二、简单控件
1、文本显示
(1)文本内容
💬 Tip:文本内容设置共有三种方式
- 硬编码到XML布局文件
- 硬编码到代码中
- 编码到strings.xml,然后其他文件(如:布局文件、代码中)引用即可
硬编码到XML文件:
-
Layout布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".TextContent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/m1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" android:text="XML硬编码" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/m2" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/m2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" android:text="@string/tc_m2" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/m1" app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/m3" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/m3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/m2" app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/m4" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/m4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/m3" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout> -
字符串文件:
<resources> <string name="app_name">My Application</string> <string name="song">My Song</string> <string name="tc_m2">xml引用</string> <string name="tc_m4">代码引用</string> </resources> -
代码文件:
public class TextContent extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_content); TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.m3); textView.setText("代码硬编码"); TextView textView4 = findViewById(R.id.m4); textView4.setText(R.string.tc_m4); } }
总结:常用两种引用方式
- 在XML文件中引用:
@string/*** - 在Java代码中引用:
R.string.***
(2)文本大小
文本大小的三个单位:
- px:也称为图像元素(Pixel),构成图像的基本单位,与设备显示屏相关,单个像素大小不固定,跟随屏幕大小和像素数量的关系变化
-
分辨率(Resolution):指屏幕的垂直和水平方向的像素速率,如果分辨率是
1920*1080,则垂直方向有1920个像素,水平反向1080个像素- 如果不同尺寸的屏幕,如15.6英寸和17英寸的分辨率都是
1920*1080,因为单个像素大小不固定,那么17英寸的屏幕的单个像素更大
- 如果不同尺寸的屏幕,如15.6英寸和17英寸的分辨率都是
-
像素密度(dpi):每英寸距离中有多少个像素点

- 像素密度 = c / 屏幕尺寸
-
密度:每平方英尺中有多少像素点
-
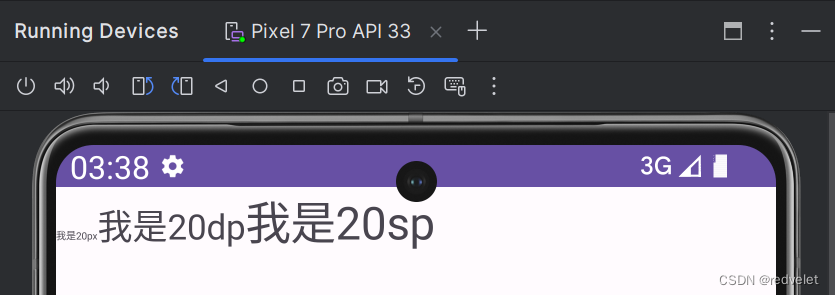
- dp/dip:也称独立设备像素,与屏幕尺寸相关,与设备无关,是一种长度的单位,本质还是px
- 特点:相同屏幕尺寸的设备,如果dp相同,则显示效果相同
- sp:与系统设置相关,系统设置中调整文字大小,则其也会相对应变化,是dp的增强版
示例:
-
