ansible的脚本-----playbook剧本
playbook组成部分:
1、tasks任务:包含要在目标主机上执行的操作,使用模块定义这些操作。每个任务都是一个模块的调用
2、variables变量:存储和传递数据,变量可以自定义,可以在playbook当中定义为全局变量,也可以外部传参
3、Templates模板:用于生成配置文件。模板是包含占位符的文件,占位符由ansible在执行时转化为变量值
4、handlers处理器:当需要有变更的时候,可以执行触发器
5、Roles角色:是一种组织和封装playbook的,允许把相关的任务,变量,模板和处理器组织成一个可复用的单元
playbook的条件判断:
when是一个比较常见的应用场景,实现满足条件即执行,不满足条件即跳过的任务
when是满足条件即执行,不满足不执行
循环:
ansible有多种循环模式,
with_items:循环遍历
with_list:列表分组循环
with_together:列表对应的列,数据结合的方式循环
with_nested:相当于双重循环,第一层定义了循环的次数,第二层表示第一层的每个元素会循环几次
实例模板:
要先vim /etc/ansible/hosts让他们主机之间ping的通
再写一个yml的配置文件
![]()
#this is our first playbook
- name: first play
gather_facts: false
hosts: 192.168.233.20
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: ping test
ping:
- name: close selinux
command: '/sbin/setenforce 0'
ignore_errors: True
- name: close firewalld
service: name=firewalld state=stopped
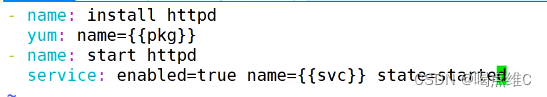
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: start httpd
service: enabled=true name=httpd state=started
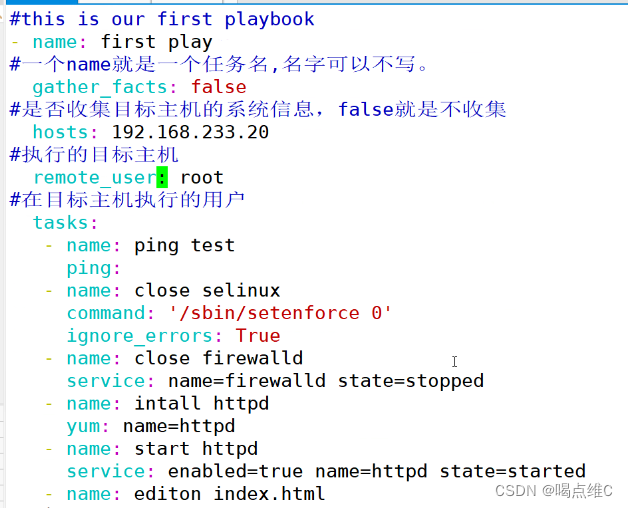
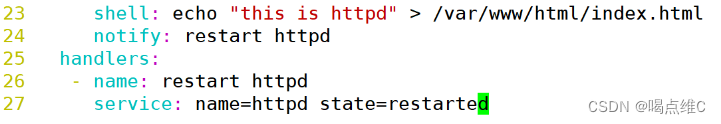
- name: editon index.html
shell: echo "this is httpd" > /var/www/html/index.html
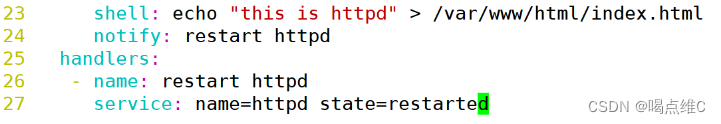
notify: restart httpd
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
检查yml的语法是否正确
![]()
运行脚本


指定任务从哪一步开始
![]()

