目录
一、实验目的
二、实验原理
1. 节点
2. 指针
3.链表的类型
3.1 单向链表
3.2 双向链表
3.3 单向循环链表
3.4 双向循环链表
4. 单链表的插入
4.1 头插法
4.2 尾插法
4.3 在指定位置插入元素
5. 单链表的删除
5.1 删除指定数值的节点
5.2 删除指定位置的节点
6. 单链表的查找
6.1 按照值域查找
6.2 按照位置查找
7. 链表的遍历
三、实验内容
问题描述
代码
截图
一、实验目的
1、 熟练掌握链表结构体的实现。
2、 熟练掌握链表的存储结构上实现基本操 作:查找、插入和删除算法
二、实验原理
链表(Linked List)是一种基本的数据结构,它用于存储和组织数据元素。链表中的元素被称为节点(Node),每个节点包含两部分:数据域和指针域。
1. 节点
每个节点包含两个部分:数据域和指针域。
-
数据域(Data Field): 存储节点的数据元素。这可以是任何数据类型,例如整数、字符、对象等。
-
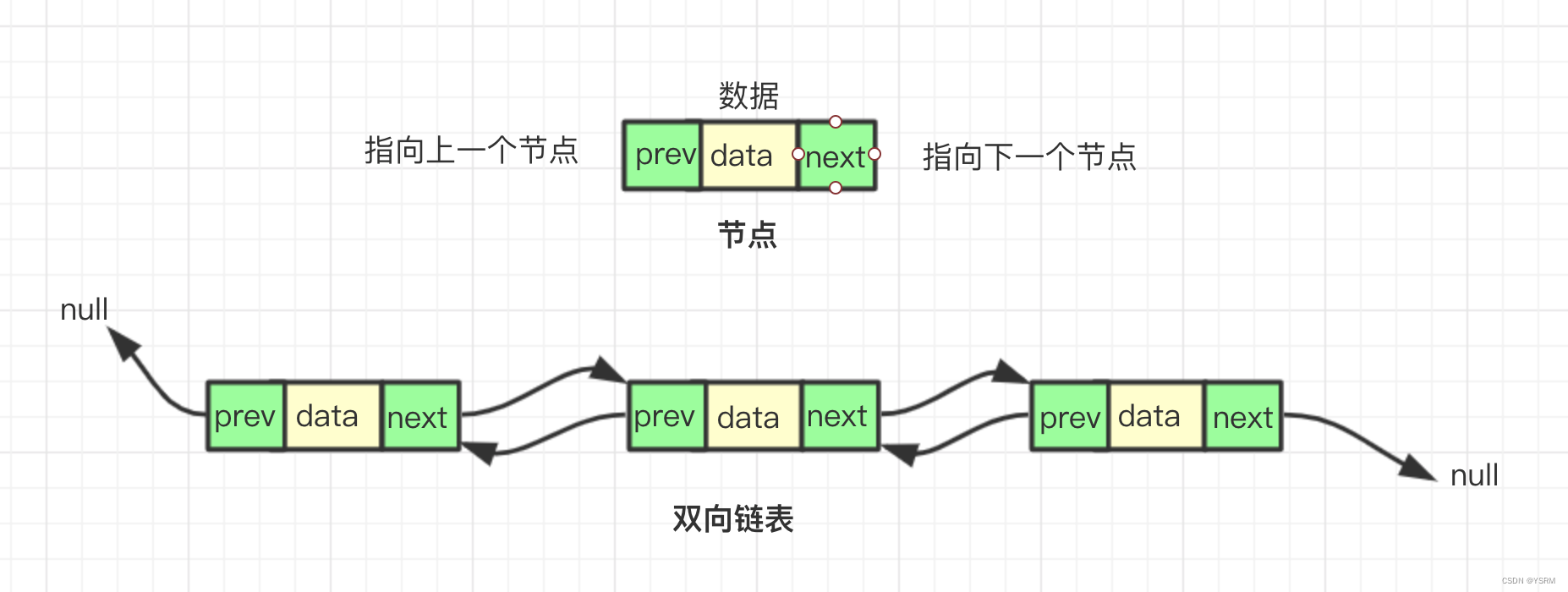
指针域(Pointer Field): 存储指向下一个节点的引用(地址)。对于双向链表,可能还有指向前一个节点的引用。
2. 指针
链表的节点通过指针相互连接。指针存储了节点的地址,使得可以按顺序遍历链表。
3.链表的类型
3.1 单向链表
每个节点只有一个指针,指向下一个节点。
最后一个节点指向空节点(NULL)。
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct LinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};3.2 双向链表
每个节点有两个指针,一个指向前一个节点,另一个指向下一个节点。
第一个节点的prev指向NULL,最后一个节点的next指向NULL
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
struct ListNode* prev;// 指针域,指向前一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct DoublyLinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};
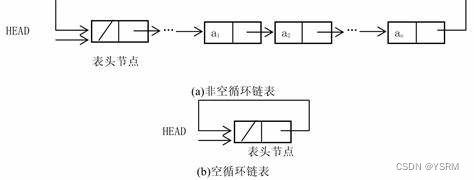
3.3 单向循环链表
尾节点的指针指向头节点,形成一个闭环。
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct CircularLinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
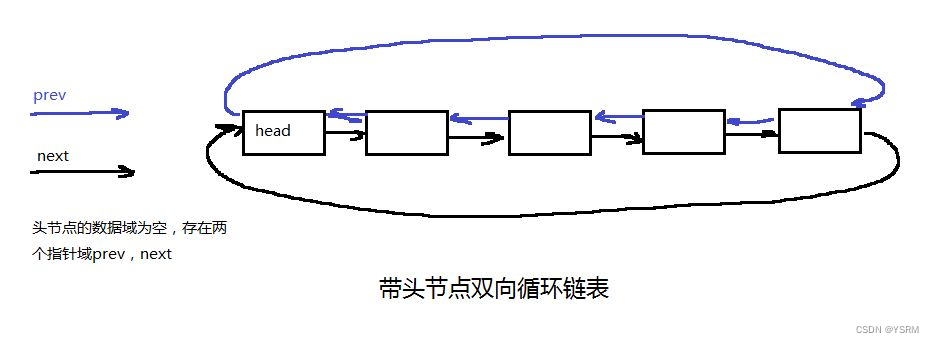
};3.4 双向循环链表
带头结点的循环双向链表在链表尾部连接到头结点,同时每个节点都有一个指向前一个节点的指针。
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
struct ListNode* prev;// 指针域,指向前一个节点的地址
};对于头节点的定义
struct CircularDoublyLinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};4. 单链表的插入
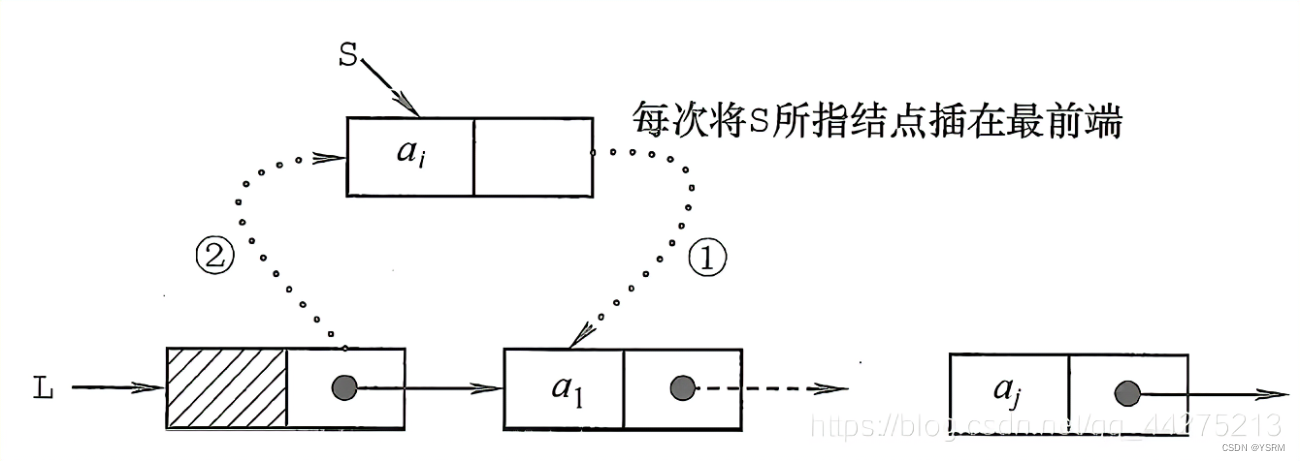
4.1 头插法
头插法是一种在单链表中插入节点的方法,它将新节点插入到链表的头部,成为新的头结点。
- 创建一个新的节点。
- 将新节点的
next指针指向当前链表的头结点。- 更新链表的头结点,使其指向新节点。
struct ListNode* insertAtBeginning(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
//创建新节点
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return;
}
newNode->data = elem;//赋值
newNode->next = head;//newNode的指针指向head
head = newNode;//newNode成为新的头节点
return head;
}示例
依次插入4 3 2 1
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
for (int i = 4; i > 0; i--) {
head = insertAtBeginning(head, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
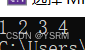
正好与输入顺序相反,这就是头插法的特色
4.2 尾插法
尾插法是一种在单链表中插入节点的方法,它将新节点插入到链表的尾部。相对于头插法,尾插法需要遍历整个链表找到尾节点,然后在尾节点之后插入新节点。
- 创建一个新的节点。
- 若链表为空,将新节点设置为头结点。
- 若链表不为空,遍历链表找到尾节点。
- 将尾节点的
next指针指向新节点。
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
//查找尾节点
if (head == NULL) {//如果该链表为空链表,头节点指向该新节点
head = newNode;
}
else {
struct ListNode* tail = head;//定义尾节点
