1.字符串的合法检验
现在有一个字符串验证码 我们需要检验其的合法性 什么条件才能够使得字符串合法呢?就是6-10个字符串长度 并且以字母开头 并且其中由字母、数字、下划线构成
那么我们可以先通过自定义的方式进行检验
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(validate("aaaaaa"));
}
private static boolean validate(String email){
// 如果参数为空的话 那么说明不合法 提醒一下并且返回false
if(email == null){
System.out.println("邮箱不能为空");
return false;
}
// 由于之后获取参数字符串中的字符方法charAt()开头需要对字符串进行长度判断 如果多次调用的话 时间方面的效率肯定很低 但是好在他是在原先字符串的基础上进行获取的 所以我们利用空间换时间的方法 拷贝一个字符串的内存 优化了时间 但多开辟了空间
char[] chs = email.toCharArray();
int len = chs.length;
// 如果参数的长度不合要求的话 那么提醒一下并且返回false 由于长度需要多次获取 所以提前定义一个变量 用于保存这个参数的长度
if(len < 6 || len > 10){
System.out.println("长度不合法");
return false;
}
// 是否以字母开头
if(!isLetter(chs[0])){
System.out.println("不是以字母开头");
return false;
}
// 是否由字母、数字、下划线构成
for(int i = 1; i < len; ++i){
// 获取当前遍历的字符
char ch = chs[i];
if(isLetter(ch) || isDigit(ch) || ch == '_')continue;
return false;
}
// 如果上述判断都没有返回false的话 那么说明这个邮箱字符串是合法的
return true;
}
private static boolean isLetter(char ch){
if((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'))return true;
return false;
}
private static boolean isDigit(char ch){
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')return true;
return false;
}
}
但是我们可以看到其实我们自己自定义的方法写的很繁杂 所以我们可以引入正则表达式来替代复杂的验证逻辑
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{5,9}";
System.out.println("aaaaaa".matches(regex));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "[a-zA-Z]\\w{5,9}";
System.out.println("aaaaa".matches(regex));
}
}
2.单字符匹配
1.[bcr]–可以匹配括号内的任意一个字符
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 等价于[b|c|r]或者(b|c|r) 但是一般写成[bcr]比较简练一点 推荐使用[bcr]写法
String regex = "[bcr]at";
System.out.println("bat".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("cat".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("rat".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("hat".matches(regex));// false
}
}
2.[ ^bcr ]–可以匹配除了括号内以外的任意一个字符
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "[^bcr]";
System.out.println("bat".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("cat".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("rat".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("hat".matches(regex));// true
}
}
3.[1-5]–可以匹配括号内指定范围内的任意一个字符
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "foo[1-5]";
System.out.println("foo1".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo2".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo3".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo4".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo5".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo6".matches(regex));// false
}
}
4.[ ^1-5 ]–可以匹配括号指定范围以外的任意一个字符
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "foo[^1-5]";
System.out.println("fook".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo6".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("foo5".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "foo1-5";
System.out.println("foo6".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("foo5".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("foo1-5".matches(regex));// true
}
}
5.[0-46-8]或者[0-4[6-8]]–匹配两个范围的并集部分的任意一个字符
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "[0-46-8]";
System.out.println("4".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("5".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "[0-4[6-8]]";
System.out.println("4".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("5".matches(regex));// false
}
}
6.[a-z&&[def]]–匹配两个范围的交集部分的任意一个字符
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 也可以写成[a-z&&[def]]
String regex = "[a-z&&def]";
System.out.println("d".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("e".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("f".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("o".matches(regex));// false
}
}
7.[a-z&&[ ^bc ]]–匹配两个范围的差集部分的任意一个字符 即前面范围和后面范围的差集(就是属于前面范围但是不属于后面范围的任意一个字符 相当于[ad-z])
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "[a-z&&[^bc]]";
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("b".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("c".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("d".matches(regex));// true
}
}
3.预定义字符
在正则表达式中 其实已经存在了许多提前定义好的字符:
. – 匹配任意一个字符
\d – 匹配数字中的任意一个字符(等价于[0-9])
\D – 匹配非数字中的任意一个字符(等价于[ ^0-9 ])
\s – 匹配空白字符中的任意一个字符(等价于[ \t\n\f\r] 注意前面有一个空格 因为空格也属于空白字符)
\S – 匹配非空白字符中的任意一个字符(等价于[ ^\s ])
\w – 匹配单词字符中的任意一个字符(单词字符包括数字、字母、下划线 等价于[a-zA-Z0-9])
\W – 匹配非单词字符中的任意一个字符(等价于[ ^\w ])
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = ".";
System.out.println("123".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// true
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 我们都知道.可以匹配任意一个字符 但是其实有一种用法只能匹配.这个字符 就是\\.
