一、@RequestParam注解
作用:用于将指定的请求参数赋值给方法中的形参。
属性:
1)value:请求参数名(必须配置)
2)required:是否必需,默认为 true,即请求中必须包含该参数,如果没有包含,将会抛出异常(可选配置)
3)defaultValue:设置默认值,如果设置了该值,required 将自动设为 false,无论你是否配置了required,配置了什么值,都是 false(可选配置)
用法:
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/RequestParam")
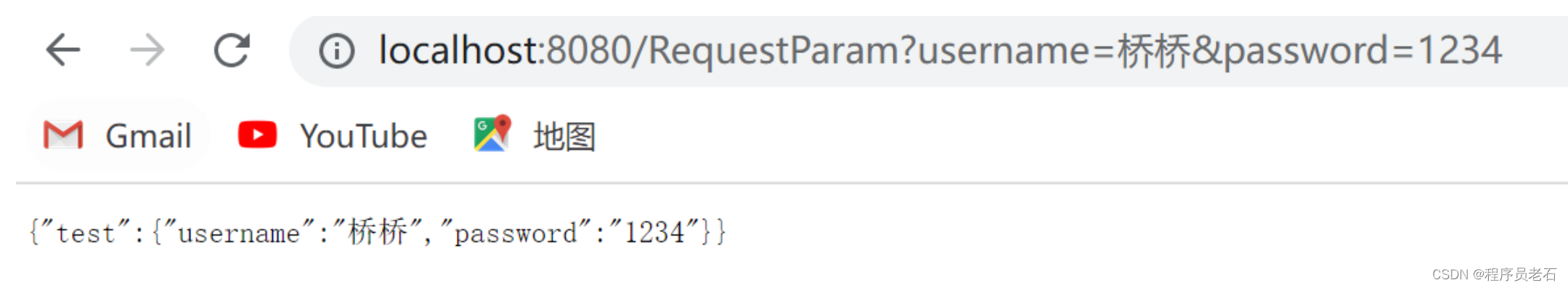
public Map test(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") List<String > password){
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("username",username);
map.put("password",password);
return map;
}
注意:GET请求时,请求的参数是拼接在请求地址URL后面的

也可以通过一个@RequestParam注解与Map集合类型参数同时获取多个参数:
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/RequestParam")
public Map test(@RequestParam Map<String,String> map1){
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("test",map1);
return map;
}
二、@PathVariable注解
1、get方式的安全性较Post方式要差些,包含机密信息的话,建议用Post数据提交方式;
2、在做数据查询时,建议用Get方式;而在做数据添加、修改或删除时,建议用Post方式;post需要token来防止跨站请求漏洞。
@PathVariable注解在应用时,在@RequestMapping请求路径中,将需要传递的参数用花括号{}括起来,然后,通过@PathVariable(“参数名称”)获取URL中对应的参数值。如果@PathVariable标明参数名称,则参数名称必须和URL中的参数名称保持一致。
用法:
@ResponseBody
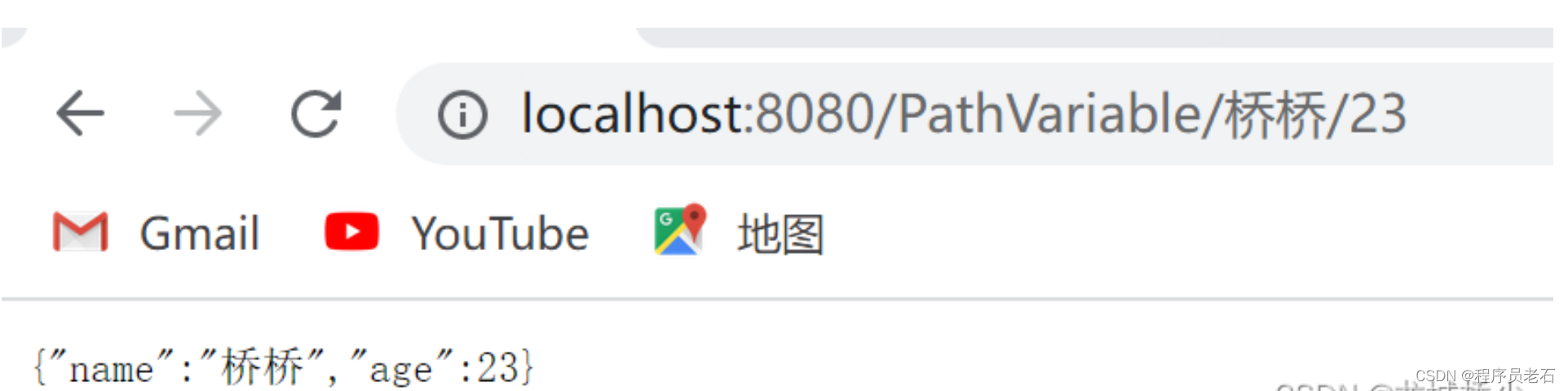
@GetMapping("/PathVariable/{name}/{age}")
public Map test(@PathVariable("name") String name,@PathVariable("age") Integer age){
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("name",name);
map.put("age",age);
return map;
}
也可以使用一次注解获取多个参数:
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/PathVariable/{name}/{age}")
public Map test(@PathVariable Map<String,String> map3){
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("params",map3);
return map;
}
三、@RequestBody注解
主要用来接收前端传递给后端的json字符串中的数据,也就是请求体中的数据,GET方式无请求体,所以使用**@RequestBody接收数据时,前端不能使用GET方式提交数据,而是用POST方式进行提交。**
在后端的同一个接收方法里,@RequestBody与@RequestParam()可以同时使用,@RequestBody最多只能有一个,而@RequestParam()可以有多个。
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/save")
//获取请求体参数
public String getRequestBody(@RequestBody String body){
return body;
}
四、@RequestAttribute注解:
获取请求域中所保存的属性的值。
用法:首先向浏览器发起goto请求并添加自定义值到请求域中,再转发到success请求去获取这些请求域中的值。
@GetMapping("/goto")
public String toSuccess(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("msg","成功了!");
request.setAttribute("code",200);
return "forward:/success";
}
//使用@RequestAttribute注解获取请求域中的值与//不使用注解获取请求域中的值
@GetMapping("/success")
public String success(@RequestAttribute("msg")String msg,
@RequestAttribute("code") Integer code,
HttpServletRequest request){
Object msg1 = request.getAttribute("msg");
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("msg",msg);
map.put("code",code);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(msg1);
return "success";
}



![[图像和LiDAR点云的可微分配准]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c75ee0cf7b3b4544a02dc4fdf176cf81.png)