前言
RM是资源的管理者 处理分支事务的开启和提交回滚 当TM注册完全局事务之后进行分支事务的提交
RM一阶段处理本地事务,主要是在DataSource、Connection、Statement上做文章。
DataSource 创建
项目启动的时候SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator为所有DataSource类型Bean创建了SpringAop代理,代理逻辑在SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice的invoke方法中。
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(boolean useJdkProxy, String[] excludes, String dataSourceProxyMode) {
this.excludes = Arrays.asList(excludes);
//创建SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice对象执行代理逻辑
this.advisor = new DefaultIntroductionAdvisor(new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice(dataSourceProxyMode));
setProxyTargetClass(!useJdkProxy);
}
而在SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice中 因为这里是AT模式所以会使用DataSourceProxy的代理来处理
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice(String dataSourceProxyMode) {
if (BranchType.AT.name().equalsIgnoreCase(dataSourceProxyMode)) {
this.dataSourceProxyMode = BranchType.AT;
this.dataSourceProxyClazz = DataSourceProxy.class;
} else if (BranchType.XA.name().equalsIgnoreCase(dataSourceProxyMode)) {
this.dataSourceProxyMode = BranchType.XA;
this.dataSourceProxyClazz = DataSourceProxyXA.class;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown dataSourceProxyMode: " + dataSourceProxyMode);
}
//Set the default branch type in the RootContext.
RootContext.setDefaultBranchType(this.dataSourceProxyMode);
}
业务SQL执行
TransactionalTemplate
......
rs = business.execute();
......
当业务SQL执行的时候PreparedStatementProxy执行sql都交给ExecuteTemplate执行模板,传入业务方法(实际执行sql)作为callback在模板中被回调。
@Override
public boolean execute() throws SQLException {
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.execute());
}
ExecuteTemplate
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,
StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
//如果没获取全局锁 或者当前类型不是AT模式 直接执行原始事务
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
// Just work as original statement
return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
}
//获取 执行类型
String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
//sql的解构
sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(
statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),
dbType);
}
Executor<T> executor;
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
//获取sql类型
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
case INSERT:
executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,
new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},
new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
break;
case UPDATE:
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE:
if (JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equals(dbType)) {
executor = new MySQLInsertOrUpdateExecutor(statementProxy,statementCallback,sqlRecognizer);
} else {
throw new NotSupportYetException(dbType + " not support to INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE");
}
break;
default:
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
