文章目录
- 图的遍历
- 深度优先遍历
- 思路
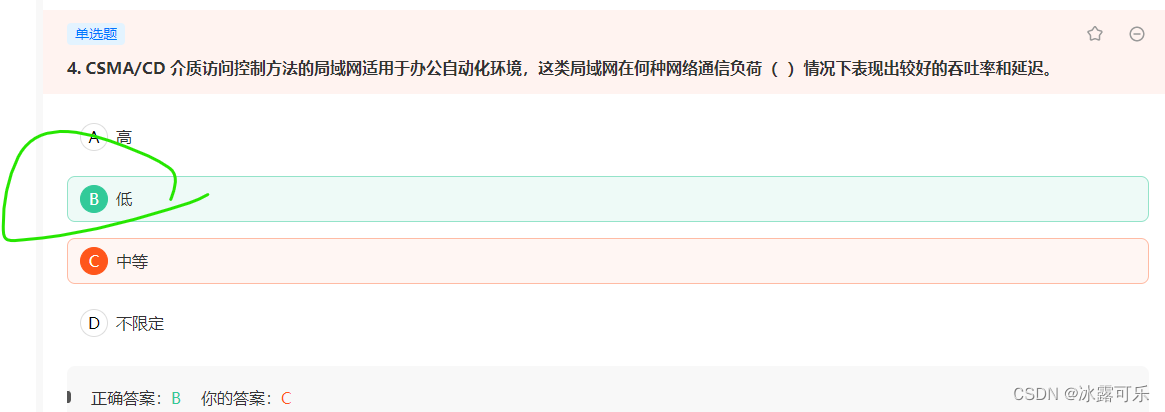
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
- 性能分析
- 广度优先遍历
- 思路
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
- 性能分析
- 源代码
图的遍历
**对有向图和无向图进行遍历是按照某种次序系统地访问图中的所有顶点, 并且使得每一个顶点只能访问一次. **
对于图的遍历需要解决掉两个问题:
- 如果存在回路/环的图, 会陷入死循环.
- 对于非连通图, 从一顶点出发, 不能到达所有其它的顶点.
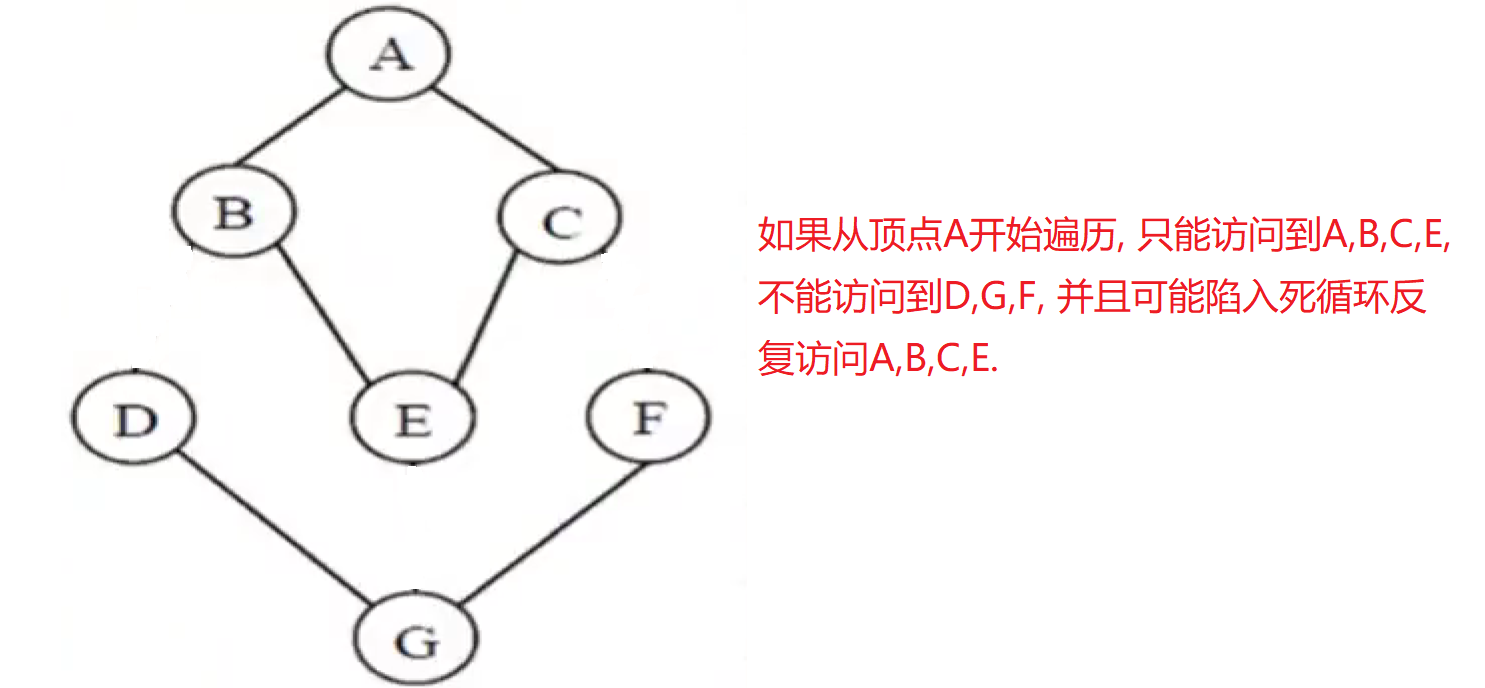
**解决方法: **
**为每一个顶点保留一个标志位数组visited, 算法开始时, 所有顶点的标志位都置为false. **
在遍历的过程中, 当某个顶点被访问时, 其标志位就可以被标记为已访问true.
深度优先遍历
思路
- 首先选定一个未被访问的顶点src, 访问此顶点并作已访问标志.
- 然后依次从src的未被访问的邻接顶点出发进行深度优先遍历图.
