背景
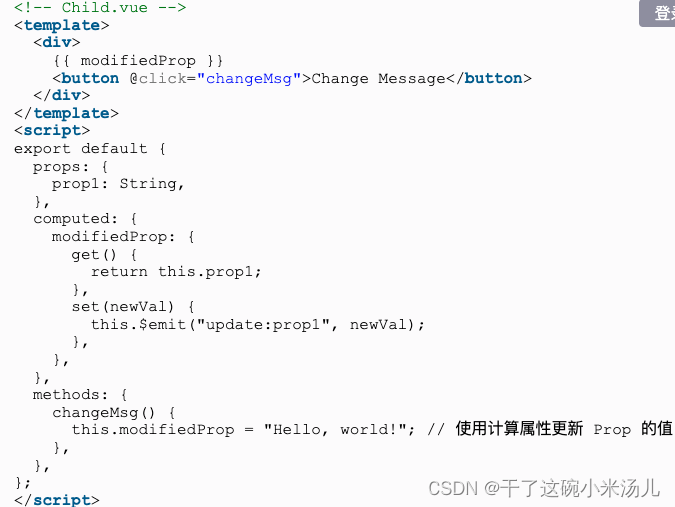
项目开发过程中,有一些情况下将配置文件放在resource下能简化代码实现和部署时的打包步骤。例如: 项目中使用的数据库升级脚本、初始化脚本。将文件放到resource下,打包在jar包中,不能直接通过File路径读取。下面介绍两种读取文本文件内容和获取文件夹下所有子文件名的方法。
示例文件目录:

读取文本文件内容
/**
* 读取 resource下文件内容
*
* @param resourceFilePath resource下文件相对路径. 例如: dbscript/123.sql
* @return 文件内容列表
*/
public List<String> readFileInResource(String resourceFilePath) {
List<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("/" + resourceFilePath);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String line = "";
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
lines.add(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Read file fail. resourceFilePath:" + resourceFilePath, e);
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
LOGGER.error("Close file fail.", e);
}
}
}
return lines;
}
获取文件夹下子文件名称
/**
* 获取resource下文件夹中的文件名列表
*
* @param folderPath 文件夹路径. 行对路径. 如: dbscript
* @return 文件名称列表
*/
public List<String> getFileListInResource(String folderPath) {
List<String> files = new ArrayList<>();
try {
File folderDir = ResourceUtils.getFile(ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX + folderPath);
if (!folderDir.exists()) {
return files;
}
files = Arrays.asList(Objects.requireNonNull(folderDir.list())) ;
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Get file list fail. folderPath:" + folderPath, e);
}
return files;
}