切换用户实验:
要先vim /etc/ansible/hosts让他们主机之间ping的通
再写一个yml的配置文件
![]()
#this is our first playbook
- name: first play
#一个name就是一个任务名,名字可以不写
gather_facts: false
#是否收集目标主机的系统信息,false就是不收集
hosts: 192.168.233.20
#执行的目标主机是20
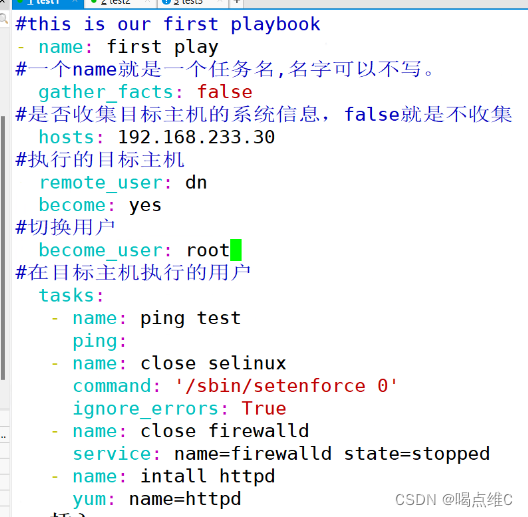
remote_user: dn
become: yes
#切换用户
become_user: root
#在目标主机执行的用户
tasks:
- name: ping test
ping:
- name: close selinux
command: '/sbin/setenforce 0'
ignore_errors: True
- name: close firewalld
service: name=firewalld state=stopped
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: start httpd
service: enabled=true name=httpd state=started
- name: editon index.html
shell: echo "this is httpd" > /var/www/html/index.html
notify: restart httpd
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service:name=httpd state=restarted
打开配置文件,71行取消注释
![]()
指定用户,输入密码

也可以不在脚本里声明用户,在命令行输入用户
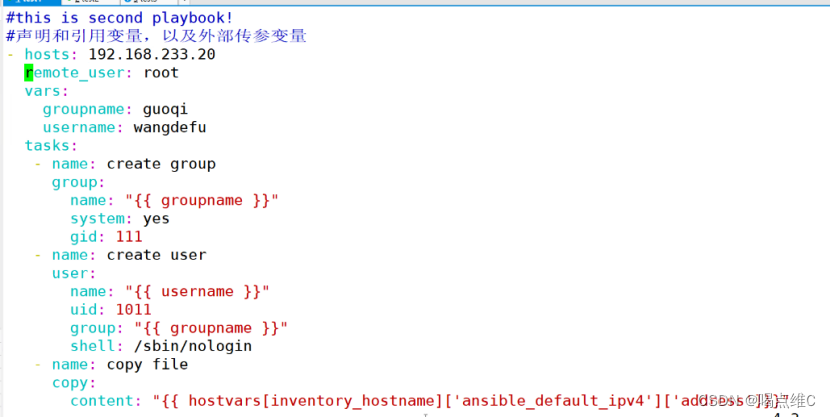
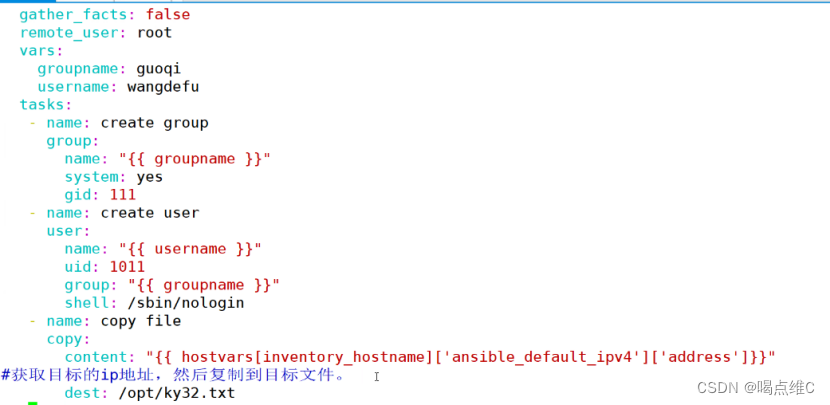
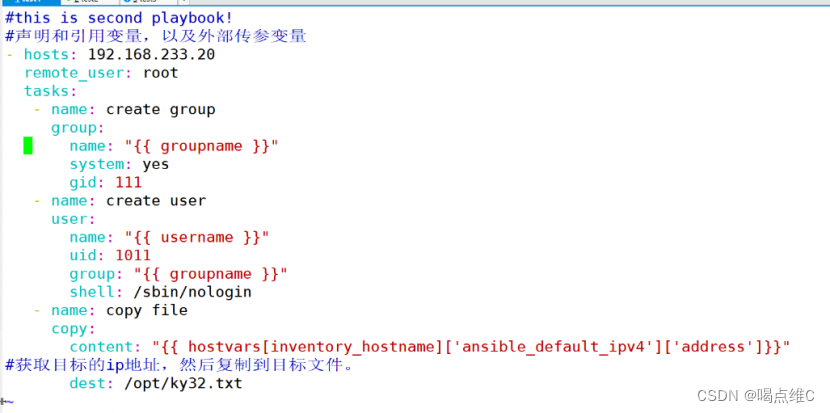
声明和引用变量,以及外部传参变量实验:
#this is second playbook!
#声明和引用变量,以及外部传参变量
- hosts: 192.168.233.20
remote_user: root
vars:
groupname: guoqi
username: wangdefu
tasks:
- name: create group
group:
name: "{{ groupname }}"
system: yes
gid: 111
- name: create user
user:
name: "{{ username }}"
uid: 1011
group: "{{ groupname }}"
shell: /sbin/nologin
- name: copy file
copy:
content: "{{ hostvars[inventory_hostname]['ansible_default_ipv4']['address']}}"
#获取目标主机的IP地址,然后打印,复制到目标文件
dest: /opt/ky32.txt
"{{ hostvars[inventory_hostname]['ansible_default_ipv4']['address']}}"
包含所有主机变量的字典
inventory_hostname:目标的主机名
ansible_default_ipv4:获取目标主机名
['ansible_default_ipv4']['address']:索引