- 重复上述过程直至图中所有和src有路径想通的顶点都被访问到.
- 如果还有顶点未被访问, 再选取其它未被访问的顶点, 重复以上遍历过程, 直到图中所有的顶点都被访问过.
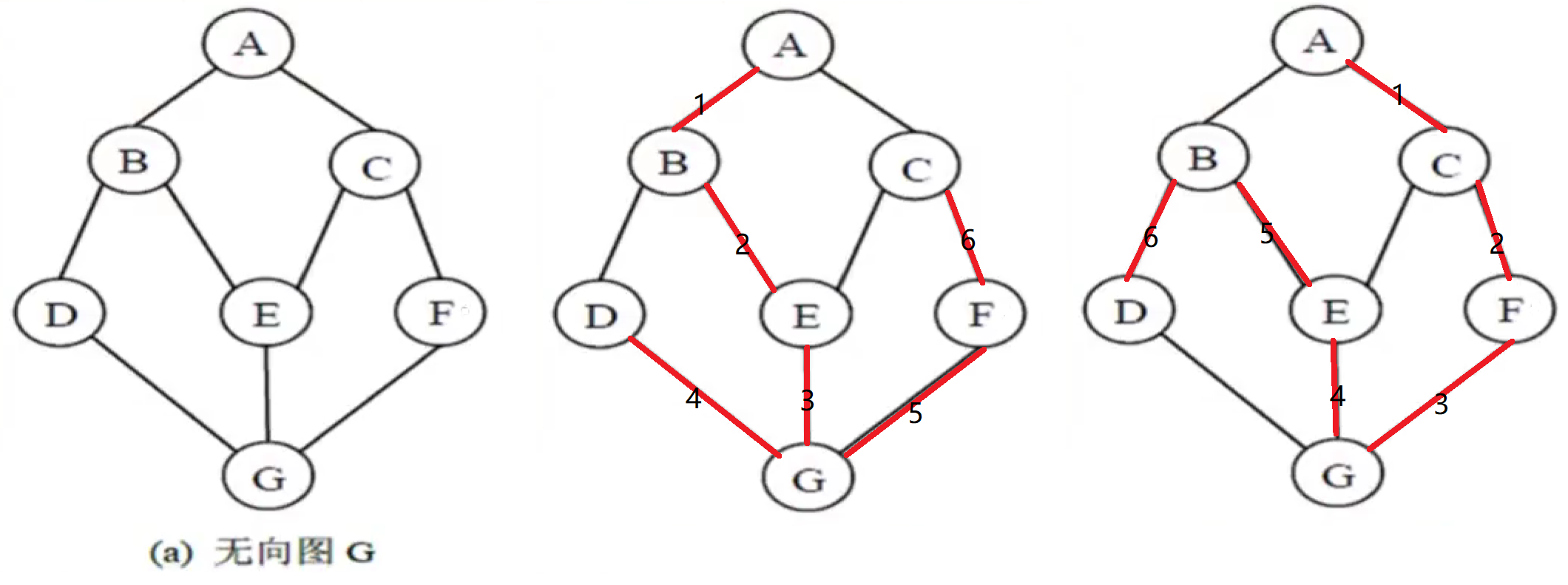
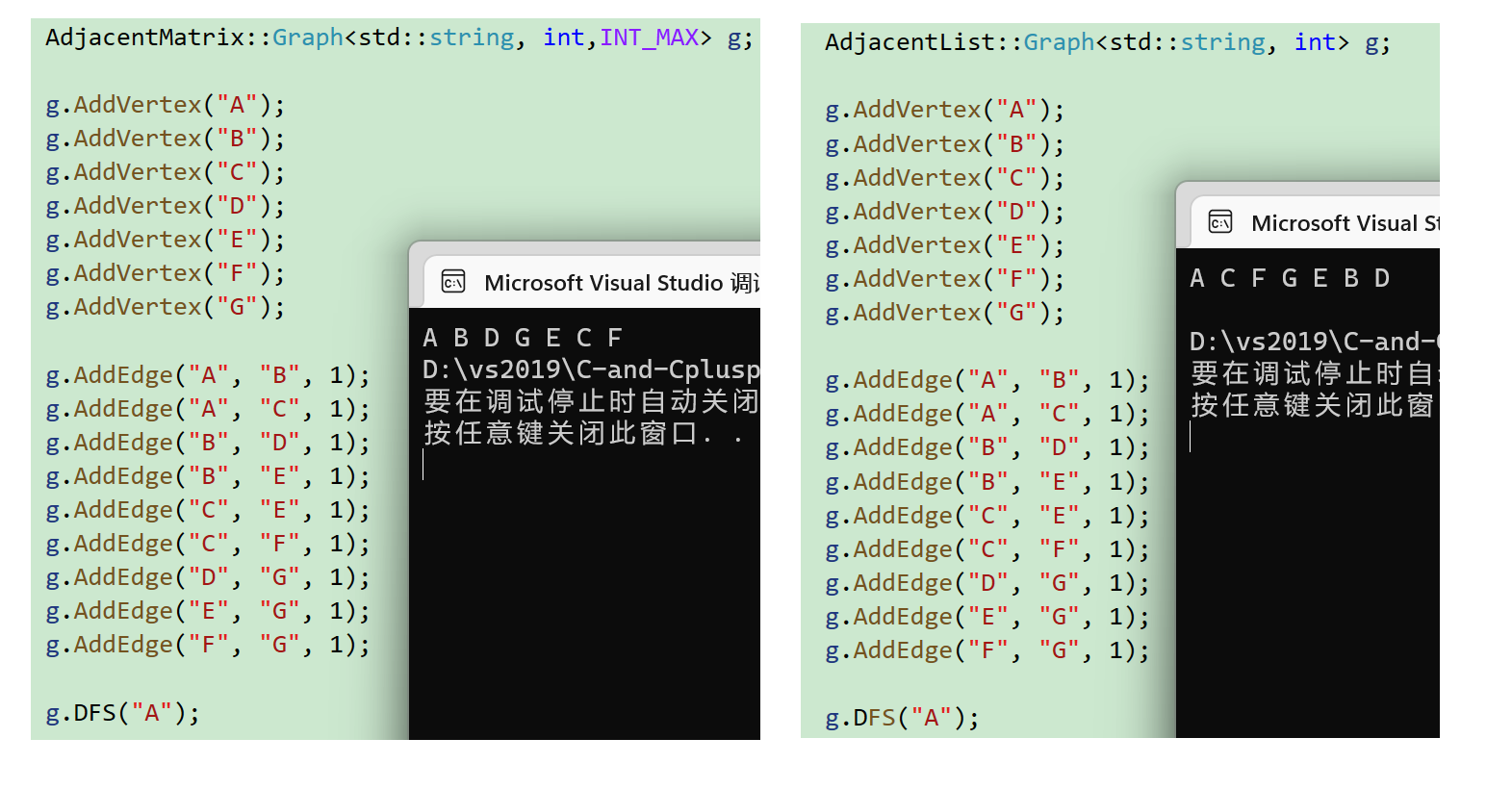
无向图G, 从顶点A出发, 一种可能的深度优先遍历: A,B,E,G,D,F,C. 另一种可能的深度优先遍历: A,C,F,G,E,B,D. 所以当存储结构和遍历算法不确定时, 其遍历结果可能不唯一.
