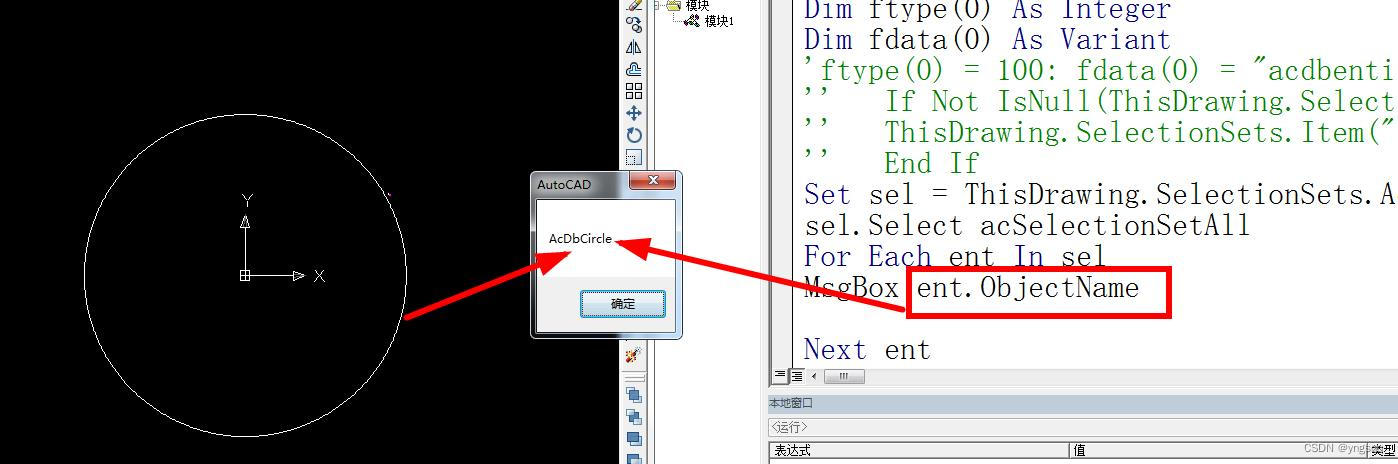
效果展示:
原图:(图片来自 b站up 借我300去洗牙)

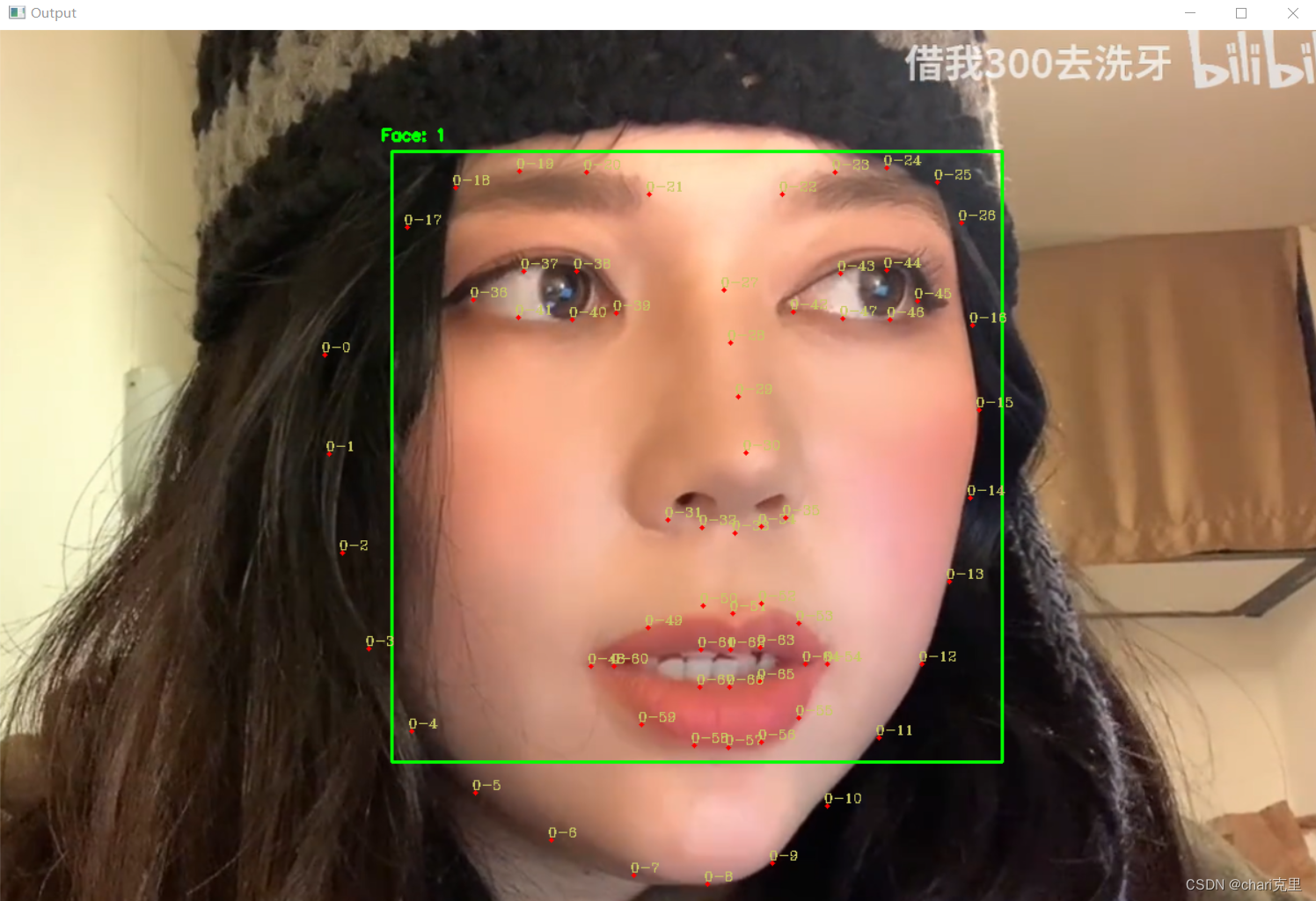
dlib实现的特征点检测
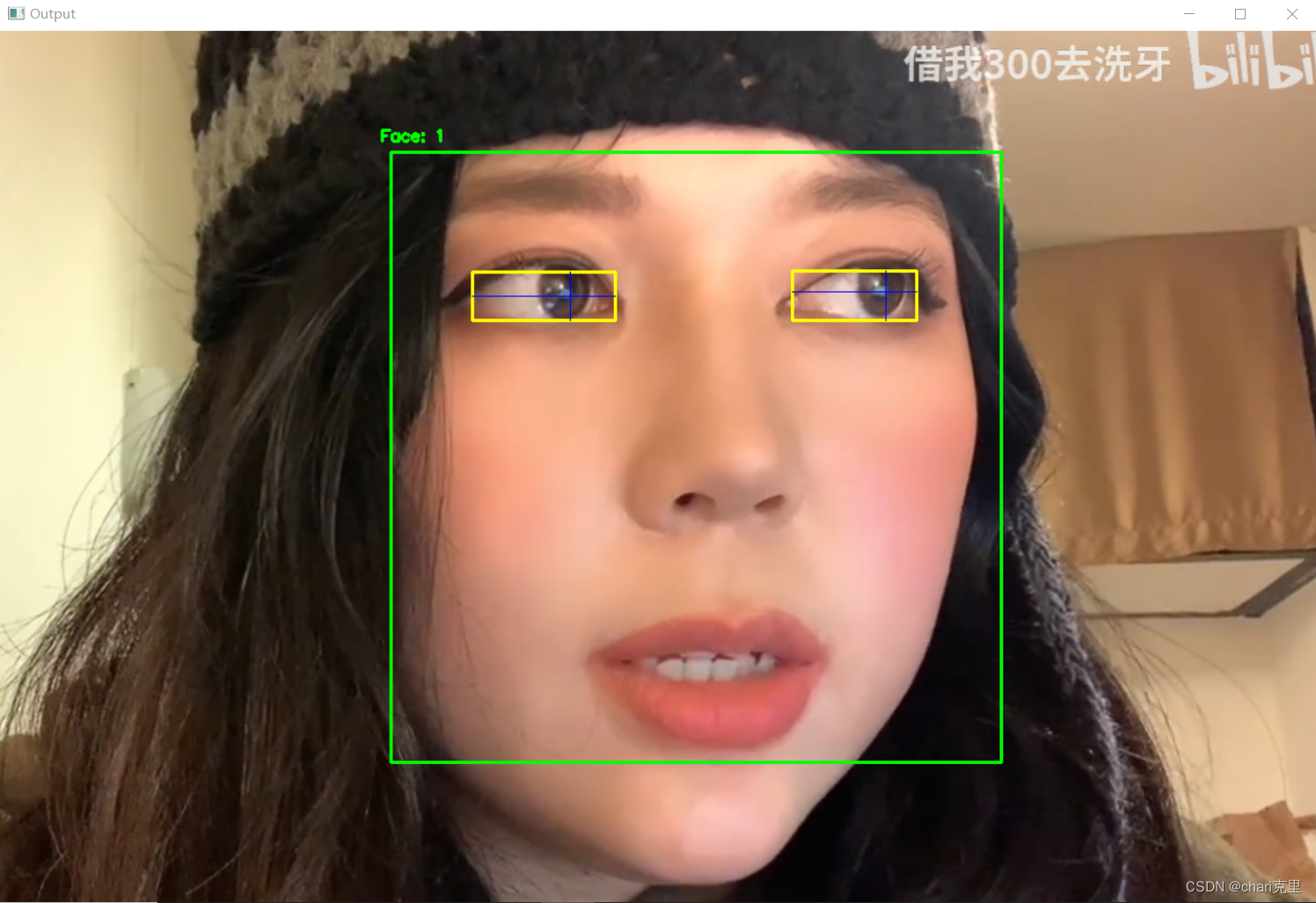
瞳孔检测结果
完整代码:
# encoding:utf-8
import dlib
import numpy as np
import cv2
def rect_to_bb(rect): # 获得人脸矩形的坐标信息
x = rect.left()
y = rect.top()
w = rect.right() - x
h = rect.bottom() - y
return (x, y, w, h)
def shape_to_np(shape, dtype="int"): # 将包含68个特征的的shape转换为numpy array格式
coords = np.zeros((68, 2), dtype=dtype)
for i in range(0, 68):
coords[i] = (shape.part(i).x, shape.part(i).y)
return coords
def resize(image, width=1200): # 将待检测的image进行resize
r = width * 1.0 / image.shape[1]
dim = (width, int(image.shape[0] * r))
resized = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
return resized
def feature():
image_file = r"F:\project_python\facenet\2.PNG"
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(r"F:\project_python\facenet\shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
image = cv2.imread(image_file)
image = resize(image, width=1200)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(gray, 1)
shapes = []
for (i, rect) in enumerate(rects):
shape = predictor(gray, rect)
shape = shape_to_np(shape)
shapes.append(shape)
(x, y, w, h) = rect_to_bb(rect)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, "Face: {}".format(i + 1), (x - 10, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
count1 = 0
count2 = 0# encoding:utf-8
import dlib
import numpy as np
import cv2
def rect_to_bb(rect): # 获得人脸矩形的坐标信息
x = rect.left()
y = rect.top()
w = rect.right() - x
h = rect.bottom() - y
return (x, y, w, h)
def shape_to_np(shape, dtype="int"): # 将包含68个特征的的shape转换为numpy array格式
coords = np.zeros((68, 2), dtype=dtype)
for i in range(0, 68):
coords[i] = (shape.part(i).x, shape.part(i).y)
return coords
def resize(image, width=1200): # 将待检测的image进行resize
r = width * 1.0 / image.shape[1]
