写作背景
SpringCloud Netflix作为SpringCloud第一代产品很经典,而且公司的老项目还在用SpringCloud Netflix的技术栈,有必要对SpringCloud Netflix的各种核心组件回归复习一下了。
本次复习的主角是微服务注册中心Eureka,本文的书写思路是五个方面
- Eureka是用来干什么的,为什么会有Eureka
- Eureka的核心功能有哪些
- 上手搭建Eureka的服务端和客户端实战一下
- 从源码的角度验证一下Eureka的核心功能
- Eureka常见问题FAQ
Eureka是用来干什么的?
首先来想一个问题,在微服务的架构下,服务之间的调用关系如何维护?
服务A调用服务B,那我服务A需要在代码里记录服务B的访问的IP和端口,现在一个请求经过API网关然后调用多个下游服务,然后聚合各个下游服务返回请求的响应是很常见的,如果都是把下游服务的IP和端口硬编码在代码里,很不优雅。
还是拿服务A调用服务B举例,服务A想知道服务B的访问IP和端口,有没有一个组件可以告诉我服务A,我给你服务B的名字,你返回我服务B的访问IP和端口等信息,这样我服务A就不用自己在代码里去维护服务B的请求IP和端口了。Eureka的一个核心功能之一就是服务发现,服务A可以通过Eureka来发现服务B的访问IP和端口,在实现服务发现的基础上需要Eureka的客户端先进行服务注册,也就是Eureka的客户端程序也就是你的服务,比如服务B先将自己注册到Eureka的服务端,然后服务A就可以通过Eureka拉取到服务注册表信息找到服务B的访问IP和端口。
Eureka的核心功能
1、服务注册(register)
Eureka Client在服务启动时会发送Rest请求的方式向Eureka Server注册自己的服务,注册的时候会提供服务自身的一些元数据,比如IP和端口。Eureka Server在接收到注册请求后,会将这些元数据信息存储在一个双层的Map中,这个Map其实就是服务注册表。
2、服务续约(renew)
服务续约是Eureka Client在服务注册后,会定时(默认每30s)向Eureka Server发送心跳通知Eureka Server 我还活着,还是处于可用的状态,防止被Eureka Server剔除。
3、服务下线(cancel)
Eureka Client在服务关闭或者重启时,会主动向Eureka Server发送Rest请求,告诉Eureka Server自己要下线了,Eureka Server在收到下线请求后,会把该服务的状态设置为DOWN
4、服务同步
在生产环境下,为了防止单点问题,Eureka往往会搭建HA架构,Eureka Server之间会互相进行注册,构建一个Eureka Server集群,不同的Eureka Server之间会进行服务同步,来保证服务信息的一致性。
5、服务剔除(evict)
服务剔除是Eureka Server在启动时会启动一个定时任务,默认每60s扫描一次服务注册表,如果发现服务超过90s没有续约,那么就把这个服务实例剔除掉,后续在这个服务恢复之前,这个服务实例将不再对外提供服务。
6、自我保护
因为有服务剔除机制,那么就有可能因为是网络故障等原因,导致服务续约没有成功,而实际上服务还是可用的情况,但是Eureka Server把所有服务都剔除下线了,这样显然不太合理。为了防止因短期网络波动引起的服务续约失败,导致Eureka Server剔除所有服务的情况,就有了自我保护机制。具体的做法其实就是在短期内,统计服务续约失败的比例,如果达到了一个阈值,那么就触发自我保护Eureka Server不再提出任务服务,直到比例恢复正常后,才退出自我保护。
7、获取服务
Eureka Client在启动的时候,会发送一个REST请求给Eureka Server,获取服务注册表,并且缓存在Eureka Client本地,默认缓存30秒更新缓存一次。同时,为了性能考虑,Eureka Server也会维护一份只读缓存readOnlyCacheMap,该缓存每隔30秒更新一次
上手搭建Eureka的服务端和客户端实战一下
说明一下基于SpringBoot 2.x搭建的Eureka Server
1、pom.xml引入Eureka的依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、启动了开启服务注册
/**
* @author zhangyu
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
3、配置文件application.yml里增加Eureka 的配置信息
#端口
server:
port: 8761
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
#eureka相关配置
eureka:
client:
#表示是否将自己注册到Eureka Server,默认为true,由于当前应用就是Eureka Server,故而设为false
register-with-eureka: false
# 表示是否从Eureka Server获取注册信息,默认为true,因为这是一个单点的Eureka Server,不需要同步其他的Eureka Server节点的数据,故而设为false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
#Eureka 服务端配置,其实都是默认配置,这里写出来增加记忆
