1. 目标
完成大作业T2

作业提示:

多线程方法主要包括以下几种(参考博客):
- MPI(多主机多线程开发),
- OpenMP(为单主机多线程开发而设计)
- SSE(主要增强CPU浮点运算的能力)
- CUDA
- Stream processing,
之前已经了解过std::thread和pthread,拓展1中makeHessian使用的是p_thread,这次正好用这几种方法与p_thread进行对比。
1. OpenMP
1.1 简单介绍
- 并行计算变量,共享则无需声明,如果需要该变量在每个线程中不同,则需要声明为private,如下,计算img中各个pixel的颜色,x共享,但y每个线程独立,即每个线程单独处理一行,都从第0列开始处理。
- 线程的分配方式是顺序分配给所有核(core),如果多于核的个数,则再从第0个核开始分配。
- 语法,大概为两种,一种是普通代码的多线程,另一种是循环的多线程:
//普通多线程
#pragma omp parallel private(shared_var, tid)
{
related code
}
//多线程循环
#pragma omp parallel for private(y, tid)
//循环的代码
for(){
for()//二层循环等,不是必须
}
//多线程结束,其它代码
1.2 快速上手
根据tutorial的实验代码:
#include <cstdio>
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include <omp.h>//需要的头文件
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// This statement should only print once
printf("Starting Program!\n");
int nThreads, tid;
int shared_var = 200000;
int x,y;
int width=3, height=3;
#pragma omp parallel for private(y, tid)
for(x=0; x < height; x++)
{
for(y=0; y < width; y++)
{
tid = omp_get_thread_num();
printf("thread: %d, x: %d, y: %d\n", tid, x, y);
}
}
// We're out of the parallelized secion.
// Therefor, this should execute only once
printf("Finished!\n");
return 0;
}
Cmakelists:
find_package(OpenMP REQUIRED)
add_executable(test_OpenMP OpenMP/test_OpenMP.cpp)
target_link_libraries(test_OpenMP PUBLIC OpenMP::OpenMP_CXX)
实验结果:
关于private的探究:
y为共享:
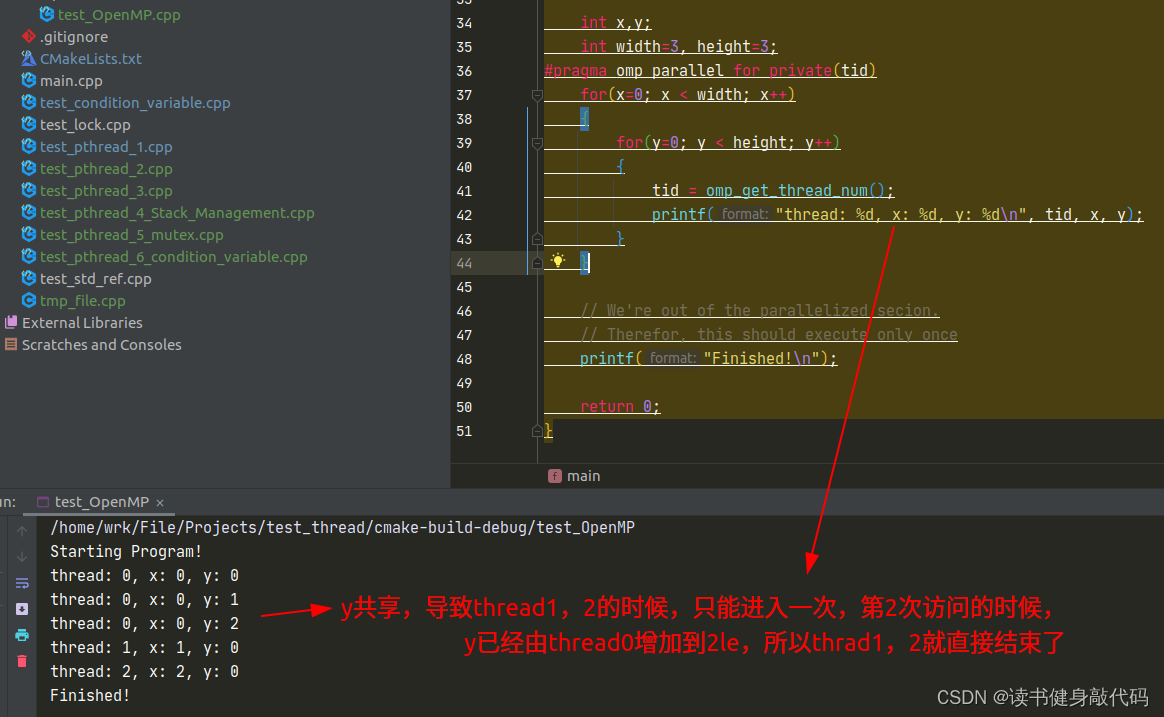
y为private

所以tutorial中的例程,意义是利用OpenMp多线程处理一张图片中的每一行,从每行的第0列开始处理:

for中线程的分配:
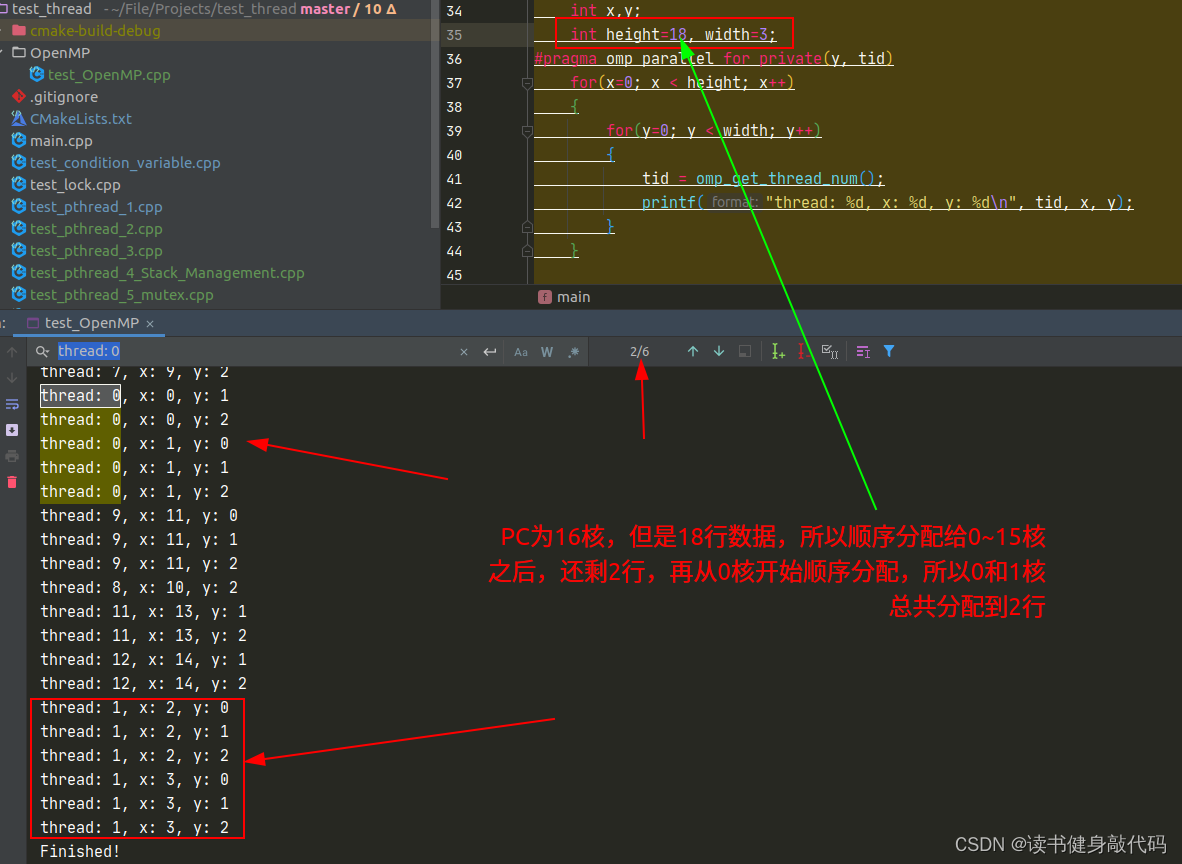
1.3 VINS-MONO移植
VINS-MONO中已经提供了pthread多线程和单线程makeHessian的方法,了解了OpenMP之后,我们需要使用单线程的方法,并告诉编译器使用OpenMP来进行,makeHessian代码如下:
void Solver::makeHessian()
{
int pos = 0;//Hessian矩阵整体维度
//it.first是要被marg掉的变量的地址,将其size累加起来就得到了所有被marg的变量的总localSize=m
//marg的放一起,共m维,remain放一起,共n维