//执行sql语句
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
}
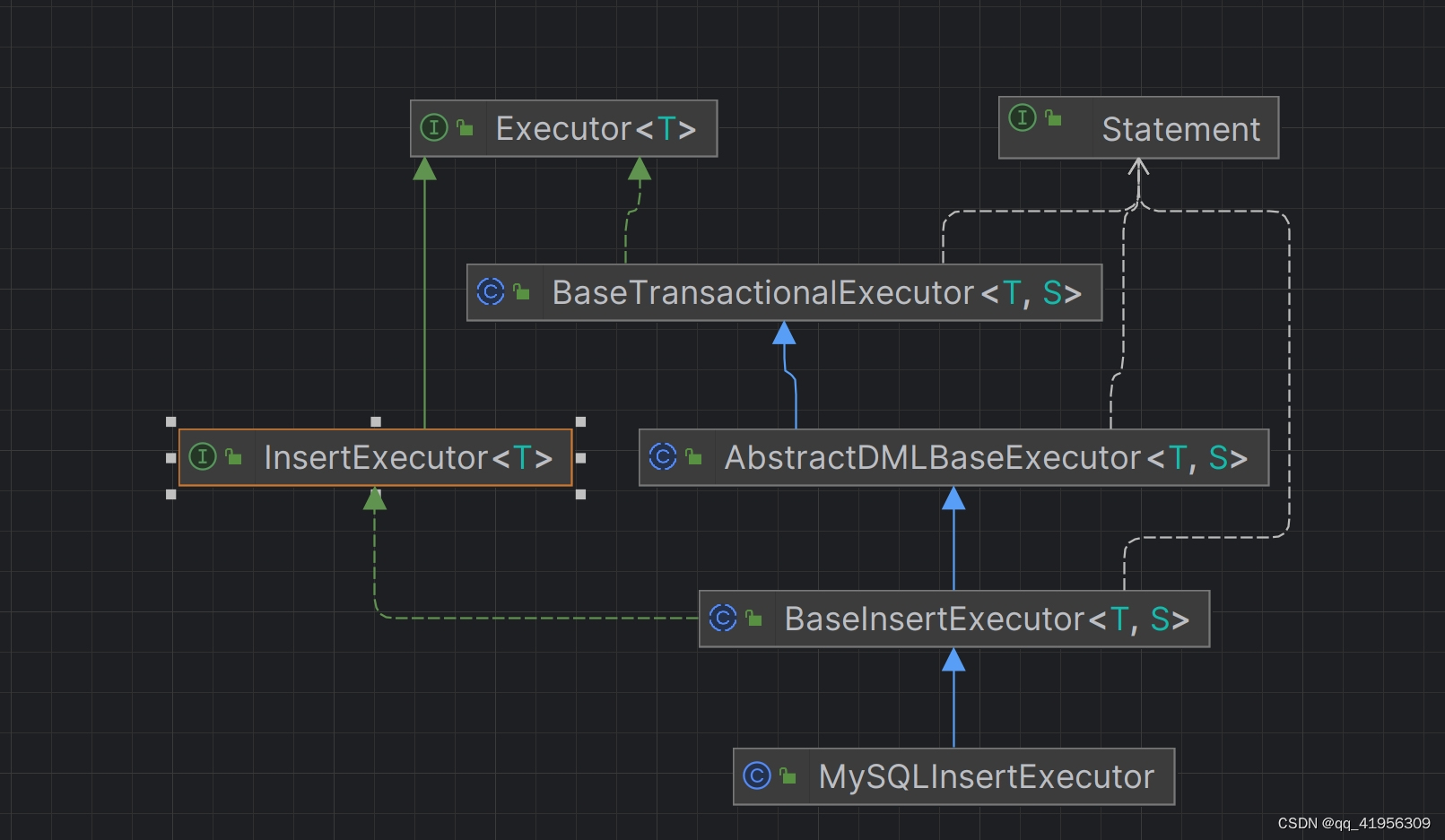
我这里的例子是insert操作所以会基于InsertExecutor去处理 可以从下图中看出 最终继承自BaseTransactionalExecutor所以会到BaseTransactionalExecutor的execute方法来处理
@Override
public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
//获取Xid
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
if (xid != null) {
//绑定
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
}
//设置全局事务锁
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
//执行
return doExecute(args);
}
AbstractDMLBaseExecutor
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
//是否是自动提交
if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
} else {
// 当autocommit=false时,处于本地事务中
return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
}
}
当autocommit=true时,seata自己开启了事务,设置autocommit=false,目的是本地事务与seata的undolog在一个事务中提交,其底层还是调用了autocommit=false的逻辑。
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
// 手动修改autocommit=false,开启本地事务,为了undolog和这个sql放在一个事务里提交
connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();
// commit阶段 获取全局锁的重试策略
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
// 执行autocommit=false的逻辑
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
//提交事务
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
// 恢复autocommit=true
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}
@Override
protected Object executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().size() > 1) {
throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
}
// 1. 构建beforeImage(前置镜像)
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(beforeImage.getRows())) {
isUpdateFlag = true;
} else {
beforeImage = TableRecords.empty(getTableMeta());
}
// 2. 执行sql
Object result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
//构建后置镜像
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
//构建undolog放入ConnectionProxy
prepareUndoLogAll(beforeImage, afterImage);
return result;
}
构建前置镜像
Update语句
对于update语句来说,UpdateExecutor通过select for update获取前置镜像如update语句是:update storage_tbl set count = count - ? where commodity_code = ?,seata获取前置镜像拼接的sql是:SELECT id, count FROM storage_tbl WHERE commodity_code = ? FOR UPDATE。
// UpdateExecutor
protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
// 构建select for update
String selectSQL = buildBeforeImageSQL(tmeta, paramAppenderList);
// 执行select for update 返回结果即beforeImage
return buildTableRecords(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
}
private String buildBeforeImageSQL(TableMeta tableMeta, ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList) {
SQLUpdateRecognizer recognizer = (SQLUpdateRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
List<String> updateColumns = recognizer.getUpdateColumns();
StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
suffix.append(WHERE).append(whereCondition);
}
// ...
suffix.append(" FOR UPDATE");
StringJoiner selectSQLJoin = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix.toString());
// ...