server:
#是否开启自我保护机制,默认是true也就是开启
enable-self-preservation: true
#开启自我保护后,期望心跳次数的阈值
renewal-percent-threshold: 0.85
#是否开启只读缓存,默认开启
use-read-only-response-cache: true
#将readWriteCache读写缓存数据定时刷入readOnlyCache只读缓存的时间,默认30秒
response-cache-update-interval-ms: 30000
#readWriteCache读写缓存被动过期时间,默认180秒更新一次读写缓存
response-cache-auto-expiration-in-seconds: 180
启动eureka-server服务,然后访问http://localhost:8761/ 就会看到Eureka Server的UI界面

生产环境下一般访问Eureka界面都是要账户密码的,所以需要和Security整合
Eureka与Security整合安全访问
1、pom.xml引入Security的依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、开启Web的Security保护
/**
* @author zhangyu
*/
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//关闭csrf
http.csrf().disable();
super.configure(http);
}
}
3、配置文件application.yml配置访问Security的账户和密码
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
security:
user:
name: root
password: 123456
4、修改暴露给其他Eureka Client注册的地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
#改动的在这里
defaultZone: http://${spring.security.user.name}:${spring.security.user.password}@localhost:8761/eureka/
重启eureka-server服务,然后再次访问http://localhost:8761/ 你会发现页面被转发到登录页面http://localhost:8761/login

输入root和123456才会进入Eureka Server的UI界面。
快速用SpringBoot搭建一个服务然后注册到Eureka Server
1、pom.xml引入Eureka Client的依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、启动类开启Eureka Client
启动类增加@EnableEurekaClient注解
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServiceScreenApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceScreenApplication.class, args);
}
}
3、配置文件applicatiion.yml配置Eureka信息
#端口
server:
port: 8003
spring:
application:
name: fc-service-screen
#eureka相关配置
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://root:123456@localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
#显示的微服务名称
instance-id: ms-service-screen-8003
#eureka客户端向服务端发送心跳时间默认30s
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 10
#Eureka服务器在接收到实例的最后一次发出的心跳后,需要等待多久才可以将此实例删除,默认为90秒
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 30
启动fc-service-screen服务,然后去刷新http://localhost:8761/ 页面看看服务注册上去了没

搭建Eureka HA架构
再新起一个Eureka Server服务,端口设置为8762,然后最关键的地方是application.yml里关于Eureka的两个配置要结合起来使用。
新搭建的eureka-server8762服务的配置文件
#端口
server:
port: 8762
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server8762
security:
user:
name: root
password: 123456
#eureka相关配置