用-e往ansible-playbook里面传参数
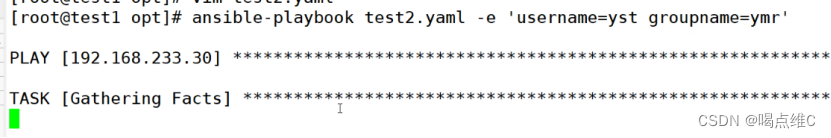
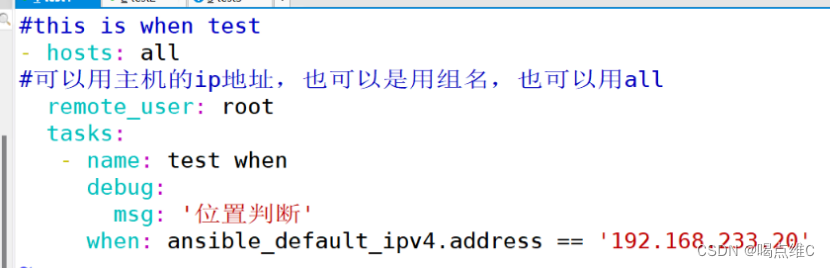
条件判断实验:
#this is when test
- hosts: all
#可以用主机的IP地址,也可以使用组名,也可以用all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test when
debug:
msg: '位置判断'
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == '192.168.233.20'
(做这些之前要先在/etc/ansible/hosts里面把其他的IP地址删掉)
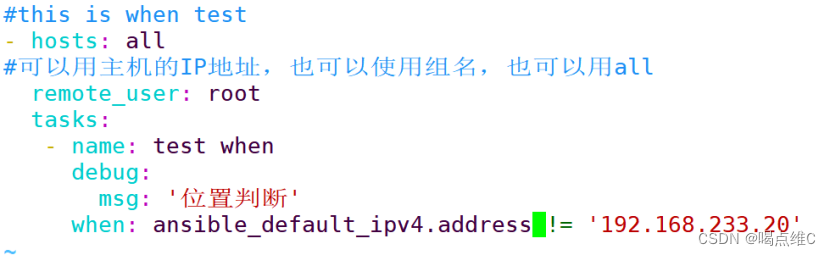
取反
#this is when test
- hosts: all
#可以用主机的IP地址,也可以使用组名,也可以用all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test when
debug:
msg: '位置判断'
#echo $a echo ok echo 123 debug=echo msg:输出的内容,用于脚本的调试,在正式脚本中要去除
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address != '192.168.233.20'
实验安装nginx和httpd:
20安装nginx
30安装httpd
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: nginx info
debug:
msg: "安装nginx"
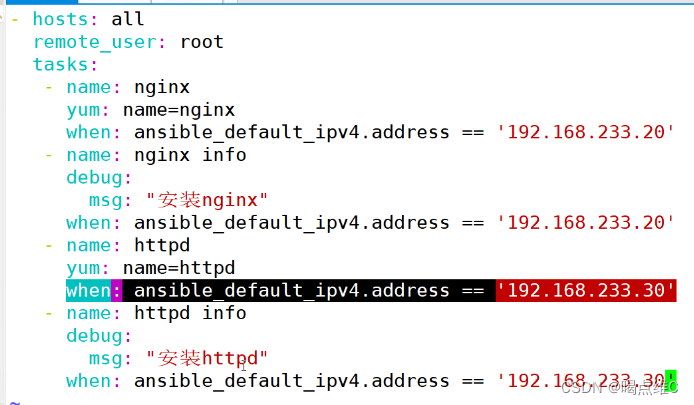
或(两个选一个用)