return selectSQLJoin.toString();
}
Delete语句
对于delete语句来说,和update一样,也是通过select for update获取镜像数据,不同点在于默认情况下,update只会将更新字段放到前置镜像中,而delete会将所有字段放到前置镜像。
// DeleteExecutor
protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
SQLDeleteRecognizer visitor = (SQLDeleteRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta(visitor.getTableName());
ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
String selectSQL = buildBeforeImageSQL(visitor, tmeta, paramAppenderList);
return buildTableRecords(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
}
private String buildBeforeImageSQL(SQLDeleteRecognizer visitor, TableMeta tableMeta, ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList) {
String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(visitor, paramAppenderList);
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
suffix.append(WHERE).append(whereCondition);
}
suffix.append(" FOR UPDATE");
StringJoiner selectSQLAppender = new StringJoiner(", ", "SELECT ", suffix.toString());
for (String column : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
selectSQLAppender.add(getColumnNameInSQL(ColumnUtils.addEscape(column, getDbType())));
}
return selectSQLAppender.toString();
}
Insert
对于insert on duplicate key update,底层还是select for update获取的前置镜像
// MySQLInsertOrUpdateExecutor
public TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
//after image sql the same of before image
if (StringUtils.isBlank(selectSQL)) {
paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
selectSQL = buildImageSQL(tmeta);
}
return buildTableRecords2(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
}
public TableRecords buildTableRecords2(TableMeta tableMeta, String selectSQL, ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = null;
try (PreparedStatement ps = statementProxy.getConnection().prepareStatement(selectSQL + " FOR UPDATE")) {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(paramAppenderList)) {
for (int i = 0, ts = paramAppenderList.size(); i < ts; i++) {
List<Object> paramAppender = paramAppenderList.get(i);
for (int j = 0, ds = paramAppender.size(); j < ds; j++) {
ps.setObject(i * ds + j + 1, "NULL".equals(paramAppender.get(j).toString()) ? null : paramAppender.get(j));
}
}
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
return TableRecords.buildRecords(tableMeta, rs);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(rs);
}
}
执行SQL
Object result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
构建后置镜像
构建后置镜像逻辑都类似,通过普通select语句即可得到后置镜像。delete的后置镜像和insert的前置镜像一样,只有表结构。
后镜像的查询条件使用的是前镜像对应的主键值,就没有用业务SQL的查询条件;不同的Executor处理方式不同,需要根据具体的业务SQL来区分
查询后镜像的SQL没有使用FOR UPDATE加锁,直接拿的快照数据
比如UpdateExecutor的后置镜像,通过执行SELECT id, count FROM storage_tbl WHERE (id) in ( (?) )得到。
// UpdateExecutor
protected TableRecords afterImage(TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
if (beforeImage == null || beforeImage.size() == 0) {
return TableRecords.empty(getTableMeta());
}
// 普通select语句by主键,查询字段仅包含更新字段
String selectSQL = buildAfterImageSQL(tmeta, beforeImage);
ResultSet rs = null;
try (PreparedStatement pst = statementProxy.getConnection().prepareStatement(selectSQL)) {
SqlGenerateUtils.setParamForPk(beforeImage.pkRows(), getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName(), pst);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
return TableRecords.buildRecords(tmeta, rs);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(rs);
}
}
构建undoLog
构建完后置镜像后,执行sql的最后一步是构建undoLog,这一步仅仅是构造undoLog,在一阶段提交undoLog才起作用。
BaseTransactionalExecutor#prepareUndoLog在构建undoLog之前,还构建了lockKeys,即全局锁的key。
对于MySQL来说,只有一个主键,lockKeys的模式是:{表名}:{主键值1},…,{主键值n}。比如update storage_tbl set count = count - ? where commodity_code = ?,对应的数据记录是id=8和id=9,那么lockKeys=storage_tbl:8,9。
// BaseTransactionalExecutor
protected void prepareUndoLog(TableRecords beforeImage, TableRecords afterImage) throws SQLException {
if (beforeImage.getRows().isEmpty() && afterImage.getRows().isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (SQLType.UPDATE == sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
if (beforeImage.getRows().size() != afterImage.getRows().size()) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("Before image size is not equaled to after image size, probably because you updated the primary keys.");
}
}
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
// 构建lockKeys放入ConnectionProxy,{表名}:{主键值1},...,{主键值n}
TableRecords lockKeyRecords = sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.DELETE ? beforeImage : afterImage;
String lockKeys = buildLockKey(lockKeyRecords);
if (null != lockKeys) {
connectionProxy.appendLockKey(lockKeys);
// 构建undolog放入ConnectionProxy
SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog = buildUndoItem(beforeImage, afterImage);
connectionProxy.appendUndoLog(sqlUndoLog);
}
}
protected SQLUndoLog buildUndoItem(TableRecords beforeImage, TableRecords afterImage) {
SQLType sqlType = sqlRecognizer.getSQLType();
String tableName = sqlRecognizer.getTableName();
SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog = new SQLUndoLog();
sqlUndoLog.setSqlType(sqlType);
sqlUndoLog.setTableName(tableName);
sqlUndoLog.setBeforeImage(beforeImage);
sqlUndoLog.setAfterImage(afterImage);
return sqlUndoLog;
}
RM分支事务提交
当执行完sql语句之后会执行 executeAutoCommitTrue方法中的connectionProxy.commit(); 来到ConnectionProxy的comnmit方法中
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
......
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
//执行commit
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
......