dim = (width, int(image.shape[0] * r))
resized = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
return resized
def feature():
image_file = r"F:\project_python\facenet\2.PNG"
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(r"F:\project_python\facenet\shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
image = cv2.imread(image_file)
image = resize(image, width=1200)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(gray, 1)
shapes = []
for (i, rect) in enumerate(rects):
shape = predictor(gray, rect)
shape = shape_to_np(shape)
shapes.append(shape)
(x, y, w, h) = rect_to_bb(rect)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, "Face: {}".format(i + 1), (x - 10, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
count1 = 0
count2 = 0
image1=image.copy()
eyes=[]
eyes2=[]
for shape in shapes:
left_eye=[]
right_eye=[]
left_eye2=[]
right_eye2=[]
for (x, y) in shape:
cv2.circle(image1, (x, y), 2, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.putText(image1, str(count1)+"-"+str(count2), (x-3, y-3), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.4, (100, 200, 200), 1)
if count2>=36 and count2<=41:
left_eye.append([x,y])
left_eye2.append((x,y))
elif count2>=42 and count2<=47:
right_eye.append([x,y])
right_eye2.append((x,y))
count2+=1
count1+=1
eyes.append([left_eye,right_eye])
eyes2.append([left_eye2,right_eye2])
cv2.imshow("Output", image1)
cv2.waitKey(0)
image2=image.copy()
for i in range(len(eyes)):
e=eyes[i]
for j in range(len(e)):
points=e[j]
# 六边形的顶点坐标
pts = np.array(points, np.int32)
pts = pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2))
# 创建一个空白图像作为掩模
mask = np.zeros_like(image)
# 在掩模上绘制填充了白色的六边形
cv2.fillPoly(mask, [pts], (255, 255, 255))
# 创建一个白色背景图像
white_background = np.ones_like(image) * 255
# 在白色背景上绘制填充了原始图像的六边形
cv2.fillPoly(white_background, [pts], (0, 0, 0))
