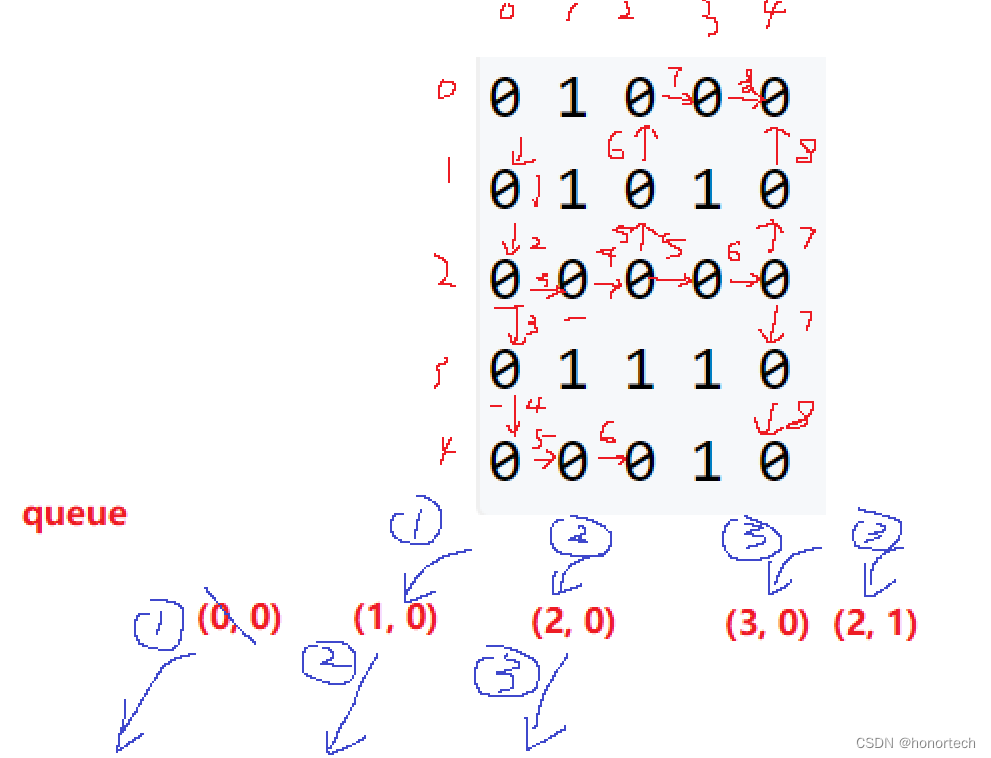
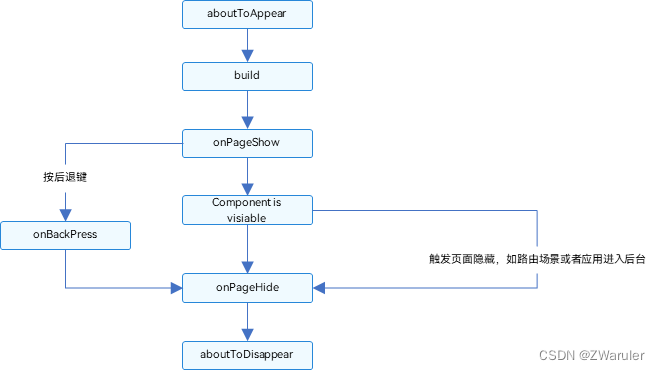
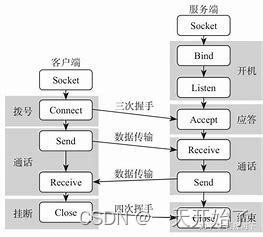
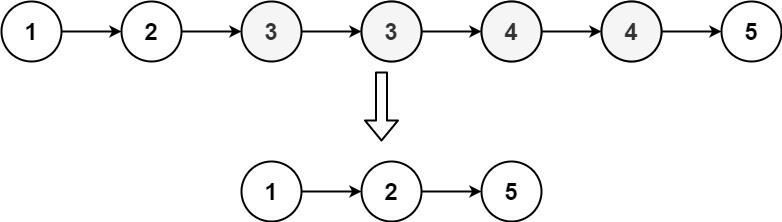
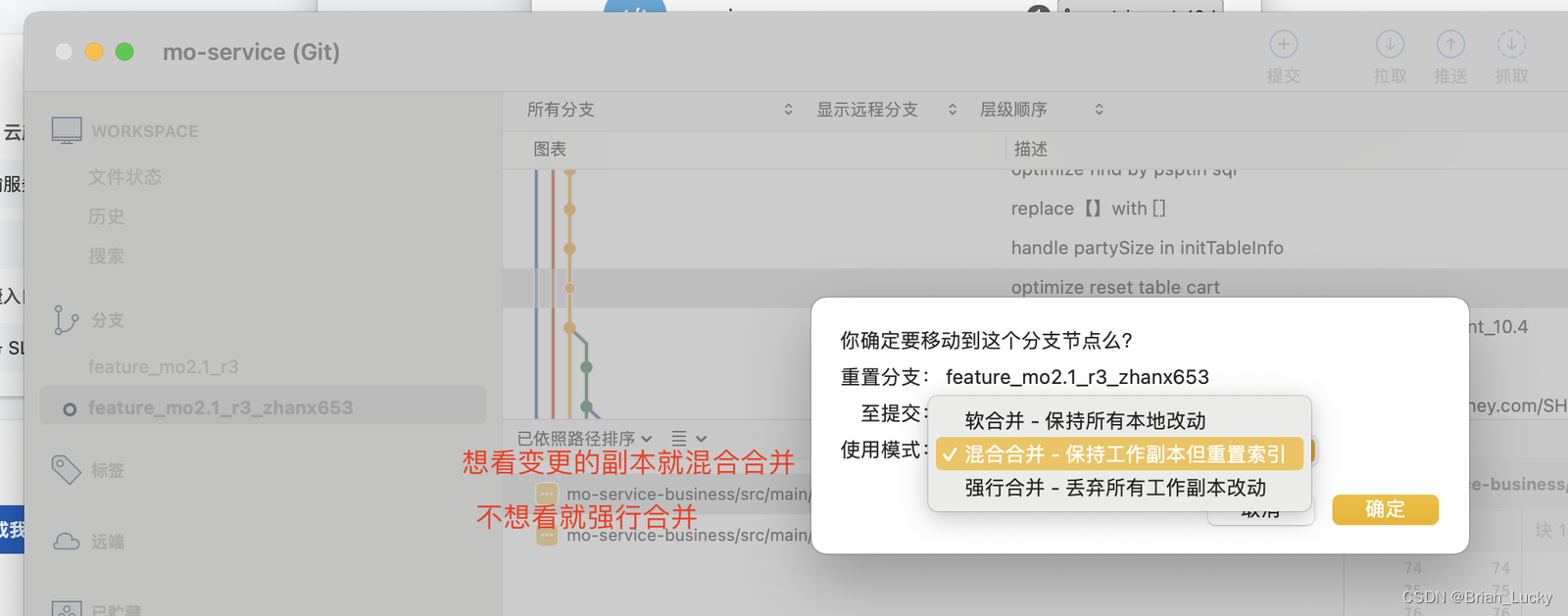
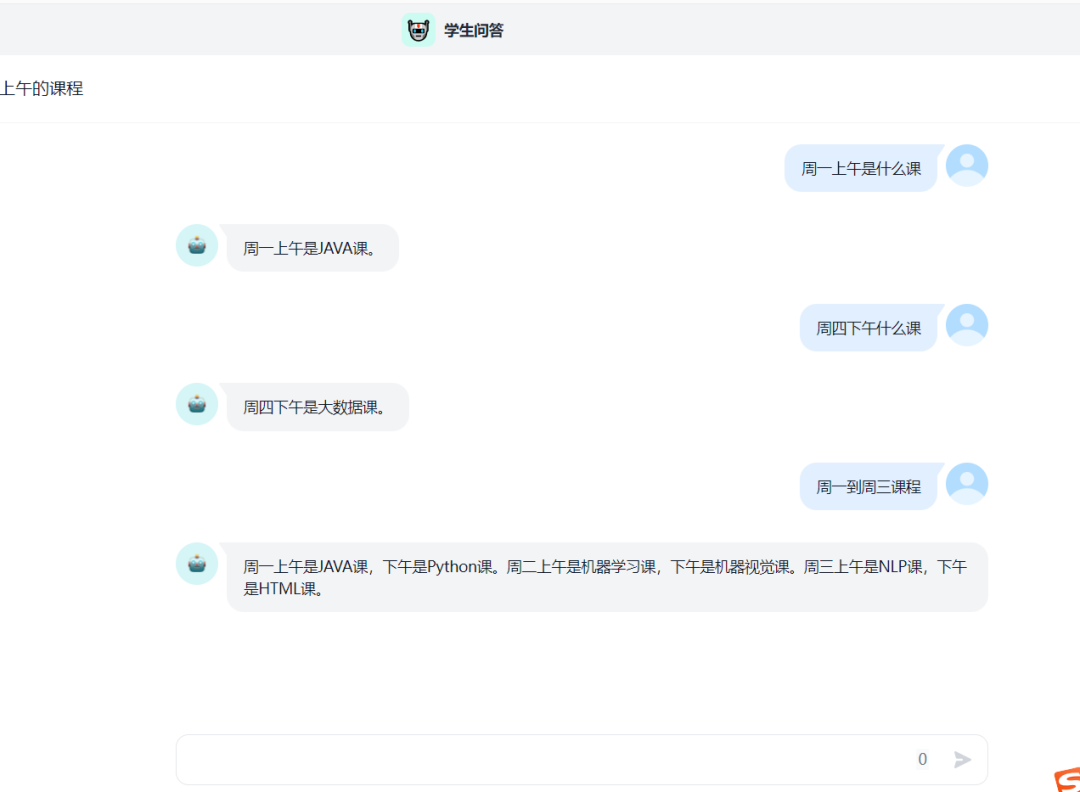
BFS 重点就是要使用 队列 进行每一层的搜索 不同题目 队列中保存的元素形式都各不相同,并且也会用到其他辅助结构 走迷宫一题,队列中存的是每一层(当前步能走的所有坐标)的坐标,并保存了每一层对应走过的步数 八数码一题,队列中存的是每一层(当前x位置可以发生交换位置对应的交换后的结果)可能的交换后的序列,并保存了每种交换后的序列所对应的交换次数 二叉树的层序遍历就是 BFS
# include <iostream> # include <cstring> # include <algorithm> # include <queue> using namespace std;
const int N = 109 , MAX = 0x3f3f3f3f ;
int n, m, maze[ N] [ N] , ret, d[ N] [ N] ;
queue< pair< int , int >> m_next;
int bfs ( int x, int y)
{
int dx[ 4 ] = { - 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 } , dy[ 4 ] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , - 1 } ;
m_next. push ( { x, y} ) ;
maze[ x] [ y] = 1 ;