for (auto &it : parameter_block_idx)
{
it.second = pos;//也算是排序1
pos += localSize(parameter_block_size[it.first]);//PQ7为改为6维
}
m = pos;//要被marg的变量的总维度
int tmp_n = 0;
//与[0]相关总维度
for (const auto &it : parameter_block_size)
{
if (parameter_block_idx.find(it.first) == parameter_block_idx.end())//将不在drop_set中的剩下的维度加起来,这一步实际上算的就是n
{
parameter_block_idx[it.first] = pos;//排序2
tmp_n += localSize(it.second);
pos += localSize(it.second);
}
}
n = pos - m;//remain变量的总维度,这样写建立了n和m间的关系,表意更强
ROS_DEBUG("\nn: %d, tmp_n: %d", n, tmp_n);
ROS_DEBUG("\nSolver, pos: %d, m: %d, n: %d, size: %d", pos, m, n, (int)parameter_block_idx.size());
TicToc t_summing;
Eigen::MatrixXd A(pos, pos);//总系数矩阵
Eigen::VectorXd b(pos);//总误差项
A.setZero();
b.setZero();
Hessian_.resize(pos,pos);
b_.resize(pos);
delta_x_.resize(pos);
//multi thread
TicToc t_thread_summing;
ROS_DEBUG("\nmulti thread: %s", MULTI_THREAD.c_str());
if(MULTI_THREAD=="pthread") {
pthread_t tids[NUM_THREADS];//4个线程构建
//携带每个线程的输入输出信息
ThreadsStruct threadsstruct[NUM_THREADS];
//将先验约束因子平均分配到4个线程中
int i = 0;
for (auto it : factors)
{
threadsstruct[i].sub_factors.push_back(it);
i++;
i = i % NUM_THREADS;
}
//将每个线程构建的A和b加起来
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
{
TicToc zero_matrix;
threadsstruct[i].A = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(pos,pos);
threadsstruct[i].b = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(pos);
threadsstruct[i].parameter_block_size = parameter_block_size;//marg里的block_size,4个线程共享
threadsstruct[i].parameter_block_idx = parameter_block_idx;
int ret = pthread_create( &tids[i], NULL, ThreadsConstructA ,(void*)&(threadsstruct[i]));//参数4是arg,void*类型,取其地址并强制类型转换
if (ret != 0)
{
ROS_WARN("pthread_create error");
ROS_BREAK();
}
}
//将每个线程构建的A和b加起来
for( int i = NUM_THREADS - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