eureka:
client:
# HA架构的关键配置就是下面两个配置联合使用
# 将自己注册到Eureka Server,默认为true
register-with-eureka: true
# 表示是否从Eureka Server获取注册信息,默认为true,因为本身就是Eureka Server不需要
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://${spring.security.user.name}:${spring.security.user.password}@localhost:8761/eureka/,http://${spring.security.user.name}:${spring.security.user.password}@localhost:8762/eureka/
#Eureka 服务端配置,其实都是默认配置,这里写出来增加记忆
server:
#是否开启自我保护机制,默认是true也就是开启
enable-self-preservation: true
#开启自我保护后,期望心跳次数的阈值
renewal-percent-threshold: 0.85
#是否开启只读缓存,默认开启
use-read-only-response-cache: true
#将readWriteCache读写缓存数据定时刷入readOnlyCache只读缓存的时间,默认30秒
response-cache-update-interval-ms: 30000
#readWriteCache读写缓存被动过期时间,默认180秒更新一次读写缓存
response-cache-auto-expiration-in-seconds: 180
关键的地方是register-with-eureka 设置为true,相当于本身也是Eureka Client,然后就是fetch-registry设置为false,因为eureka-server8762本身也是Eureka Server它在服务启动时会从相邻的Eureka Server节点拉取注册表数据,然后服务注册时也会往其他Eureka Server节点转发注册保持数据一致性。然后就是暴露给Eureka Client注册的地址变成两个,用逗号隔开。
我们启动eureka-server和eureka-server8762两个服务,然后再启动fc-service-screen服务,然后访问两个Eureka Server的UI界面看看
eureka-server的

eureka-server8762的

你会发现两个Eureka Server的服务注册信息是一样,但是我的fc-service-sreen的Eureka注册地址只配置了http://root:123456@localhost:8761/eureka/也就是eureka-server这一台的。后面源码会分析,这个就是Eureka的服务同步功能。
从源码的角度验证一下Eureka的核心功能
先说明一下,我用的SpringBoot版本是2.2.2.RELEASE,小于2.7也就是说SpringBoot自动装配等的配置还是在META-INF/spring.factories文件里。
EurekaServer自动装配源码
我们知道在Eureka Server的启动类有加@EnableEurekaServer这个注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableEurekaServer {
}
这个注解导入了EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration,我们看下这个Marker配置类有啥
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration {
@Bean
public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() {
return new Marker();
}
class Marker {
}
}
我们发现这个EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration里就是声明了一个叫Marker的Bean。我们想想SpringBoot的自动装配的原理,一般都是XXXAutoConfiguration,大胆猜测一下是不是有个EurekaServerAutoConfiguration,果然在spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server-2.2.1.RELEASE.jar的META-INF/spring.factories文件里找到了。
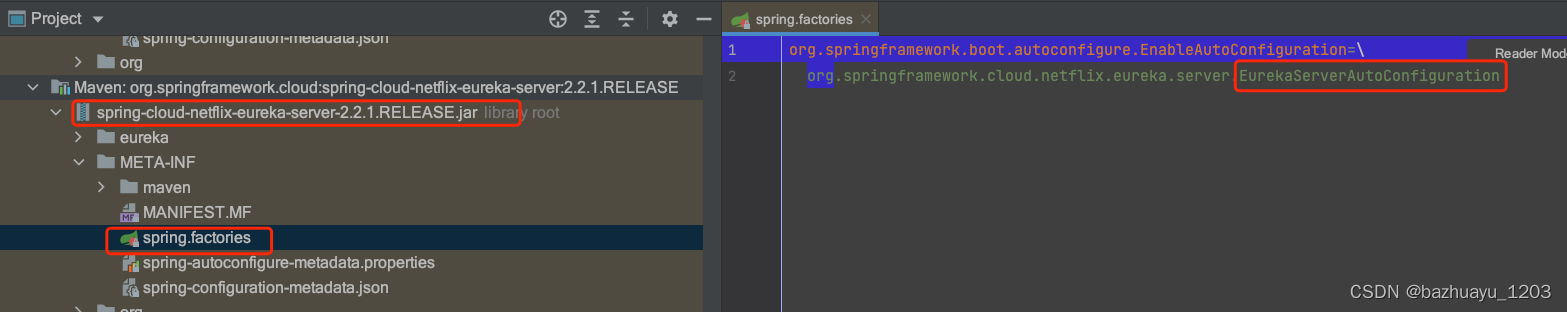
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,
InstanceRegistryProperties.class })
@PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties")
public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
...
