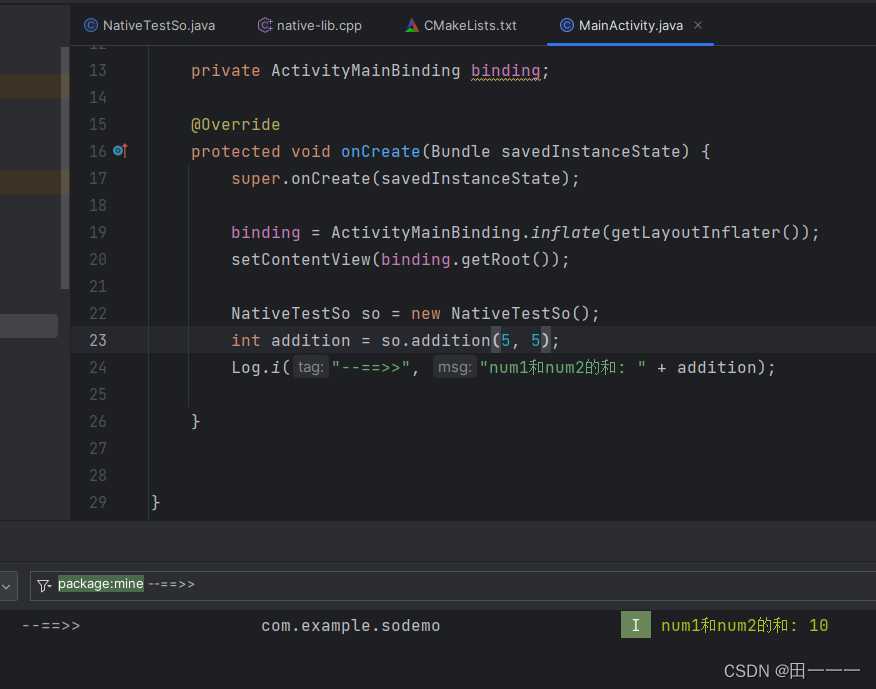
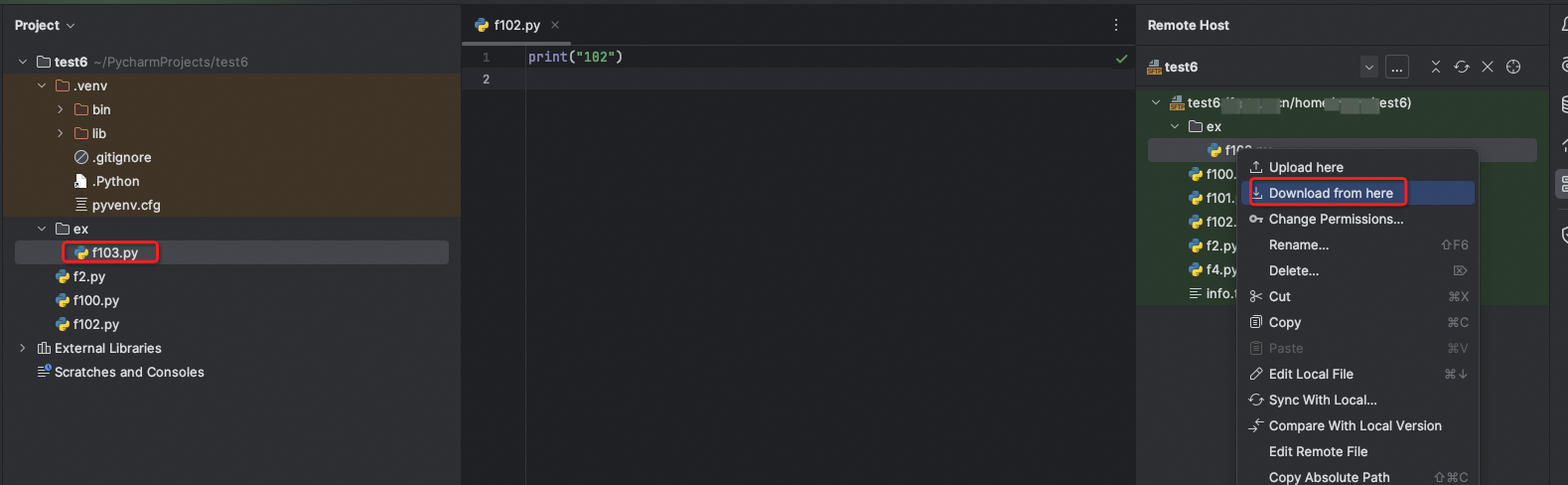
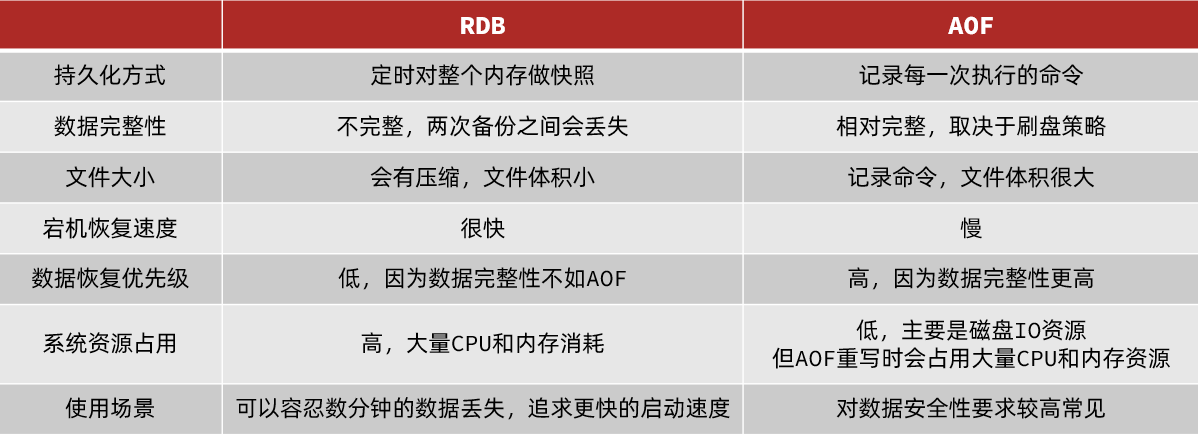
题目链接
本题是2003年ICPC亚洲区域赛会津(日本)赛区的H题
题意
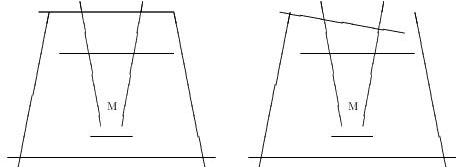
给出一些线段障碍,你的任务是判断怪物能否逃到无穷远处。如下图所示,左图无法逃出,右图的可以逃出。
输入包含多组数据。每组数据第一行为整数n(1≤n≤100),即线段条数。以下n 行每行4 个整数,即一条线段两端的坐标。假定线段的长度均为正,坐标绝对值不超过50。假设任意两条线段最多只有一个公共点,无三线共点。任意两个交点的距离大于1e-5。输入结束标志为n=0。
分析
《训练指南》上的例题,按照其题解做,发现一个套模板的坑点:本题卡阈值!
