一、前言
在复杂业务场景中,有些数据需要远程调用,导致查询时间缓慢,影响以下代码逻辑运行,并且这些浪费时间的逻辑与以后的请求并没有关系,这样会大大增加服务的时间。
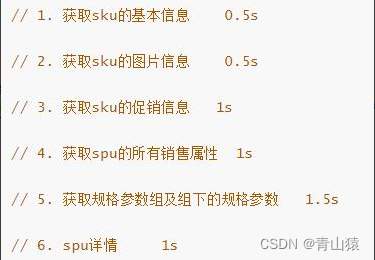
假如商品详情页的每个查询,需要如下标注的时间才能完成 。那么,用户需要 5.5s 后才能看到商品详情页的内容。很显然是不能接受的。 如果有多个线程同时完成这 6 步操作,也许只需要 1.5s 即可完成响应。
在 Java 8 中 , 新增加了一个包含 50 个方法左右的类 : CompletableFuture ,提供了非常强大的 Future 的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,提供了函数式编程的能力,可以 通过回调的方式处理计算结果,并且提供了转换和组合 CompletableFuture 的方法。 CompletableFuture 类实现了 Future 接口,所以你还是可以像以前一样通过 `get` 方法阻塞或 者轮询的方式获得结果,但是这种方式不推荐使用。 CompletableFuture 和 FutureTask 同属于 Future 接口的实现类,都可以获取线程的执行结果。
1、创建异步对象
public static Completab1eFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static completableFuturecVoid> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Suppliersupplier)
public static CompletableFuturecU> supplyAsync(Supplier supplier,Executor executor)
1 、 runXxxx 都是没有返回结果的, supplyXxx 都是可以获取返回结果的2 、可以传入自定义的线程池,否则就用默认的线程池;3、Async代表异步方法
1.1 runAsync 不带返回值
public class ThreadTest {
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>( 100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果...."+i);
}, executor);
}
}1.2 supplyAsync 带返回值
public class ThreadTest {
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>( 100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor);
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
}
2、计算完成时回调方法
public completableFuture whencomplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action);
public CompletableFuturewhenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer <? super T,? super Throwable> action);
public completableFuture whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action,Executor executor);
public completableFutureexceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn);
whenComplete可以处理正常和异常的计算结果,exceptionally处理异常情况。
whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
whenComplete: 是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行 whenComplete 的任务。
whenCompleteAsync: 是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池
来进行执行。
方法不以 Async 结尾, 意味着 Action 使用相同的线程执行, 而 Async 可能会使用其他线程执行(如果是使用相同的线程池, 也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)
2.1 whenCompleteAsync 完成回调 (没有异常情况情况)
public class ThreadTest {
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>( 100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenCompleteAsync((res, exception) -> {
System.out.println("异步任务完成....感知到返回值为:"+res+"异常:"+exception);
},executor);
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
}
有异常情况
public class ThreadTest {
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>( 100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenCompleteAsync((res, exception) -> {
System.out.println("异步任务完成....感知到返回值为:"+res+"异常:"+exception);
},executor);
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
}
此处虽然得到了异常信息但是没有办法修改返回数据,使用
exceptionally自定义异常时的返回值
2.2 exceptionally 异常感知及处理
异常情况
public class ThreadTest {
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>( 100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenCompleteAsync((res, exception) -> {
System.out.println("异步任务完成....感知到返回值为:"+res+"异常:"+exception);
},executor).exceptionally(throwable -> {
return 0;
});
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
}
无异常,情况正常返回不会进exceptionally
public class ThreadTest {
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>( 100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenCompleteAsync((res, exception) -> {
System.out.println("异步任务完成....感知到返回值为:"+res+"异常:"+exception);
},executor).exceptionally(throwable -> {
return 0;
});
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
}
2.3 最终处理 handle 方法
和 complete 一样, 可对结果做最后的处理(可处理异常),可改变返回值。
总结:使用R apply(T t, U u); 可以感知异常,和修改返回值的功能。
public completionStage handle(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn);
public completionStagehandleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn);
public > CompletionStage handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn,Executor executor ) ;有异常情况
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor).handleAsync((res, throwable) -> {
if (res!=null){
return res*2;
}
if (throwable!=null){
System.out.println("出现异常"+throwable.getMessage());
return -1;
}
return 0;
},executor);
