一、QML语法(QML Syntax)
QML是一种描述用户界面的声明式语言。它将用户界面分解成一些更小的元素,这些元素能够结合成一个组件。QML语言描述了用户界面元素的形状和行为。用户界面能够使用JavaScript来提供修饰,或者增加更加复杂的逻辑
- import声明导入了一个指定的模块版本,一般来说会导入QtQuick2.0来作为初始元素的引用。
- 使用//可以单行注释,使用/**/可以多行注释,就像C/C++和JavaScript一样。
- 每一个QML文件都需要一个根元素,就像HTML一样。
- 一个元素使用它的类型声明,然后使用{}进行包含。
- 元素拥有属性,他们按照name:value的格式来赋值。
- 任何在QML文档中的元素都可以使用它们的id进行访问(id是一个任意的标识符)。
- 元素可以嵌套,这意味着一个父元素可以拥有多个子元素。子元素可以通过访问parent关键字来访问它们的父元素。
1、属性(Properties)
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Rectangle{
id: root
width: 300; height: 300
Text {
// (1) identifier
id: thisLabel
// (2) set x- and y-position
x: 24; y: 16
// (3) bind height to 2 * width
height: 2 * width
// (4) custom property
property int times: 24
// (5) property alias
property alias anotherTimes: thisLabel.times
// (6) set text appended by value
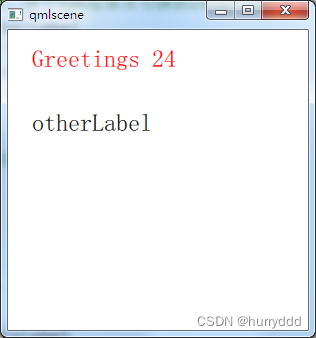
text: "Greetings " + times
// (7) font is a grouped property
font.family: "Ubuntu"
font.pixelSize: 24
// (8) KeyNavigation is an attached property
// 快速切换焦点,按下tab后焦点切换到otherLael
KeyNavigation.tab: otherLabel
// (9) signal handler for property changes
onHeightChanged: console.log('height:', height)
// focus is neeed to receive key events
focus: true
// change color based on focus value
color: focus?"red":"black"
}
Text {
id: otherLabel
x:24; y:80
font.family: "Ubuntu"
font.pixelSize: 24
KeyNavigation.tab: thisLabel
focus: !thisLabel.focus
color: focus? "red" : "black"
text: qsTr("otherLabel")
}
}- id是一个非常特殊的属性值,它在一个QML文件中被用来引用元素。id不是一个字符串,而是一个标识符和QML语法的一部分。一个id在一个QML文档中是唯一的,并且不能被设置为其它值,也无法被查询(它的行为更像C++世界里的指针)。
- 一个属性能够设置一个值,这个值依赖于它的类型。如果没有对一个属性赋值,那么它将会被初始化为一个默认值。你可以查看特定的元素的文档来获得这些初始值的信息。
- 一个属性能够依赖一个或多个其它的属性,这种操作称作属性绑定。当它依赖的属性改变时,它的值也会更新。这就像订了一个协议,在这个例子中height始终是width的两倍。
- 添加自己定义的属性需要使用property修饰符,然后跟上类型,名字和可选择的初始化值(property : )。如果没有初始值将会给定一个系统初始值作为初始值。注意如果属性名与已定义的默认属性名不重复,使用default关键字你可以将一个属性定义为默认属性。这在你添加子元素时用得着,如果他们是可视化的元素,子元素会自动的添加默认属性的子类型链表(children propertylist)。
- 另一个重要的声明属性的方法是使用alias关键字(property alias : )。alias关键字允许我们转发一个属性或者转发一个属性对象自身到另一个作用域。我们将在后面定义组件导出内部属性或者引用根级元素id会使用到这个技术。一个属性别名不需要类型,它使用引用的属性类型或者对象类型。
- text属性依赖于自定义的timers(int整型数据类型)属性。int整型数据会自动的转换为string字符串类型数据。这样的表达方式本身也是另一种属性绑定的例子,文本结果会在times属性每次改变时刷新。
- 一些属性是按组分配的属性。当一个属性需要结构化并且相关的属性需要联系在一起时,我们可以这样使用它。另一个组属性的编码方式是 font{family:"UBuntu"; pixelSize: 24 }。
- 一些属性是元素自身的附加属性。这样做是为了全局的相关元素在应用程序中只出现一次(例如键盘输入)。编码方式.: 。
- 对于每个元素你都可以提供一个信号操作。这个操作在属性值改变时被调用。例如这里我们完成了当height(高度)改变时会使用控制台输出一个信息。
注意:只有根级目录的属性才能够被其它文件的组件访问,可以使用 property alias 导出外部需要访问的属性
2 、脚本(scripting)
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Text {
id: label
x:24; y:24
height: 300; width: 300
//自定义int类型属性 spacePresses