布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".TextSize"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="409dp" android:layout_height="83dp" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="1dp" tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="1dp" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tsPx" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/tsPx" android:textSize="20px" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tsDp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/tsDp" android:textSize="20dp" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tsSp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/tsSp" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" /> </LinearLayout> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout> -
Java代码:
public class TextSize extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_size); TextView sp = findViewById(R.id.tsSp); //默认sp大小单位 sp.setTextSize(20); } } -
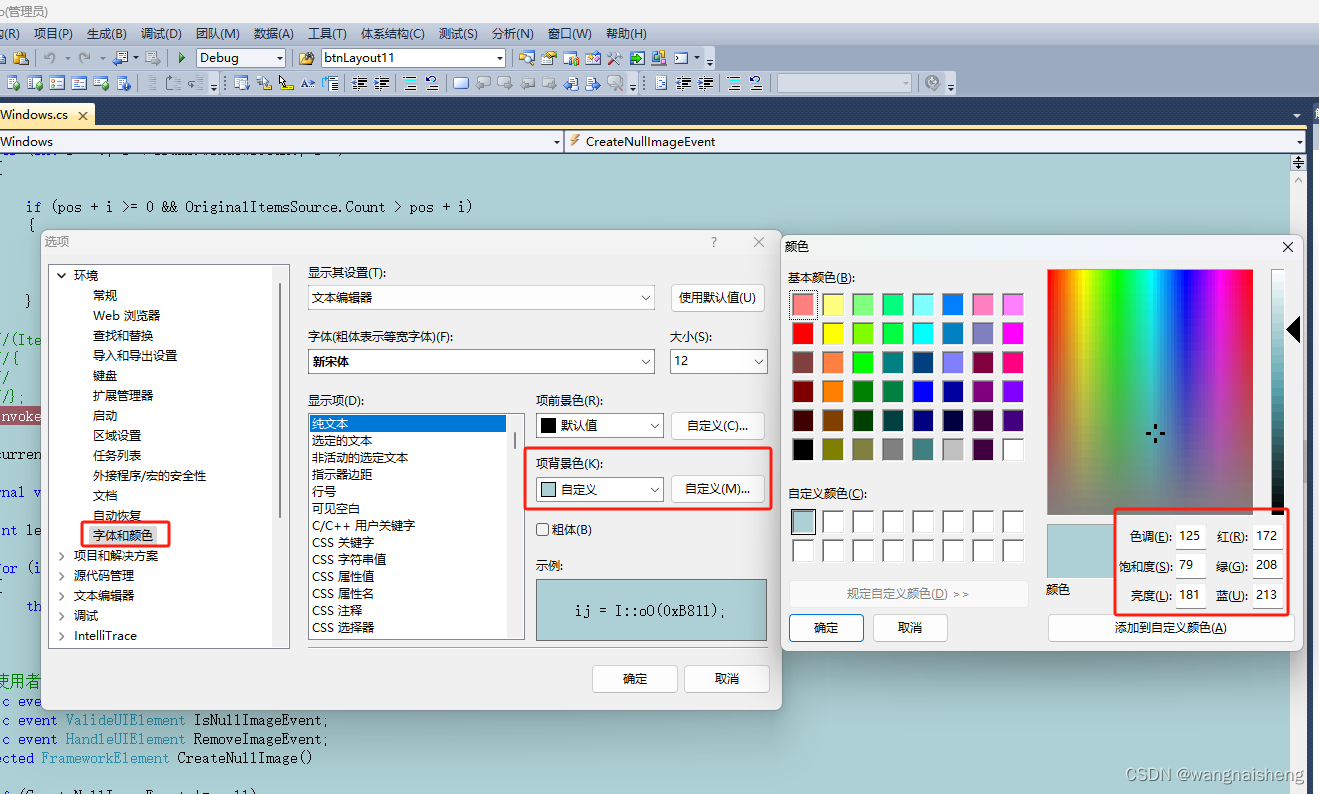
手机 —> 设置 —> 调整文字大小:
(3)文本颜色
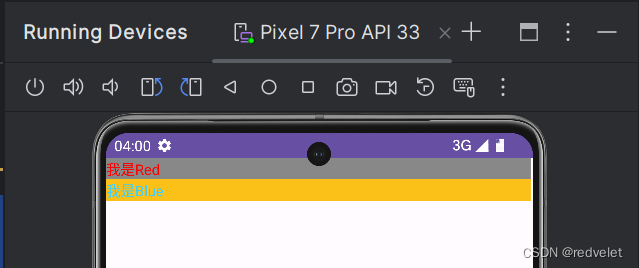
文本颜色包括:背景颜色、文字颜色
-
布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".TextColor"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="409dp" android:layout_height="729dp" android:orientation="vertical" tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="1dp" tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="1dp" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tcRed" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/tcRed" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tcBlue" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/tcBlue" android:textColor="#3ECEF6" android:background="#FBC118"/> </LinearLayout> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout> -
Java代码:
public class TextColor extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_color); TextView tcRed = findViewById(R.id.tcRed); tcRed.setTextColor(Color.RED); tcRed.setBackgroundColor(Color.GRAY); } } -
效果图:
2、视图基础
待续

![P1059 [NOIP2006 普及组] 明明的随机数————C++、Python](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/bba9d0da5f8643c3ad2fe4a76973e062.png)