邻接表
namespace AdjacentList
{
template<typename W>
struct Edge
{
int _dsti;
W _weight;
struct Edge<W>* _next;
Edge(int dsti, const W& weight)
:_dsti(dsti)
, _weight(weight)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<typename V, typename W, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
using Edge = Edge<W>;
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet; // 顶点的集合
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex; // 顶点映射下标
std::vector<Edge*> _table; // 出度边表
}
}

邻接矩阵
namespace AdjacentMatrix
{
template<typename V, typename W, W W_MAX, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet;
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex;
std::vector<std::vector<W>> _matrix;
}
}

性能分析
**设图G有n个顶点, e条边, 深度优先遍历算法将对图中所有的顶点和边进行访问, 因此它的时间代价和顶点数n及边弧数e是相关联的. **
若采用邻接表实现, 算法的时间复杂度为O(n+e).
若采用邻接矩阵实现, 算法的时间复杂度为O(n2).
广度优先遍历
思路
图的广度优先遍历类似树的层次遍历, 算法思想如下:
- 首先选定一个未被访问过的顶点src, 访问此顶点并作已访问标志.
- 然后依次访问与顶点src邻接的未被访问的全部邻接点, 然后从这些访问过的邻接点出发依次访问它们各自未被访问的邻接点, 并使"先被访问的顶点的邻接点"先于"后被访问的顶点的邻接点"被访问.
- 重复上述过程, 直至图中所有与顶点src有路径相连的顶点都被访问到.
- 若图中还有其他顶点未访问到, 则任选其中一个做源点, 继续进行广度优先遍历搜索, 直到访问完图中的所有顶点为止.
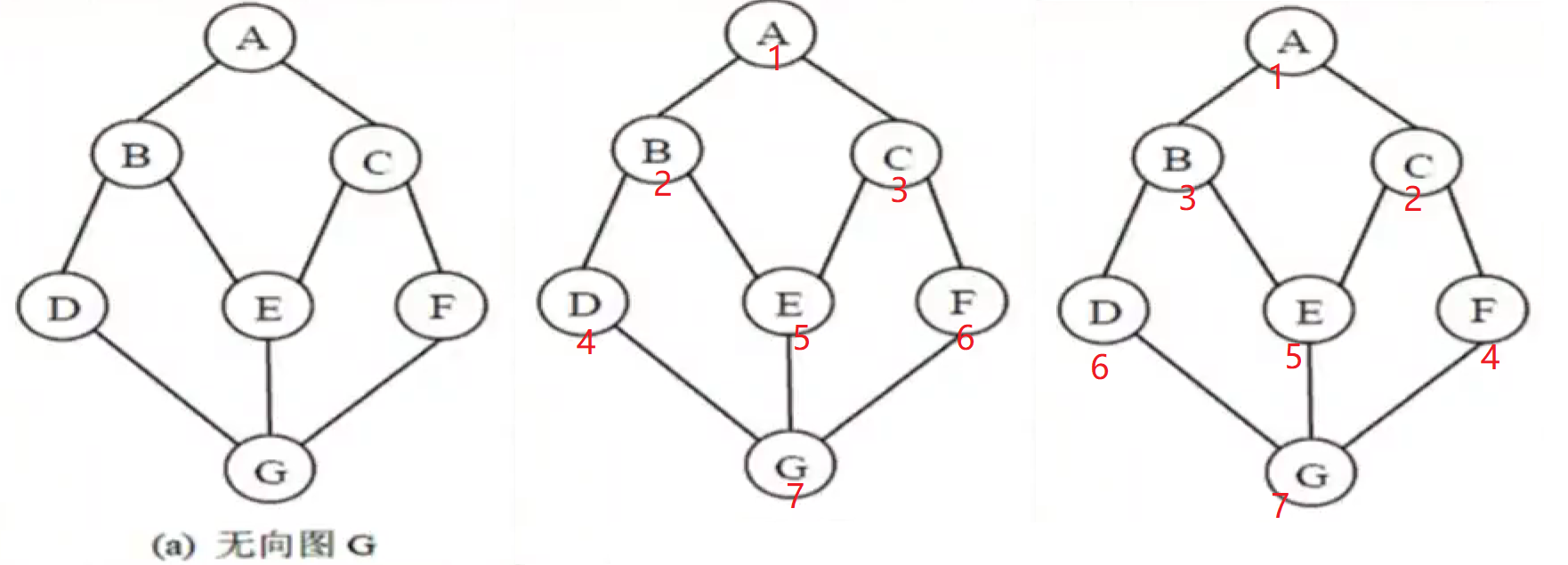
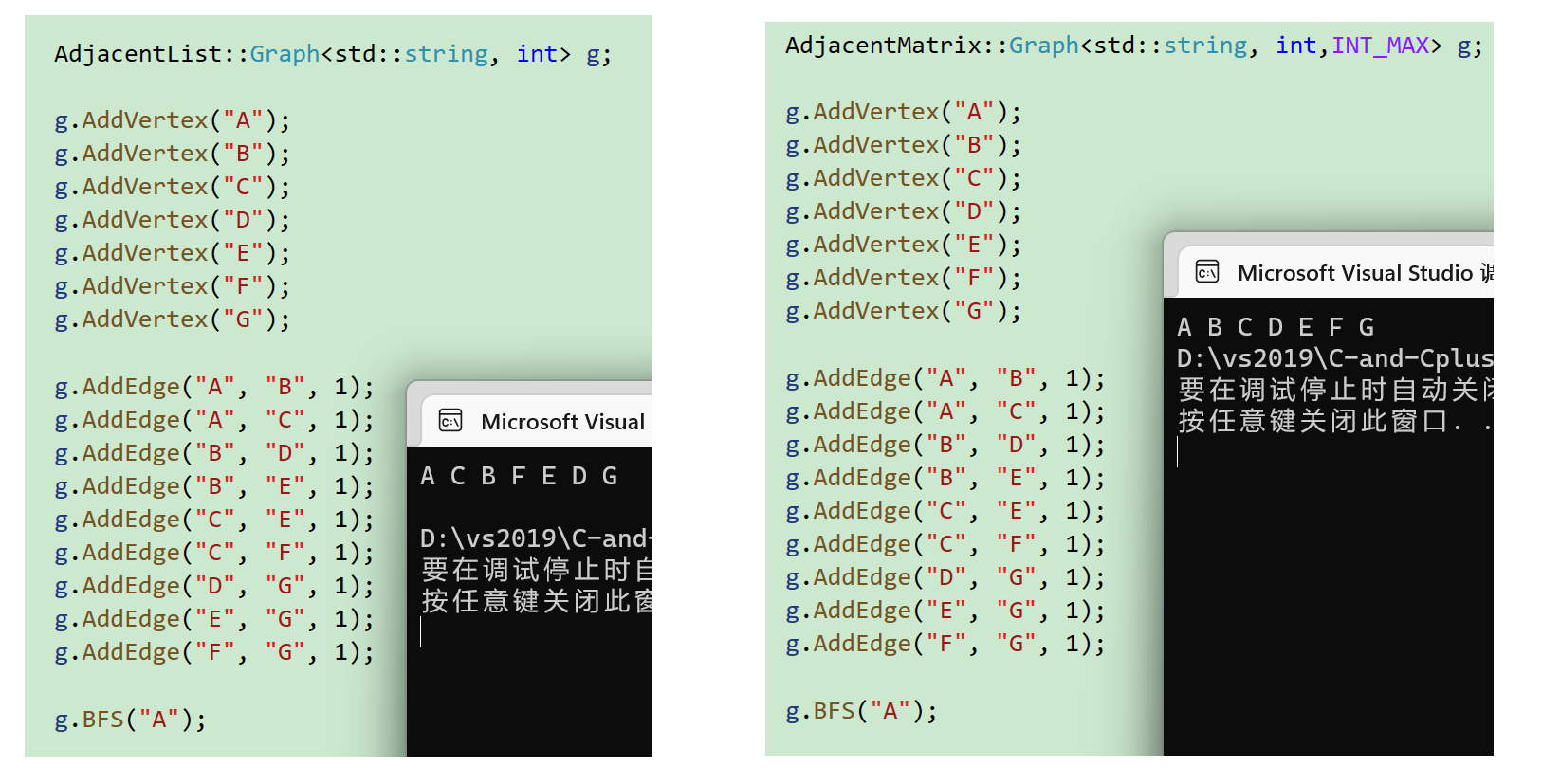
从顶点A出发一种可能的广度优先遍历序列: A,B,C,D,E,F,G.