pthread_join( tids[i], NULL );//阻塞等待线程完成,这里的A和b的+=操作在主线程中是阻塞的,+=的顺序是pthread_join的顺序
A += threadsstruct[i].A;
b += threadsstruct[i].b;
}
} else if(MULTI_THREAD=="openmp") {
//OpenMP多线程
#pragma omp parallel for
for(size_t k = 0; k < factors.size(); ++k) { // for (auto it : factors){
ResidualBlockInfo* it = factors[k];
//J^T*J
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); i++)
{
int idx_i = parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])];//要被marg的second=0
int size_i = localSize(parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[i])]);
Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_i = it->jacobians[i].leftCols(size_i);//remain变量的初始jacobian
for (int j = i; j < static_cast<int>(it->parameter_blocks.size()); j++)
{
int idx_j = parameter_block_idx[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])];
int size_j = localSize(parameter_block_size[reinterpret_cast<long>(it->parameter_blocks[j])]);
Eigen::MatrixXd jacobian_j = it->jacobians[j].leftCols(size_j);//marg变量的初始jacobian
//主对角线,注意这里是+=,可能之前别的变量在这个地方已经有过值了,所以要+=
if (i == j)
A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
//非主对角线
else
{
A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j) += jacobian_i.transpose() * jacobian_j;
A.block(idx_j, idx_i, size_j, size_i) = A.block(idx_i, idx_j, size_i, size_j).transpose();
}
}
b.segment(idx_i, size_i) += jacobian_i.transpose() * it->residuals;//J^T*e
}
// ROS_DEBUG("\nTotal number of threads: %d\n", omp_get_num_threads());
}
}
//统计multi thread makeHessian时间
double pure_finish_time = t_thread_summing.toc();
*pure_makeHessian_time_sum_ += pure_finish_time;
++(*pure_makeHessian_times_);
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_thread_summing cost: %f ms, avg_pure_makeHessian_time: %f ms, pure_makeHessian_time_sum_: %f, pure_makeHessian_times_: %f",
