目录
JAVA后端项目
一、创建项目
1、使用aliyun的server url
2、初始化项目结构
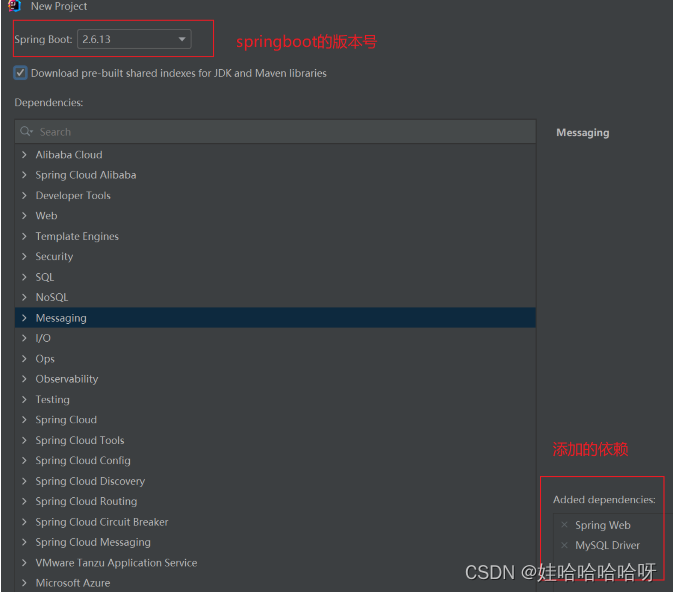
3、添加依赖
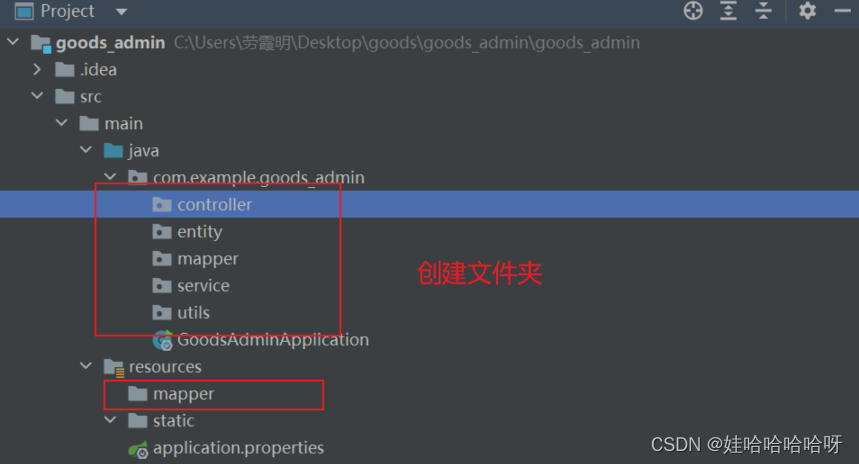
4、创建文件夹
5、把mapper类交给spring容器管理
5.1、方法1
5.2、方法2
6、在yaml文件中配置数据库信息
7、在yaml文件中配置mapper的xml文件的路径
8、配置mapper的xml文件
二、编写程序
1、登录功能
1.1、编写UserController
1.2、编写UserserviceImpl
1.3、编写接口Userservice
1.4、编写mapper
1.5、编写xml
1.6、前端发请求
JAVA后端项目
一、创建项目
1、使用aliyun的server url
https://start.aliyun.com
2、初始化项目结构

3、添加依赖
4、创建文件夹
5、把mapper类交给spring容器管理
5.1、方法1
在每一个mapper类上加上注解@Mapper
@Mapper
public class UserMapper {
}缺点:每个mapper文件都得添加
5.2、方法2
在主程序启动类上添加扫描所有mapper
@MapperScan("com.example.goods_admin.mapper")注意:路径可以是指定文件,或者文件夹。
6、在yaml文件中配置数据库信息
server:
port: 9090
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/goods_admin?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver7、在yaml文件中配置mapper的xml文件的路径
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml //classpath是resources文件夹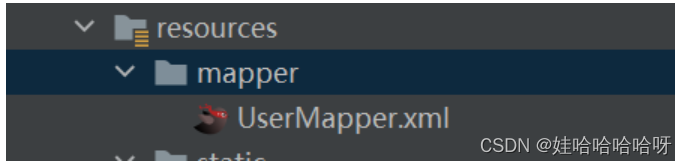
8、配置mapper的xml文件
<!--XML头部(固定的)-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.goods_admin.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 结果映射:数据库字段与实体类字段的映射关系-->
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.goods_admin.entity.User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="id" />
<result column="userId" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userId" />
<result column="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName" />
<result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" />
<result column="sex" jdbcType="TINYINT" property="sex" />
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" />
<result column="location" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="location" />
</resultMap>
</mapper>二、编写程序
user实体类
package com.example.goods_admin.entity;
public class User {
private String id;
private String userId;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String sex;
private int age;
private String location;
//无参构造函数
public User() {
}
//构造函数:用来实例化对象的
//有参构造函数
public User(String id, String userId, String userName, String password, String sex, int age, String location) {
this.id = id;
this.userId = userId;
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.location = location;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
}
1、登录功能
1.1、编写UserController
@RestController
//@RequestMapping用于将 HTTP 请求映射到控制器方法上
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
Userservice userservice;
/*
**登录
*/
@PostMapping("/login")