从顶点A出发的另一种可能的广度优先遍历序列: A,C,B,F,E,D,G.
-
那么, 怎样才能实现如步骤2所指定的顶点的访问顺序呢?
-
这就需要借助队列来存放顶点的邻接点.
- 先将遍历的起始源点入队, 然后标记该顶点被访问过.
- 在队列不为空的情况下, 反复进行如下操作: 队头元素出队, 访问该队头元素顶点, 然后将该队头元素顶点的未被访问的邻接点入队, 并标记入队的顶点被访问过.直至队列为空.
- 如果图中还有未被访问的顶点, 说明图不是连通图, 则需要再选择任一未被访问过的顶点, 重复上述过程, 直到所有顶点都被访问过.

邻接表

邻接矩阵

性能分析
**设图G有n个顶点, e条边, 在广度优先遍历算法中, 每一个顶点都会进一次队列且只进一次, 同时每次要遍历每个顶点对应的链表中所有边表顶点一次, 因此若采用邻接表作为存储结构, 广度优先遍历的时间为O(n+e).若采用邻接矩阵作为存储结构, 则时间为O(n2), 而空间复杂度均为O(n). **
源代码
namespace AdjacentMatrix
{
template<typename V, typename W, W W_MAX, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet;
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex;
std::vector<std::vector<W>> _matrix;
public:
Graph() = default;
int GetVertexIndex(const V& v)
{
typename std::map<V, int>::iterator pos = _vertexIndex.find(v);
if (pos != _vertexIndex.end())
{
return pos->second;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
bool AddVertex(const V& v)
{
// 顶点存在不需要继续增加
if (GetVertexIndex(v) != -1)
return false;
_vertexSet.push_back(v);
_vertexIndex.insert(std::make_pair(v, _vertexSet.size() - 1));
// 先在原有的行上一列
for (int i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); i++)
{
_matrix[i].push_back(W_MAX);
}
// 增加一行
_matrix.push_back(std::vector<W>(_vertexSet.size(), W_MAX));
return true;
}
bool AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& weight)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
int dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
// 顶点不在图中,添加边失败
if (srci == -1 || dsti == -1)
return false;
_matrix[srci][dsti] = weight;
// 如果为无向图,则需要再添加一条dst->src的边
if (!Directed)
{
_matrix[dsti][srci] = weight;
}
return true;
}
void _BFS(int srci,vector<bool>& visited)
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(srci);
visited[srci] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
auto front = q.front();
q.pop();
std::cout << _vertexSet[front] << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()); i++)
{
if (_matrix[front][i] != W_MAX && !visited[i])
{
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
// 广度优先遍历
void BFS(const V& src)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
// 遍历源点不存在,不能进行遍历
if (srci == -1)
{
printf("输入的遍历源点不存在\n");
return;
}
vector<bool> visited(_vertexSet.size(), false);
_BFS(srci, visited);
// 避免非连通图的出现
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()); i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
_BFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
void _DFS(int srci, vector<bool>& visited)
{
std::cout << _vertexSet[srci] << " ";
visited[srci] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()); i++)
{
if (_matrix[srci][i] != W_MAX && !visited[i])
{
_DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
// 深度优先遍历
void DFS(const V& src)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
// 遍历源点不存在,不能进行遍历
if (srci == -1)
{
printf("输入的遍历源点不存在\n");
return;
}
vector<bool> visited(_vertexSet.size(), false);
_DFS(srci, visited);
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()); i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
_DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
};
}
int main(int, char**, char**)
{
AdjacentMatrix::Graph<std::string, int,INT_MAX> g;
g.AddVertex("A");
g.AddVertex("B");
g.AddVertex("C");
g.AddVertex("D");
g.AddVertex("E");
g.AddVertex("F");
g.AddVertex("G");
g.AddEdge("A", "B", 1);
g.AddEdge("A", "C", 1);
g.AddEdge("B", "D", 1);
g.AddEdge("B", "E", 1);
g.AddEdge("C", "E", 1);
g.AddEdge("C", "F", 1);