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
无异常情况
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 6;
System.out.println("运行结果...." + i);
return i;
}, executor).handleAsync((res, throwable) -> {
if (res!=null){
return res*2;
}
if (throwable!=null){
System.out.println("出现异常"+throwable.getMessage());
return -1;
}
return 0;
},executor);
Integer integer = supplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("返回数据:"+integer);
}
2.3.1总结
总结:一般用handle,因为whencomplete如果异常不能给定默认返回结果,需要再调用exceptionally,而handle可以
该方法作用:获得前一任务的返回值【自己也可以是异步执行的】,也可以处理上一任务的异常,调用exceptionally修改前一任务的返回值【例如异常情况时给一个默认返回值】而handle方法可以简化操作
以下用法大致相同,只列举具体方法
2.4 线程串行化方法
public CompletableFuture thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public Completab1eFuture thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public CompletableFuture thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor)
public completionstage thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public completionStage thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStagecVoid> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
public Completionstage thenRun(Runnable action);
public Completionstage thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public completionStage thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);thenApply:继续执行,感知上一任务的返回结果,并且自己的返回结果也被下一个任务所感知
thenAccept:继续执行,接受上一个任务的返回结果,自己执行完没有返回结果
thenRun:继续执行,不接受上一个任务的返回结果,自己执行完也没有返回结果
以上都要前置任务成功完成。
Function<? super T,? extends U>
T: 上一个任务返回结果的类型
U: 当前任务的返回值类型
2.5 两任务组合 - 都要完成
public <U,V> CompletableFuture thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor);
public CompletableFuture thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public CompletableFuture thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public CompletableFuture thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
public CompletableFuture runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor);thenCombine:组合两个future,获取前两个future的返回结果,并返回当前任务的返回值
thenAcceptBoth:组合两个future,获取前两个future任务的返回结果,然后处理任务,没有返回值。
runAfterBoth:组合两个future,不需要获取之前任务future的结果,只需两个future处理完任务后,处理该任务。
2.5.1 runAfterBothAsync
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务一线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 2;
System.out.println("任务一运行结束...." + i);
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务二线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("任务二运行结束....");
return "hello";
}, executor);
future01.runAfterBothAsync(future02,() -> {
System.out.println("任务三开始...");
});
System.out.println("返回数据:");
}
2.6 两个任务 - 一个完成
- applyToEither: 两个任务有一个执行完成, 获取它的返回值, 处理任务并有新的返回值。
- acceptEither: 两个任务有一个执行完成, 获取它的返回值, 处理任务, 没有新的返回值。
- runAfterEither: 两个任务有一个执行完成, 不需要获取 future 的结果, 处理任务, 也没有返回值。
2.7 多任务组合
//allOf: 等待所有任务完成
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
//anyOf: 只要有一个任务完成
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return orTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
2.7.1 allOf
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务一线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 2;
System.out.println("任务一运行结束...." + i);
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务二线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务二运行结束....");
return "hello";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future03 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务三线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务三运行结束....");
return "hello2";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(future01, future02, future03);
allOf.get();//等待所有任务完成
System.out.println("返回数据:");
}
2.7.2 anyOf
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务一线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 12 / 2;
System.out.println("任务一运行结束...." + i);
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务二线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务二运行结束....");
return "hello";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future03 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务三线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务三运行结束....");
return "hello2";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future01, future02, future03);
anyOf.get();//等待其中之一任务完成
System.out.println("返回数据:");
}