文章目录
- 效果图
- 引言
- 玩法
- 拖拽概念
- 基本概念
- 如何在Qt中使用拖放
- 注意事项
- 游戏关键问题
- 总结
效果图


引言
- 在学习QT demo时,发现有一个拼图demo,介绍拖拽事件的。以此为蓝本加了亿点修饰,就诞生了这个游戏。
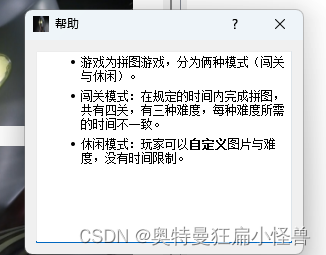
玩法
- 游戏为拼图游戏,分为俩种模式(闯关与休闲)。
- 闯关模式:在规定的时间内完成拼图,共有四关,有三种难度,每种难度所需的时间不一致。
- 休闲模式:玩家可以自定义图片与难度,没有时间限制。
拖拽概念
基本概念
- 在Qt中,拖放(Drag and Drop)是一种非常直观的方式来处理对象的移动或复制。拖放可以在单个应用程序内进行,也可以在不同应用程序之间进行。Qt为此提供了一组丰富的API来支持拖放操作。
- 拖动 (Drag)
- 开始一个拖动操作,通常是当用户在一个可拖动的组件上按下鼠标按钮,并移动一定距离时。在Qt中,你需要创建一个
QDrag对象,并指定要拖动的数据。
- 放下 (Drop)
- 放下操作发生在拖动过程的最后,当用户释放鼠标按钮时。如果释放位置是一个可以接受放下的组件(一个设置为接受放下的
QWidget或者QGraphicsItem),那么会发生放下操作。
- MIME 数据
- 拖动和放下的数据是通过MIME(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)类型封装的。在Qt中通常使用
QMimeData对象来处理拖放的数据。
如何在Qt中使用拖放
- 启用组件的拖放
- 首先,确保你的QWidget派生类允许拖放。使用
setDragEnabled(true)可以使得组件可以被拖动,使用setAcceptDrops(true)使得组件可以接收放下。
- 处理拖动事件
- 在源组件中,你需要重写
mousePressEvent和mouseMoveEvent。这些本是处理鼠标事件的函数在此也被用来发起拖动。在鼠标移动事件中,你可以使用QDrag来开始拖动操作,并将QMimeData附加到QDrag对象。
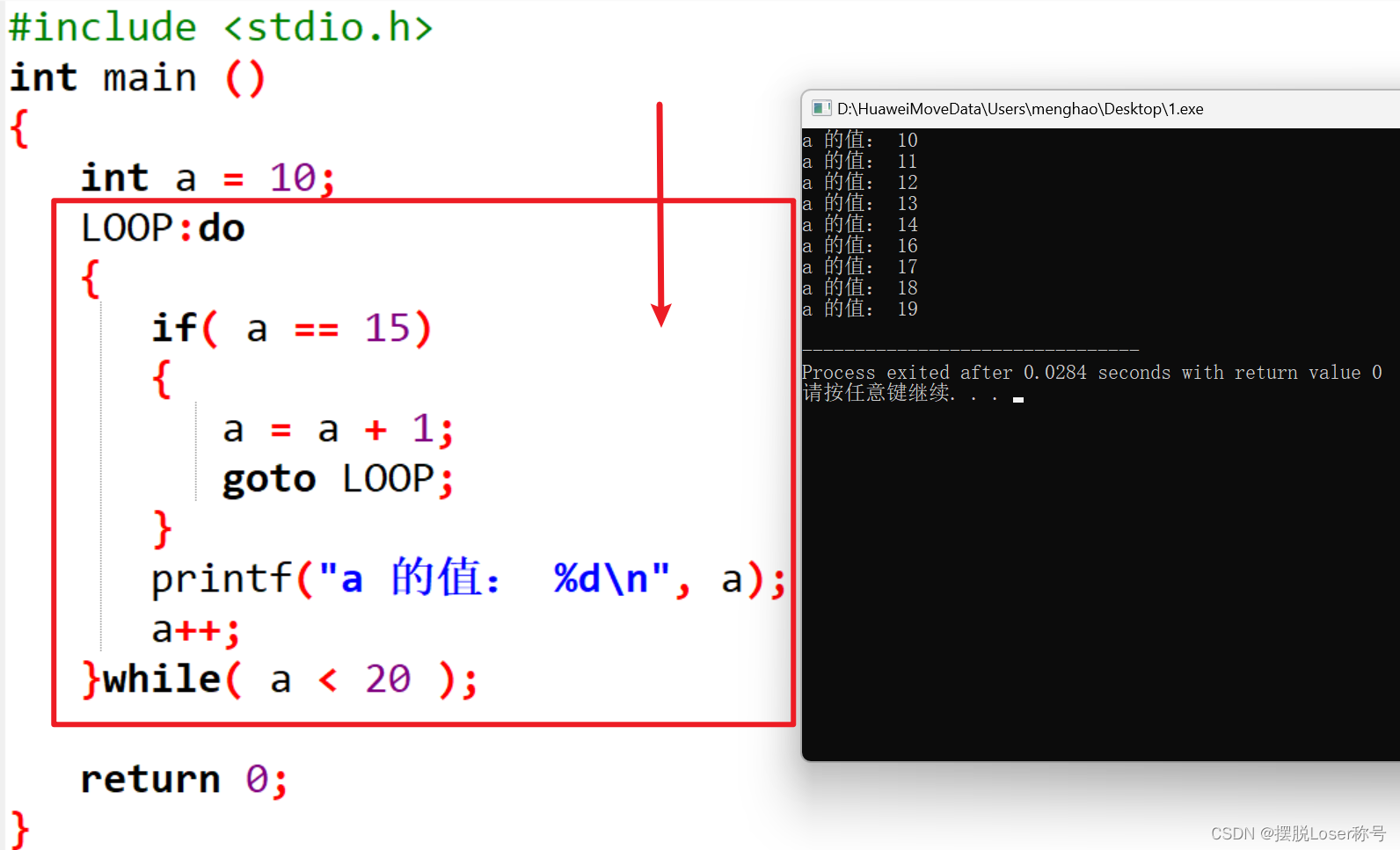
void SourceWidget::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event) {
if (!(event->buttons() & Qt::LeftButton)) {
return;
}
QDrag *drag = new QDrag(this);
QMimeData *mimeData = new QMimeData;
// 设置数据 mimeData->setData(...) 或 mimeData->setText(...)
drag->setMimeData(mimeData);
// 开始拖动操作
Qt::DropAction dropAction = drag->exec(Qt::CopyAction | Qt::MoveAction);
}
- 处理放下事件
- 在目标组件中,你需要重写几个事件处理函数以处理放下事件:
dragEnterEvent、dragMoveEvent(可选)和dropEvent。通过这些事件,你可以确定是否接受拖动进来的数据,以及如何处理这些数据。
void TargetWidget::dragEnterEvent(QDragEnterEvent *event) {
if (event->mimeData()->hasFormat("custom/format")) {
event->acceptProposedAction();
}
}
void TargetWidget::dropEvent(QDropEvent *event) {
const QMimeData *mimeData = event->mimeData();
// 处理放下的数据 mimeData->data(...) 或 mimeData->text()
event->acceptProposedAction();
}
注意事项
- 你也许会需要处理
dragLeaveEvent,用来处理拖动物体离开组件时的事件。 - 拖放事件与标准的鼠标事件是相互独立的,在处理拖放事件时不会影响鼠标事件的处理。
- 拖放操作可以包括图片、文本、HTML等多种数据类型,基本上任何种类的数据都可以通过MIME数据进行传输。
- 要实现跨不同应用程序的拖放,需要确保所有参与的应用程序都能理解相关的MIME类型。
游戏关键问题
- 游戏的总体结构是怎么样的
- 界面主要由俩块组成,左边为一个
QListView设置了继承于QAbstractListModel的代理模型,右边为一个QWidget。 - 游戏维护了一个全局的结构体指针中,该结构体用于保存游戏的信息,如模式,难度,当前关卡等信息。
- 游戏实现的主要难点就是拖拽的实现
- 如何将一张图片分割为指定的x*x的图片
// 计算新的图像大小,取原始图片宽高的最小值作为新的尺寸size
int size = qMin(pixmap.width(), pixmap.height());