g.AddEdge("D", "G", 1);
g.AddEdge("E", "G", 1);
g.AddEdge("F", "G", 1);
g.DFS("A");
g.BFS("A");
return 0;
}
namespace AdjacentList
{
template<typename W>
struct Edge
{
int _dsti;
W _weight;
struct Edge<W>* _next;
Edge(int dsti, const W& weight)
:_dsti(dsti)
, _weight(weight)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<typename V, typename W, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
using Edge = Edge<W>;
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet; // 顶点的集合
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex; // 顶点映射下标
std::vector<Edge*> _table; // 出度边表
public:
Graph() = default;
int GetVertexIndex(const V& v)
{
typename std::map<V, int>::iterator pos = _vertexIndex.find(v);
if (pos != _vertexIndex.end())
{
return pos->second;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
bool AddVertex(const V& v)
{
if (GetVertexIndex(v) != -1)
return false;
_vertexSet.push_back(v);
_vertexIndex.insert(std::make_pair(v, _vertexSet.size() - 1));
_table.push_back(nullptr);
return true;
}
bool AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& weight)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
int dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
// 顶点不在图中,添加边失败
if (srci == -1 || dsti == -1)
return false;
Edge* edge = new Edge(dsti, weight);
// 头插
edge->_next = _table[srci];
_table[srci] = edge;
// 无向图
if (!Directed)
{
edge = new Edge(srci, weight);
edge->_next = _table[dsti];
_table[dsti] = edge;
}
return true;
}
void _DFS(int srci, vector<bool>& visited)
{
// 访问并标记已经访问过
std::cout << _vertexSet[srci] << " ";
visited[srci] = true;
// 遍历与顶点src相连的顶点
Edge* curr = _table[srci];
while (curr != nullptr)
{
// 只有与src相连并且没有被访问过的顶点才可以进行访问
if (!visited[curr->_dsti])
{
_DFS(curr->_dsti, visited);
}
curr = curr->_next;
}
}
// 深度优先遍历
void DFS(const V& src)
{
// err:
/*static const int N = _vertexSet.size();
bitset<_vertexSet.size()> bitMap;*/
// 标记顶点是否被访问过
vector<bool> visited(_vertexSet.size(),false);
this->_DFS(GetVertexIndex(src), visited);
// 检查是否还有顶点没有遍历过
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(visited.size()); i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
_DFS(i, visited);
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void _BFS(int srci, vector<bool>& visited)
{
queue<int> q;
// 只要入进队列了就可以标记访问过
q.push(srci);
visited[srci] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
auto front = q.front();
q.pop();
std::cout << _vertexSet[front] << " ";
// 遍历与src顶点相连的边
Edge* curr = _table[front];
while (curr != nullptr)
{
// 只有与src相连并且没有被访问过的顶点才可以进行访问
if (!visited[curr->_dsti])
{
q.push(curr->_dsti);
visited[curr->_dsti] = true;
}
curr = curr->_next;
}
}
}
// 广度优先遍历
void BFS(const V& src)
{
vector<bool> visited(_vertexSet.size(), false);
_BFS(GetVertexIndex(src), visited);
// 检查是否还有顶点没有遍历过
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(visited.size()); i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
_BFS(i, visited);
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
};
}
int main(int, char**, char**)
{
AdjacentList::Graph<std::string, int> g;
g.AddVertex("A");
g.AddVertex("B");
g.AddVertex("C");
g.AddVertex("D");
g.AddVertex("E");
g.AddVertex("F");
g.AddVertex("G");
g.AddEdge("A", "B", 1);
g.AddEdge("A", "C", 1);
g.AddEdge("B", "D", 1);
g.AddEdge("B", "E", 1);
g.AddEdge("C", "E", 1);
g.AddEdge("C", "F", 1);
g.AddEdge("D", "G", 1);
g.AddEdge("E", "G", 1);
g.AddEdge("F", "G", 1);
g.DFS("A");
g.BFS("A");
return 0;
}