}
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)看这个,有EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker这个Bean,EurekaServerAutoConfiguration才会生效,所以上面说到的EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration里其实就是开启一个Marker的开关用于控制EurekaServer自动装配的开关。
然后再看看@Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class) 一般这种导入的类肯定是很关键的,我们进去看一下
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration
implements ServletContextAware, SmartLifecycle, Ordered {
}
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration实现了SmartLifecycle接口,这个SmartLifecycle是spring-context包里的东西,它的作用是在Spring容器的refresh()方法里的finishRefresh()方法里会去调用SmartLifecycle的start()方法,我们看下EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration的start()方法
@Override
public void start() {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 初始化EurekaServer
eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext);
log.info("Started Eureka Server");
publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true;
publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Help!
log.error("Could not initialize Eureka servlet context", ex);
}
}).start();
}
eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized这个方法跟进去看看
ublic void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) {
try {
initEurekaEnvironment();
//我们主要关心这个,看名字就知道是初始化EurekaServerContext
initEurekaServerContext();
context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
}
}
Eureka Server服务同步源码
继续上面的初始化EurekaServerContext的源码跟进去
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception {
EurekaServerContextHolder.initialize(this.serverContext);
log.info("Initialized server context");
// Copy registry from neighboring eureka node
//从这行注释里就看的出来是从隔壁的eureka里拷贝注册表
int registryCount = this.registry.syncUp();
//这行代码也很关键,开启服务剔除在这里,registryCount是其他节点的服务注册数
this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount);
// Register all monitoring statistics.
EurekaMonitors.registerAllStats();
}
从源码的原始注释里也说明了this.registry.syncUp()方法就是从其他Eureka Server节点同步服务注册表
com.netflix.eureka.registry.PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl#syncUp
@Override
public int syncUp() {
// Copy entire entry from neighboring DS node
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; ((i < serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetries()) && (count == 0)); i++) {
if (i > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetryWaitMs());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.warn("Interrupted during registry transfer..");
break;
}
}
//获取应用服务数据
Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();
for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
try {
if (isRegisterable(instance)) {
//将其他节点注册服务到本地
register(instance, instance.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs(), true);
count++;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("During DS init copy", t);
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
Eureka Server 自我保护和服务剔除源码
自我保护体现在两个地方,一个是Eureka Server定时更新每分钟续约的客户端个数的阈值,一个是在服务剔除时,如果开启了自我保护,那么就会判断最近一分钟续约的个数是否超过每分钟续约的客户端个数的阈值,没有超过就不剔除。
回到EurekaServerAutoConfiguration里来,我们看到注册了一个EurekaServerContext
@Bean
public EurekaServerContext eurekaServerContext(ServerCodecs serverCodecs,
PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) {
return new DefaultEurekaServerContext(this.eurekaServerConfig, serverCodecs,
registry, peerEurekaNodes, this.applicationInfoManager);
}
然后DefaultEurekaServerContext里有个@PostConstruct注解的init()方法
@PostConstruct
@Override
public void initialize() {
logger.info("Initializing ...");
peerEurekaNodes.start();
try {
//初始化服务注册表,这里面就有自我保护的机制在里面
registry.init(peerEurekaNodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
logger.info("Initialized");
}
peerEurekaNodes.start()方法主要搞了一个只有一个线程的线程池,然后默认每10分钟更新一次集群中当前Eureka Server节点的元数据
public void start() {
taskExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
//Eureka集群节点的更新线程
Thread thread = new Thread(r, "Eureka-PeerNodesUpdater");
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
}
}
);
try {
//初次进来直接更新节点元数据
updatePeerEurekaNodes(resolvePeerUrls());
Runnable peersUpdateTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
updatePeerEurekaNodes(resolvePeerUrls());
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot update the replica Nodes", e);
}
}
};
//周期性的更新
taskExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
peersUpdateTask,
//默认10分钟
serverConfig.getPeerEurekaNodesUpdateIntervalMs(),
serverConfig.getPeerEurekaNodesUpdateIntervalMs(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
for (PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes) {
logger.info("Replica node URL: {}", node.getServiceUrl());
}
}
定时更新每分钟续约的客户端数的阈值,为自我保护
@Override
public void init(PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) throws Exception {
this.numberOfReplicationsLastMin.start();
this.peerEurekaNodes = peerEurekaNodes;
//主要初始化两个缓存Map,一个readOnlyCacheMap一个readWriteCacheMap
