GitHub - LittleFox99/B_A_star: Bidirectional A Star
 其中a,b分别为双向A*搜索的权重
其中a,b分别为双向A*搜索的权重
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/11/11 1:21 下午
# @Author : LittleFox99
# File : a_star.py
# 参考:
# https://blog.csdn.net/lustyoung/article/details/105027607
# https://www.jianshu.com/p/5704e67f40aa
import numpy as np
import queue
from queue import PriorityQueue
from pylab import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class A_star:
def __init__(self, a, b, start, end, max_row, max_col, barrier_map):
"""
A_star 初始化
:param a:
:param b:
:param start:
:param end:
:param max_row:
:param max_col:
:param barrier_map:
"""
# 权重参数
self.a = a
self.b = b
# 起始点、终点
self.start = start
self.end = end
# 相遇点
self.stop_point = None
self.stop_point_back = None
#采用优先队列实现的小顶堆,用于存放待扩展结点,同时利用f值作为排序指标;
self.opened_list1 = PriorityQueue()
self.opened_list2 = PriorityQueue()
self.open_all_list = []
#储存记录所有走过的openlist
self.open_list = set()
#采用set(红黑树)实现,便于快速查找当前point是否存在于closed_list中;
self.closed_list1 = set()
self.closed_list2 = set()
# 地图边界
self.max_row = max_row
self.max_col = max_col
# 论文中设定为四个移动方向
self.direction = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]
# 障碍地图
self.barrier_map = barrier_map
#遍历结点数
self.travel_num = 0
def bound(self, row, col):
"""
边界条件检测:
1.如果该点坐标超出地图区域,则非法
2.如果该点是障碍,则非法
:param row:
:param col:
:return:
"""
if row < 0 or row > self.max_row:
return True
if col < 0 or col > self.max_col:
return True
if [row, col] in self.barrier_map:
return True
return False
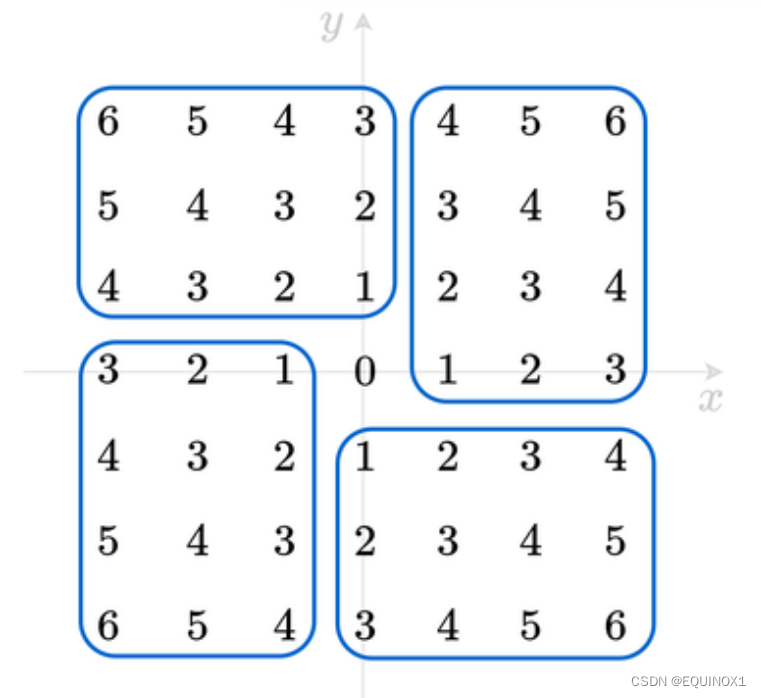
def euclidean_distance(self, point1, point2):
"""
欧式距离计算
:param point1:
:param point2:
:return:
"""
x_ = abs(point1.getx() - point2.getx())
y_ = abs(point1.gety() - point2.gety())
return ((x_**2)+(y_**2))**(0.5)*1.0
def find_path(self, point):
"""
用栈回溯查找B-A*给出的路径
:param point:
:return:
"""
stack = []
father_point = point
while father_point is not None:
stack.append(father_point.get_coordinate())
father_point = father_point.father
return stack
def heuristic_h(self, end_point, point1, point2):
"""
启发函数h值计算
h:正向搜索当前点n1到终点的欧式距离
h_:正向搜索当前点n1到反向搜索当前点n2的距离
:param end_point:
:param point1:
:param point2:
:return:
"""
h = self.euclidean_distance(point1, end_point)
h_ = self.euclidean_distance(point1, point2)
return (1 - self.b) * (h*1.0 / (1 + self.a) + self.a * h_*1.0 / (1 + self.a))
def heuristic_g(self, point):
"""
启发函数g值计算
g:当前点父亲的g值
g_:当前点到其父亲的欧式距离
:param point:
:return:
"""
g = point.father.g
g_ = self.euclidean_distance(point, point.father)
return self.b * (g + g_)*1.0
def heuristic_f(self, h, g):
# 计算启发式函数f值
return h + g
def compute_child_node(self, current_point, back_current_point, search_forward):