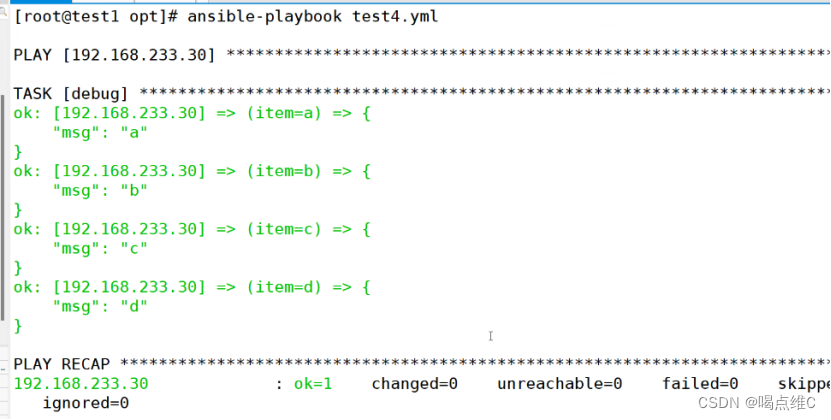
循环
- hosts: 192.168.233.30
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
with_items: [a,b,c,d]
#声明变量item,playbook的内置变量,with_items,会把item的值,遍历>列表当中的a,b,c,d

定义两个列表,但是会一块遍历打印出来
- hosts: 192.168.233.30
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- [a,b,c,d]
- [1,2,3,4]
#声明变量item,playbook的内置变量,with_items,会把item的值,遍历>列表当中的a,b,c,d
#虽然我声明的列表是两个,但是with_items还是把两个列表当成整体进行
遍历