}
ConnectionProxy
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
try {
//LockRetryPolicy重试
LOCK_RETRY_POLICY.execute(() -> {
doCommit();
return null;
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
rollback();
}
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException(e);
}
}
private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
//当前是否处在全局事务中
if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
processGlobalTransactionCommit();
} else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
} else {
targetConnection.commit();
}
}
processGlobalTransactionCommit是RM提交事务的核心方法一共分为以下几步:
1.向TC注册分支事务,获取全局锁,如果获取全局锁失败,抛出LockConflictException异常,其他情况抛出SQLException;
2.写入undolog,之前在执行sql的时候保存到ConnectionProxy的undoLog写入db;
3.提交本地事务,将业务DML和undolog一起提交;
4.如果本地提交失败,向TC发送BranchReportRequest,并表明一阶段提交失败;
5.如果本地提交成功,默认情况下就直接结束返回;
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
// 1. 向TC注册分支事务,获取全局锁
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
// 获取全局锁失败,抛出LockConflictException异常
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
// 2. mysql写入undolog
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
// 3. 提交本地事务,释放本地锁
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
// 4. 本地事务提交失败,发送BranchReportRequest PhaseOne_Failed
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) { // 这里默认为false
// 5. 本地事务提交成功,发送BranchReportRequest PhaseOne_Done
report(true);
}
context.reset();
}
分支事务注册
RM发送分支事务注册请求
注册分支事务基于分支类型AT委派到DataSourceManager处理,其父类AbstractResourceManager实现的branchRegister方法向TC发送BranchRegisterRequest。
AbstractResourceManager
@Override
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
try {
//设置请求信息
BranchRegisterRequest request = new BranchRegisterRequest();
request.setXid(xid);
request.setLockKey(lockKeys);
request.setResourceId(resourceId);
request.setBranchType(branchType);
request.setApplicationData(applicationData);
//想TC发送请求
BranchRegisterResponse response = (BranchRegisterResponse) RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new RmTransactionException(response.getTransactionExceptionCode(), String.format("Response[ %s ]", response.getMsg()));
}
//返回分支事务id
return response.getBranchId();
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC Timeout", toe);
} catch (RuntimeException rex) {
throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRegisterFailed, "Runtime", rex);
}
}
TC接收RM分支事务注册的请求
TC接收请求信息之后会交给AbstractCore来处理分支事务的注册
@Override
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,
String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
//根据xid查询global_table得到GlobalSession
GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);
// 对于存储模式=file的情况,由于GlobalSession在内存中,所以需要获取锁后再执行
// 对于存储模式=db/redis的情况,不需要获取锁
return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
// 状态校验 必须为begin
globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId,
applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_BRANCH_ID, String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()));
//创建全局锁
branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
try {
//保存分支事务
globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// 保存分支事务失败,释放全局锁
branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);
throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String
.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}",
globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);
}