"""
遍历当前点的子节点
:param current_point: 当前点
:param back_current_point: 相反方向搜索的当前点
:param search_forward: 搜索方向设置,True为正向,反之亦然
:return:
"""
# 四个方向的遍历
for direct in self.direction:
col_index = current_point.gety() + direct[0]
row_index = current_point.getx() + direct[1]
# 创建子节点,将当前点设置为子节点的父节点
child_point = Point(row_index, col_index, current_point)
# 查找open_list中是否存在子节点中,用于备份节点
old_child_point = None
#前向搜索
if search_forward == True:
#计算子节点各个启发函数值
child_point.h = self.heuristic_h(self.end, current_point, back_current_point)
child_point.g = self.heuristic_g(child_point)
child_point.f = self.heuristic_f(child_point.h, child_point.g)
# 边界检测, 如果它不可通过或者已经在关闭列表中, 跳过
if (row_index, col_index) in self.closed_list1 or self.bound(row_index, col_index)==True:
continue
else:
self.travel_num = self.travel_num + 1
# 通过检测则将子节点加入openlist(记录所有加入过openlist的点)
self.open_list.add(child_point.get_coordinate())
# 找到最短路径
if (row_index, col_index) in self.closed_list2:
self.stop_point_back = self.search_back_point(child_point, self.open_all_list)
self.stop_point = child_point
if self.stop_point_back is None:
self.stop_point_back = self.stop_point
print("forward!")
return True
"""
如果可到达的节点存在于OPEN1列表中,称该节点为x点,计算经过n1点到达x点的g1(x)值,
如果该g1(x)值小于原g1(x)值,则将n1点作为x点的父节点,更新OPEN1列表中的f1(x)和g1(x)。
"""
tmp_queue = [] # opened_list的备份
while not self.opened_list1.empty():
tmp_point = self.opened_list1.get()
if child_point.get_coordinate() == tmp_point.get_coordinate(): #找到x点,跳过
old_child_point = tmp_point
continue
tmp_queue.append(tmp_point)
while len(tmp_queue) != 0:
self.opened_list1.put(tmp_queue.pop())
if old_child_point is None: #如果没找到,直接加入子节点
self.opened_list1.put(child_point)
else:
# 找到x点
# 用g值为参考检查新的路径是否更好。更低的g值意味着更好的路径。
if old_child_point.g > child_point.g:
self.opened_list1.put(child_point)
else:
# print(2)
self.opened_list1.put(old_child_point)
# print(2)
# 反向搜索,同理如上
else:
# 边界检测, 如果它不可通过或者已经在关闭列表中, 跳过
child_point.h = self.heuristic_h(self.start, current_point, back_current_point)
child_point.g = self.heuristic_g(child_point)
child_point.f = self.heuristic_f(child_point.h, child_point.g)
if (row_index, col_index) in self.closed_list2 or self.bound(row_index, col_index):
continue
else:
self.travel_num = self.travel_num + 1
self.open_list.add(child_point.get_coordinate())
# 找到最短路径
if (row_index, col_index) in self.closed_list1:
# self.stop_point_back = self.search_father_point(child_point,self.opened_list2)
self.stop_point_back = self.search_back_point(child_point, self.open_all_list)
self.stop_point = child_point
if self.stop_point_back is None:
self.stop_point_back = self.stop_point
print("backward!")