initializedResponseCache();
//定时更新每分钟续约的客户端数
scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTask();
initRemoteRegionRegistry();
try {
Monitors.registerObject(this);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Cannot register the JMX monitor for the InstanceRegistry :", e);
}
}
private void scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTask() {
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
//15分钟后,每15分钟更新续约的客户端阈值
updateRenewalThreshold();
}//renewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs = 15 * MINUTES
}, serverConfig.getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs(),
serverConfig.getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs());
}
看看如何更新的续约客户端阈值
private void updateRenewalThreshold() {
try {
//所有的本地注册的应用实例
Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();
//拿到所有已注册的实例
int count = 0;
for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
if (this.isRegisterable(instance)) {
++count;
}
}
}
synchronized (lock) {
// Update threshold only if the threshold is greater than the
// current expected threshold or if self preservation is disabled.
//从这两行注释也可以看出,只有本地注册实例数超过0.85比例的客户端续约并且关闭自我保护机制,才会更新每分钟续约的客户端阈值
if ((count) > (serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews)
|| (!this.isSelfPreservationModeEnabled())) {
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
logger.info("Current renewal threshold is : {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot update renewal threshold", e);
}
}
上面初始化EurekaServerContext里有行代码this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount);我们跟进去看下
@Override
public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) {
// Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2.
//期望每分钟续约的客户端数是其他Eureka Server节点的注册客户端数
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count;
//默认每30s续约一次,所以这个里面是用60 / 30
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
。。。
logger.info("Changing status to UP");
//修改实例状态为UP
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP);
//这行代码可厉害了,服务剔除就在这里
super.postInit();
}
protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() {
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews
//默认续约时间是30
* (60.0 / serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds())
//默认发送续约的比例是0.85
* serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
}
上面的代码的意思就是更新续约的客户端数,更新本次续约的客户端个数的阈值=期望续约的客户端次数 *(60 / 30) * 0.85
举个例子,加入100个客户端,那么更新没分种期望续约的个数阈值为 100 * 2 * 0.85 = 170
private void updateRenewalThreshold() {
try {
Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();
int count = 0;
for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
if (this.isRegisterable(instance)) {
++count;
}
}
}
synchronized (lock) {
// Update threshold only if the threshold is greater than the
// current expected threshold or if self preservation is disabled.
if ((count) > (serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews)
|| (!this.isSelfPreservationModeEnabled())) {
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
logger.info("Current renewal threshold is : {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot update renewal threshold", e);
}
}
服务剔除
protected void postInit() {
renewsLastMin.start();
if (evictionTaskRef.get() != null) {
evictionTaskRef.get().cancel();
}
evictionTaskRef.set(new EvictionTask());
evictionTimer.schedule(evictionTaskRef.get(),
//默认60s
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs());
}
开启一个定时任务,默认60s后执行,然后每60s执行一次EvictionTask,我们看下EvictionTask的run方法里干了啥
class EvictionTask extends TimerTask {
private final AtomicLong lastExecutionNanosRef = new AtomicLong(0l);
@Override
public void run() {
try {
long compensationTimeMs = getCompensationTimeMs();
logger.info("Running the evict task with compensationTime {}ms", compensationTimeMs);
evict(compensationTimeMs);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Could not run the evict task", e);
}
}
//剔除的源码很长
public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) {
logger.debug("Running the evict task");
//如果开启了自我保护,就要看最近的续约个数有没有超过每分钟续约的阈值,如果没有超过直接返回
if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) {
logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled.");
return;
}
List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历服务注册表
for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) {
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue();
if (leaseMap != null) {
for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) {
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue();
//如果实例已经失效
if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) { //收集已失效的服务实例
expiredLeases.add(lease);
}
}
}
}
//执行内部的下线操作
internalCancel(appName, id, false);
}
}
}
重点再看一眼这个跟自我保护的判断
public boolean isLeaseExpirationEnabled() {
//开启自我保护就不会进入这个分支
if (!isSelfPreservationModeEnabled()) {
// The self preservation mode is disabled, hence allowing the instances to expire.
