Vuex的环境搭建
-
Vuex是Vue实现集中式数据管理的Vue的一个插件,集中式可以理解为一个老师给多个学生讲课。
-
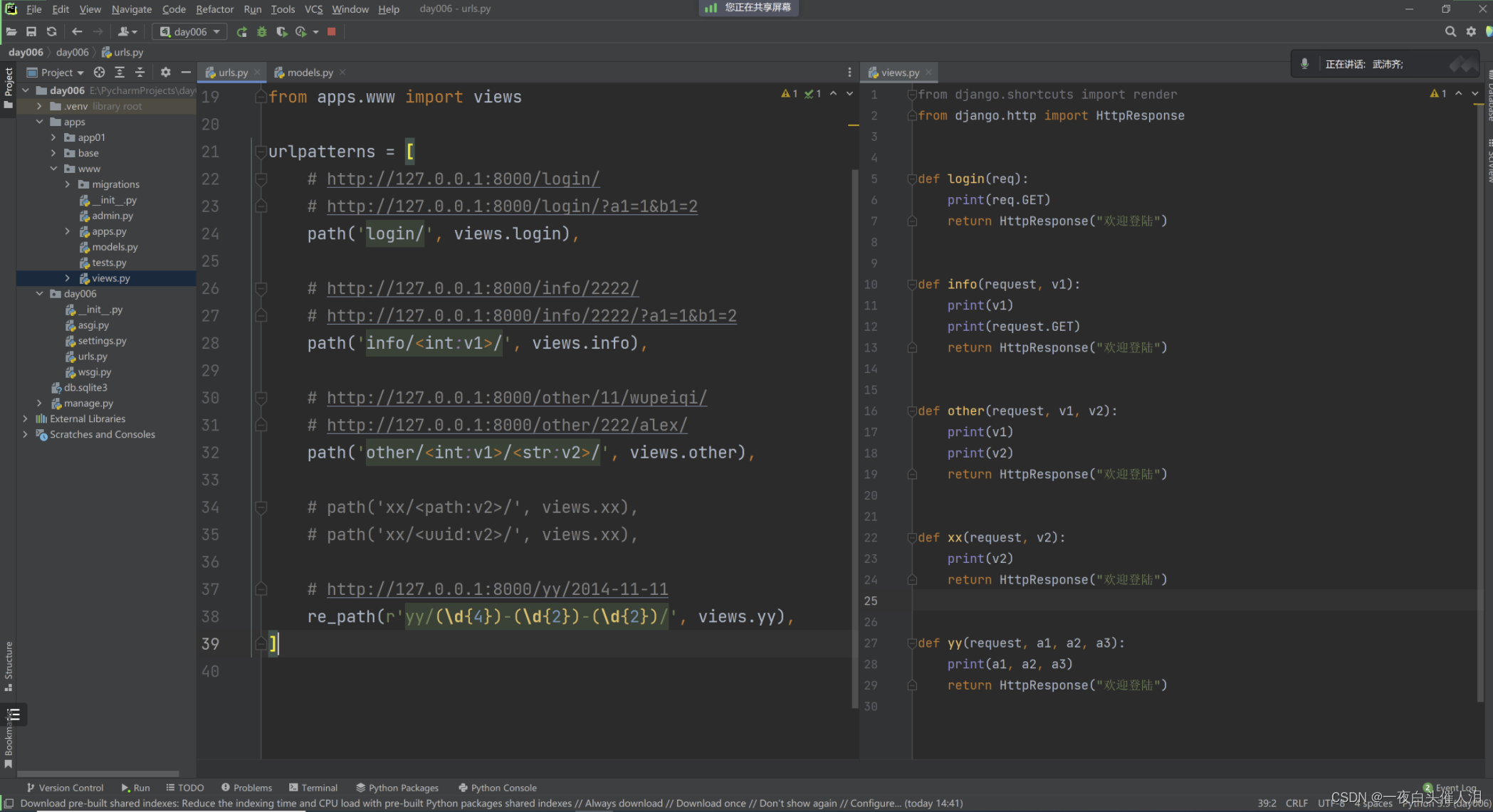
Vue2.0版本的安装:
-
npm i vuex@3 -
使用Vuex需要在store中的index.js引入Vuex和main.js中引入store,目的是让vm和vc都能看到$store。实现多个组件对数据集中式的管理(读/写)。
-
main.js文件
-
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' //正确的应用应该是Vuex插件使用后才能有store这个平台。但store创建完毕后Vuex插件还没有使用也就是Vue.use(Vuex)没运行在store创建之前,故将其放到store中的index.js中 import store from './store' new Vue({ router, // 引入之后要使用store,这里使用了缩写形式 store, render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app') -
操作Vuex要用到$store,故创建store文件和包含在store文件的index.js文件
-
import Vue from 'vue' // 在创建store之前,将Vuex配置完成 import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // 准备actions--用来响应组件中的动作 const actions = {} // 准备mutations--用于操作数据(state) const mutations = {} // 准备state--用于存储数据 const state = {} // 创建并暴露store export default new Vuex.Store({ // 下面的代码state:state可以缩写成state。 state:state, // getters:getters, mutations:mutations, actions:actions, // modules:modules, })
Vuex的原理分析及使用
-
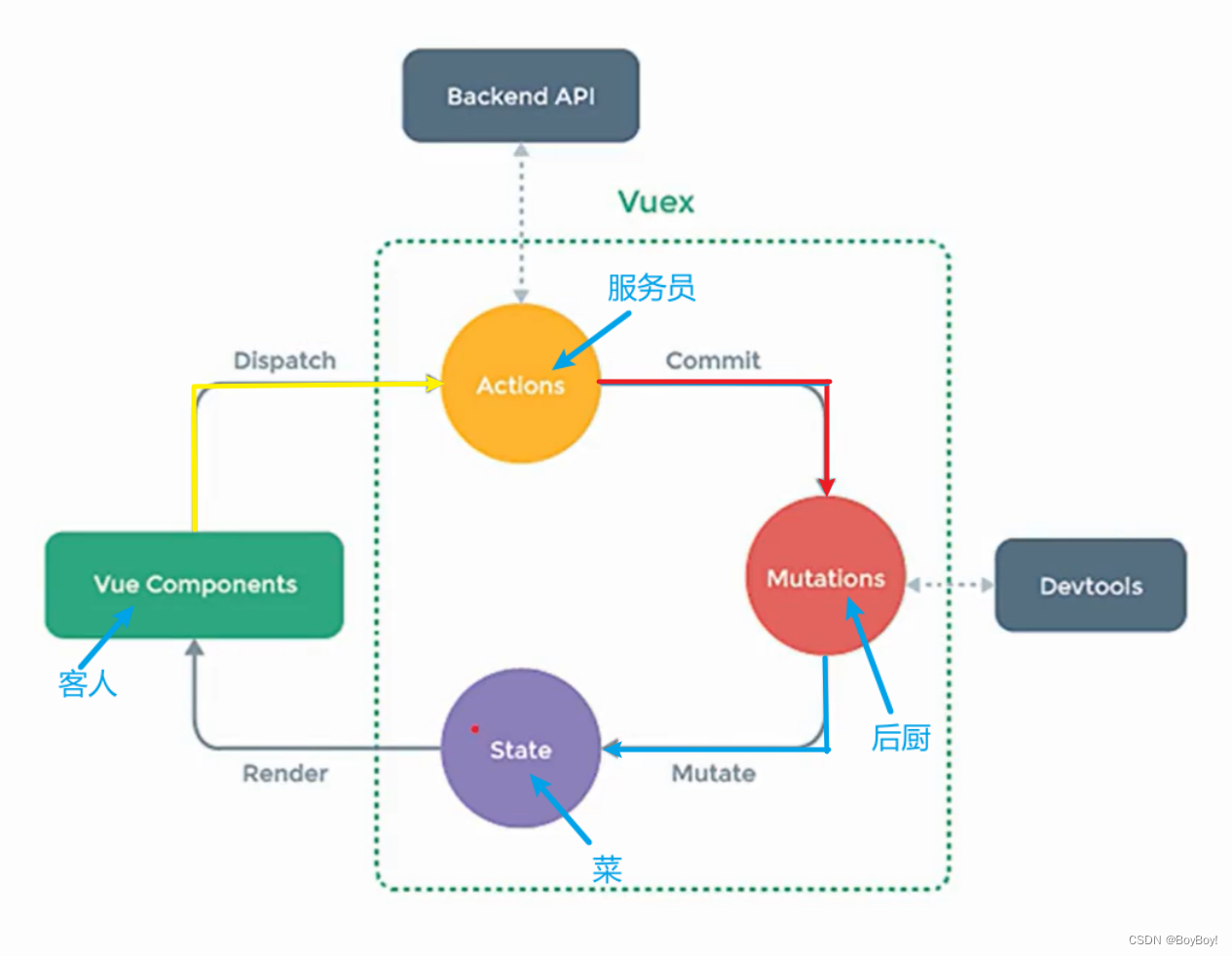
Vuex的原理分析:
1、黄线:从VueComponents(组件)出发,组件通过dispatch("key",value)函数将key(动作类型)和value(数据)传给Actions。Actions本质上是对象,Actions有一个和传过来的key相对应的key值而Action中的value是一个函数并且该函数会调用,将组件传过来的value值接收。
2、红线:Commit的作用和Dispatch一致,Mutations和Action不同的是,Mutations的value函数有State和value值(组件传过来的)
