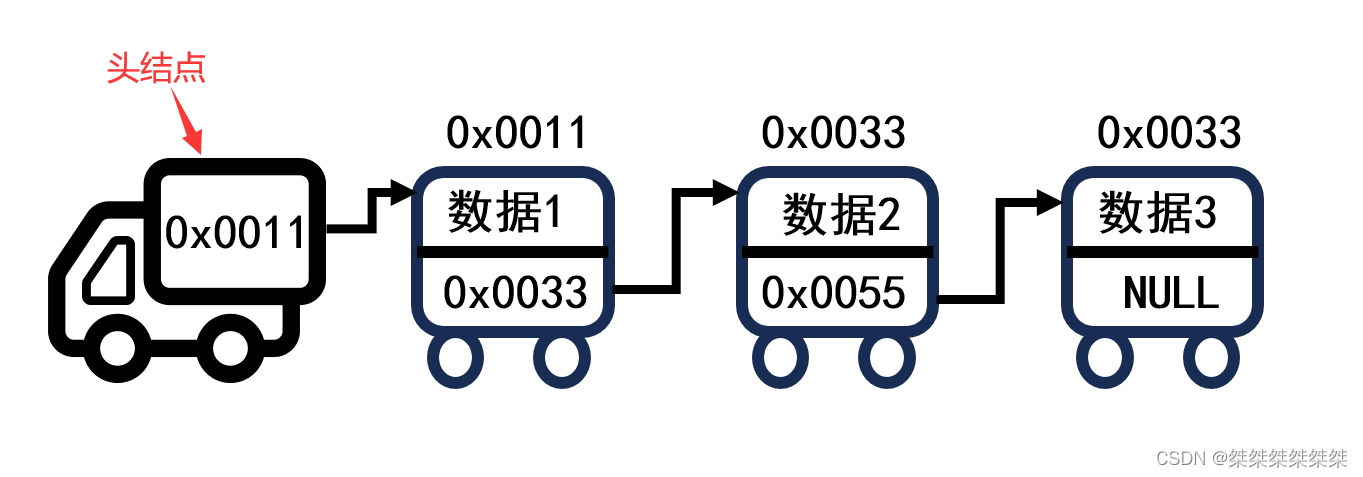
其中的火车头表示链表的头街点,对于单链表来说,分为带头结点的单链表和不带头结点的单链表。 因为在平时使用中,对于不带头结点的单链表使用得最为频繁,所以本篇以不带头结点的单链表为重点。(带头结点的单链表的头结点为:存储第一个元素位置的结点。而平时说的头结点指第一个结点)。
为什么需要用指针来保存下一个结点的位置呢?
因为链表中的每个元素都是独立申请的(需要插入数据时才会去申请一块结点的空间),所以需要使用指针来保存下一个结点位置。方便之后查找。
2.链表和顺序表的优点/缺点
顺序表和链表都属于数据结构中的线性结构,那么这两种线性数据结构有什么区别呢?
