欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
往期相关背景半平面求交 点击前往
凸包点击前往
题目大意
题目链接
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2600
有一座山,可以用一条山的上方轮廓折线(x1, y1), (x2, y2), …. (xn, yn)来描述H村的形状,这里x1 < x2 < …< xn。瞭望塔可以建造在[x1, xn]间的任意位置, 但必须满足从瞭望塔的顶端可以看到山的任意位置。可见在不同的位置建造瞭望塔,所需要建造的高度是不同的。为了节省开支,村长希望建造的塔高度尽可能小。
解析
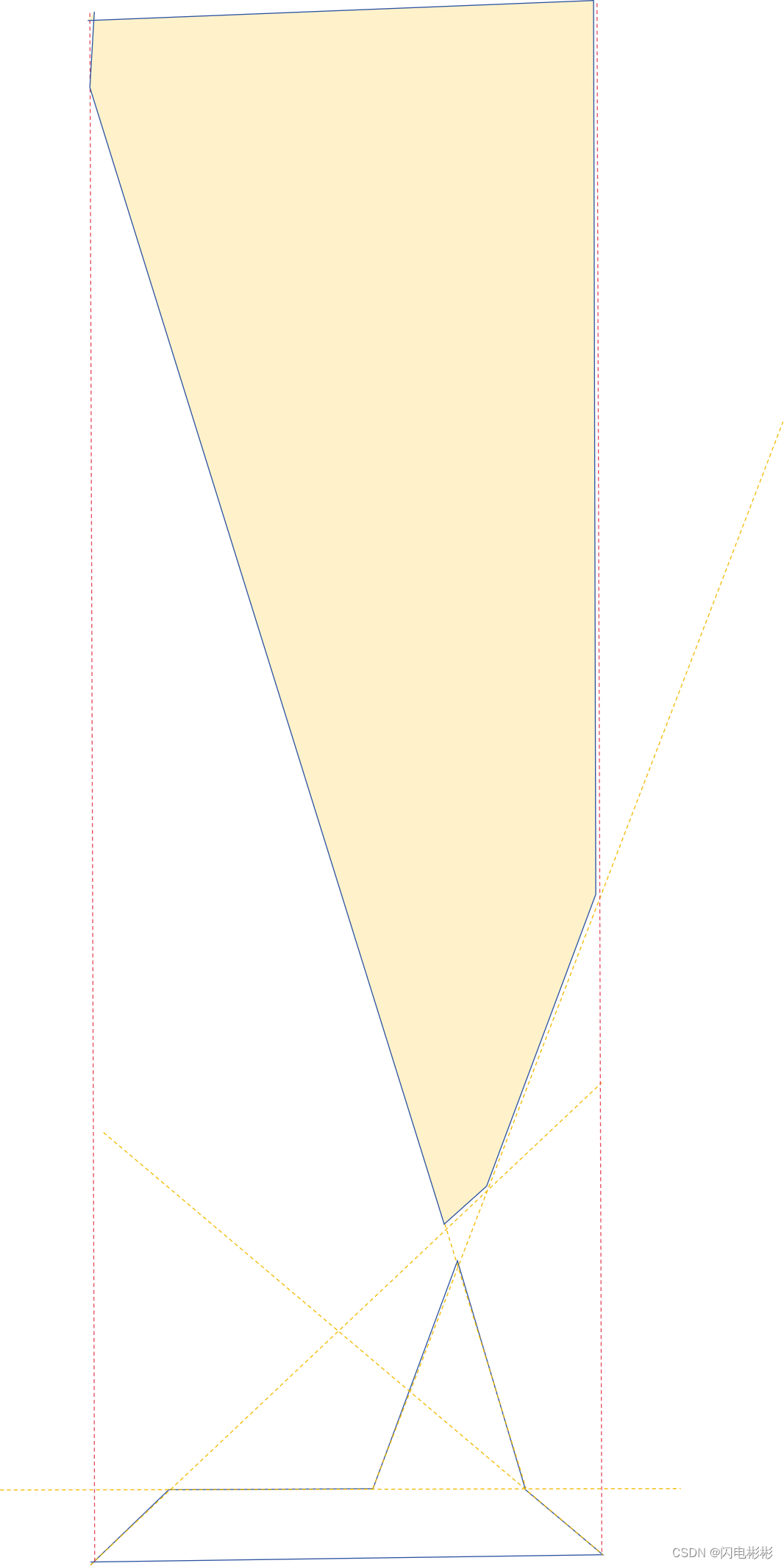
根据题意,可以看到山的任意地方的区域为所有山坡所在直线的半平面求交区域。即图中的黄色区域。2条红线是根据题意添加的辅助边,因为塔只能建在x1到xn以内。
现在要求塔的高度最小,也就是求黄色区域最下部分与山的最上部分之差最小。可以通过枚举黄色区域下方顶点找一遍,再通过山的顶点找一遍。
特殊情况只有1个点的时候直接返回0即可。
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-12;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
namespace FloatSys {
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d > 0)return 1;
return -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
int id;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), id(p.id) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%.3f %.3f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (abs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return abs(x - a.x) < EPS && abs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b, const Point& c) {
return cross(b - a, c - a);
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Line {
public:
Point front, tail;
double ang;
int u, v;
Line() {}
Line(const Point& a, const Point& b) :front(a), tail(b) {
ang = atan2(front.y - tail.y, front.x - tail.x);
}
void initAng() {
ang = atan2(front.y - tail.y, front.x - tail.x);
}
};
int cmp(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
//if (a.u == b.u && a.v == b.v)return 0;
return cmp(a.ang - b.ang);
}
// 点在直线哪一边>0 左边,<0边
double SideJudge(const Line& a, const Point& b) {
return cmp(cross(a.front - a.tail, b - a.tail));
//return cross(a.front - a.tail, b - a.tail);
}
int LineSort(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
int c = cmp(a, b);
if (c)return c < 0;
return cross(b.front - b.tail, a.front - b.tail) > 0;
}
/*
点p 到 p+r 表示线段1
点q 到 q+s 表示线段2
线段1 上1点用 p' = p+t*r (0<=t<=1)
线段2 上1点用 q' = q+u*s (0<=u<=1)
让两式相等求交点 p+t*r = q+u*s
两边都叉乘s
(p+t*r)Xs = (q+u*s)Xs
pXs + t*rXs = qXs
t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
同理,
u = (p-q)Xr/(sXr) -> u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
以下分4种情况:
1. 共线,sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr==0, 计算 (q-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t0,
计算(q+s-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t1,查看[t0, t1]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
如果t0>t1, 则比较[t1, t0]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
t0 = (q-p)*r/(r*r)
t1 = (q+s-p)*r/(r*r) = t0 + s · r / (r · r)
2. 平行sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr!=0
3. 0<=u<=1 && 0<=t<=1 有交点
4. 其他u, t不在0到范围内,没有交点。
*/
