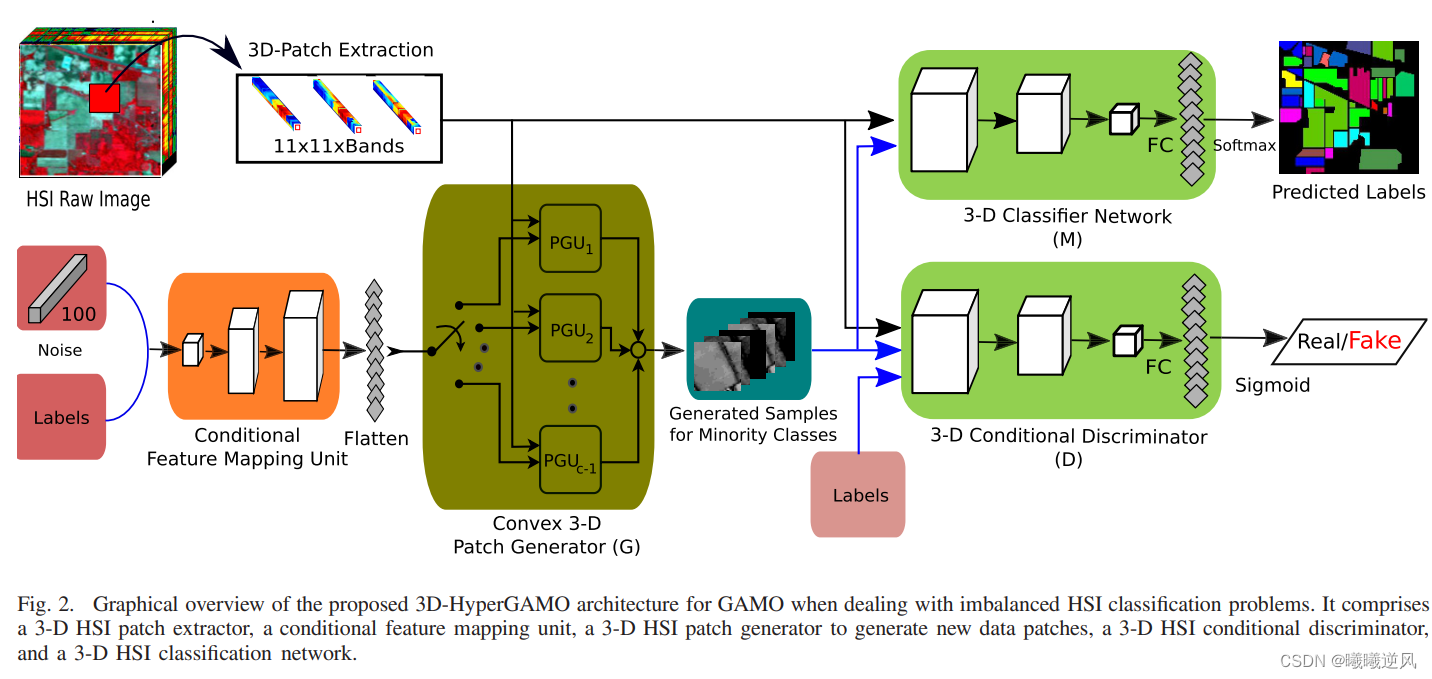
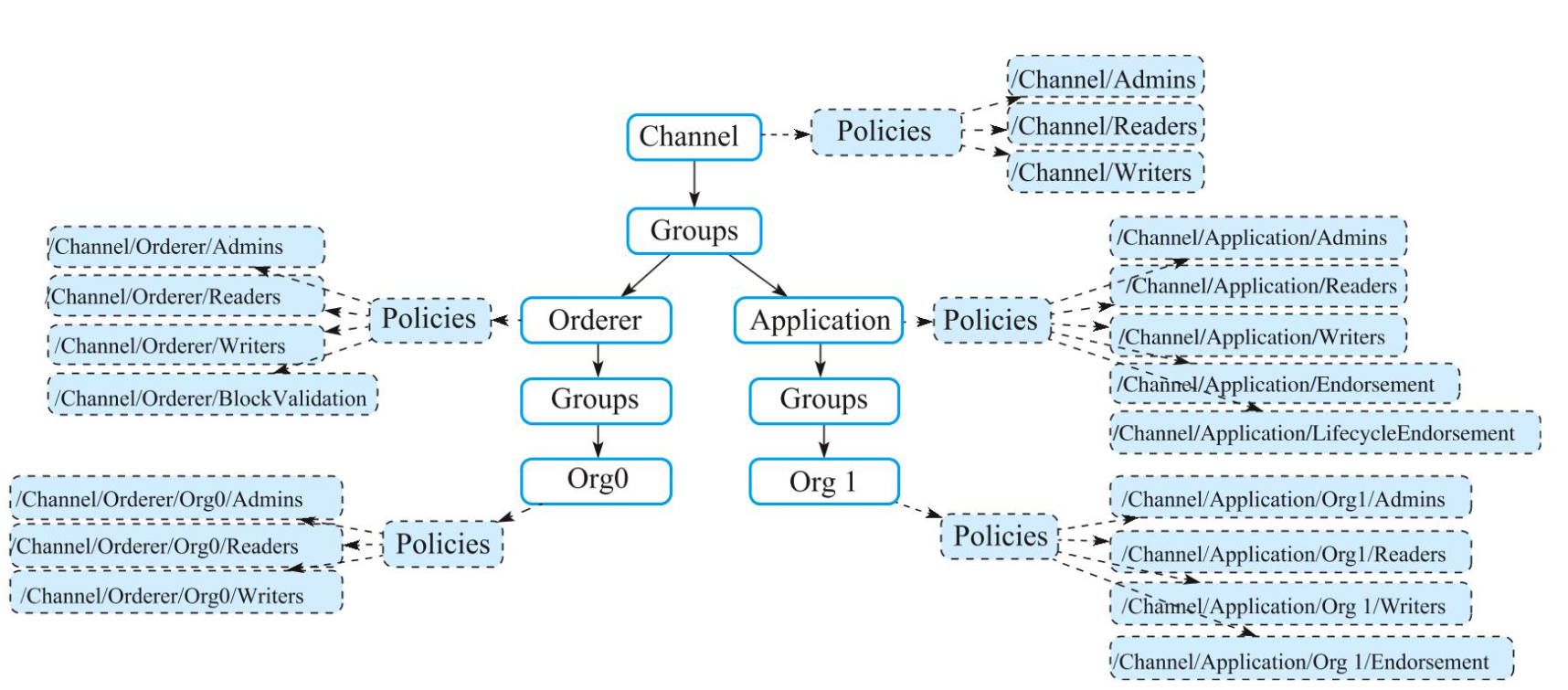
图的深度优先搜索
题目描述:
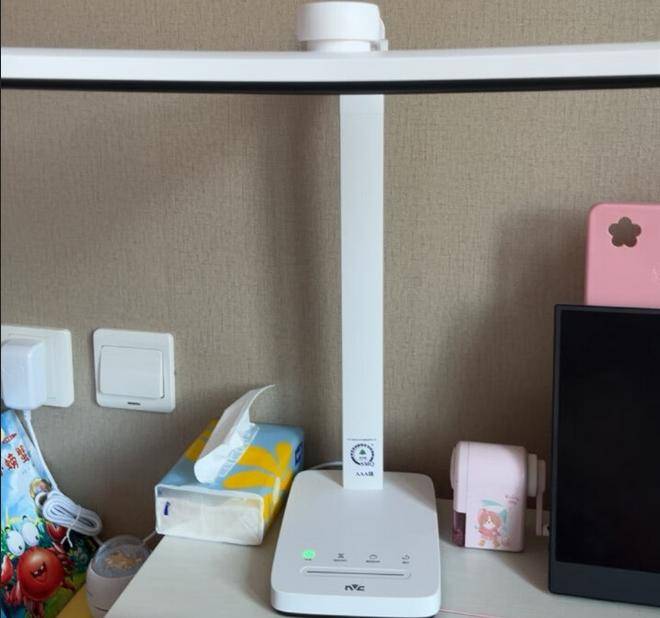
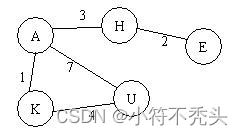
图的深度优先搜索类似于树的先根遍历,是树的先根遍历的推广。即从某个结点开始,先访问该结点,然后深度访问该结点的第一棵子树,依次为第二顶子树。如此进行下去,直到所有的结点都访问为止。在该题中,假定所有的结点以“A”至“Z”中的若干字符表示,且要求结点的访问顺序根据“A”至“Z”的字典顺序进行访问。例如有如下图:
如果要求从H开始进行深度优先搜索,则搜索结果为:H->A->K->U->E.
输入:
输入只包含一个测试用例,第一行为一个自然数n,表示顶点的个数,第二行为n个大写字母构成的字符串,表示顶点,接下来是为一个n*n大小的矩阵,表示图的邻接关系。数字为0表示不邻接,否则为相应的边的长度。
最后一行为一个字符,表示要求进行深度优先搜索的起始顶点。
输出:
用一行输出深度优先搜索结果,起始点为给定的顶点,各顶点之间用一个空格隔开(注意后面的提示)。
样例输入:
5
HUEAK
0 0 2 3 0
0 0 0 7 4
2 0 0 0 0
3 7 0 0 1
0 4 0 1 0
H
样例输出:
H A K U E
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
string str;
int a[26][26],book[26];
char c;
int main(){
cin >> n;
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++)
for(int j = 0;j < n;j ++)
cin >> a[str[i] - 'A'][str[j] - 'A'];
cin >> c;
stack<int> st;
st.push(c-'A');
book[c-'A'] = 1;
cout << c << ' ';
while(st.size()){
auto t = st.top();
st.pop();
if(!book[t])
cout << (char)(t + 'A') << " ";
book[t] = 1;
for(int i = 25;i >= 0;i --){
if(a[t][i] != 0 && book[i] == 0){
st.push(i);
}
}
}
return 0;
}