while ( m_next. size ( ) )
{
pair< int , int > cur = m_next. front ( ) ;
m_next. pop ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i ++ )
{
int cx = cur. first + dx[ i] , cy = cur. second + dy[ i] ;
if ( cx >= 0 && cx < n && cy >= 0 && cy < m && maze[ cx] [ cy] == 0 )
{
m_next. push ( { cx, cy} ) ;
maze[ cx] [ cy] = 1 ;
d[ cx] [ cy] = d[ cur. first] [ cur. second] + 1 ;
}
}
}
return d[ n - 1 ] [ m - 1 ] ;
}
int main ( )
{
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j < m; j ++ )
cin >> maze[ i] [ j] ;
cout << bfs ( 0 , 0 ) ;
return 0 ;
}
# include <iostream> # include <cstring> # include <algorithm> # include <string> # include <queue> # include <unordered_map> using namespace std;
queue< string> m_next;
unordered_map< string, int > m_step;
char grid[ 3 ] [ 3 ] ;
string str;
int main ( )
{
int index = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++ i)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++ j)
{
cin >> grid[ i] [ j] ;
str += grid[ i] [ j] ;
}
}
m_next. push ( str) ;
m_step[ str] = 0 ;
int dx[ 4 ] = { - 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 } , dy[ 4 ] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , - 1 } ;
while ( m_next. size ( ) )
{
string cur = m_next. front ( ) ;
m_next. pop ( ) ;
int step = m_step[ cur] ;
if ( cur == "12345678x" )
{
cout << m_step[ cur] ;
return 0 ;
}
int xcur = cur. find ( 'x' ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++ i)
{
int cx = xcur / 3 + dx[ i] , cy = xcur % 3 + dy[ i] ;
if ( cx >= 0 && cx < 3 && cy >= 0 && cy < 3 )
{
swap ( cur[ xcur] , cur[ cx * 3 + cy] ) ;
if ( m_step. find ( cur) == m_step. end ( ) )
{
m_step[ cur] = step + 1 ;
m_next. push ( cur) ;
}
swap ( cur[ xcur] , cur[ cx * 3 + cy] ) ;
}
}
}
cout << - 1 ;
return 0 ;
}