分组打印:
- hosts: 192.168.233.40
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
with_list:
- [a,b,c,d]
- [1,2,3,4]
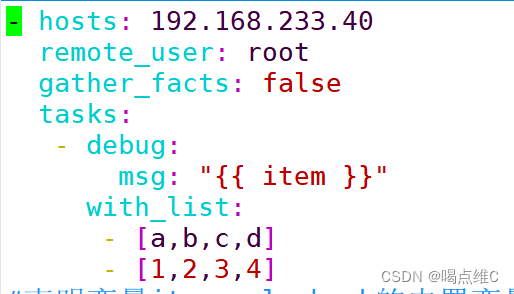

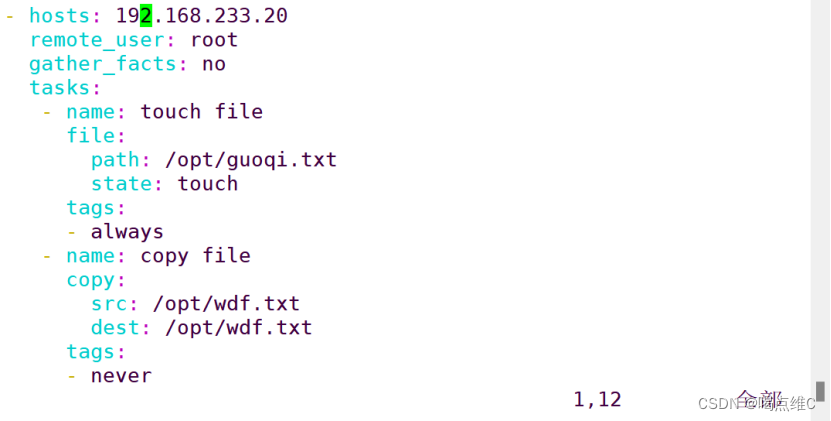
遍历循环在主机上创建文件实验:
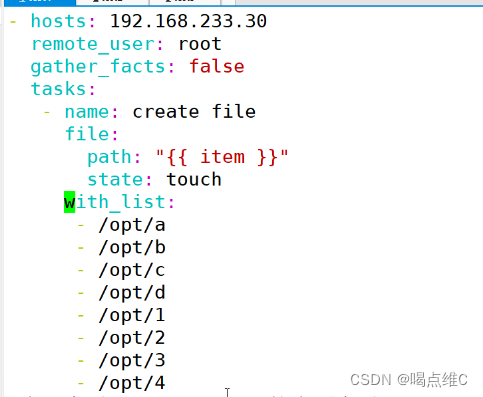
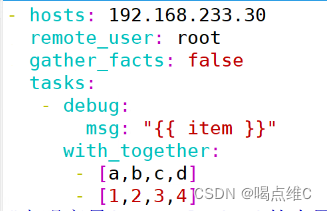
双重循环实验:
- hosts: 192.168.233.40
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
with_nested:
- [a,b,c,d]
- [1,2,3,4]
#列表里面的元素定义了循环的次数,第二层列表相当于内循环
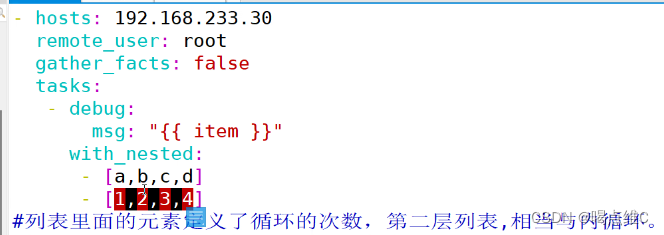