t_thread_summing.toc(), (*pure_makeHessian_time_sum_)/(*pure_makeHessian_times_), *pure_makeHessian_time_sum_, *pure_makeHessian_times_);
Hessian_ = A;
b_ = -b;
//DOGLEG需反解出J和e
if(method_==solve::Solver::kDOGLEG) {
TicToc t_solve_J;
TicToc t_SelfAdjoint;
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes2(A);//这一句24.3ms
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_SelfAdjoint cost: %f ms", t_SelfAdjoint.toc());
Eigen::VectorXd S = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array(), 0));
Eigen::VectorXd S_sqrt = S.cwiseSqrt();//开根号
linearized_jacobians = S_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().transpose();
Eigen::VectorXd S_inv = Eigen::VectorXd((saes2.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes2.eigenvalues().array().inverse(), 0));
Eigen::VectorXd S_inv_sqrt = S_inv.cwiseSqrt();
linearized_residuals = S_inv_sqrt.asDiagonal() * saes2.eigenvectors().real().transpose() * b;
ROS_DEBUG("\nt_solve_J cost: %f ms", t_solve_J.toc());//25ms
}
}
其中注意for循环的写法,OpenMP似乎只支持for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)这种类型的循环,使用
for(auto i t :factors)这种写法则编译不过。
实验发现,openmp makeHessian的精度可能比pthread差,查看原因是
ρ
\rho
ρ经常
<
0
<0
<0,怀疑Hessian精度问题。makeHessian的时间跟Hessian的稠密程度也有关,发散时的makeHessian速度也很快,因为非常稀疏。所以对makeHessian速度的对比需要在收敛的情况下进行。
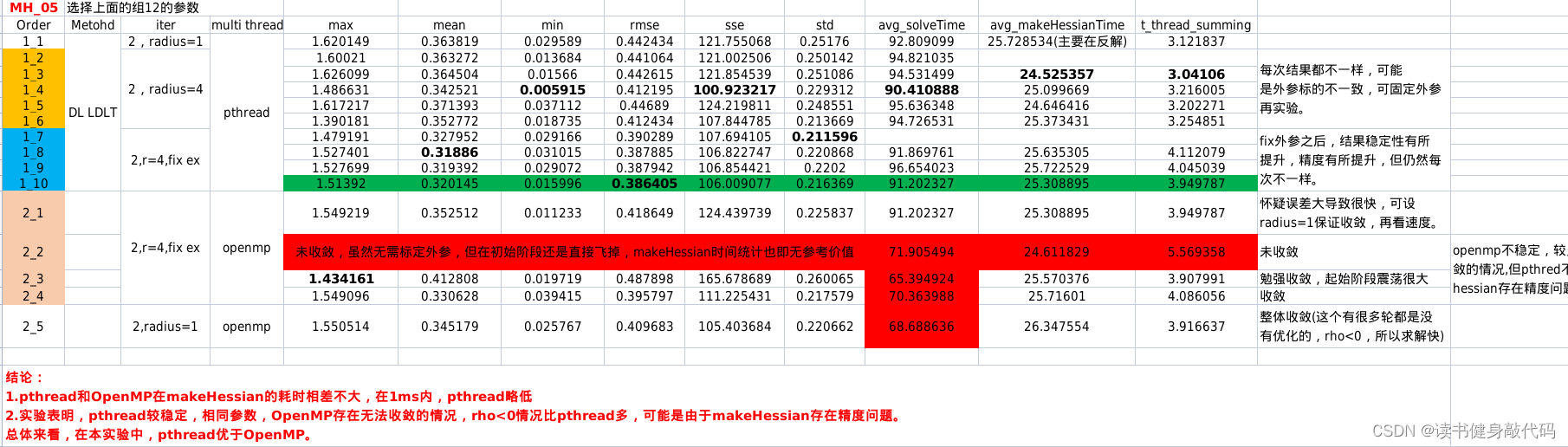
1.4 pthread与OpenMP对比
对比实验结果如下,倾向于使用pthread:
2. SSE
SSE 的指令集是 X86 架构 CPU 特有的,对于 ARM 架构、MIPS 架构等 CPU
是不支持的,所以使用了 SSE 指令集的程序,是不具备可移植标准的。而移动机器人平台
使用的 CPU 大多为了保证低功耗采用了 ARM 架构,所以这样的加速在移动机器人平台上
会失效。
大概看了下SSE的用法,如果需要用SSE,可能需要大改VINS0-MONO中的数据结构,有些不划算,暂不考虑。
3. CUDA
参考文章



![漫谈大模型的[幻觉]问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2811493988cb432dbfd13fc9c0fb8f8f.png)


![[JavaWeb玩耍日记] 数据库](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6e7e1a288b2147639760530781dc090f.png)