while (tail->next != NULL) {//找到尾节点
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;//尾节点的指针指向新节点
}
return head;
}示例
依次插入4 3 2 1
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
for (int i = 4; i > 0; i--) {
head = insertAtEnd(head, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
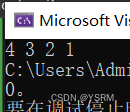
结果与输入顺序相同,看似更好,但是时间复杂度较高(while循环)。
4.3 在指定位置插入元素
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd_index(struct ListNode* head, int elem,int index) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
//index是否合法
if (index == 1) {//插入的节点为头节点
head = newNode;
newNode->next = current->next;
return;
}
while (current != NULL && index!=1) {
prev = current;
current = current->next;
index--;
}
if (current == NULL) {//遍历到末尾
if (index != 0) {
cout << "索引越界" << endl;
}
else {//prev后插入
prev->next = newNode;
}
}
else {//中间插入
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = current;
}
return head;
}5. 单链表的删除
5.1 删除指定数值的节点
删除链表中所有数值域与指定数值相同的节点。
struct ListNode* deleteNodeWithValue(struct ListNode* head, int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;//prev只有刚开始等于NULL的时候才发挥作用,其余时候没用
// 遍历链表删除所有匹配的节点
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {//如果符合条件
if (prev == NULL) {// 如果目标节点是头结点
head = current->next;
free(current);
current = head;
}
else {
prev->next = current->next;
free(current);
current = prev->next;
}
}
else {//不符合条件,直接右移
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
}
return head;
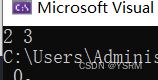
}示例,尾插法插入1 2 1 3
再删除1
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
head = deleteNodeWithValue(head, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
5.2 删除指定位置的节点
若指定位置无节点,会特殊处理
struct ListNode* deleteNodeAtPosition(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return head;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
while (index != 1 && current!=NULL) {
index--;
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return head;
}
if (index == 1) {
if (current == head) {//删除的节点是头节点
head = current->next;
free(current);
}
else {
current = current->next;
prev->next = current;
}
}
return head;
}示例,尾插法插入1 2 1 3
再删除第一个节点
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
head = deleteNodeAtPosition(head, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}结果为
2 1 3
6. 单链表的查找
在链表中查找元素的操作通常包括遍历链表,逐一比较节点的值,直到找到匹配的元素或者到达链表的末尾。
6.1 按照值域查找
void search_target(struct ListNode* head,int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
int count = 1;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {
cout << "在第"<<count<<"个位置" << endl;
return;
}
count++;
current=current->next;
}
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}依次插入1 2 1 3
查找1 4
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
search_target(head, 1);
search_target(head, 4);
return 0;
}结果为
1在第一个位置
4不存在
6.2 按照位置查找
void search_index(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (index != 1 && current != NULL) {
index--;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return;
}
cout << current->data;
}依次插入1 2 1 3
查找1 4
int main(){
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 2);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 3);
search_index(head, 1);
search_index(head, 4);
return 0;
}结果为
1
3
7. 链表的遍历
从头节点遍历
void traversal(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
cout << current->data<<" ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
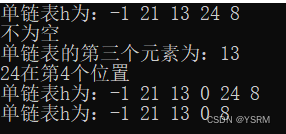
}三、实验内容
问题描述
1、 初始化单链表 h;
2、 依次采用头插法插入元素-1,21,13,24,8;
3、 输出单链表 h;
4、 输出单链表 h 长度;
5、 判断单链表 h 是否为空;
6、 输出单链表 h 的第 3 个元素;
7、 输出元素 24 的位置;
8、 在 h 的第 4 个元素前插入元素 0;
9、 输出单链表 h;
10、 删除 h 的第 5 个元素;
11、 输出单链表 h
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int data;// 数据域,存储节点的数据
struct ListNode* next;// 指针域,指向下一个节点的地址
};
struct LinkedList {
struct ListNode* head;
};
struct ListNode* insertAtBeginning(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
//创建新节点
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
newNode->data = elem;//赋值
newNode->next = head;//newNode的指针指向head
head = newNode;//newNode成为新的头节点
return head;
}
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd(struct ListNode* head, int elem) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
//查找尾节点
if (head == NULL) {//如果该链表为空链表,头节点指向该新节点
head = newNode;
}
else {
struct ListNode* tail = head;//定义尾节点
while (tail->next != NULL) {//找到尾节点
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;//尾节点的指针指向新节点
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode* insertAtEnd_index(struct ListNode* head, int elem,int index) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
cout << "内存分配失败" << endl;
return head;
}
//设置新节点的数据和指针
newNode->data = elem;
newNode->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
//index是否合法
if (index == 1) {//插入的节点为头节点
head = newNode;
newNode->next = current->next;
return head;
}
while (current != NULL && index!=1) {
prev = current;
current = current->next;
index--;
}
if (current == NULL) {//遍历到末尾
if (index != 0) {
cout << "索引越界" << endl;
}
else {//prev后插入
prev->next = newNode;