// 从原始图片中剪切出一个大小为 sizexsize 的部分作为新的puzzleImage,
// 重新调整新的puzzleImage大小为puzzleWidget的imageSize,使用Qt::SmoothTransformation平滑缩放
pixmap = pixmap.copy((pixmap.width() - size) / 2, (pixmap.height() - size) / 2, size, size)
.scaled(puzzleWidget->imageSize(), puzzleWidget->imageSize(), Qt::IgnoreAspectRatio, Qt::SmoothTransformation);
// 制作每一片拼图片段。m_PieceSize图片大小,m行列数
for (int y = 0; y < m; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < m; ++x)
{
QPixmap pieceImage = pixmap.copy(x * m_PieceSize, y * m_PieceSize, m_PieceSize, m_PieceSize);
addPiece(pieceImage, QPoint(x, y));
}
}
- 如何判断拼图是否完成
- 在切割图片的时候,我们已经将将图片正确位置存放到图片中,只需要全局维护一个计数器,当计数器等于拼图数量时,即是完成。
// 图片资源结构体
struct Piece
{
QPixmap pixmap;
QRect rect;
QPoint location;
Piece() {}
Piece(QPixmap Vpixmap, QPoint Vlocation, QRect Vrect) : pixmap(Vpixmap), location(Vlocation), rect(Vrect) {}
Piece(const Piece &other)
{
pixmap = other.pixmap;
rect = other.rect;
location = other.location;
}
};
- 计数器的增加规则是:若是当前图片所有在矩形与存放的位置相同,计数器+1
void PuzzleWidget::addInPlace(Piece piece)
{
if (piece.location == piece.rect.topLeft() / pieceSize())
{
inPlace++;
if (inPlace == MacroDf::getCloum() * MacroDf::getCloum())
emit puzzleCompleted();
}
}
- 图片是如何出现在widget上的
- 通过绘制实现,
pieces存放的是保存的图片结构体列表,highlightedRect为高亮区域。
void PuzzleWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event)
{
QPainter painter(this);
painter.fillRect(event->rect(), Qt::white);
if (highlightedRect.isValid())
{
painter.setBrush(QColor("#98FB98"));
painter.setPen(Qt::NoPen);
painter.drawRect(highlightedRect.adjusted(0, 0, -1, -1));
}
for (const Piece &piece : pieces)
{
painter.drawPixmap(piece.rect, piece.pixmap);
}
}
- widget窗口上图片是如何拖动的
- 在鼠标点击事件中,先判断当前点击的位置是否存在图片,若是有就去存好的图片链表中获取该图片的资源,创建拖动操作的数据对象
void PuzzleWidget::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
// 获取鼠标点击位置的方块
QRect square = targetSquareMove(event->pos());
// 查找方块是否有图片
int found = findPiece(square);
if (found == -1)
return;
// 移除找到的拼图块
Piece piece = pieces.takeAt(found);
// 如果拼图块的位置与方块的顶点位置一致,表示该拼图块为正确位置,移除时更新完成计数位
if (piece.location == square.topLeft() / pieceSize())
inPlace--;
update(square);
// 将拼图块的图像和位置信息存入数据流
QByteArray itemData;
QDataStream dataStream(&itemData, QIODevice::WriteOnly);