return branchSession.getBranchId();
});
}
获取全局锁
ATCore
protected void branchSessionLock(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession)
throws TransactionException {
String applicationData = branchSession.getApplicationData();
boolean autoCommit = true; // 客户端是否开启事务(seata开启事务不算)
boolean skipCheckLock = false; // 是否跳过锁检查,当客户端本次提交的事务中,所有sql前置镜像为空时,可以跳过
// 从扩展属性中,获取autoCommit和skipCheckLock
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(applicationData)) {
if (objectMapper == null) {
objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
try {
Map<String, Object> data = objectMapper.readValue(applicationData, HashMap.class);
Object clientAutoCommit = data.get(AUTO_COMMIT);
if (clientAutoCommit != null && !(boolean)clientAutoCommit) {
autoCommit = (boolean)clientAutoCommit; // 客户端开启事务autocommit=false
}
Object clientSkipCheckLock = data.get(SKIP_CHECK_LOCK);
if (clientSkipCheckLock instanceof Boolean) {
skipCheckLock = (boolean)clientSkipCheckLock;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
LOGGER.error("failed to get application data: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
try {
// 获取全局锁
if (!branchSession.lock(autoCommit, skipCheckLock)) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(LockKeyConflict,
String.format("Global lock acquire failed xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId()));
}
} catch (StoreException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof BranchTransactionException) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(((BranchTransactionException)e.getCause()).getCode(),
String.format("Global lock acquire failed xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId()));
}
throw e;
}
}
lock 分为下图的四种 我这里用的是db所以会走到DataBaseLocker

@Override
public boolean acquireLock(List<RowLock> locks, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(locks)) {
// no lock
return true;
}
try {
//尝试获取锁
return lockStore.acquireLock(convertToLockDO(locks), autoCommit, skipCheckLock);
} catch (StoreException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception t) {
LOGGER.error("AcquireLock error, locks:{}", CollectionUtils.toString(locks), t);
return false;
}
}
LockStoreDataBaseDAO
LockStoreDataBaseDAO处理获取DB全局锁的逻辑。一共分为两步:
1.校验row_key是否被其他全局事务占用:如果row_key对应记录不存在,代表锁未占用;如果row_key对应记录存在,且记录的xid与当前xid一致,代表锁未占用;其他情况代表锁被占用,返回false获取全局锁失败。
针对skipCheckLock=true情况,即RM所有SQL没有前置镜像,跳过校验;
针对autocommit=false情况,即RM开启本地事务,若发生锁争用且row_key处于rollback状态(其他全局事务在执行二阶段回滚),抛出快速失败异常。因为当前RM持有db行锁,如果持续重试获取全局锁,会阻塞另一个持有相同db行锁的全局事务的二阶段回滚;
2.获取row_key对应全局锁:插入row_key对应锁记录到lock_table,如果没发生主键冲突,则返回true,否则会抛出一个StoreException;
public boolean acquireLock(List<LockDO> lockDOs, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Set<String> dbExistedRowKeys = new HashSet<>();
boolean originalAutoCommit = true;
if (lockDOs.size() > 1) {
lockDOs = lockDOs.stream().filter(LambdaUtils.distinctByKey(LockDO::getRowKey)).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
try {
conn = lockStoreDataSource.getConnection();
if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
}
List<LockDO> unrepeatedLockDOs = lockDOs;
// Step1 校验row_key是否在lock_table中,如果是则发生锁冲突
if (!skipCheckLock) {
boolean canLock = true;
//query
String checkLockSQL = LockStoreSqlFactory.getLogStoreSql(dbType).getCheckLockableSql(lockTable, lockDOs.size());
ps = conn.prepareStatement(checkLockSQL);
for (int i = 0; i < lockDOs.size(); i++) {