}
}
else {//中间插入
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = current;
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode* deleteNodeWithValue(struct ListNode* head, int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;//prev只有刚开始等于NULL的时候才发挥作用,其余时候没用,prev的next指向current
// 遍历链表删除所有匹配的节点
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {//如果符合条件
if (prev == NULL) {// 如果目标节点是头结点
head = current->next;
free(current);
current = head;
}
else {
prev->next = current->next;
free(current);
current = prev->next;
}
}
else {//不符合条件,直接右移
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode* deleteNodeAtPosition(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return head;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
while (index != 1 && current!=NULL) {
index--;
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return head;
}
if (index == 1) {
if (current == head) {//删除的节点是头节点
head = current->next;
free(current);
}
else {
current = current->next;
prev->next = current;
}
}
return head;
}
void search_target(struct ListNode* head,int target) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
int count = 1;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == target) {
cout << "在第"<<count<<"个位置" << endl;
return;
}
count++;
current=current->next;
}
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}
void search_index(struct ListNode* head, int index) {
if (index < 1) {
cout << "输入无效" << endl;
return;
}
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (index != 1 && current != NULL) {
index--;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL) {//越界
cout << "访问越界" << endl;
return;
}
cout << current->data<<endl;
}
void traversal(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
cout << current->data<<" ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
//初始化单链表
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insertAtEnd(head, -1);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 21);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 13);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 24);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 8);
cout << "单链表h为:";
traversal(head);
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "单链表为空"<<endl;
}
else {
cout << "不为空" << endl;
}
cout << "单链表的第三个元素为:";
search_index(head, 3);
cout << "24";
search_target(head, 24);
insertAtEnd_index(head, 0, 4);
cout << "单链表h为:";
traversal(head);
deleteNodeAtPosition(head, 5);
cout << "单链表h为:";
traversal(head);
return 0;
}截图