# 将原始图像和白色背景图像按位取反
inverse_mask = cv2.bitwise_not(mask)
# 将原始图像中六边形内的部分与白色背景中六边形外的部分相结合
result = cv2.bitwise_and(image, mask) + cv2.bitwise_and(white_background, inverse_mask)
# 显示最终结果
cv2.imshow('Result', result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 找到最小长方形的左上角和右下角坐标
min_x = min(point[0] for point in points)
max_x = max(point[0] for point in points)
min_y = min(point[1] for point in points)
max_y = max(point[1] for point in points)
cv2.rectangle(image2, (min_x, min_y), (max_x, max_y), (0, 255, 255), 2)
# 获取最小长方形中的图像部分
roi = result[min_y:max_y, min_x:max_x]
# 将图像部分转换为灰度图
gray_roi = cv2.cvtColor(roi, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# define a threshold, 128 is the middle of black and white in grey scale
thresh = 100
# assign blue channel to zeros
img_binary = cv2.threshold(gray_roi, thresh, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
cv2.imshow("Output", img_binary)
cv2.waitKey(0)
#处理眼睛反光形成的白点
# 获取图像高度
img_binary1=img_binary.copy()
height = img_binary1.shape[0]
# 遍历每一列像素
for col in range(img_binary1.shape[1]):
white_run_length = 0
start_index = 0
end_index = 0
for row in range(height):
if img_binary1[row, col] == 255: # 白色像素
if white_run_length == 0:
start_index = row
white_run_length += 1
end_index = row
else: # 黑色像素
if white_run_length > 0 and white_run_length < height / 2 and (start_index == 0 or img_binary1[start_index - 1, col] == 0) and (end_index == height - 1 or img_binary1[end_index + 1, col] == 0):
img_binary1[start_index:end_index + 1, col] = 0 # 将连续的白色像素改为黑色像素
white_run_length = 0
cv2.imshow("Output", img_binary1)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 计算每一列的像素值总和
column_sums = np.sum(img_binary1, axis=0)
# 计算每一列与相邻的n列的总和
neighbor_sums = np.convolve(column_sums, np.ones(1), mode='valid')
# 找到结果最小的n列的列号
min_indices = np.argpartition(neighbor_sums, 20)[:20]
# 将列号按数字排序
sorted_indices = np.sort(min_indices)
