文章目录
- 接口(Interface)介绍
- 接口在C++中的应用
- 接口在UE中的使用
接口(Interface)介绍
接口是一系列抽象方法的声明,是一些方法特征的集合,这些方法都应该是抽象的,需要由具体的类去实现,然后第三方就可以通过这组抽象方法调用,让具体的类执行具体的方法。
用c++实现接口类时需要注意一下几点:
- 接口类中不可以声明成员变量,静态变量。
- 可以声明静态常量作为接口的返回值状态,需要在对应的cpp中定义并初始化,访问时需要使用"接口类型::静态常量名"访问
- 定义的接口方法使用virtual 修饰符 和 “=0” 修饰,表示该方法是纯虚的。
- 因为接口类是无法创建对象的,所以不应该编写构造函数和析构函数
接口在C++中的应用
主要实现小鸟:==> 出生 ==> 飞行 ==> 活动区域 ==> 死亡 这个过程
实现-接口类-飞行动作
IAction.h
#ifndef IACTION_H
#define IACTION_H
//接口类 表示飞行动作
class IAction
{
public:
virtual void fly() = 0;
};
#endif // IACTION_H
实现-接口类-活动区域
IShape.h
#ifndef ISHAPE_H
#define ISHAPE_H
// 接口类 表示活动区域
class IShape
{
public:
virtual int area() = 0;
static const int MIN_AREA;
};
#endif // ISHAPE_H
IShape.cpp
#include "IShape.h"
const int IShape::MIN_AREA = 0;
实现-小鸟实体类
Bird.h
// 这是一种防止多次包含头文件的预处理器技术
#ifndef BIRD_H
#define BIRD_H
#include "IAction.h"
#include "IShape.h"
class Bird : public IShape, public IAction
{
public:
Bird();
~Bird();
// IAction interface
public:
void fly() override;
// IShape interface
public:
int area() override;
};
#endif // BIRD_H
Bird.cpp
#include "Bird.h"
#include <iostream>
Bird::Bird()
{
std::cout << "initialize : The bird is born. " << std::endl;
}
Bird::~Bird()
{
std::cout << "dispose : The bird is die." << std::endl;
}
void Bird::fly()
{
std::cout << "execute : The bird is flying. " << std::endl;
}
int Bird::area()
{
std::cout << "activity area : " << IShape::MIN_AREA << std::endl;
return 0;
}
创建程序入口
main.cpp
#include "Bird.h"
int main()
{
Bird *bird = new Bird();
bird->fly();
bird->area();
delete bird;
return 0;
}
目录
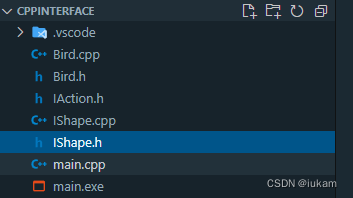
编译C++ 文件,我这里使用是g++编译脚本,指定生成 main.exe运行文件
PS D:\Project\C++\Temp\Cppinterface> g++ main.cpp Bird.cpp IShape.cpp -o main.exe
然后执行运行文件
PS D:\Project\C++\Temp\Cppinterface> ./main.exe
打印结果
initialize : The bird is born.
execute : The bird is flying.
activity area : 0
dispose : The bird is die.
接口在UE中的使用