property int spacePresses: 0
//将spacePresses绑定到text
text: "space pressed: " + spacePresses + " times"
//text发生变化时的处理函数:打印 text changed to: ...
onTextChanged: console.log("text changed to:", text)
//设置具有焦点
focus: true
//space按键按下处理函数,调用JS函数,作用为按下space按键后spacePresses变化--->text变化--->onTextChanged执行
Keys.onSpacePressed: {
increment()
}
//ESC按键按下处理函数,解除spacePresses跟text的绑定,再按下space时text不太发现变化
Keys.onEscapePressed: {
label.text = ''
}
//定义的JS功能函数increment
function increment() {
spacePresses = spacePresses + 1
}
}
二、基本元素(Bsaic Elements)
元素可以被分为可视化元素与非可视化元素。一个可视化元素(例如矩形框Rectangle)有着几何形状并且可以在屏幕上显示。一个非可视化元素(例如计时器Timer)提供了常用的功能,通常用于操作可视化元素。现在我们将专注于几个基础的可视化元素,例如 Item(基础元素对象),Rectangle(矩形框),Text(文本),Image(图像)和MouseArea(鼠标区域)
1、基础元素对象(Item Element)
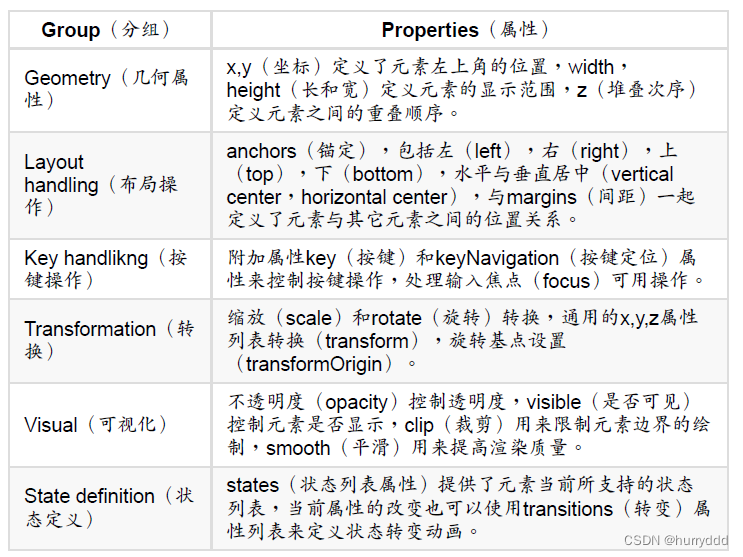
Item(基础元素对象)是所有可视化元素的基础对象,所有其它的可视化元素都继承自Item。它自身不会有任何绘制操作,但是定义了所有可视化元素共有的属性:
2、矩形框元素(Rectangle Element)
Rectangle(矩形框)是基本元素对象的一个扩展,增加了一个颜色来填充它。它还支持边界的定义,使用 border.color(边界颜色),border.width(边界宽度)来自定义边界。你可以使用radius(半径)属性来创建一个圆角矩形。
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Window {
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
title: qsTr("Hello World")
//矩形框
Rectangle{
id: rect1
x:20; y:20
width: 100; height: 100
color: 'lightsteelblue'
}
//中空的圆角矩形框
Rectangle{
id: rect2
x:150; y:20
width: 100; height: 100
border.color: 'lightsteelblue'
border.width: 5
radius: 20
}
//颜色渐变的圆角矩形框
Rectangle{
id: rect3
x:280; y:20
width: 100; height: 100
border.color: 'lightsteelblue'
border.width: 5
radius: 20
gradient: Gradient{ //渐变
GradientStop{position: 0.0; color: 'red'}
GradientStop{position: 1.0; color: 'blue'}
}
}
}
3、文本元素(Text Element)
- 显示文本你需要使用Text元素(Text Element)。它最值得注意的属性是 字符串类型的text属性。这个元素会使用给出的 text(文本)与 font(字体)来计算初始化的宽度与高度。可以使用字体属性组来(font property group)来改变当前的字体,例如 font.family,font.pixelSize,等等。改变文本的颜色值只需要改变颜色属性color就可以了
- 还可以使用 horizontalAlignment 与 verticalAlignment 属性来设置它的对齐效果。为了提高文本的渲染效果,你可以使用 style 和 styleColor 属性来配置文字的外框效果,浮雕效果或者凹陷效果
- 对于过长的文本,如果想要使用省略号来表示,例如A very ... long text,可以使用elide属性来完成这个操作。elide属性允许设置省略位置在文本左边,右边或者中间
- 如果你不想'....'省略号出现,并且希望使用文字换行的方式显示所有的文本,你可以使用 wrapMode 属性(这个属性只在明确设置了宽度后才生效)
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Window {
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
title: qsTr("Text Demo")
Text {
id: text1
text: "The quick brown fox"
color: "#303030"
font.family: "Ubuntu"
font.pixelSize: 28
}
Text {
id: text2
text: "一个很长很长的句子!!!!!"
y: text1.y + text1.height + 20
color: "#ffffff"
font.family: "Ubuntu"
font.pixelSize: 28
width: 100
// //1、省略的效果
// elide: Text.ElideMiddle //省略号在中间
//2、自动换行效果
wrapMode: Text.WrapAnywhere
//3、凹陷的效果
style: Text.Sunken
styleColor: "#000000"
}
}


