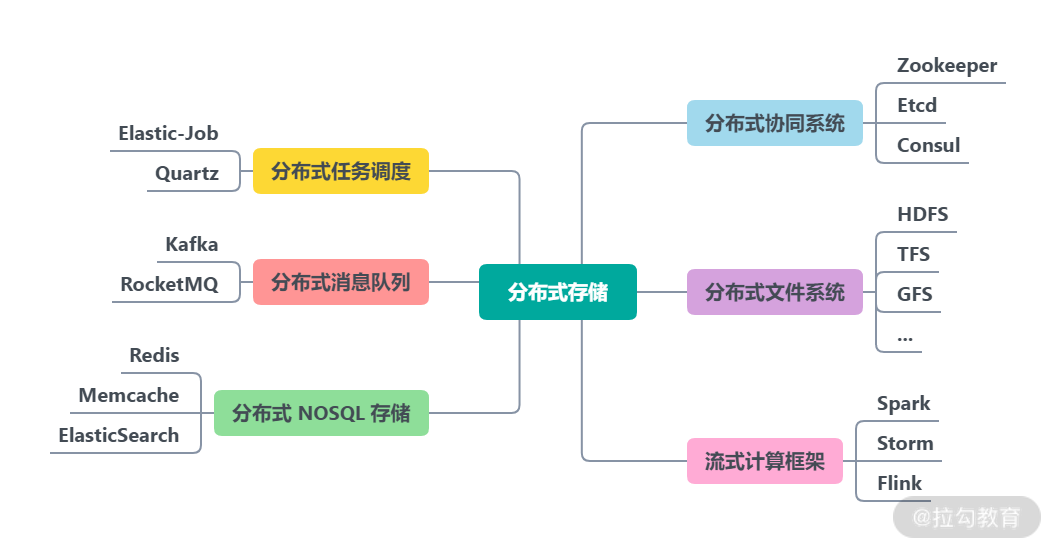
链表总结
- 增加表头元素
- 倒数节点,使用快慢指针
- 环形链表(快慢指针)
- 合并有序链表,归并排序
- LRU缓存
算法题
删除链表元素
删除链表中的节点
LeetCode237. 删除链表中的节点
复制后一个节点的值,删除后面的节点(1->5->3->4,删除5的话,先调整为1->3->3->4,再删除第二个3的节点)
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
LeetCode19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
快慢节点,使用虚拟节点,删除节点
当fast的next节点到了链表外,slow的next节点是第n个节点。找到slow的next节点,删除。
class Solution_LC19 {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode slow = dummy;
ListNode fast = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素
LeetCode83 删除排序链表中的重复元素
和当前节点比较值,相同则删掉,不同则下一个节点
class Solution_LC83 {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
int val = cur.val;
if (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素 II(**)
LeetCode82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
定义两个节点。cur节点是用来比较的节点,pre节点是用来删除的。找到cur节点,该节点和next节点不一致,
pre.next=cur,等于是删除了pre和cur之间的元素。
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
int x = cur.val;
if (cur.next.val == x) {
while (cur != null && cur.val == x) {
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = cur;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
旋转链表
反转链表
LeetCode206. 反转链表
头插法。pre和cur不断向后移动,直到cur为空,pre为最后一个节点(遍历顺序的最后一个)。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
K 个一组翻转链表
LeetCode25. K 个一组翻转链表
获取k个节点一组的链表
翻转链表
pre的后面一个节点是start,end的最后一个节点是next。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode end = dummy;
while (end.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k&&end!=null; i++) {
end = end.next;
}
if (end == null) {
break;
}
ListNode next = end.next;
ListNode start = pre.next;
end.next = null;
pre.next = reverse(start);
start.next = next;
pre = start;
end = start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
LeetCode61. 旋转链表
LeetCode61. 旋转链表.
获取链表的尾结点
尾结点连接头节点
找到切割点(切割点的前一个节点)
切割。获取next节点,将当前节点的next置为空,切断。
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (k == 0 || head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
int n = 1;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
n++;
}
int add = n - k % n;
if (add == n) {
return head;
}
cur.next = head;
while (add > 0) {
cur = cur.next;
add--;
}
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
return next;
}
}
交换链表节点
LeetCode24. 两两交换链表中的节点(⭐️高频)
LeetCode24. 两两交换链表中的节点
定义虚拟头结点
获取可以交换的节点,进行节点操作
将node1节点置为前置结点,进行下一轮操作
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
ListNode node1 = cur.next;
ListNode node2 = node1.next;
ListNode next = node2.next;
cur.next = node2;
node2.next = node1;
node1.next = next;
cur = node1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
环形/相交/回文链表
LeetCode141. 环形链表(腾讯)
LeetCode141. 环形链表(腾讯)
使用快慢指针,如果快指针最后到达慢指针,则存在环。
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
LeetCode142. 环形链表II
LeetCode142. 环形链表II.