ps.setString(i + 1, lockDOs.get(i).getRowKey());
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
String currentXID = lockDOs.get(0).getXid();
boolean failFast = false;
while (rs.next()) {
String dbXID = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_XID);
// db里持有锁的全局事务与当前全局事务不一致,发生锁竞争canLock=false
if (!StringUtils.equals(dbXID, currentXID)) {
// 如果客户端开启本地事务,且锁记录处于二阶段回滚状态,执行快速失败failFast=true
if (!autoCommit) {
int status = rs.getInt(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_STATUS);
if (status == LockStatus.Rollbacking.getCode()) {
failFast = true;
}
}
canLock = false;
break;
}
dbExistedRowKeys.add(rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_ROW_KEY));
}
if (!canLock) {
conn.rollback();
if (failFast) {
throw new StoreException(new BranchTransactionException(LockKeyConflictFailFast));
}
return false;
}
// If the lock has been exists in db, remove it from the lockDOs
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(dbExistedRowKeys)) {
unrepeatedLockDOs = lockDOs.stream().filter(lockDO -> !dbExistedRowKeys.contains(lockDO.getRowKey()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(unrepeatedLockDOs)) {
conn.rollback();
return true;
}
}
// Step2 获取锁 插入row_key对应LockDO锁记录到lock_table
if (unrepeatedLockDOs.size() == 1) { // 单个锁
LockDO lockDO = unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0);
if (!doAcquireLock(conn, lockDO)) {
conn.rollback();
return false;
}
} else { // 批量锁
if (!doAcquireLocks(conn, unrepeatedLockDOs)) {
conn.rollback();
return false;
}
}
conn.commit();
return true;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new StoreException(e);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(rs, ps);
if (conn != null) {
try {
if (originalAutoCommit) {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
}
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
}
}
}
}
可以看到这里最后在lock_table中生成了一条全局锁记录
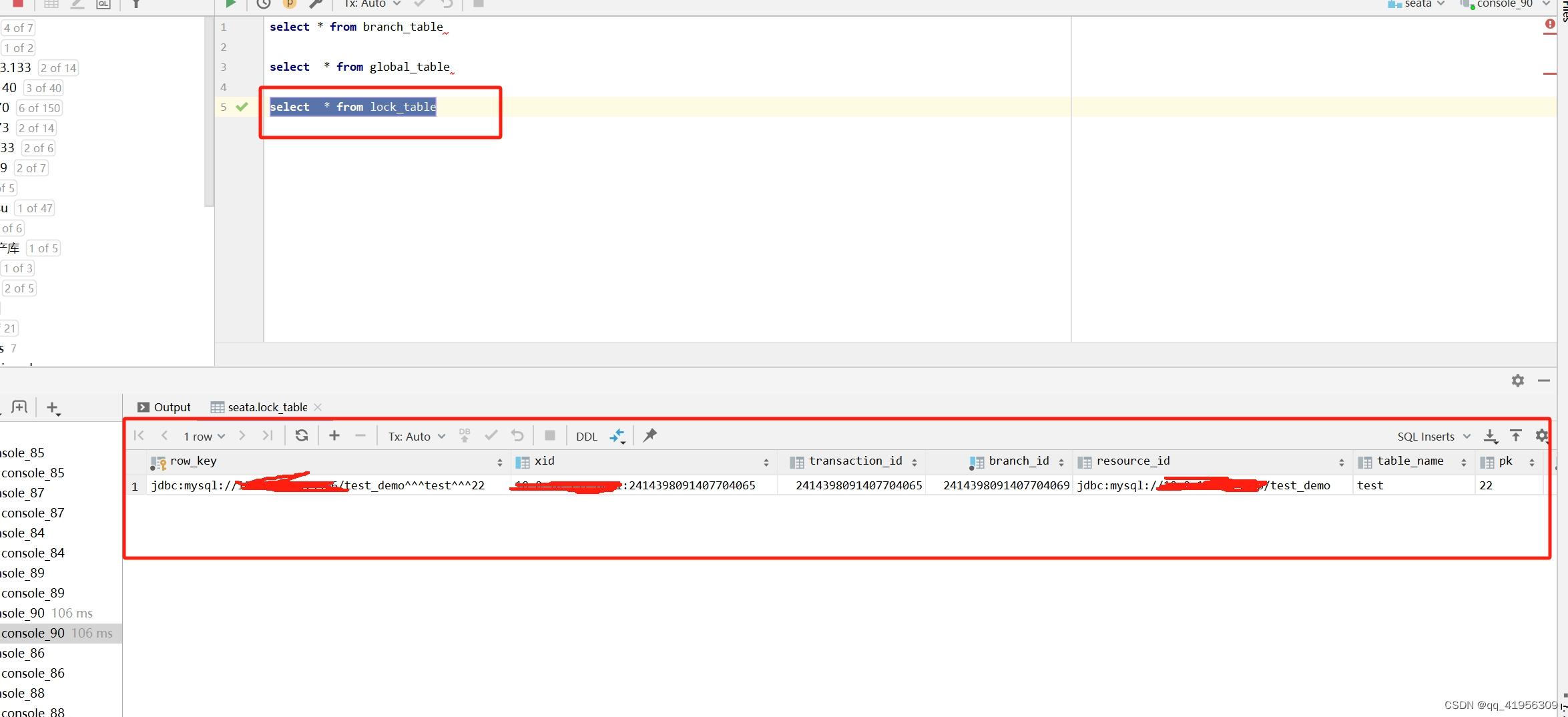
创建分支事务
GlobalSession
@Override
public void addBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
//这里拿到的lifecycleListeners是DataBaseSessionManager 然后会执行DataBaseSessionManager的addBranchSession方法
for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
lifecycleListener.onAddBranch(this, branchSession);
}
branchSession.setStatus(BranchStatus.Registered);
add(branchSession);
}
DataBaseSessionManager
@Override
public void addBranchSession(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession session) throws TransactionException {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(taskName)) {
return;
}
boolean ret = transactionStoreManager.writeSession(LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD, session);
if (!ret) {
throw new StoreException("addBranchSession failed.");
}
}
这里最终会在branch_table分支事务表中插入一条分支事务记录
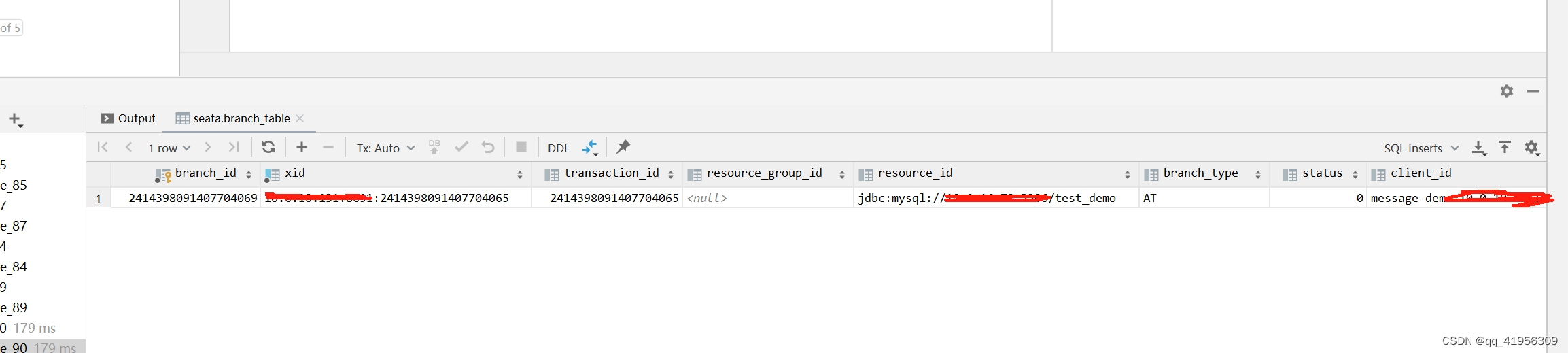
保存UndoLog
ConnectionProxy
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
AbstractUndoLogManager
// AbstractUndoLogManager
public void flushUndoLogs(ConnectionProxy cp) throws SQLException {
ConnectionContext connectionContext = cp.getContext();
if (!connectionContext.hasUndoLog()) {
return;
}
String xid = connectionContext.getXid();
long branchId = connectionContext.getBranchId();
// UndoLog内容,包含xid、branchId、执行sql阶段存储的SQLUndoLog集合
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = new BranchUndoLog();
branchUndoLog.setXid(xid);
branchUndoLog.setBranchId(branchId);