# 找到这7列的最中间的列的列号
middle_column = sorted_indices[len(sorted_indices) // 2]
print("每一列与相邻的6列的总和:", neighbor_sums)
print("结果最小的7列的列号(按数字排序):", sorted_indices)
print("这7列的最中间的列的列号:", middle_column)
cv2.line(image2, (min_x+middle_column, min_y), (min_x+middle_column, max_y), (255, 0, 0))
# 找出结果最小的列
min_column = img_binary[:, middle_column]
# 找出连续相邻的白色像素点
white_pixels = np.where(min_column == 255)[0]
# 找出连续相邻的白色像素点中最长的一段
longest_start = 0
longest_end = 0
max_length = 0
current_start = 0
current_length = 0
for i in range(1, len(white_pixels)):
if white_pixels[i] == white_pixels[i-1] + 1:
current_length += 1
else:
if current_length > max_length:
max_length = current_length
longest_start = white_pixels[current_start]
longest_end = white_pixels[i-1]
current_start = i
current_length = 0
# 判断起始位置和结束位置的中点在图像的上半部分还是下半部分
mid_point = (longest_start + longest_end) // 2
height = img_binary.shape[0]
if mid_point < height // 2:
print("最长的白色像素段起始位置:", longest_start)
print("最长的白色像素段结束位置:", longest_end)
print("连续的长度:", max_length)
print("中点在图像的上半部分")
cv2.line(image2, (min_x,min_y+ height // 2-max_length), (max_x,min_y+ height // 2-max_length), (255, 0, 0))
else:
print("最长的白色像素段起始位置:", longest_start)
print("最长的白色像素段结束位置:", longest_end)
print("连续的长度:", max_length)
print("中点在图像的下半部分")
cv2.line(image2, (min_x,min_y+ height // 2+max_length), (max_x,min_y+ height // 2+max_length), (255, 0, 0))
cv2.imshow("Output", image2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
feature()
文件下载:
1.shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat 下载地址
1.官方下载地址(会比较慢) http://dlib.net/files/
2.我的网盘: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ORhqLS1bkHyyYfzbmftNpg 提取码:va12
3.我的资源(免费下载):https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_51985653/15122811
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51985653/article/details/113748025