return true;
}
//最近一分钟的续约数和每分钟续约阈值比较
return numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold;
}
服务剔除的方法源码里比较多,主要是先收集已失效准备剔除的服务实例,然后把服务实例添加到两个Queue,一个最近下线的队列recentCanceledQueue,一个最近变化的队列recentlyChangedQueue,然后将服务状态改成下线,最后清除readWriteCacheMap的缓存
protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
try {
read.lock();
CANCEL.increment(isReplication);
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);
Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null;
if (gMap != null) {
leaseToCancel = gMap.remove(id);
}
synchronized (recentCanceledQueue) {
//将下线的服务实例添加到最近下线的队列里
recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")"));
}
InstanceStatus instanceStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id);
if (instanceStatus != null) {
logger.debug("Removed instance id {} from the overridden map which has value {}", id, instanceStatus.name());
}
if (leaseToCancel == null) {
CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
logger.warn("DS: Registry: cancel failed because Lease is not registered for: {}/{}", appName, id);
return false;
} else {//服务下线
leaseToCancel.cancel();
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToCancel.getHolder();
String vip = null;
String svip = null;
if (instanceInfo != null) {
instanceInfo.setActionType(ActionType.DELETED);
//将下线的服务实例添加到最近变更的队列里,这个队列跟后续服务获取的多级缓存有关
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(leaseToCancel));
instanceInfo.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
vip = instanceInfo.getVIPAddress();
svip = instanceInfo.getSecureVipAddress();
}//删缓存
invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip);
logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", appName, id, isReplication);
return true;
}
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
Eureka Client自动装配源码
老套路SpringBoot自动装配,先猜测是不是有EurekaClientAutoConfiguration类,果然在spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client-2.2.1.RELEASE.jar的META-INF/spring.factories文件里找到了
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class)
@Import(DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled
@AutoConfigureBefore({ NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class,
CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class, ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = {
"org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration" })
public class EurekaClientAutoConfiguration {
EurekaClientAutoConfiguration里有几个关键类说一下,首先是注入了一个EurekaClientConfigBean主要用于初始化EurekaClientConfig,读取配置文件里的eureka.client开头的配置
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClientConfig.class,
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClientConfigBean eurekaClientConfigBean(ConfigurableEnvironment env) {
EurekaClientConfigBean client = new EurekaClientConfigBean();
if ("bootstrap".equals(this.env.getProperty("spring.config.name"))) {
// We don't register during bootstrap by default, but there will be another
// chance later.