branchUndoLog.setSqlUndoLogs(connectionContext.getUndoItems());
// 默认使用jackson序列化UndoLog
UndoLogParser parser = UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance();
byte[] undoLogContent = parser.encode(branchUndoLog);
// 如果UndoLog大于64KB启用压缩,默认使用zip压缩
CompressorType compressorType = CompressorType.NONE;
if (needCompress(undoLogContent)) {
compressorType = ROLLBACK_INFO_COMPRESS_TYPE;
undoLogContent = CompressorFactory.getCompressor(compressorType.getCode()).compress(undoLogContent);
}
// 子类实现
insertUndoLogWithNormal(xid, branchId, buildContext(parser.getName(), compressorType), undoLogContent, cp.getTargetConnection());
}
protected void insertUndoLogWithNormal(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent,
Connection conn) throws SQLException {
insertUndoLog(xid, branchId, rollbackCtx, undoLogContent, State.Normal, conn);
}
private void insertUndoLog(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent,
State state, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
try (PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(INSERT_UNDO_LOG_SQL)) {
pst.setLong(1, branchId); // 分支事务id
pst.setString(2, xid); // 全局事务id
pst.setString(3, rollbackCtx); // 回滚上下文,包含序列化方式、压缩方式
pst.setBytes(4, undoLogContent); // UndoLog
pst.setInt(5, state.getValue()); // 状态
pst.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!(e instanceof SQLException)) {
e = new SQLException(e);
}
throw (SQLException) e;
}
}
这里最终会在undo_log表里插入一条记录

RM反馈结果
如果提交失败,RM向TC汇报BranchReportRequest,告知TC一阶段提交失败;如果提交成功,默认情况下不做任何操作
private void report(boolean commitDone) throws SQLException {
if (context.getBranchId() == null) {
return;
}
int retry = REPORT_RETRY_COUNT; // 5次
while (retry > 0) {
try {
//提交
DefaultResourceManager.get().branchReport(BranchType.AT, context.getXid(), context.getBranchId(),
commitDone ? BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Done : BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed, null);
return;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to report [" + context.getBranchId() + "/" + context.getXid() + "] commit done ["
+ commitDone + "] Retry Countdown: " + retry);
retry--;
if (retry == 0) {
throw new SQLException("Failed to report branch status " + commitDone, ex);
}
}
}
}
AbstractResourceManager
@Override
public void branchReport(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, BranchStatus status, String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
try {
BranchReportRequest request = new BranchReportRequest();
request.setXid(xid);
request.setBranchId(branchId);
request.setStatus(status);
request.setApplicationData(applicationData);
BranchReportResponse response = (BranchReportResponse) RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new RmTransactionException(response.getTransactionExceptionCode(), String.format("Response[ %s ]", response.getMsg()));
}
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC Timeout", toe);
} catch (RuntimeException rex) {
throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BranchReportFailed, "Runtime", rex);
}
}
AbstractCore
@Override
public void branchReport(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, BranchStatus status,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, true);
BranchSession branchSession = globalSession.getBranch(branchId);
if (branchSession == null) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(BranchTransactionNotExist,