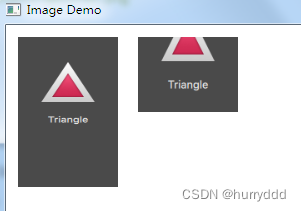
4、图像元素(Image Element)
一个图像元素(Image Element)能够显示不同格式的图像(例如PNG,JPG,GIF,BMP)。想要知道更加详细的图像格式支持信息,可以查看Qt的相关文档。source属性(source property)提供了图像文件的链接信息,fillMode(文件模式)属性
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Window {
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
title: qsTr("Image Demo")
Image {
id: image1
x: 12; y: 12
width: 100; height: 150
source: "assets/qmltree.png"
}
Image {
id: image2
x: image1.width + image1.x + 20; y: 12
fillMode: Image.PreserveAspectCrop
clip: true
width: 100; height: 150 / 2
source: "assets/qmltree.png"
}
}
5、鼠标区域元素(MouseArea Element)
为了与不同的元素交互,你通常需要使用 MouseArea(鼠标区域)元素。这是一个矩形的非可视化元素对象,你可以通过它来捕捉鼠标事件。当用户与可视化端口交互时,mouseArea通常被用来与可视化元素对象一起执行命令。
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Window {
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
title: qsTr("mouseArea Demo")
Rectangle {
id: rect1
x: 12; y: 12
width: 76; height: 96
color: "lightsteelblue"
MouseArea {
id: area
width: parent.width
height: parent.height
onClicked: rect2.visible = !rect2.visible
}
}
Rectangle {
id: rect2
x: 112; y: 12
width: 76; height: 96
border.color: "lightsteelblue"
border.width: 4
radius: 8
}
}点击rect1时,rect2会消失