dataStream << piece.pixmap << piece.location << piece.rect;
// 创建拖动操作的数据对象
QMimeData *mimeData = new QMimeData;
mimeData->setData("DJ-NB", itemData);
// 创建拖动操作
QDrag *drag = new QDrag(this);
drag->setMimeData(mimeData);
drag->setHotSpot(event->pos() - square.topLeft());
drag->setPixmap(piece.pixmap);
// 判断拖动操作的结果是否为Qt::IgnoreAction,表示拖拽失败,将拼图块放回原位置
if (drag->exec(Qt::MoveAction) == Qt::IgnoreAction) // 拖放到其他应用程序。我们使用Qt::IgnoreAction来限制它。
{
pieces.insert(found, piece);
update(targetSquareMove(event->pos()));
if (piece.location == QPoint(square.x() / pieceSize(), square.y() / pieceSize()))
inPlace++;
}
}
- 图片是如何拖入widget以及交换图片的
- 在
dropEvent事件中,先检查数据格式是否正确,再判断当前要放入的位置是否存在图片,不存在图片直接加入到列表中就行,若是存在,则需要交换俩个图片的信息,同时要判断计数位。
void PuzzleWidget::dropEvent(QDropEvent *event)
{
// 检查事件是否含有我们需要的数据格式
if (event->mimeData()->hasFormat("DJ-NB"))
{
// 接受事件默认的复制动作
event->setDropAction(Qt::MoveAction);
event->accept();
auto square = targetSquareMove(event->pos()); // 目标位置
int existingPieceIndex = findPiece(square); // 寻找目标位置是否有拼图块
// 从拖放事件的数据中读取拼图块的信息
QByteArray pieceData = event->mimeData()->data("DJ-NB");
QDataStream dataStream(&pieceData, QIODevice::ReadOnly);
// 将拼图块添加到列表中或与现有拼图块交换
if (existingPieceIndex == -1)
{
// 目标位置没有拼图块,直接放置新拼图块
Piece piece;
piece.rect = targetSquareMove(event->pos());
dataStream >> piece.pixmap >> piece.location;
// 将拼图块添加到列表中
pieces.append(piece);
// 清除高亮的区域并更新拼图块的区域
highlightedRect = QRect();
update(piece.rect);
// 如果拼图块放置在正确的位置
addInPlace(piece);
}
else
{
// 目标位置已有拼图块,和拖入的拼图块互换位置
// 起始位置资源
Piece piece;
dataStream >> piece.pixmap >> piece.location >> piece.rect;
// 目标位置资源
Piece rPic = pieces[existingPieceIndex];
// 删除掉原有的,以便重新写入新值
if (rPic.location == rPic.rect.topLeft() / pieceSize())
inPlace--;
pieces.takeAt(existingPieceIndex);
// 数据交互
Piece tempPiece = piece;
piece.location = rPic.location;
piece.pixmap = rPic.pixmap;
rPic.location = tempPiece.location;
rPic.pixmap = tempPiece.pixmap;
// 存放俩组数据
pieces.append(piece);
pieces.append(rPic);
// 重绘涉及的区域
highlightedRect = QRect();
update(piece.rect);
update(rPic.rect);
// 如果拼图块放置在正确的位piece
addInPlace(rPic);
addInPlace(piece);
}
}
else
{
highlightedRect = QRect();
// 不是我们支持的数据格式,保留默认行为
event->ignore();
}
}
- list以拖入widget中的图片如何删除,更新链表视图的
- 在继承与
QAbstractListModel的代理中的removeRows函数实现