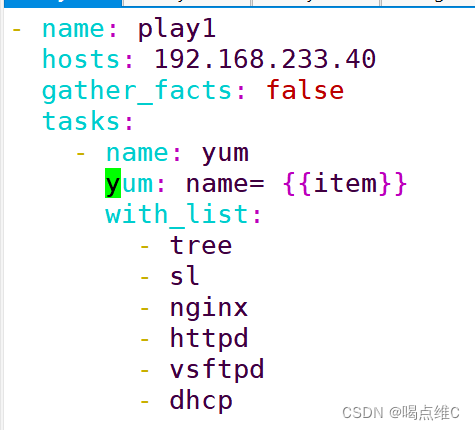
一键yum安装tree sl nginx httpd vsftpd dhcp软件:
- name: play1
hosts: 192.168.233.40
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: yum
yum: name= {{item}}
with_list:
- tree
- sl
- nginx
- httpd
- vsftpd
- dhcp
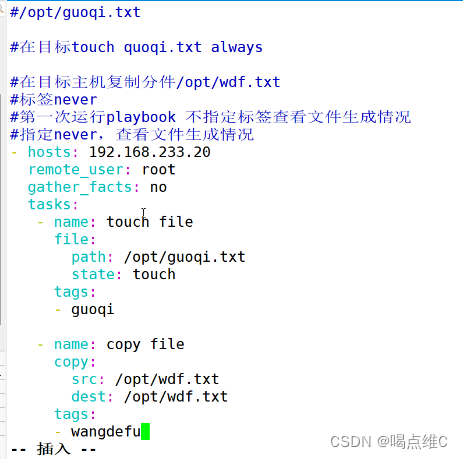
创建test1 2 3,然后把源主机的test1 2 3发给目标主机 再给一个判断的实验:
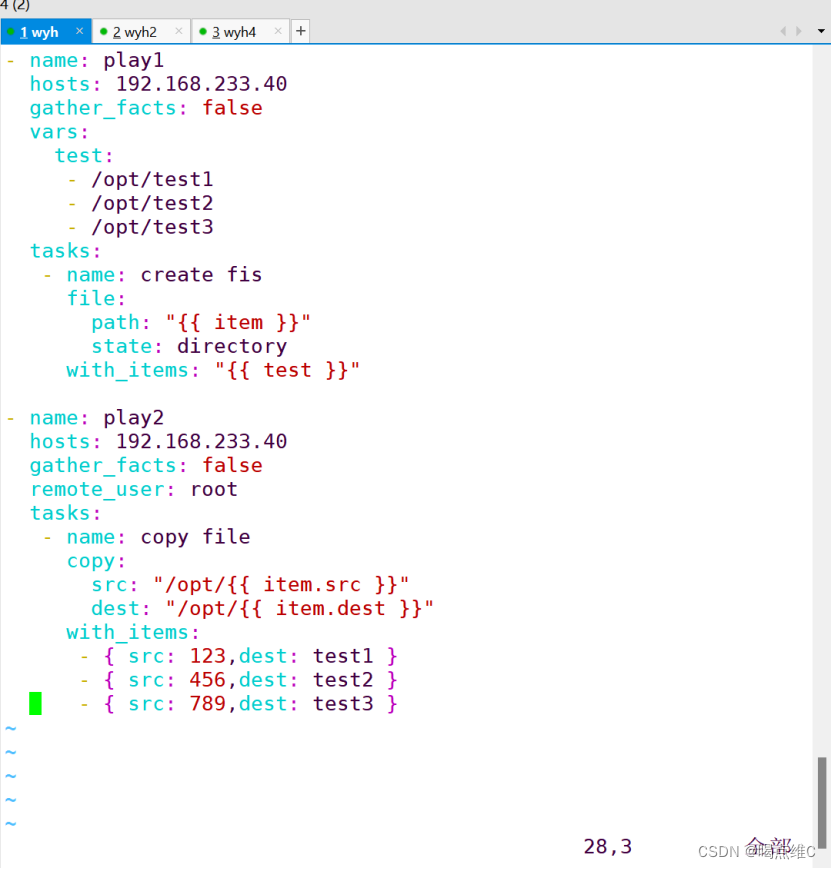
两个都可以用

Templates模块:
Jinja模板架构,通过模板可以实现向模板文件传参(python转义)把占位符参数传到配置文件中去
生成一个目标文本文件,传递变量到需要的配置文件当中(web开发)
声明占位符之后,往httpd里面塞东西实验:

![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()


![]()
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars:
- package: httpd
- service: httpd
tasks:
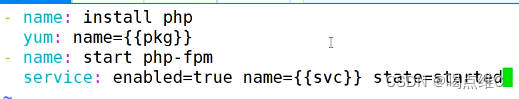
- name: install httpd
yum: name={{package}}
- name: install configure file
template: src=/opt/httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart httpd
- name: cfreate root_dir
file:
path: /etc/httpd/htdocs
state: directory
- name: start httpd
service: name={{service}} enabled=true state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name={{service}} state=restarted
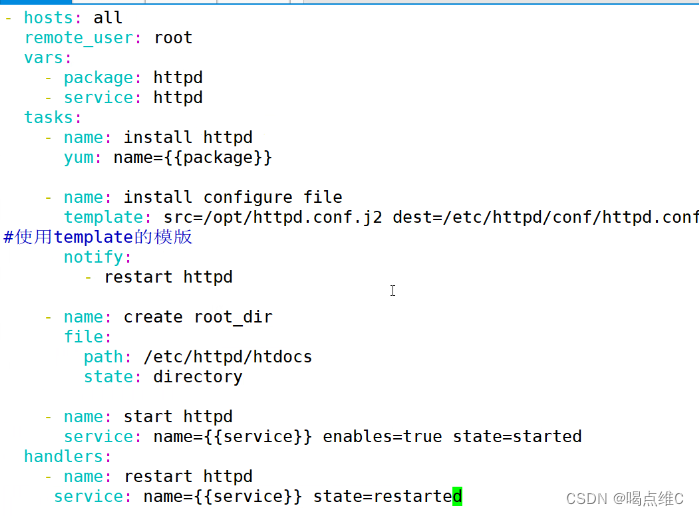
最下面的service要和上面的service对齐
httpd.conf.j2在文件当中配置的是占位符(声明的变量)
/etc/ansible/hosts 配置了主机的占位符名称和j2文件中的占位符一致(定义参数:占位符的参数的参数声明好)
playbook当中,用template模块来把参数传给目标的主机的配置文件
nginx实验:
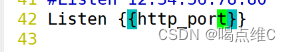
端口号改成8080
root目录改成/opt/nginx/html
(其他步骤与http一样)
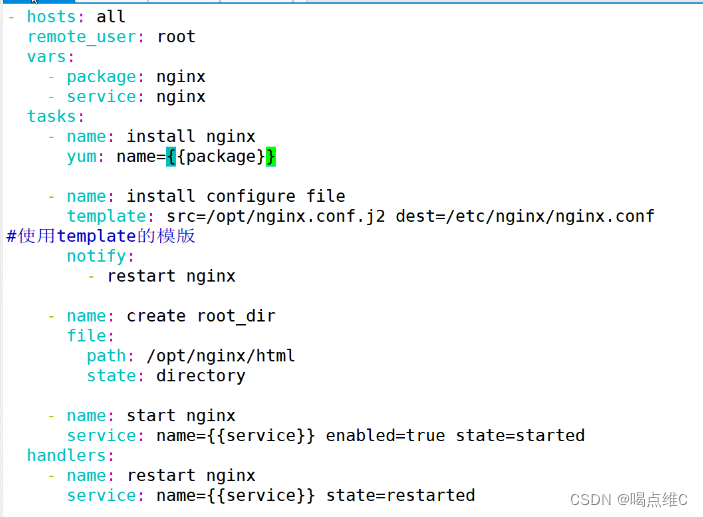
tags模块:
标签模块:标签模块,可以在playbook当中为任务设定标签(tags),我们在运行playbook时可以通过指定任务标签,来实现只运行设定的标签任务
例如:
- name
tags:
debug
--start-at-task=‘wdf’
任务标签的种类:
always:不管你是否指定了运行标签,任务都会执行
never:即使运行了指定标签,该任务也不会执行
debug:调试任务
setup:收集主机信息
自定义标签:
per_tasks:指定标签之前的任务
post_tasks:运行指定标签之后的任务