1.存储方式上:顺序表的存储为逻辑相邻+物理项链;而链表的存储方式仅仅为逻辑相邻,使用指针作为链接。
2.插入和删除操作的效率:顺序表的插入和删除操作都需要移动元素来维持原来的相对顺序,平均时间复杂度为O(n);链表的插入和删除操作只需要调整相对应的指针,无需移动元素,平均时间复杂度为O(1)。
3.随机访问的效率:对于顺序表来说,元素的在内存中的存储是连续的,可以直接通过下标进行访问,时间复杂度为O(1);对于链表来说,由于元素在内存中是不连续存储的,需要通过指针依次访问查找,时间复杂度为O(n)。
4.空间利用上:对于顺序表来说,每次开辟或者增容的空间,可能会存在浪费的情况;而对于链表来说,虽然开辟的空间都能用到,但存在许多的内存碎片。
3.单链表操作的实现
以下为不带头结点的单链表的抽象数据结构,以及对应的一些操作。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 //在vs2022中解除对部分函数的警告
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node {
DataType data;
struct Node* next;
}SLTNode;
//打印单链表
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
//头部插入删除/尾部插入删除
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
//单链表的查找
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, DataType x);
//指定位置之前插入
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* position, DataType x);
//指定位置之后插入
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* position, DataType x);
//指定位置删除/指定位置后删除
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* position);
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* position);
//链表的销毁
void SLTDestroy(SLTNode** pphead);对于以上的函数,我们可以发现:只有打印当前链表和查找数据传入头结点的一级指针,而其他有关头结点的操作传入的都是头结点的二级指针,是因为:
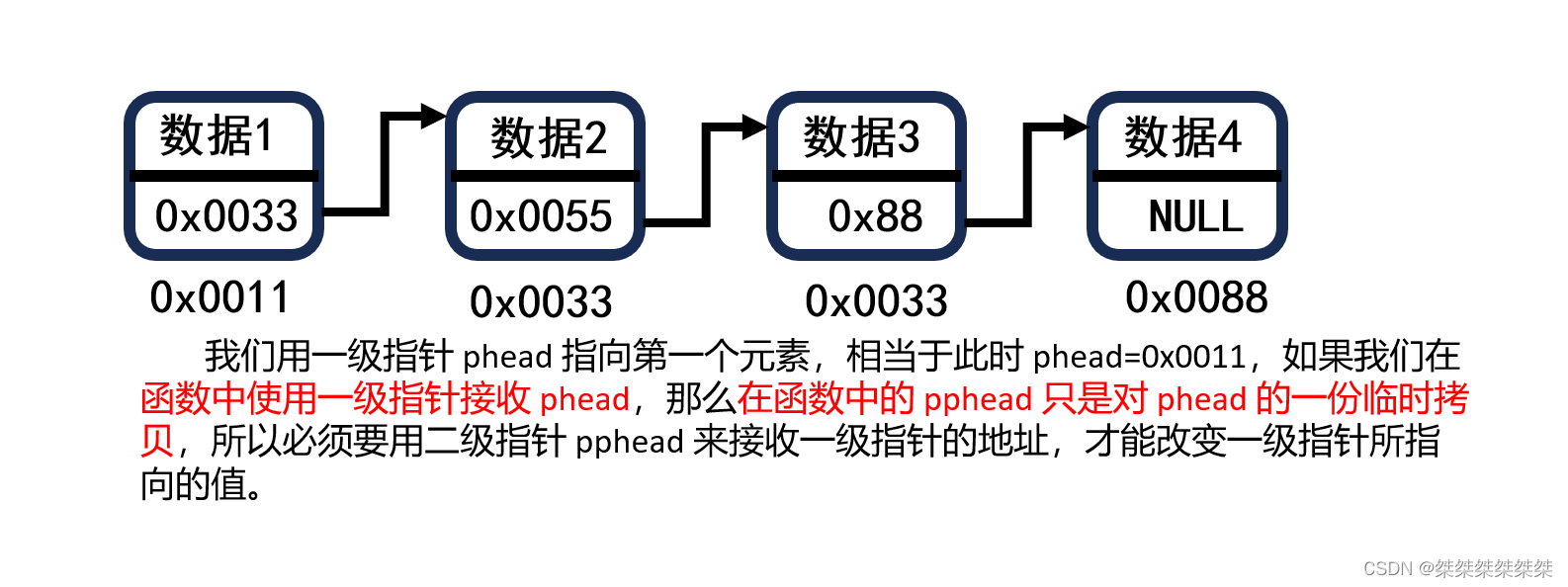
以下为对应函数的实现方式,在每个函数中都有对应的注释解释:
//打印所有的元素
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead) {
//先判断当前链表是否为NULL
if (phead == NULL) {
printf("该链表没有元素!\n");
return;
}
SLTNode* current = phead;
while (current) {
printf("%d->", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//创建一个新的结点
SLTNode* CreateNode(DataType x) {
SLTNode* newNode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
perror("MALLOC:");
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//尾结点插入
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x) {
//传过来的单链表地址不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//若需要插入的为头结点,直接插入
if (*pphead == NULL) {
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//若不为头结点,找到最后一个结点
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
while (current->next) {
current = current->next;
}
//此时current的下一个为NULL
current->next = newNode;
return;
}
//头结点插入
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x) {
//传过来的头结点指针不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//若头结点为NULL,直接插入
if (*pphead == NULL) {
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//将新节点的指针指向当前头结点
newNode->next = *pphead;
//头结点移动
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//删除尾结点
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead) {
//删除结点,头结点和头结点地址都不能为NULL
assert(pphead && (*pphead));
//若单单链表只有一个结点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) {
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
//若只有头结点一个元素
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) {
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
//找到尾结点,同时需要找到尾结点的前一个结点,便于删除
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
SLTNode* previous = *pphead;
//当指针为NULL是表明为尾结点
while (current->next) {
previous = current;
current = current->next;
}
//当前current为最后一个结点,previous为倒数第二个结点
free(current);
current = NULL;
previous->next = NULL;
return;
}
//头结点位置删除
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead) {
//删除结点,头结点和头结点地址都不能为NULL
assert(pphead && (*pphead));
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
//将头结点指向下一个结点
*pphead = current->next;
free(current);
current = NULL;
return;
}
//查找元素
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, DataType x) {
if (phead == NULL) {
printf("该链表没有任何信息\n");
return NULL;
}
SLTNode* current = phead;
while (current) {
if (current->data == x) {
return current;