String regex = "\\.";
System.out.println(".".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// false
}
}
相当于123位置处必须填写123 而不是任意从中取出一个字符来 而[和]位置处也必须写上[和]才行
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 其实不止是\\.有匹配仅有的.的作用 \\[ \\]也有类似的作用
String regex = "\\[123\\]";
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("[1]".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("[123]".matches(regex));// true
}
}
需要注意的是由于Java中存在转义字符 所以\和诸如t这样的字符组合会将t转义为其他的字符 要在最前面在加上一个\ 即\t
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "\\d";
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("12".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "\\D";
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("ab".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "\\s";
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("\t".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("\n".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("\f".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("\r".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "\\S";
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("\t".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("\n".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("\f".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("\r".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// true
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 单词只包括数字、字母、下划线
String regex = "\\w";
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("_".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("#".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 单词只包括数字、字母、下划线
String regex = "\\W";
System.out.println("1".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("a".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("_".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("#".matches(regex));// true
}
}
4.量词
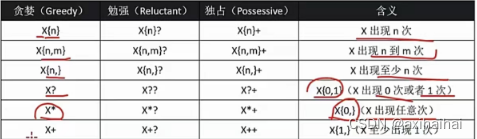
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x{n} 说明x出现了n次
String regex = "6{3}";
System.out.println("66".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("666".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("6666".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x{n, m} 说明x出现了指定范围内的任意一个次数
String regex = "6{2,4}";
System.out.println("6".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("66".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("666".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("6666".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("66666".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x{n, m} 说明x至少出现了n次
String regex = "6{2,}";
System.out.println("6".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("66".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("666".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("6666".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("66666".matches(regex));// true
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x? 说明x出现了0次或者1次
String regex = "6?";
System.out.println("".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("6".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("66".matches(regex));// false
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x* 说明x至少出现了0次
String regex = "6*";
System.out.println("".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("6".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("66".matches(regex));// true
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x+ 说明x至少出现了1次
String regex = "6+";
System.out.println("".matches(regex));// false
System.out.println("6".matches(regex));// true
System.out.println("66".matches(regex));// true
}
}
5.Pattern和Matcher
其实我们所使用的String类中的match方法底层使用到了Pattern和Matcher两个类
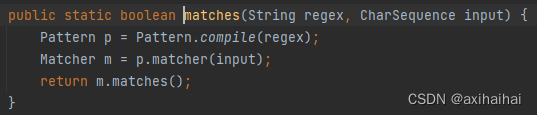
第一行是检查我们所写的正则表达式语法是否正确 第二行则是对两者进行匹配 第三行则是返回匹配结果
其实Matcher不止有matches方法 还有其他常用的方法
1.find方法
该方法属于部分匹配 即查看是否包含符合条件的子串 而matches则属于完全匹配
并且和while循环搭配使用的话 就可以查找指定字符串中的所有符合条件的子串 直到找不到为止
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// match方法是完全匹配 而find方法则是部分匹配 也就是查看正则表达式中是否包含字符串
// 检查正则表达式是否合法
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\d{3}");
// 然后将正则表达式和字符串进行匹配
Matcher m = p.matcher("123_456_789");
// 然后打印匹配结果
System.out.println(m.find());
}
}
2.find、group、start、end方法
以下这个案例可以找到指定字符串中符合正则表达式的所有子串 并且打印他的内容以及他的开始索引以及结束索引信息
一般如果你不使用这个flags的话 那么直接传递一个0即可
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "123_456_789_101_112";
String regex = "\\d{3}";
findAll(regex, input);
}
// 定义一个方法 用于查找所有符合条件的子串
public static void findAll(String regex, String input){
findAll(regex, input, 0);
}
// 定义一个方法 用于查找所有符合条件的子串
public static void findAll(String regex, String input, int flags){
// 如果正则表达式为空或者字符串为空的话 那么就执行下面操作
if(regex == null || input == null)return;
// 首先我们先检查合法的正则表达式
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex, flags);
// 然后定义一个匹配器 参数为两个参与匹配的字符串
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
// 定义一个变量 用于查看是否存在符合条件的子串
boolean found = false;
// 然后遍历每一个符合条件的子串 并且获取每一个子串的内容以及开始和结束索引 注意是[开始索引, 结束索引)
while(m.find()){
found = true;
System.out.print("\"" + m.group() + "\", ");
System.out.println("[" + m.start() + ", " + m.end() + "]");
}
// 如果不存在符合条件的子串 那么就打印不存在符合条件的子串
if(!found){
System.out.println("no match.");
}
}
}

![[flutter]GIF速度极快问题的两种解决方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6b15f202057f42daaae1ba8dd7b63301.png)