这篇文章的题目稍微难一点
题目建议: 本题关键还是在转圈的逻辑,在二分搜索中提到的区间定义,在这里又用上了。
一、59. 螺旋矩阵 II
题目:
给你一个正整数 n ,生成一个包含 1 到 n2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的 n x n 正方形矩阵 matrix 。
示例 1:

输入:n = 3 输出:[[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 20
思路
这道题目可以说在面试中出现频率较高的题目,本题并不涉及到什么算法,就是模拟过程,但却十分考察对代码的掌控能力。
要如何画出这个螺旋排列的正方形矩阵呢?
相信很多同学刚开始做这种题目的时候,上来就是一波判断猛如虎。
结果运行的时候各种问题,然后开始各种修修补补,最后发现改了这里那里有问题,改了那里这里又跑不起来了。
大家还记得我们在这篇文章数组:每次遇到二分法,都是一看就会,一写就废
(opens new window)中讲解了二分法,提到如果要写出正确的二分法一定要坚持循环不变量原则。
而求解本题依然是要坚持循环不变量原则。
模拟顺时针画矩阵的过程:
- 填充上行从左到右
- 填充右列从上到下
- 填充下行从右到左
- 填充左列从下到上
由外向内一圈一圈这么画下去。
可以发现这里的边界条件非常多,在一个循环中,如此多的边界条件,如果不按照固定规则来遍历,那就是一进循环深似海,从此offer是路人。
这里一圈下来,我们要画每四条边,这四条边怎么画,每画一条边都要坚持一致的左闭右开,或者左开右闭的原则,这样这一圈才能按照统一的规则画下来。
那么我按照左闭右开的原则,来画一圈,大家看一下:
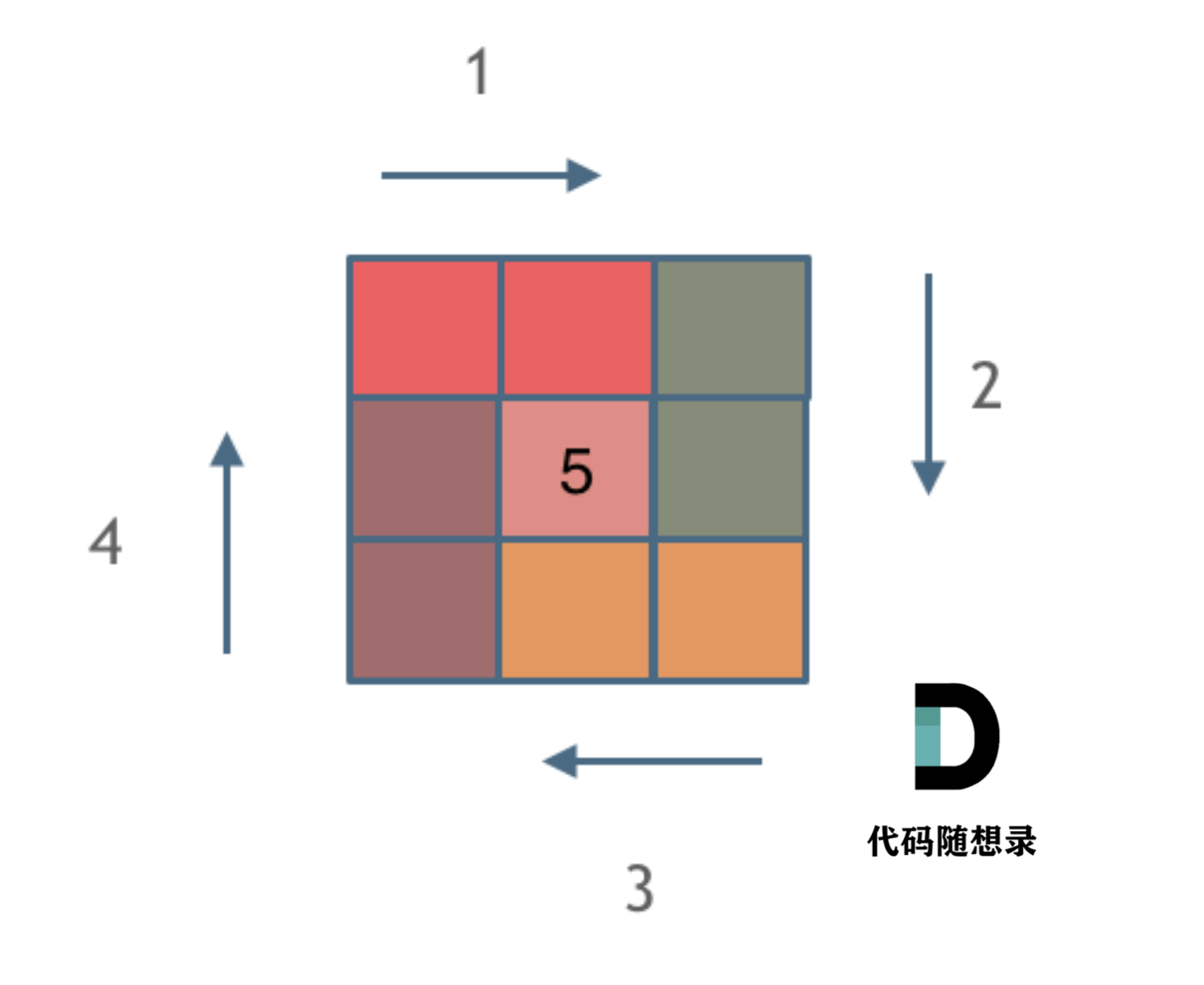
这里每一种颜色,代表一条边,我们遍历的长度,可以看出每一个拐角处的处理规则,拐角处让给新的一条边来继续画。
这也是坚持了每条边左闭右开的原则。
一些同学做这道题目之所以一直写不好,代码越写越乱。
就是因为在画每一条边的时候,一会左开右闭,一会左闭右闭,一会又来左闭右开,岂能不乱。
代码如下,已经详细注释了每一步的目的,可以看出while循环里判断的情况是很多的,代码里处理的原则也是统一的左闭右开。
整体C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> res(n, vector<int>(n, 0)); // 使用vector定义一个二维数组
int startx = 0, starty = 0; // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
int loop = n / 2; // 每个圈循环几次,例如n为奇数3,那么loop = 1 只是循环一圈,矩阵中间的值需要单独处理
int mid = n / 2; // 矩阵中间的位置,例如:n为3, 中间的位置就是(1,1),n为5,中间位置为(2, 2)
int count = 1; // 用来给矩阵中每一个空格赋值
int offset = 1; // 需要控制每一条边遍历的长度,每次循环右边界收缩一位
int i,j;
while (loop --) {
i = startx;
j = starty;
// 下面开始的四个for就是模拟转了一圈
// 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
for (j = starty; j < n - offset; j++) {
res[startx][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
for (i = startx; i < n - offset; i++) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
for (; j > starty; j--) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充左列从下到上(左闭右开)
for (; i > startx; i--) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 第二圈开始的时候,起始位置要各自加1, 例如:第一圈起始位置是(0, 0),第二圈起始位置是(1, 1)
startx++;
starty++;
// offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
offset += 1;
}
// 如果n为奇数的话,需要单独给矩阵最中间的位置赋值
if (n % 2) {
res[mid][mid] = count;
}
return res;
}
};
- 时间复杂度 O(n^2): 模拟遍历二维矩阵的时间
- 空间复杂度 O(1)
-
类似题目
- 54.螺旋矩阵
- (opens new window)
- 剑指Offer 29.顺时针打印矩阵
- (opens new window)
二、54. 螺旋矩阵
题目:
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
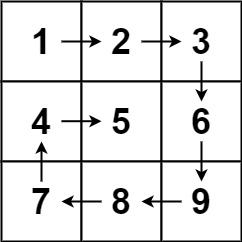