}
current = current->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在position前插入元素
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* position, DataType x) {
//头结点的地址不能为NULL,对应位置的元素也不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
assert(position);
//既然对应位置不能为NULL,说明链表一定存在元素,链表头结点也不能为NULL
assert(*pphead);
//如果此时只有头结点一个元素,且刚好为position
if (*pphead == position) {
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//需要找打position前的一个元素
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
while (current->next != position&¤t!=NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {
printf("没找不到该元素位置,插入失败!\n");
return;
}
else {
//当前current为position的前一个元素
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//将新生成的结点链接起来
newNode->next = position;
current->next = newNode;
}
}
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* position, DataType x) {
assert(position);
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//下面两句不能调换顺序!
newNode->next = position->next;
position->next = newNode;
}
void SLTDestroy(SLTNode** pphead) {
//传过来的链表不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
if (current != NULL) {
SLTNode* next = current->next;
free(current);
current = next;
}
current = NULL;
*pphead = NULL;
}
//指定位置删除
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* position) {
//头结点及其地址不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(position);
//如果删除的为第一个结点
if (position == *pphead) {
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
free(position);
position = NULL;
return;
}
//找到对应位置的前一个结点
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
while (current->next != position&¤t!=NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
//找到最后一个结点都没有找到position
if (current == NULL) {
printf("没有找到对应结点!\n");
return;
}
else {
//当前current指针指向position的前一个位置
current->next = position->next;
free(position);
position = NULL;
}
}
//指定位置之后删除
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* position) {
assert(position);
//之后一个结点也不能为NULL
assert(position->next);
SLTNode* next = position->next;
position->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
}以下为所有代码,及其运行测试结果:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node {
DataType data;
struct Node* next;
}SLTNode;
//打印所有的元素
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead) {
//先判断当前链表是否为NULL
if (phead == NULL) {
printf("该链表没有元素!\n");
return;
}
SLTNode* current = phead;
while (current) {
printf("%d->", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//创建一个新的结点
SLTNode* CreateNode(DataType x) {
SLTNode* newNode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
perror("MALLOC:");
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//尾结点插入
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x) {
//传过来的单链表地址不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//若需要插入的为头结点,直接插入
if (*pphead == NULL) {
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//若不为头结点,找到最后一个结点
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
while (current->next) {
current = current->next;
}
//此时current的下一个为NULL
current->next = newNode;
return;
}
//头结点插入
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x) {
//传过来的头结点指针不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//若头结点为NULL,直接插入
if (*pphead == NULL) {
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//将新节点的指针指向当前头结点
newNode->next = *pphead;
//头结点移动
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//删除尾结点
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead) {
//删除结点,头结点和头结点地址都不能为NULL
assert(pphead && (*pphead));
//若单单链表只有一个结点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) {