return True
tmp_queue = []
while not self.opened_list2.empty():
tmp_point = self.opened_list2.get()
if child_point.get_coordinate() == tmp_point.get_coordinate():
old_child_point = tmp_point
continue
tmp_queue.append(tmp_point)
while len(tmp_queue) != 0:
self.opened_list2.put(tmp_queue.pop())
if old_child_point is None: #open_list没有找到子节点,则将
self.opened_list2.put(child_point)
else:
# 用g值为参考检查新的路径是否更好。更低的G值意味着更好的路径。
if old_child_point.g > child_point.g:
self.opened_list2.put(child_point)
else:
self.opened_list2.put(old_child_point)
# print(3)
return False
def search_back_point(self, point, opened_list):
back_point = None
while len(opened_list)!=0:
tmp_point = opened_list.pop()
if point.get_coordinate() == tmp_point.get_coordinate():
return tmp_point
return back_point
def search(self):
# 将起始点s设置为正向当前结点n1、终点e设置为反向当前结点n2
current_point1 = self.start
current_point2 = self.end
# 并加入open1、open2
self.opened_list1.put(current_point1)
self.opened_list2.put(current_point2)
forward_path, backward_path =None, None
# opened_list1与opened_list2全部非空,输出寻路提示失败
find_stop = False
min_f_point1 = self.opened_list1.get()
self.closed_list1.add((min_f_point1.getx(), min_f_point1.gety()))
min_f_point2 = self.opened_list2.get()
self.closed_list2.add((min_f_point2.getx(), min_f_point2.gety()))
while True:
# # 取出open_list1中f值最小的点,加入closed_list1
# 将其作为当前结点,遍历寻找它的子节点
# min_f_point1 = self.opened_list1.get()
# self.closed_list1.add((min_f_point1.getx(), min_f_point1.gety()))
self.open_all_list.append(current_point1)
self.open_all_list.append(current_point2)
find_stop = self.compute_child_node(current_point1, current_point2, True)
if find_stop:
# forward_path = self.find_path(current_point1)
forward_path = self.find_path(self.stop_point)
backward_path = self.find_path(self.stop_point_back)
break
# min_f_point1 = self.opened_list1.get()
# print(1)
min_f_point1 = self.opened_list1.get()
# self.open_all_list.append(min_f_point1)
self.closed_list1.add((min_f_point1.getx(), min_f_point1.gety()))
current_point1 = min_f_point1
self.open_all_list.append(current_point1)
# 取出open_list1中f值最小的点,加入closed_list1
# current_point1 = self.opened_list1.get()
find_stop = self.compute_child_node(current_point2, current_point1, False)
if find_stop:
forward_path = self.find_path(self.stop_point)
backward_path = self.find_path(self.stop_point_back)
# backward_path = self.find_path(self.stop_point)
break
# min_f_point2 = self.opened_list2.get()
min_f_point2 = self.opened_list2.get()
# self.open_all_list.append(min_f_point1)
self.closed_list2.add((min_f_point2.getx(), min_f_point2.gety()))
current_point2 = min_f_point2
if self.opened_list1.qsize() == 0 or self.opened_list2.qsize() == 0:
break
# current_point2 = self.opened_list2.get()
if backward_path==None and forward_path==None:
print("Fail to find the path!")
return None
else:
forward_path = forward_path + backward_path
return forward_path, self.open_list, self.stop_point, self.travel_num
class Point:
"""
Point——地图上的格子,或者理解为点
1.坐标
2.g,h,f,father
"""
def __init__(self, x, y, father):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.g = 0
self.h = 0
self.f = 0
self.father = father
# 用于优先队列中f值的排序
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.f < other.f
# 获取x坐标
def getx(self):
return self.x
# 获取y坐标
def gety(self):
return self.y
# 获取x, y坐标
def get_coordinate(self):
return self.x, self.y
def draw_path(max_row, max_col, barrier_map, path=None, openlist=None, stop_point=None, start=None ,end=None):
"""
画出B-A*算法的结果模拟地图
:param max_row:地图x最大距离
:param max_col:地图y最大距离
:param barrier_map:障碍地图
:param path:B-A*给出的较优路径
:param openlist:B-A*中的openlist
:param stop_point:B-A*中的相遇结点
:param start:起始点
:param end:终点
:return:
"""
"""划分数组的x,y坐标"""
barrier_map_x = [i[0] for i in barrier_map]
barrier_map_y = [i[1] for i in barrier_map]
path_x = [i[0] for i in path]
path_y = [i[1] for i in path]
open_list_x = [i[0] for i in openlist]
open_list_y = [i[1] for i in openlist]
"""对画布进行属性设置"""
# plt.subplot(2, 2, subplot)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15)) # 为了防止x,y轴间隔不一样长,影响最后的表现效果,所以手动设定等长
plt.xlim(-1, max_row)
plt.ylim(-1, max_col)