快慢指针
a+b+n(b+c)=2(a+b) --> a=(n-1)(b+c)+c
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) {
ListNode node1 = head;
ListNode node2 = fast;
while (node1 != node2) {
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
return node1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
LeetCode160.相交链表
160. 相交链表
要进行临界值判断
相交的链表后面一段是公共的,a+b+c=c+b+a。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode p1 = headA;
ListNode p2 = headB;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1 == null ? headB : p1.next;
p2 = p2 == null ? headA : p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
LeetCode234. 回文链表
234. 回文链表
寻找中间节点,并反转前面列表
pre是反转链表的头结点,slow是后面链表的头结点。比较节点的值,判断是否回文
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//1-2-3-2-1
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = pre;
pre = slow;
slow = next;
}
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while (pre != null && slow != null) {
if (slow.val != pre.val) {
return false;
} else {
slow = slow.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return true;
}
}
链表合并
LeetCode2: 两数相加
LeetCode2: 两数相加
对应数位的值相加,计算当前节点以及向上的值。
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) {
int sum = (l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val) + (l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val) + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp;
l1 = l1 == null ? null : l1.next;
l2 = l2 == null ? null : l2.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
LeetCode445: 两数相加II
LeetCode445: 两数相加II
使用堆栈,用于顺序相反获取值
链表的拼接和上一题不同。上一题是不断往链表后面添加元素;这一题是不断往前面添加元素。
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode cur = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int sum = (stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop()) + (stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop()) + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tmp.next = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
}
LeetCode21: 合并两个有序链表
21. 合并两个有序链表
挨个遍历比较大小,是最容易想到的方案
使用递归。当
l1.val < l2.val,l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
cur.next = new ListNode(list1.val);
cur = cur.next;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
cur.next = new ListNode(list2.val);
cur = cur.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
} else {
cur.next = list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
LeetCode23: 合并K个排序链表
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
挨个遍历处理
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode ans = null;
for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
ans =mergeTwoLists(ans, lists[i]);
}
return ans;
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null || list2 == null) {
return list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
cur.next = new ListNode(list1.val);
cur = cur.next;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
cur.next = new ListNode(list2.val);
cur = cur.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
} else {
cur.next = list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
分治合并,将链表数组拆分成2段,处理好后合并。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return lists[l];
}
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null || list2 == null) {
return list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
cur.next = new ListNode(list1.val);
cur = cur.next;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
cur.next = new ListNode(list2.val);
cur = cur.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
} else {
cur.next = list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
使用优先队列
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//优先队列默认是小顶堆,最小的元素放在队头,即a-b
PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>((a, b) -> {
return a.val - b.val;
});
for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
if(lists[i]!=null){
priorityQueue.add(lists[i]);
}
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode listNode = priorityQueue.poll();
ListNode next = listNode.next;
cur.next = listNode;
cur = listNode;
if (next != null) {
priorityQueue.add(next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
LeetCode148: 排序链表
148. 排序链表
使用优先队列,最简单。
使用归并排序。做链表拆分。
可以和回文链表做比较,必须熟悉掌握两个链表合并的逻辑。
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode fast = head.next;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode listNode1 = sortList(head);
ListNode listNode2 = sortList(next);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur =dummy;
while (listNode1 != null && listNode2 != null) {
if (listNode1.val < listNode2.val) {
cur.next = listNode1;
cur = cur.next;
listNode1 = listNode1.next;
} else {
cur.next = listNode2;
cur = cur.next;
listNode2 = listNode2.next;
}
}
cur.next = listNode1 == null ? listNode2 : listNode1;
return dummy.next;
}
}
LRU缓存
LeetCode146. LRU 缓存
146. LRU 缓存
使用
LinkedHashMap,设置accessOrder为true,最近访问的元素会排在最后。而removeEldestEntry当条件满足的时候会移除最老的元素。
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> {
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
super(capacity, 0.75f, true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
return super.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
super.put(key, value);
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry) {
return size() > this.capacity;
}
}
使用Hash表和双向链表
双向链表记录访问顺序,Hash表获取元素
获取元素,将元素放在最前(移除当前元素在双向链表中的原位置,放在前面)。
存放元素,如果元素已存在,进行更新值,且将元素放在最前;如果元素不存在,添加元素要判断边界,超过边界要移除最早访问的元素(从链表和Hash表中移除)。
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> {
public class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int val;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {
}
public DLinkedNode(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> map = new HashMap<>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
size = 0;
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode dLinkedNode = map.get(key);
if (dLinkedNode == null) {
return -1;
} else {
moveToHead(dLinkedNode);
return dLinkedNode.val;
}
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
DLinkedNode next = head.next;
head.next = node;
node.prev = head;
node.next = next;
next.prev = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
DLinkedNode prev = node.prev;
DLinkedNode next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode prev = tail.prev;
removeNode(prev);
return prev;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
map.put(key, newNode);
addToHead(newNode);
size++;
if (size > capacity) {
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
map.remove(tail.key);
size--;
}
} else {
node.val = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
}