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
示例 2:

输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] 输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
题解:
两种题解:一种是根据上面那一题的思路去改的,稍微复杂一点
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) {
return {};
}
vector<int> res;
int i, j;
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int startx = 0, starty = 0;
int offset = 1;
// 特判:只有一行
if (m == 1) {
return matrix[0];
}
// 特判:只有一列
if (n == 1) {
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][0]);
}
return res;
}
while (startx <= n - offset && starty <= m - offset) {
i = startx;
j = starty;
for (j = starty; j < n - offset && res.size() < m * n; j++) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
}
for (i = startx; i < m - offset && res.size() < m * n; i++) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
}
for (; j > starty && res.size() < m * n; j--) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
}
for (; i > startx && res.size() < m * n; i--) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
}
startx++;
starty++;
offset += 1;
}
if (res.size() < m * n) {
if (n % 2 && m % 2) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
} else if (n % 2) {
for (; i >= startx && res.size() < m * n; i--) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
}
} else if (m % 2) {
for (; j >= starty && res.size() < m * n; j--) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
第二种是力扣上的题解,比较简洁一点
可以将矩阵看成若干层,首先输出最外层的元素,其次输出次外层的元素,直到输出最内层的元素。
定义矩阵的第 kkk 层是到最近边界距离为 kkk 的所有顶点。例如,下图矩阵最外层元素都是第 111 层,次外层元素都是第 222 层,剩下的元素都是第 333 层。
[[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]
对于每层,从左上方开始以顺时针的顺序遍历所有元素。假设当前层的左上角位于 (top,left)(\textit{top}, \textit{left})(top,left),右下角位于 (bottom,right)(\textit{bottom}, \textit{right})(bottom,right),按照如下顺序遍历当前层的元素。
从左到右遍历上侧元素,依次为 (top,left)(\textit{top}, \textit{left})(top,left) 到 (top,right)(\textit{top}, \textit{right})(top,right)。
从上到下遍历右侧元素,依次为 (top+1,right)(\textit{top} + 1, \textit{right})(top+1,right) 到 (bottom,right)(\textit{bottom}, \textit{right})(bottom,right)。
如果 left<right\textit{left} < \textit{right}left<right 且 top<bottom\textit{top} < \textit{bottom}top<bottom,则从右到左遍历下侧元素,依次为 (bottom,right−1)(\textit{bottom}, \textit{right} - 1)(bottom,right−1) 到 (bottom,left+1)(\textit{bottom}, \textit{left} + 1)(bottom,left+1),以及从下到上遍历左侧元素,依次为 (bottom,left)(\textit{bottom}, \textit{left})(bottom,left) 到 (top+1,left)(\textit{top} + 1, \textit{left})(top+1,left)。