3、蓝线:Mutate为加工的意思,Mutate不是API不需要他传数据,因为Mutations已经有State的通信
4、灰线:Render将State中的数据重新渲染交给VueComponents
5、VueComponents可以调用commit函数直接将数据value传给Mutations。可以这样理解:客人和后厨很熟不需要经过服务员,后厨直接可以做菜
6、Backend API为后端的接口,组件传递的value值可以是从后端获取的value值。Devtools为开发者工具
7、Vuex是有一个store来管理Actions、Mutations、State。store为存储的意思
-
下面为Vuex的案例展示
-
案例目的:将sum变量作为共享数据,通过store操作Vuex实现数据的更新
-
MyFooter组件
-
<template> <div > <!-- 找到state --> <h1>当前的求和为:{{ $store.state.sum }}</h1> <select v-model.number="n"> <!-- value前面加入冒号将引号的内容将表达式解析,这样避免了选择数字Vue当成字符串 --> <!-- 也可以在select标签中v-model.number强制转换成数字 --> <option value="1">1</option> <option value="2">2</option> <option value="3">3</option> </select> <button @click="increment">+</button> <button @click="decrement">-</button> <button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数在加</button> <button @click="incrementWait">等等在加</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'MyFooter', data(){ return { n:1, sum:0 } }, methods:{ //increment和decrement没有业务要求,故可以直接省略服务员和后厨对话。 increment(){ // jia这个动作类型Actions要有对应。故去score的index.js配置 this.$store.dispatch('jia',this.n) // this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n) 直接commit和后厨对话,还要删除score的index.js中的jia和jian两个函数才能正常运行 }, decrement(){ this.$store.dispatch('jian', this.n) // this.$store.commit('JIAN', this.n) }, incrementOdd(){ //判断偶数的条件到store的index.js的actions中写 this.$store.dispatch('jiaOdd', this.n) }, incrementWait(){ this.$store.dispatch('jiaWait', this.n) } } } </script> <style lang="css"> button{ margin-left: 5px; } </style> -