三、组件(Compontents)
一个组件是一个可以重复使用的元素,QML提供几种不同的方法来创建组件。但是目前我们只对其中一种方法进行讲解:一个文件就是一个基础组件。一个以文件为基础的组件在文件中创建了一个QML元素,并且将文件以元素类型来命名(例如Button.qml)。你可以像任何其它的QtQuick模块中使用元素一样来使用这个组件


有一点很重要,只有根级目录的属性才能够被其它文件的组件访问

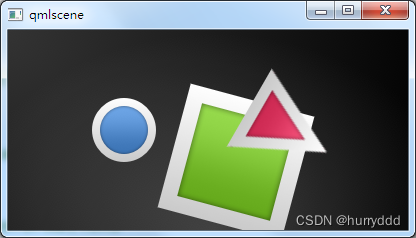
四、简单的转换(Simple Transformations)
简单变换包括平移、旋转和缩放操作
- 平移:通过改变x、y位置完成简单的平移
- 旋转:旋转是改变rotation(旋转)属性来完成的,这个值使用角度作为单位(0~360)
- 缩放:缩放是通过改变 scale(比例)的属性来完成的,小于1意味着缩小,大于1意味着放大
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Item {
// set width based on given background
width: bg.width
height: bg.height
Image { // nice background image
id: bg
source: "assets/background.png"
}
//必须在图像之前,因为顺序很重要,否则这个鼠标区域将在其他元素之前,并消耗鼠标事件!!!
MouseArea {
id: backgroundClicker
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
// reset our little scene
circle.x = 84
box.rotation = 0
triangle.rotation = 0
triangle.scale = 1.0
}
}
ClickableImage { //平移
id: circle
x: 84; y: 68
source: "assets/circle_blue.png"
antialiasing: true
onClicked: {
// increase the x-position on click
x += 20
}
}
ClickableImage { //旋转
id: box
x: 164; y: 68
source: "assets/box_green.png"
antialiasing: true
onClicked: {
// increase the rotation on click
rotation += 15
}
}
ClickableImage { //旋转+缩放
id: triangle
x: 248; y: 68
source: "assets/triangle_red.png"
antialiasing: true
onClicked: {
// several transformations
rotation += 15
scale += 0.05
}
}
function _test_transformed() {
circle.x += 20
box.rotation = 15
triangle.scale = 1.2
triangle.rotation = -15
}
function _test_overlap() {
circle.x += 40
box.rotation = 15
triangle.scale = 2.0
triangle.rotation = 45
}
}
五、定位元素(Positioning Element)
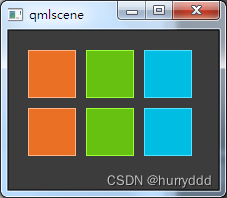
QML中有许多用于定位的元素,这些称为定位器,其中Qt Quick模块提供了以下功能:Row、Column、Grid 和 Flow
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
DarkSquare{
id: root
width: 300; height: 300
// //1、使用Column列定位元素进行定位
// Column{
// id: column
// anchors.centerIn: parent
// spacing: 10
// //布局中有3个小方块,GreenSquare重新设置了width要宽些
// RedSquare{}
// GreenSquare{width: 96}
// BlueSquare{}
// }
// //2、使用Row行定位元素进行定位
// Row{
// id: row
// anchors.centerIn: parent
// spacing: 10
// //布局中有3个小方块,GreenSquare重新设置了width要宽些
// RedSquare{}
// GreenSquare{width: 96}
// BlueSquare{}
// }
// //3、使用Grid网格定位元素进行定位
// Grid{
// id: grid
// anchors.centerIn: parent
// spacing: 10
// //需要指定行、列的数量
// rows: 2
// columns: 3
// //布局中有3个小方块,GreenSquare重新设置了width要宽些
// RedSquare{}
// GreenSquare{width: 96}
// BlueSquare{}
// RedSquare{}
// GreenSquare{width: 96}
// BlueSquare{}
// }
// //4、使用Flow流定位元素进行定位
// Flow{
// id: flow
// anchors.fill: parent //填充到整个父窗口
// anchors.margins: 20 //设置边距
// spacing: 10
// //布局中有3个小方块
// RedSquare{}
// GreenSquare{}
// BlueSquare{}
// RedSquare{}
// GreenSquare{}
// BlueSquare{}
// }
//4、使用Flow流定位元素进行定位
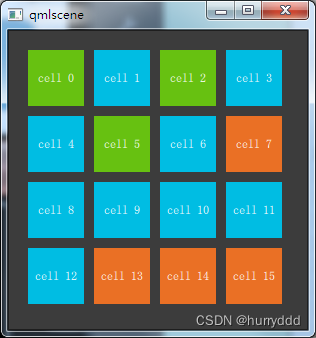
Grid{ //columns默认值为4
id: grid
anchors.fill: parent //填充到整个父窗口
anchors.margins: 20 //设置边距
spacing: 10
property variant colorArray: ["#00bde3", "#67c111", "#ea7025"]
Repeater{ //循环、重复
model: 16 //16次,生成16个矩形框
Rectangle{
id: rect
property int colorIndex: Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
color: grid.colorArray[colorIndex]
width: 56; height: 56
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
color: "white"
text: "cell " + rect.Positioner.index
}
}
}
}
}Column定位:

Row定位:

Grid定位:

Flow定位:
宽度拉伸时

宽度缩短时
通常 Repeater(重复元素)与定位器一起使用。它的工作方式就像for循环与迭代器的模式一样
六、布局(Layout Items)
QML使用 anchors(锚)对元素进行布局。anchoring(锚定)是基础元素对象的基本属性,可以被所有的可视化QML元素使用。一个anchors(锚)就像一个协议,并且比几何变化更加强大。Anchors(锚)是相对关系的表达式,你通常需要与其它元素搭配使用。

一个元素有6条锚定线(top顶,bottom底,left左,right右,horizontalCenter水平中,verticalCenter垂直中)。在文本元素(Text Element)中有一条文本的锚定基线(baseline)。每一条锚定线都有一个偏移(offset)值,在top(顶),bottom(底),left(左),right(右)的锚定线中它们也被称作边距。对于horizontalCenter(水平中)与verticalCenter(垂直中)与baseline(文本基线)中被称作偏移值。
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Window {
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
title: qsTr("layout")
// 1. 元素填充它的父元素。
// GreenSquare{
// BlueSquare{
// text: '(1)'
// anchors.fill: parent
// anchors.margins: 8
// }
// }
// 2. 元素左对齐它的父元素。
GreenSquare {
BlueSquare {
width: 48
y: 8
anchors.left: parent.left
anchors.leftMargin: 8
text: '(2)'
}
}
// //3、元素的左边与它父元素的右边对齐。
// GreenSquare {
// BlueSquare {
// width: 48
// anchors.left: parent.right
// text: '(3)'
// }
// }
// 4. 元素中间对齐。Blue1与它的父元素水平中间对齐。Blue2与Blue1中间对齐,
// 并且它的顶部对齐Blue1的底部。
// GreenSquare {
// BlueSquare {
// id: blue1
// width: 48; height: 24
// y: 8
// anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
// }
// BlueSquare {
// id: blue2
// width: 72; height: 24
// anchors.top: blue1.bottom
// anchors.topMargin: 4
// anchors.horizontalCenter: blue1.horizontalCenter
// text: '(4)'
// }
// }
// 5. 元素在它的父元素中居中。
// GreenSquare {
// BlueSquare {
// width: 48
// anchors.centerIn: parent
// text: '(5)'
// }
// }
// GreenSquare {
// BlueSquare {
// width: 48
// anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
// anchors.horizontalCenterOffset: -12
// anchors.verticalCenter: parent.verticalCenter
// text: '(6)'
// }
// }
}
七、输入元素(Input Element)
我们已经使用过MouseArea(鼠标区域)作为鼠标输入元素。这里我们将更多的介绍关于键盘输入的一些东西。我们开始介绍文本编辑的元素:TextInput(文本输入)和TextEdit(文本编辑)。一个焦点区域(FocusScope)元素 定义了如果焦点区域接收到焦点,它的最后一个使用focus:true的子元素接收焦点,它将会把焦点传递给最后申请焦点的子元素
八、按键属性(Key Element)
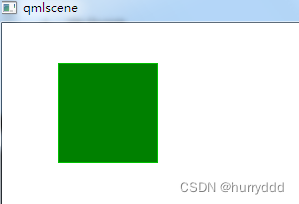
附加属性key允许你基于某个按键的点击来执行代码。例如使用up,down按键来移动一个方块,left,right按键来旋转一个元素,plus,minus按键来缩放一个元素。
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Rectangle {
width: 500; height: 500
Rectangle{
id: square
width: 100; height: 100
color: 'green'
border.color: Qt.lighter(color)
}
focus: true
Keys.onLeftPressed: square.x -= 8
Keys.onRightPressed: square.x += 8
Keys.onUpPressed: square.y -= 8
Keys.onDownPressed: square.y += 8
Keys.onPressed: function (event) {
switch(event.key) {
case Qt.Key_Plus: square.scale += 0.2; break;
case Qt.Key_Minus: square.scale -= 0.2; break;
}
}
}