遍历完当前层的元素之后,将 left\textit{left}left 和 top\textit{top}top 分别增加 111,将 right\textit{right}right 和 bottom\textit{bottom}bottom 分别减少 111,进入下一层继续遍历,直到遍历完所有元素为止。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) {
return {};
}
int rows = matrix.size(), columns = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> order;
int left = 0, right = columns - 1, top = 0, bottom = rows - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) {
order.push_back(matrix[top][column]);
}
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order.push_back(matrix[row][right]);
}
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
order.push_back(matrix[bottom][column]);
}
for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
order.push_back(matrix[row][left]);
}
}
left++;
right--;
top++;
bottom--;
}
return order;
}
};复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(mn)O(mn)O(mn),其中 mmm 和 nnn 分别是输入矩阵的行数和列数。矩阵中的每个元素都要被访问一次。
空间复杂度:O(1)O(1)O(1)。除了输出数组以外,空间复杂度是常数。
三、LCR 146. 螺旋遍历二维数组
题目:
给定一个二维数组 array,请返回「螺旋遍历」该数组的结果。
螺旋遍历:从左上角开始,按照 向右、向下、向左、向上 的顺序 依次 提取元素,然后再进入内部一层重复相同的步骤,直到提取完所有元素。
示例 1:
输入:array = [[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]] 输出:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
示例 2:
输入:array = [[1,2,3,4],[12,13,14,5],[11,16,15,6],[10,9,8,7]] 输出:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]
限制:
0 <= array.length <= 1000 <= array[i].length <= 100
注意:本题与主站 54 题相同:. - 力扣(LeetCode)
题解:
这一题基本和上面那一题一样
class Solution {
public int[] spiralArray(int[][] array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0 || array[0].length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
int rows = array.length, columns = array[0].length;
int[] order = new int[rows * columns];
int index = 0;
int left = 0, right = columns - 1, top = 0, bottom = rows - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) {
order[index++] = array[top][column];
}
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order[index++] = array[row][right];
}
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
order[index++] = array[bottom][column];
}
for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
order[index++] = array[row][left];
}
}
left++;
right--;
top++;
bottom--;
}
return order;
}
}