my_x_ticks = np.arange(0, max_row, 1)
my_y_ticks = np.arange(0, max_col, 1)
plt.xticks(my_x_ticks) # 竖线的位置与间隔
plt.yticks(my_y_ticks)
plt.grid(True) # 开启栅格
"""画图"""
plt.scatter(barrier_map_x, barrier_map_y, s=500, c='k', marker='s')
plt.scatter(open_list_x, open_list_y, s=500, c='cyan', marker='s')
plt.scatter(path_x, path_y,s=500, c='r', marker='s')
plt.scatter(stop_point.getx(), stop_point.gety(), s=500, c='g', marker='s')
plt.scatter(start.getx(),start.gety(),s=500, c='b', marker='s')
plt.scatter(end.getx(), end.gety(), s=500, c='b', marker='s')
plt.title("Bidirectiional A Star , a = {}, b = {}".format(a, b))
print(path)
plt.savefig("result_pic/a_{},b_{}.png".format(a, b))
plt.show()
def draw_arg(travel_num, path_num, a_list, b_list):
markes = ['-o', '-s', '-^', '-p', '-^','-v']
travel_num = np.array(travel_num)
path_num = np.array(path_num)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(15,12))
for i in range(0, 6):
ax[0].plot(a_list, travel_num[i*6:(i+1)*6], markes[i],label=b_list[i])
ax[0].set_ylabel('Travel num')
ax[1].plot(a_list, path_num[i*6:(i+1)*6], markes[i],label=b_list[i])
ax[1].set_xlabel('The values of a')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Path nun')
ax[0].set_title('the two args of B-A*')
box = ax[1].get_position()
ax[1].set_position([box.x0, box.y0, box.width, box.height])
ax[1].legend(loc='right', bbox_to_anchor=(1.1, 0.6), ncol=1, title="b")
plt.savefig("ab.png")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""权重的值"""
a_list = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
b_list = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
"""地图、障碍物的位置、起始点、终点"""
max_row = 30
max_col = 30
# barrier_map = [[1, 2], [3, 5], [4,7],[6, 6], [11, 19], [11, 6],[11, 5],[12,5],[12,6],[11, 16], [11, 17], [11, 18], [7, 7]]
barrier_map = [[6, 29], [7, 29], [8, 29], [6, 28], [7, 28], [8, 28], [6, 27], [7, 27], [8, 27], [6, 26], [7, 26],
[8, 26], [6, 25], [7, 25], [8, 25], [6, 24], [7, 24], [8, 24], [29, 25], [28, 25], [27, 25],
[26, 25], [25, 25], [24, 25], [23, 25], [22, 25], [21, 25], [29, 24], [28, 24], [27, 24], [26, 24],
[24, 24], [25, 24],
[23, 24], [22, 24], [21, 24], [20, 10], [21, 10], [22, 10], [23, 10], [24, 10], [20, 9], [21, 9],
[22, 9], [23, 9], [24, 9], [20, 8], [21, 8], [22, 8], [23, 8], [24, 8], [20, 7], [21, 7], [22, 7],
[23, 7], [24, 7], [20, 6], [21, 6], [22, 6], [23, 6], [24, 6], [20, 5], [21, 5], [22, 5], [23, 5],
[24, 5], [20, 4], [21, 4], [22, 4], [23, 4], [24, 4], [20, 3], [21, 3], [22, 3], [23, 3], [24, 3],
[20, 2], [21, 2], [22, 2], [23, 2], [24, 2], [20, 1], [21, 1], [22, 1], [23, 1], [24, 1], [20, 0],
[21, 0], [22, 0], [23, 0], [24, 0],
[16, 16], [16, 17], [16, 18], [17, 16], [17, 17], [17, 18], [18, 16], [18, 17], [18, 18], [19, 16],
[19, 17], [19, 18], [20, 16], [20, 17], [20, 18], [21, 16], [21, 17], [21, 18], [22, 16], [22, 17],
[22, 18], [23, 16], [23, 17], [23, 18], [24, 16], [24, 17], [24, 18], [25, 16], [25, 17], [25, 18],
[26, 16], [26, 17], [26, 18], [27, 16], [27, 17], [27, 18], [28, 16], [28, 17], [28, 18], [29, 16],
[29, 17], [29, 18]]
# barrier_map = np.array(barrier_map)
# start = Point(4, 5, None)
# end = Point(18, 8, None)
start = Point(27, 2, None)
end = Point(0, 29, None)
travel_point_num = []
path_point_num = []
"""遍历权重的值,使用B-A*算法"""
# for a, b in zip(a_list, b_list):
for b in b_list:
for a in a_list:
print(a,b)
path, open_list, stop_point, tp_num = A_star(a, b, start, end, max_row, max_col,barrier_map).search()
if path is not None:
# 找到路径
print("Find the path!")
travel_point_num.append(tp_num)
path_point_num.append(len(path))
draw_path(max_row, max_col, barrier_map, path, open_list, stop_point, start, end)
else:
print("Fail to find the path!")
print(travel_point_num)
print(path_point_num)
draw_arg(travel_point_num, path_point_num, a_list, b_list)


![webots仿真报警[ERROR] [1703399199.459991029]: Sampling period is not valid.](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c214c20c7ca24f10aedade1abb8389ce.png)



![给定一个数列,每一次操作可以使a[i]变成x,y,满足x + y = a[i] + k, 求使所有数字相同的最少操作次数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3ec666271357464d852d9efac5e4ef88.png)