client.setRegisterWithEureka(false);
}
return client;
}
然后就是这个@AutoConfigureAfter注解的EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration,代表EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration要比EurekaClientAutoConfiguration先装配,EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration里主要就是注入了EurekaDiscoveryClient,它是SpringCloud对原生Netflix的EurekaClient的封装
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public EurekaDiscoveryClient discoveryClient(EurekaClient client,
EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) {
return new EurekaDiscoveryClient(client, clientConfig);
}
Eureka Client服务启动和定时拉取服务注册表源码
上面Eureka Client自动装配那里,有对原生Netflix的EurekaClient的封装,我们看下初始化DiscoveryClient的源码,这个构造函数里代码量很多,做了很多事情
@Inject
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args,
Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider, EndpointRandomizer endpointRandomizer) {
//初始化各种定时任务
initScheduledTasks();
}
初始化定时拉取服务注册表的定时任务
TimedSupervisorTask
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
//registryFetchIntervalSeconds = 30;
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
默认每30s拉取一次服务注册表,这个拉取里面还有细节,分全量拉取和增量拉取。如果是首次拉取那就是全量拉取服务注册表然后注册到本地;非首次拉取则走增量拉取逻辑,然后计算合并后的服务实例的hashCode和EurekaServer端的注册表实例集合的hashCode是否相等,如果不等那么就清空本地服务实例走一遍全量拉取逻辑。
Eureka Client 服务续约的源码
接着上面的initScheduledTasks(),还会初始化并开启一个心跳续约的定时任务
// Heartbeat timer
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
//默认30s
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
),//延迟30s
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
看下HeartbeatThread这个线程的run()方法干了啥,其实就是发送一个Rest请求注册自己
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
//续约
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();
boolean success = register();
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
}
Eureka Client服务注册的源码
服务注册的源码入口也是在服务启动的initScheduledTasks()方法里的
//服务注册
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
//scheduler里传入的Runnable是自己,InstanceInfoReplicator本身实现了Runnable接口
public void start(int initialDelayMs) {
if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
instanceInfo.setIsDirty(); // for initial register
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, initialDelayMs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
//InstanceInfoReplicator的run方法
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
//服务注册
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
Eureka Server端接收服务注册源码
com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationResource#addInstance
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
logger.debug("Registering instance {} (replication={})", info.getId(), isReplication);
// validate that the instanceinfo contains all the necessary required fields
//参数校验,去掉不重要代码
。。。
//重点在这里
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
try {
// 上只读锁
read.lock();
// 先从本地MAP里面获取当前实例的信息。
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());
// 增加注册次数到监控信息里面去
REGISTER.increment(isReplication);
// 如果第一次进来,那么gMap为空,则创建一个ConcurrentHashMap放入到registry里面去
if (gMap == null) {
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();
// putIfAbsent方法主要是在向ConcurrentHashMap中添加键—值对的时候,它会先判断该键值对是否已经存在。
// 如果不存在(新的entry),那么会向map中添加该键值对,并返回null。
// 如果已经存在,那么不会覆盖已有的值,直接返回已经存在的值。
gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
if (gMap == null) {
// 表明map中确实不存在,则设置gMap为最新创建的那个
gMap = gNewMap;
}
}
// 从MAP中查询已经存在的Lease信息 (比如第二次来)
Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());
// 当Lease的对象不为空时。
if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {
Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();
Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();
// 当instance已经存在是,和客户端的instance的信息做比较,时间最新的那个,为有效instance信息
if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {
registrant = existingLease.getHolder();
}
} else {
// 这里只有当existinglease不存在时,才会进来。 像那种恢复心跳,信息过期的,都不会进入这里。
// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin > 0) {
// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the threshold
// (1
// for 30 seconds, 2 for a minute)
// Eureka‐Server的自我保护机制做的操作,为每分钟最大续约数+2 ,同时重新计算每分钟最小续约数
this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin + 2;
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =
(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
}
}
}
// 构建一个最新的Lease信息
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);
if (existingLease != null) {
// 当原来存在Lease的信息时,设置他的serviceUpTimestamp, 保证服务开启的时间一直是第一次的那个
lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());
}
// 放入本地Map中
gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);
// 添加到最近的注册队列里面去,以时间戳作为Key, 名称作为value,主要是为了运维界面的统计数据。
synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) {
recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(
System.currentTimeMillis(),
registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));
}
// 分析instanceStatus
if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {
if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {
overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());
}
}
InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());
if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {
registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);
}
// Set the status based on the overridden status rules
InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);
registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);
// If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp
// 得到instanceStatus,判断是否是UP状态
if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {
lease.serviceUp();
}
// 设置注册类型为添加
registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);
// 租约变更记录队列,记录了实例的每次变化, 用于注册信息的增量获取、
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));
registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
// 清理缓存 ,传入的参数为key
invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
Eureka常见问题FAQ
更新服务最近一次续约时间的Bug
源码在com.netflix.eureka.resources.InstanceResource#renewLease核心源码如下
public void renew() {
lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;
}
本来更新服务续约时间就是更新为当前时间就可以了,不知道为啥要加一个duration,然后duration是90s,也就是Eureka Client每30s发送一次心跳,然后这个最近更新时间被修改成当前时间戳+90s了。
然后再来看看服务剔除的逻辑,按说服务剔除是超过90s没有心跳的服务实例就会踢下线的,我们看下判断服务实例是否过期的方法
com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease#isExpired(long)
/**
* Checks if the lease of a given {@link com.netflix.appinfo.InstanceInfo} has expired or not.