pair<double, double> intersection(const Point& q, const Point& s, const Point& p, const Point& r, bool& oneline) {
// 计算 (q-p)Xr
auto qpr = cross(q - p, r);
auto qps = cross(q - p, s);
auto rXs = cross(r, s);
if (cmp(rXs) == 0) {
oneline = true;
return { -1, -1 }; // 平行或共线
}
// 求解t, u
// t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
auto t = qps / rXs;
// u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
auto u = qpr / rXs;
return { u, t };
}
Point LineCross(const Line& a, const Line& b, bool& f) {
Point dira = a.front - a.tail;
Point dirb = b.front - b.tail;
bool oneline = false;
auto p = intersection(a.tail, dira, b.tail, dirb, oneline);
if (oneline)f = false;
return a.tail + dira * p.first;
}
class HalfPlane {
public:
vector<Line> lines;
void addLine(const Line& a) {
lines.push_back(a);
}
vector<Point> run() {
sort(lines.begin(), lines.end(), LineSort);
vector<int> q(lines.size() + 10);
vector<Point> t(lines.size() + 10);
int l = -1, r = 0;
q[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < lines.size(); ++i) {
if (cmp(lines[i], lines[i - 1]) == 0)continue;
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[i], t[r]) <= 0)r--;
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[i], t[l + 2]) <= 0)l++;
q[++r] = i;
bool f = true;
t[r] = LineCross(lines[q[r]], lines[q[r - 1]], f);
}
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[q[l + 1]], t[r]) < 0)r--;
/*if (r - l > 1) {
bool f = true;
t[r + 1] = LineCross(lines[q[l + 1]], lines[q[r]], f);
r++;
}*/
// 统计交点
l++;
vector<Point> ans(r - l);
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) {
ans[i] = t[i + l + 1];
}
return ans;
}
};
}
// 枚举p1,求取所有高度最低点
double getMinHigh(const vector<FloatSys::Point> &p1, const vector<FloatSys::Point>& p2) {
double minHigh = abs(p1[0].y - p2[0].y);
for (int j = 0, i = 1; i < p1.size(); ++i) {
while (p2[j + 1].x < p1[i].x)++j;
double p2y = (p1[i].x-p2[j].x) / (p2[j + 1].x - p2[j].x) * (p2[j + 1].y - p2[j].y) + p2[j].y;
minHigh = min(minHigh, abs(p2y - p1[i].y));
}
return minHigh;
}
void solve() {
using namespace FloatSys;
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector<Point> tangs(n);
int a;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a);
tangs[i].x = a;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a);
tangs[i].y = a;
}
if (n < 2) {
puts("0.000");
return;
}
HalfPlane hp;
// 添加辅助线
hp.addLine({ tangs[0], tangs[0] + Point(0, 1)});
hp.addLine({ tangs[n-1]+Point(0,1), tangs[n-1]});
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
hp.addLine({ tangs[i + 1], tangs[i] });
}
vector<Point> ps = hp.run();
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end());
printf("%.3f\n", min(getMinHigh(tangs, ps), getMinHigh(ps, tangs)));
}
int main() {
solve();
return 0;
}
/*
6
1 2 4 5 6 7
1 2 2 4 2 1
2
1 2
*/
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。