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
//若只有头结点一个元素
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) {
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
//找到尾结点,同时需要找到尾结点的前一个结点,便于删除
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
SLTNode* previous = *pphead;
//当指针为NULL是表明为尾结点
while (current->next) {
previous = current;
current = current->next;
}
//当前current为最后一个结点,previous为倒数第二个结点
free(current);
current = NULL;
previous->next = NULL;
return;
}
//头结点位置删除
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead) {
//删除结点,头结点和头结点地址都不能为NULL
assert(pphead && (*pphead));
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
//将头结点指向下一个结点
*pphead = current->next;
free(current);
current = NULL;
return;
}
//查找元素
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, DataType x) {
if (phead == NULL) {
printf("该链表没有任何信息\n");
return NULL;
}
SLTNode* current = phead;
while (current) {
if (current->data == x) {
return current;
}
current = current->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在position前插入元素
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* position, DataType x) {
//头结点的地址不能为NULL,对应位置的元素也不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
assert(position);
//既然对应位置不能为NULL,说明链表一定存在元素,链表头结点也不能为NULL
assert(*pphead);
//如果此时只有头结点一个元素,且刚好为position
if (*pphead == position) {
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
//需要找打position前的一个元素
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
while (current->next != position&¤t!=NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {
printf("没找不到该元素位置,插入失败!\n");
return;
}
else {
//当前current为position的前一个元素
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//将新生成的结点链接起来
newNode->next = position;
current->next = newNode;
}
}
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* position, DataType x) {
assert(position);
SLTNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//下面两句不能调换顺序!
newNode->next = position->next;
position->next = newNode;
}
void SLTDestroy(SLTNode** pphead) {
//传过来的链表不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
if (current != NULL) {
SLTNode* next = current->next;
free(current);
current = next;
}
current = NULL;
*pphead = NULL;
}
//指定位置删除
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* position) {
//头结点及其地址不能为NULL
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(position);
//如果删除的为第一个结点
if (position == *pphead) {
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
free(position);
position = NULL;
return;
}
//找到对应位置的前一个结点
SLTNode* current = *pphead;
while (current->next != position&¤t!=NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
//找到最后一个结点都没有找到position
if (current == NULL) {
printf("没有找到对应结点!\n");
return;
}
else {
//当前current指针指向position的前一个位置
current->next = position->next;
free(position);
position = NULL;
}
}
//指定位置之后删除
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* position) {
assert(position);
//之后一个结点也不能为NULL
assert(position->next);
SLTNode* next = position->next;
position->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
}
void Test01() {
SLTNode* phead = NULL;
SLTPushBack(&phead, 1);
SLTPushBack(&phead, 2);
SLTPushBack(&phead, 3);
SLTPushBack(&phead, 4);
SLTPrint(phead); // 1 2 3 4
SLTPushFront(&phead, 8);
SLTPushFront(&phead, 7);
SLTPushFront(&phead, 9);
SLTPrint(phead); // 9 7 8 1 2 3 4
SLTPopBack(&phead);
SLTPopBack(&phead);
SLTPopBack(&phead);
SLTPrint(phead); //9 7 8 1
SLTPopFront(&phead);
SLTPopFront(&phead);
SLTPopFront(&phead);
SLTPrint(phead); //1
SLTNode* P = SLTFind(phead,1);
if (P != NULL) {
printf("找到了!\n"); //找到了!