bool PiecesModel::removeRows(int row, int count, const QModelIndex &parent)
{
if (parent.isValid())
return false;
if (row >= piece.size() || row + count <= 0)
return false;
// 修剪beginRow和endRow,限制在有效范围内。
int beginRow = qMax(0, row);
int endRow = qMin(row + count - 1, piece.size() - 1);
// 调用beginRemoveRows()告知视图将移除行,开始行beginRow和结束行endRow。
beginRemoveRows(parent, beginRow, endRow);
// 循环移除
while (beginRow <= endRow)
{
piece.removeAt(beginRow);
++beginRow;
}
// 调用endRemoveRows()告知视图完成移除行。
endRemoveRows();
return true;
}
- 如何将
widget拖回list中
- 上述中我们在
widget的点击事件中直接创建了拖拽数据,那么我们只需要在list的dropMimeData实现存放的逻辑就行
bool PiecesModel::dropMimeData(const QMimeData *data, Qt::DropAction action, int row, int column, const QModelIndex &parent)
{
// 检查mime数据是否包含正确的格式:"DJ-NB"
if (!data->hasFormat("DJ-NB"))
return false;
// 检查拖放操作:
if (action == Qt::IgnoreAction)
return true;
// 只允许插入第一列:
if (column > 0)
return false;
// 判断插入行的尾部位置endRow:
int endRow;
// 如果是根节点:
if (!parent.isValid())
{
if (row < 0)
endRow = piece.size();
else
endRow = qMin(row, piece.size());
}
else // 如果是子节点:
{
endRow = parent.row();
}
// 解析mime数据,读取 pixmap 图片和位置 location:
QByteArray encodedData = data->data("DJ-NB");
QDataStream stream(&encodedData, QIODevice::ReadOnly);
// 通过 begin/endInsertRows函数更新模型,插入数据:
while (!stream.atEnd())
{
QPixmap pixmap;
QPoint location;
QRect rect;
// 从数据流中读数据
stream >> pixmap >> location >> rect;
Piece pie(pixmap, location, rect);
// 若是以存在则返回不加入
for (auto point : piece)
{
if (point.location == location)
{
return false;
}
}
beginInsertRows(QModelIndex(), endRow, endRow);
piece.insert(endRow, pie);
endInsertRows();
++endRow;
}
return true;
}
widget中如何判断当前位置,以及图片中的矩形数据怎么存放
- 通过鼠标的点击获取的点,得到以图片为大小的当前位置左上角坐标,矩形大小也是每张图片的大小
const QRect PuzzleWidget::targetSquareMove(const QPoint &position) const
{
// point除以一个数是往前进位,这会导致坐标出现问题,所以要用Int处理
int x = position.x() / pieceSize();
int y = position.y() / pieceSize();
auto pointNew = QPoint(x, y);
auto point = pointNew * pieceSize();
auto resultRect = QRect(point.x(), point.y(), pieceSize(), pieceSize());
return resultRect;
}
总结
- 这个游戏的用了周末俩天时间做完,后面用了一天修了点BUG,细节还是很多的,像计时器如何使用,富文本内容如何显示,弹窗的事件处理等,主要还是用于理解拖拽事件,当然你也可以直接去看QT 的demo,那个没我这么复杂,搜drag就行,不过它那个有几个明显的问题,我这都优化了。
- 知识理应共享,大家相互学习,源码在此哦。