*
* Note that due to renew() doing the 'wrong" thing and setting lastUpdateTimestamp to +duration more than
* what it should be, the expiry will actually be 2 * duration. This is a minor bug and should only affect
* instances that ungracefully shutdown. Due to possible wide ranging impact to existing usage, this will
* not be fixed.
*
* 翻译:检查给定{@link的租约com.netflix.appinfo网站.InstanceInfo}是否已过期。
*
* 请注意,由于renew()执行了“错误”操作,并将lastUpdateTimestamp设置为+duration,超过了应该设置的值,因此有效期实际上是2*duration。
* 这是一个小错误,应该只影响不正常关闭的实例。由于可能对现有的使用造成广泛的影响,这将不会被修复。
*
* @param additionalLeaseMs any additional lease time to add to the lease evaluation in ms.
*/
public boolean isExpired(long additionalLeaseMs) {
return (evictionTimestamp > 0 || System.currentTimeMillis() > (lastUpdateTimestamp + duration + additionalLeaseMs));
}
这个bug的影响范围是,本来服务90s内没有发送心跳给Eureka Server,Eureka Server就会认为服务宕机了,但是因为这个bug最少需要90+90=180s Eureka Server才会认为这个服务宕机,才会剔除这个服务。
说说Eureka获取服务注册表的多级缓存机制
多级缓存实际是三级,从上往下依次是只读缓存readOnlyCacheMap,读写缓存readWriteCacheMap,和服务注册表registry
1、readOnlyCacheMap只读缓存
数据结构:是一个ConcurrentHashMap
被动过期:每30s更新一次,从readWriteCacheMap和readOnlyCacheMap中获取相同的key值比较。如果不相同就将readWriteCacheMap的值写入readOnlyCacheMap中。
2、readWriteCacheMap读写缓存
数据结构:LoadingCache<Key, Value> readWriteCacheMap;
主动过期:注册、服务下线、服务故障剔除都会失效缓存
定时过期:expireAfterWrite过期时间是180s,也就是说key180s过期之后会重新写入这个key
3、register注册表
数据结构:ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease>> registry
是一个双层Map,所有服务的注册,下线、故障剔除都会去修改registry
服务故障多久能被感知到?
场景描述:如果一个服务A故障了,Eureka Server需要多久可以感知到服务A故障了,然后将这个服务给他下线呢?我们分析一下
1、首先在Eureka Server中,是每60s去执行一次evict task(服务剔除任务),去判断一下当前所有的服务实例,是否有的服务实例出现了故障,超过90s没有发送心跳过来,是否要将故障的服务实例给他下线。
2、然后由于Eureka本身有一个Bug,服务过期的时间是90s+90s也就是180s内没有收到这个服务的心跳才会认为这个服务是过期的。
3、发现故障了以后,从服务注册表中摘除,会过期掉readWriteCacheMap缓存。readOnlyCacheMap每30s会同步一次readWriteCacheMap缓存。
4、服务B每30s执行一次增量拉取注册列表的定时任务。
很可能在极端情况下,服务A是要过了将近5分钟才能感知到服务B的某台机器故障宕机了。即使不在极端情况下,其他服务要感知到某个服务实例的故障,起码也要三分钟。