printf("%d\n", P->data);//1
}
else {
printf("未找到!\n");
}
SLTInsert(&phead, P, 100);
SLTInsertAfter(P, 8);
SLTPrint(phead); //100 1 8
SLTPushBack(&phead, 12);
SLTPushBack(&phead, 13);
SLTPushBack(&phead, 14);
SLTPrint(phead); //100 1 8 12 13 14
SLTEraseAfter(P);
SLTErase(&phead,P);
SLTPrint(phead); //100 12 13 14
SLTDestroy(&phead);
}
int main() {
Test01();
return 0;
}测试结果:

以上就为单链表的所有操作。
4. 链表的分类
链表的结果非常多样,结合以下情况组合起来一共就有8种(2*2*2)链表结构:

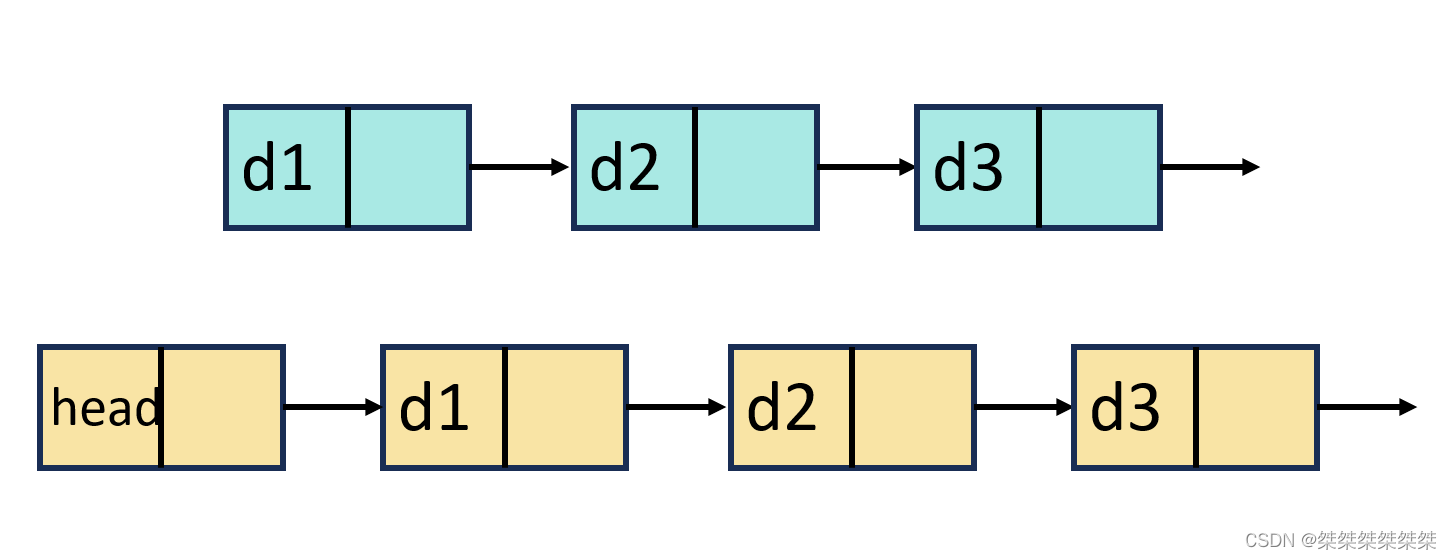
带头或者不带头:
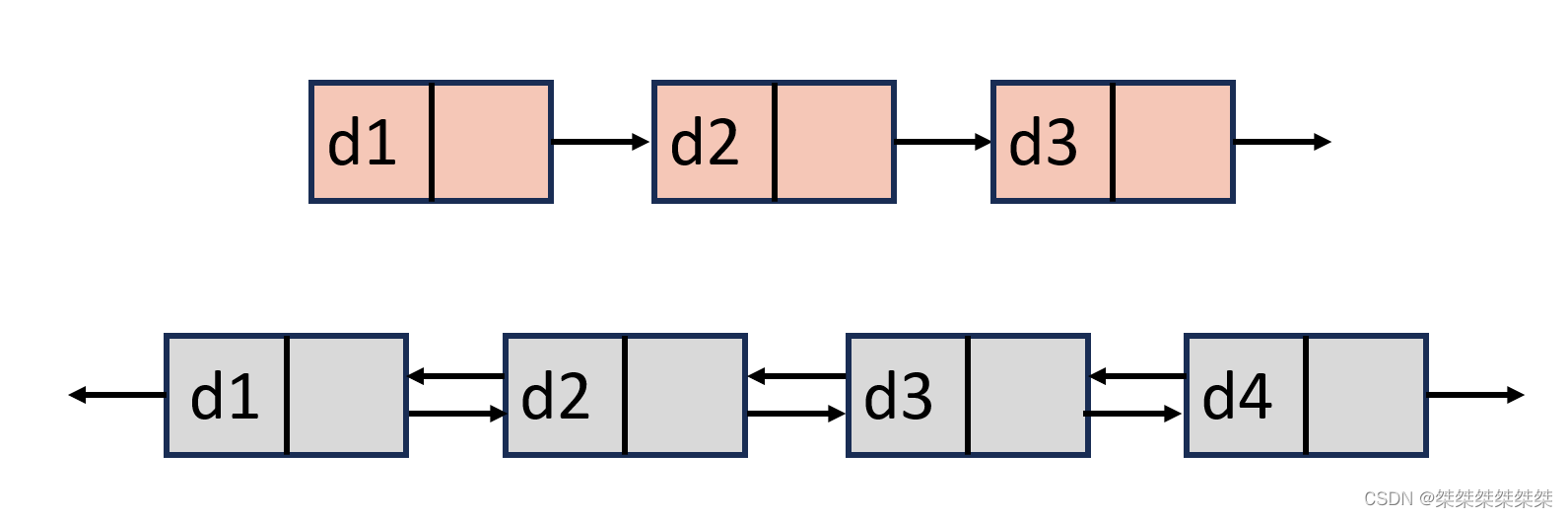
单向或者双向:
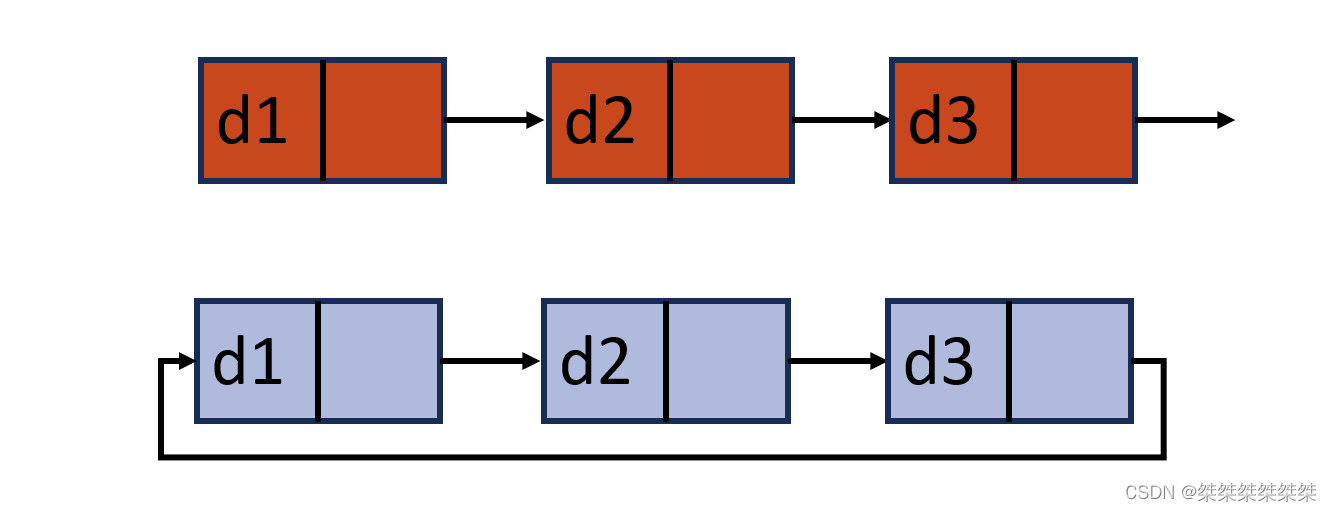
循环与不循环:
尽管有八种链表结构,但是其中用得最多的是:不带头结点的不循环单向链表、带头结点的循环双向链表。