![]()

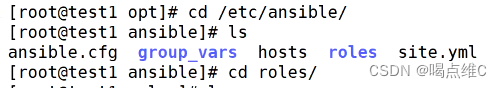
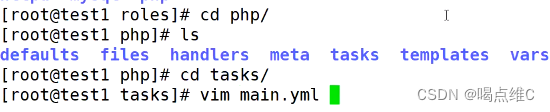
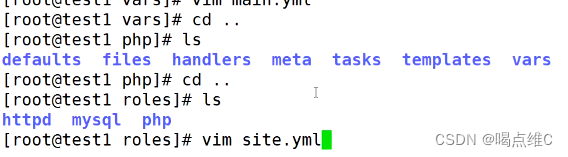
Roles模块:
roles又称为角色
ansible层次化,结构化的组织playbook,使用了rolse(角色)
可以根据层次结构,自动装载变量文件,task,以及handlers等等
roles:分别把变量 文件 任务 模块以及处理器,放在单独的目录当中,使用rolse模块来一键调用这些文件
roles:
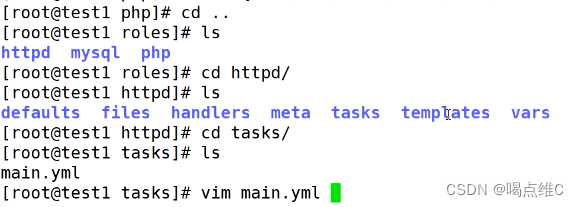
-------web-------总目录,角色
files 存放copy和sript模块调用的文件
templates 存放j2的模板文件
tasks 包含任务的目录
--------main.yml 角色运行的任务
handlers包含处理器的目录
---------main.yml
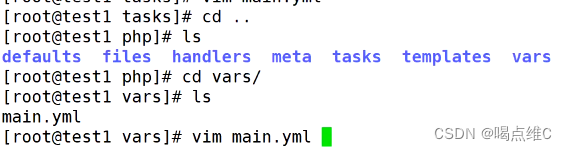
vars 存放变量的目录
---------main.yml
defaults 包含默认变量的目录
----------main.yml
meta包含元信息的目录
-----------main.yml
site.yml用来调用所有的配置文件
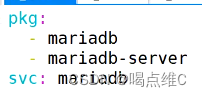
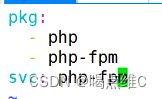
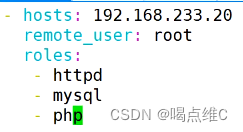
安装三个服务:
http
mysql
php
![]()

![]()




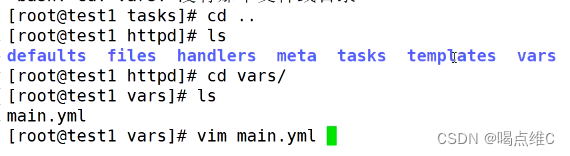
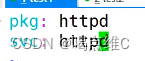

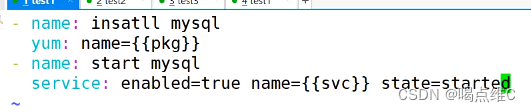
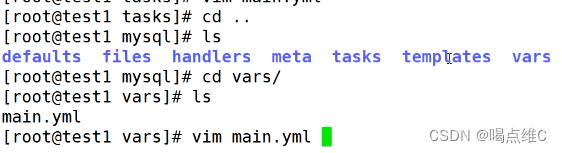
然后在20主机查看httpd、nginx、mysql







![PnetLab[网络虚拟化实验平台]下载地址](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9b3ca3ec9ec9e7811b7d222dc0881a86.png)