String.format("Could not found branch session xid = %s branchId = %s", xid, branchId));
}
branchSession.setApplicationData(applicationData);
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
//设置分支事务状态为PhaseOne_Failed 分支事务一阶段业务逻辑失败
globalSession.changeBranchStatus(branchSession, status);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Report branch status successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId());
}
}
全局锁重试
注册分支事务阶段,TC会根据BranchRegisterRequest中的lockKey去获取全局锁,可能返回异常LockConflictException,针对于这个异常LockRetryPolicy会执行重试。
public <T> T execute(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
// autocommit=true时,在AbstractDMLBaseExecutor.executeAutoCommitTrue自己管理重试,不需要在这里重复执行重试
if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT && connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
return callable.call();
} else {
return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
}
}
protected <T> T doRetryOnLockConflict(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
LockRetryController lockRetryController = new LockRetryController();
while (true) {
try {
return callable.call();
} catch (LockConflictException lockConflict) {
onException(lockConflict);
if (connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()
&& lockConflict.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflictFailFast) {
lockConflict.setCode(TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflict);
}
lockRetryController.sleep(lockConflict);
} catch (Exception e) {
onException(e);
throw e;
}
}
}
LockRetryController控制获取全局锁的重试次数和重试间隔,默认情况下重试次数lockRetryTimes=30次,重试间隔(睡眠时间)lockRetryInterval=10ms。
public LockRetryController() {
this.lockRetryInterval = getLockRetryInterval();
this.lockRetryTimes = getLockRetryTimes();
}
public void sleep(Exception e) throws LockWaitTimeoutException {
if (--lockRetryTimes < 0 || (e instanceof LockConflictException
&& ((LockConflictException)e).getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflictFailFast)) {
throw new LockWaitTimeoutException("Global lock wait timeout", e);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(lockRetryInterval);
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
}
}
回滚
1.目标Connection执行rollback;
2.如果分支事务注册成功,但是可能由于本地事务提交失败,向TC汇报一阶段提交失败(BranchReportRequest);
3.清空上下文;
ConnectionProxy
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
targetConnection.rollback();
if (context.inGlobalTransaction() && context.isBranchRegistered()) {
report(false);
}
context.reset();
}
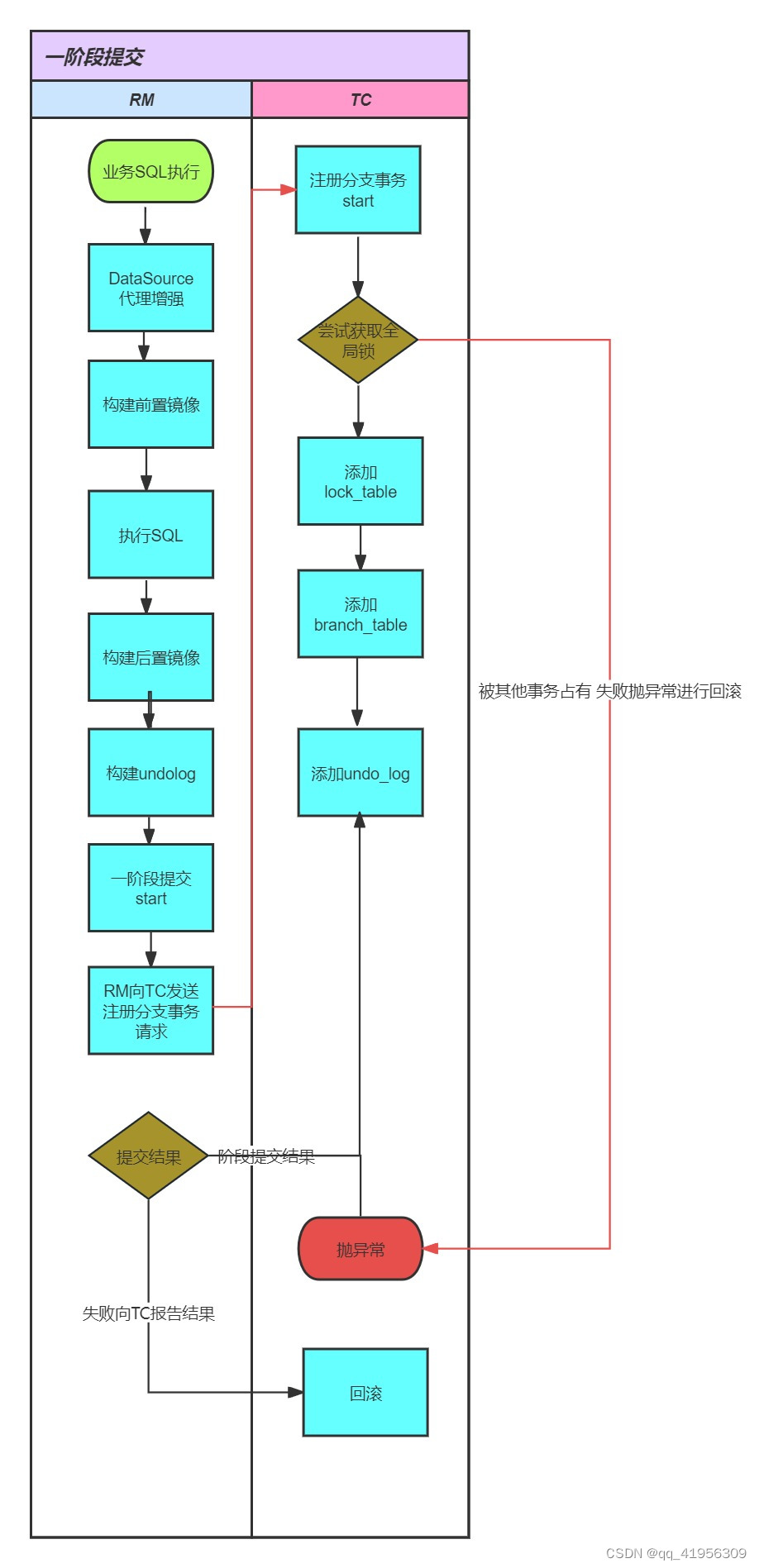
总结
1.项目启动的时候会为DataSource做增强 当全局事务开启之后执行业务代码的时候会进到DataSource的代理中然后由执行器去做语句的执行
2.开启本地事务
3.在执行业务语句之前会构建前置镜像 其实就相当于一个 select id from test where 修改条件/删除条件 = xxx for uodate 用于在后续的事务提交中提供数据的一致性保证。 以便在事务提交时使用这个镜像来比较和确认事务是否能够成功提交。
4. 然后会执行业务代码
5.构建后置镜像 以完成全局事务的最终状态。 用于最终提交或回滚阶段,以确保所有分支事务都能够正确地提交或回滚 SELECT id FROM test WHERE (id) in ( (?) ) 后置镜像是通过前置镜像的快照得到
总体来说,构建前置镜像和后置镜像是为了保障分布式事务的一致性和可靠性。前置镜像保存了事务执行前的状态,而后置镜像保存了事务执行后的状态,通过比较这两个镜像的差异,Seata能够在事务提交或回滚阶段保证数据的一致性
6.然后会构建一个undolog 但是不会真正的提交
7.注册分支事务之前会去获取一个全局锁 如果获取不成功则会抛异常 此时被其他事务在占用 如果能获取成功则往lock_table 插入一条锁记录
8.注册分支事务 就是往 branch_table里面去插入一条分支事务的记录
9.然后会保存undo_log的信息 其实就是往每个业务库的 undo_log里面插入一个记录
10.释放本地锁
11.当上述操作都做完并没有异常的话 一阶段提交完成
12.假如上述操作有异常会触发回滚向TC报告一阶段异常 然后做业务代码的回滚
自此一阶段提交宣告完毕



![[网络安全]在win2000虚拟机上创建隐藏账户](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/17e375bd0c094c97920361bd82f2ec7d.bmp)