store文件的index.js文件
-
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) // actions可以用于专门的写业务的逻辑。如:if() 理解:所有的要求跟服务员讲,后厨的地方闲人勿进 const actions = { // 可以缩写为jia(){}。jia()括号中context有上下文的意思,可以理解为小型的store。 jia:function(context,value){ console.log("actions中的jia可以使用了",context,value); // 调用commit函数。建议:写关于mutations的动作类型都改成大写 context.commit('JIA',value) }, jian(context,value){ context.commit('JIAN', value) }, //这里注意一下jiaOdd和JIA是不同的,不要固定的认为JIA的位置应该写成JIAODD。是jiaOdd和MyFooter中的incrementOdd函数中的jiaOdd对应,JIA和下面mutations中的JIA对应 jiaOdd(context,value){ if(context.state.sum %2 == 0){ context.commit("JIA", value) } }, jiaWait(context,value){ setTimeout(() => { context.commit("JIA",value) },5000) } } const mutations = { // 这里的方法名要是JIA才能正常运行, JIA(state,value){ console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用",state,value); // 实现jia函数的相加功能,JIA()中的state是一个对象和Vue中的data函数一样。如果要展示数据通过this.$store.state state.sum += value }, JIAN(state,value){ console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用", state, value); state.sum -= value } } const state = { // 定义sum变量 sum:0 } export default new Vuex.Store({ state:state, mutations:mutations, actions:actions, })