文章目录
- 前言
- 一、命名管道接口函数介绍
- 二、使用步骤
前言
上章内容,我们介绍与使用了管道。上章内容所讲的,是通过pipe接口函数让操作系统给我们申请匿名管道进行进程间通信。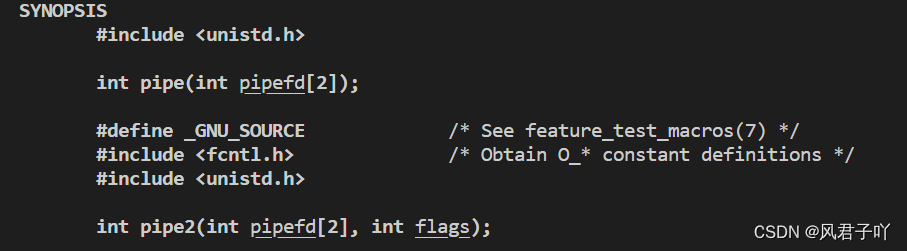
并且这种进程间通信一般只适用于父子进程之间,那么对于两个没有“血缘”关系的进程,我们还能通过怎样的方式来进行通信呢?
本章内容主要讲解命名管道的通信,而命名管道,顾名思义,既然匿名管道是没有名字的管道,那么命名管道就是有名字的管道。
一、命名管道接口函数介绍
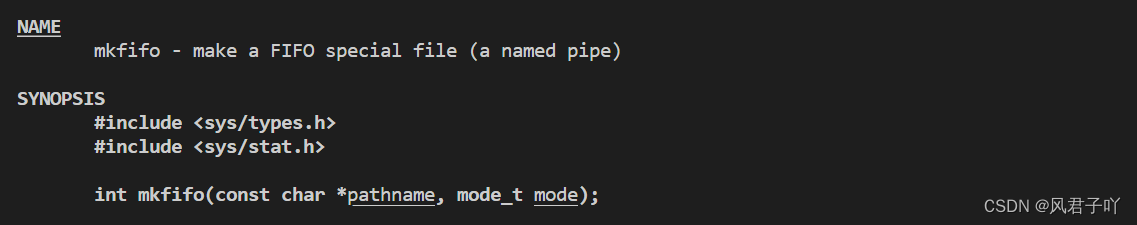
先来讲讲函数名:mk - make fifo - first in first out(先进先出),因为管道的buffer就是先进先出的策略,所以函数名为mkfifo。
第一个参数 const char* pathname: 这个参数是作为你要生成的命名管道的路径与名字。不过要注意的是,这个文件的路径最好是你有权限去进行访问,不然可能会出现各种问题。
第二个参数 mode_t mode: 因为既然你要生成一个命名管道文件,那么你就需要给它制定文件的访问权限。
二、使用步骤
使用步骤与匿名管道比较相似,只是多了需要自己调用mkfifo函数的过程
// # fifo.hpp
#ifndef _FIFO_COM
#define _FIFO_COM
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<assert.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#define PATH_NAME "./fifo.ipc"
std::string END_STR("end");
#endif
// Server端
#include "fifo.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
int main()
{
// 1.申请命名管道
int ret = mkfifo(PATH_NAME, 0666);
if (ret == -1)
{
perror("mkfifo");
exit(1);
}
int a = 0;
Log(Debug) << "Server: make named_pipe success! Step1" << std::endl;
// 2.打开命名管道文件
// Server端进行写操作
int fd = open(PATH_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (fd == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(2);
}
Log(Debug) << "Server: open named_pipe success! Step2" << std::endl;
// 3.开始写
std::string buffer;
while (1)
{
std::cout << "Please Enter Message Line ,End enter 'end' :> ";
std::getline(std::cin, buffer);
if(buffer == END_STR) break;
write(fd, buffer.c_str(), buffer.size());
}
//.关闭命名管道
close(fd);
Log(Debug) << "Server: close fc done! Step3" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// Client端
#include "fifo.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
int main()
{
// 1.打开命名管道文件
// Client端进行读
int fd = open(PATH_NAME, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(2);
}
char buffer[1024];
Log(Debug) << "Client: open named_pipe success! Step1" << std::endl;
// sleep(5);
// 开始进行读
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, '\0', sizeof(buffer));
int n = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (n == 0)
{
// 读到了文件末尾
Log(Debug) << "Read done!" << std::endl;
break;
}
else if (n > 0)
{
std::cout << "Server say: " << buffer << std::endl;
}
}
close(fd);
unlink(PATH_NAME);
Log(Debug) << "Client: close named_pipe success! Step2" << std::endl;
Log(Debug) << "Client: close fd done! Step3" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// Log.hpp 日志
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <string>
#define Debug 0
#define Error 1
const std::string com[] = {
"Debug",
"Error"};
std::ostream &Log(int command)
{
std::cout << "[" << (unsigned)time(nullptr) << "]:"
<< "[" << com[command] << "]" <
" ";
return std::cout;
}
需要特别注意的是:对于管道文件,必须读写两端都打开管道文件(也就是都进行open管道文件),否则读端或者写端就会被堵塞在open函数。