这里有官方文档可以参考
创建C++ 接口
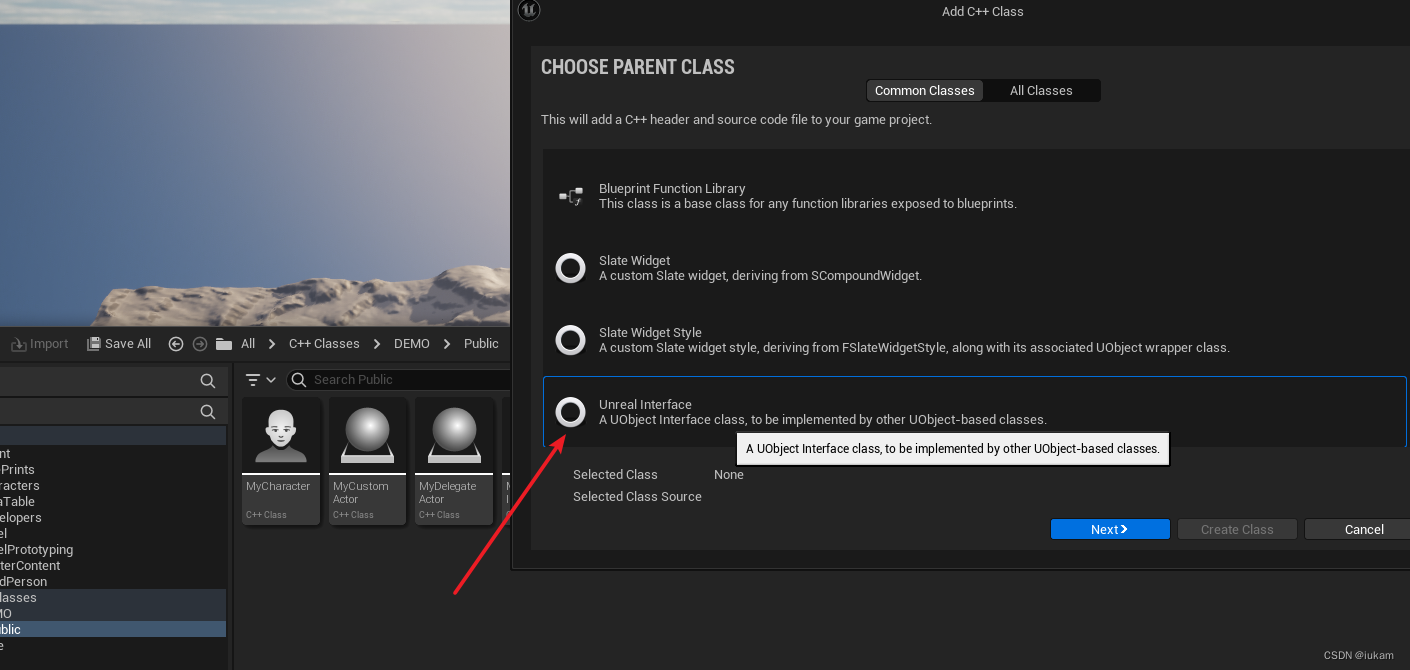
创建接口,在接口中实现两个虚函数
virtual void Attack(){};
virtual void CaclulateHealth(){};
MyInterface.h
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "UObject/Interface.h"
#include "MyInterface.generated.h"
// This class does not need to be modified.
UINTERFACE(MinimalAPI)
class UMyInterface : public UInterface
{
GENERATED_BODY()
};
/**
*
*/
class DEMO_API IMyInterface
{
GENERATED_BODY()
// Add interface functions to this class. This is the class that will be inherited to implement this interface.
public:
virtual void Attack(){};
virtual void CaclulateHealth(){};
};
编译后,在MyCharacter.h 继承自接口
#include "MyInterface.h"
#include "GameFramework/Character.h"
#include "MyCharacter.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class DEMO_API AMyCharacter : public ACharacter, public IMyInterface
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this character's properties
AMyCharacter();
protected:
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
public:
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override;
// Called to bind functionality to input
virtual void SetupPlayerInputComponent(class UInputComponent *PlayerInputComponent) override;
// 重写接口函数
virtual void Attack() override;
virtual void CaclulateHealth() override;
};
在MyCharacter.cpp 实现接口
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
void AMyCharacter::BeginPlay()
{
Super::BeginPlay();
// 执行接口
Attack();
CaclulateHealth();
}
// 重写接口函数
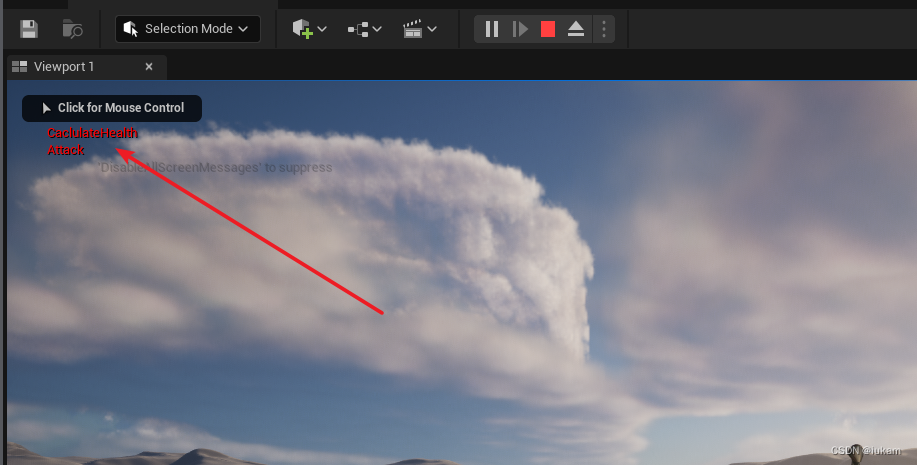
void AMyCharacter::Attack()
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("Attack"));
GEngine->AddOnScreenDebugMessage(-1, 5.f, FColor::Red, TEXT("Attack"));
}
void AMyCharacter::CaclulateHealth()
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("CaclulateHealth"));
GEngine->AddOnScreenDebugMessage(-1, 5.f, FColor::Red, TEXT("CaclulateHealth"));
}
编译后,运行打印结果