public Result login(@RequestBody User user){
return userservice.login(user);
}
}1.2、编写UserserviceImpl
@Service
public class UserserviceImpl implements Userservice {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public Result login(User user) {
/**
* 1、先根据账号查询,是否账号存在
* 2、不存在,显示该账户未注册,先注册再登录
* 3、存在,查询该账户的密码是不是数据库中的密码
* 4、如果传入的密码和数据库的密码不一样,说明密码错误,请重新输入密码
* 5、如果传入的密码和数据库的密码一样,说明账号密码都正确,显示登录成功,跳转到首页
*/
//1、根据账号查询,是否账号存在
User user2 = userMapper.seleteUserByUserId(user.getUserId());
//2、不存在,显示该账户未注册,先注册再登录
if (user2 == null) {
return Result.failed("用户不存在,请注册");
} else {
//3、存在,查询该账户的密码是不是数据库中的密码
User user3 = userMapper.seleteUserByPassword(user);
if (user3 != null && user3.getPassword().equals(user.getPassword())) {
return Result.succeed("登录成功");
} else {
return Result.failed("密码错误");
}
}
}
}1.3、编写接口Userservice
public interface Userservice {
Result login(User user);
}1.4、编写mapper
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
User seleteUserByUserId(String userId);
void login(User user);
}1.5、编写xml
<select id="seleteUserByUserId" resultType="com.example.goods_admin.entity.User">
select * from user where userId=#{userId}
</select>
<select id="login">
select * from user where userId=#{userId}
</select>1.6、前端发请求
login() {
if (this.userId === '') {
this.$message.error("请输入账号");
return;
} else if (this.password === '') {
this.$message.error("请输入密码");
return;
}
// 判断是否勾选协议
if (this.agreementChecked) {
// 发送登录请求
this.$axios({
method: "post",
url: "http://localhost:8080/api/user/login",
data: {
userId: this.userId,
password: this.password,
},
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
if (res.data.code == "200") {
// 登录成功,显示成功提示信息
this.$message({
message: res.data.message,
type: "success",
});
//1、储存token(令牌) 保存到浏览器
window.sessionStorage.setItem("token", res.data.token);
//2、储存user
window.sessionStorage.setItem(
"user",
JSON.stringify(res.data.user)
);
//3、跳转到后台主页 (编程式导航)
this.$router.push("./home"); //
} else if (res.data.code == "500") {
this.$message({
message: res.data.message,
type: "error",
});
}
})
.catch(() => {
// 登录失败,显示提示信息
this.$message({
message: "该登录失败",
type: "error",
});
});
} else {
// 未勾选协议,不执行登录逻辑
this.$message({
message: "请同意用户协议和隐私政策!",
type: "error",
});
}
},注意:先解决跨域问题(vue.config.js文件)
module.exports = {
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/api': {//表示拦截以/api开头的请求路径
target: 'http://localhost:9090',
changOrigin: true,//是否开启跨域
pathRewrite: {
'^/api': '' //重写api,把api变成空字符,因为我们真正请求的路径是没有api的
}
}
}
}
};