这里给出《训练指南》代码仓库上的源码(第10行)来说明坑点:
const double eps = 1e-12;如过把eps改为大于1e-12或者小于1e-14的值(比如1e-11、1e-15)再提交则WA,而eps写成1e-12、1e-13、1e-14则AC。
根本原因在《训练指南》给出的计算几何模板里面的dcmp、SegmentProperIntersection、OnSegment三个函数这里。
int dcmp(double x) {
return abs(x) < eps ? 0 : (x < 0. ? -1 : 1);
}
bool SegmentProperIntersection(const Point& a1, const Point& a2, const Point& b1, const Point& b2) {
double c1 = Cross(a2 - a1, b1 - a1), c2 = Cross(a2 - a1, b2 - a1);
double c3 = Cross(b2 - b1, a1 - b1), c4 = Cross(b2 - b1, a2 - b1);
return dcmp(c1) * dcmp(c2) < 0 && dcmp(c3) * dcmp(c4) < 0;
}
bool OnSegment(const Point& p, const Point& a1, const Point& a2) { // 不含端点
return dcmp(Cross(a1 - p, a2 - p)) == 0 && dcmp(Dot(a1 - p, a2 - p)) < 0;
}OnSegment函数对dcmp的阈值eps要求低一些(不可太大也不可太小,中间范围即可),但本题的做法涉及把每条线段两端延长一点点(按题意延长量为1e-6合适,因为题木交代两个交点的距离在1e-5量级以上),这样就导致SegmentProperIntersection里面叉乘的结果可能很小,极端数据会小于eps。
说一下解决方案:SegmentProperIntersection里面对叉乘直接判断符号,不用阈值。
int sign(double x) {
return x==0. ? 0 : (x < 0. ? -1 : 1);
}
bool SegmentProperIntersect(const Point& a1, const Point& a2, const Point& b1, const Point& b2) {
double c1 = Cross(a2 - a1, b1 - a1), c2 = Cross(a2 - a1, b2 - a1);
double c3 = Cross(b2 - b1, a1 - b1), c4 = Cross(b2 - b1, a2 - b1);
// return dcmp(c1) * dcmp(c2) < 0 && dcmp(c3) * dcmp(c4) < 0;
// 部分卡精度的题目需要直接判断正负号
return sign(c1) * sign(c2) < 0 && sign(c3) * sign(c4) < 0;
}附一份测试数据和用python写的画图可视化分析数据的脚本方便读者debug。
AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define eps 1e-10
struct Point {
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0): x(x), y(y) {}
void Normalize() {
double l = sqrt(x*x + y*y); x /= l; y /= l;
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator+ (const Vector& A, const Vector& B) {
return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y);
}
Vector operator- (const Vector& A, const Vector& B) {
return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y);
}
Vector operator* (const Vector& A, double p) {
return Vector(A.x * p, A.y * p);
}
bool operator< (const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x < b.x || (a.x == b.x && a.y < b.y);
}
double Cross(const Vector& A, const Vector& B) {
return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x;
}
double Dot(const Vector& A, const Vector& B) {
return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y;
}
int dcmp(double x) {
return abs(x) < eps ? 0 : (x < 0. ? -1 : 1);
}
int sign(double x) {
return x==0. ? 0 : (x < 0. ? -1 : 1);
}
bool SegmentProperIntersect(const Point& a1, const Point& a2, const Point& b1, const Point& b2) {
double c1 = Cross(a2 - a1, b1 - a1), c2 = Cross(a2 - a1, b2 - a1);
double c3 = Cross(b2 - b1, a1 - b1), c4 = Cross(b2 - b1, a2 - b1);
return sign(c1) * sign(c2) < 0 && sign(c3) * sign(c4) < 0;
}
bool OnSegment(const Point& p, const Point& a1, const Point& a2) {
return dcmp(Cross(a1 - p, a2 - p)) == 0 && dcmp(Dot(a1 - p, a2 - p)) < 0;
}
#define N 205
Point p[N]; int x[N], q[N], n, t; bool vis[N];
bool NotOnAnySegment(const Point& x) {
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) if (OnSegment(x, p[i], p[i+n])) return false;
return true;
}
bool NotIntersectWithAnySegment(int u, int v) {
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) if (SegmentProperIntersect(p[i], p[i+n], p[u], p[v])) return false;
return true;
}
bool solve() {
memset(vis, t = 0, sizeof(vis));
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y >> p[i+n].x >> p[i+n].y;
Vector v = p[i+n] - p[i]; v.Normalize(); v = v*1e-6;
p[i].x -= v.x; p[i].y -= v.y; p[i+n].x += v.x; p[i+n].y += v.y;
}
p[n<<1].x = p[n<<1].y = 0.; p[(n<<1)+1].x = -60.; p[(n<<1)+1].y = 60.; x[t++] = n<<1; x[t++] = (n<<1)+1;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
if (NotOnAnySegment(p[i])) x[t++] = i;
if (NotOnAnySegment(p[i+n])) x[t++] = i+n;
}
int head = 0, tail = 1; q[0] = 0;
while (head < tail) {
int u = q[head++];
for (int v=1; v<t; ++v) if (!vis[v] && NotIntersectWithAnySegment(x[u], x[v])) {
if (v == 1) return false;
vis[q[tail++] = v] = 1;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
while (cin >> n && n) cout << (solve() ? "yes" : "no") << endl;
return 0;
}