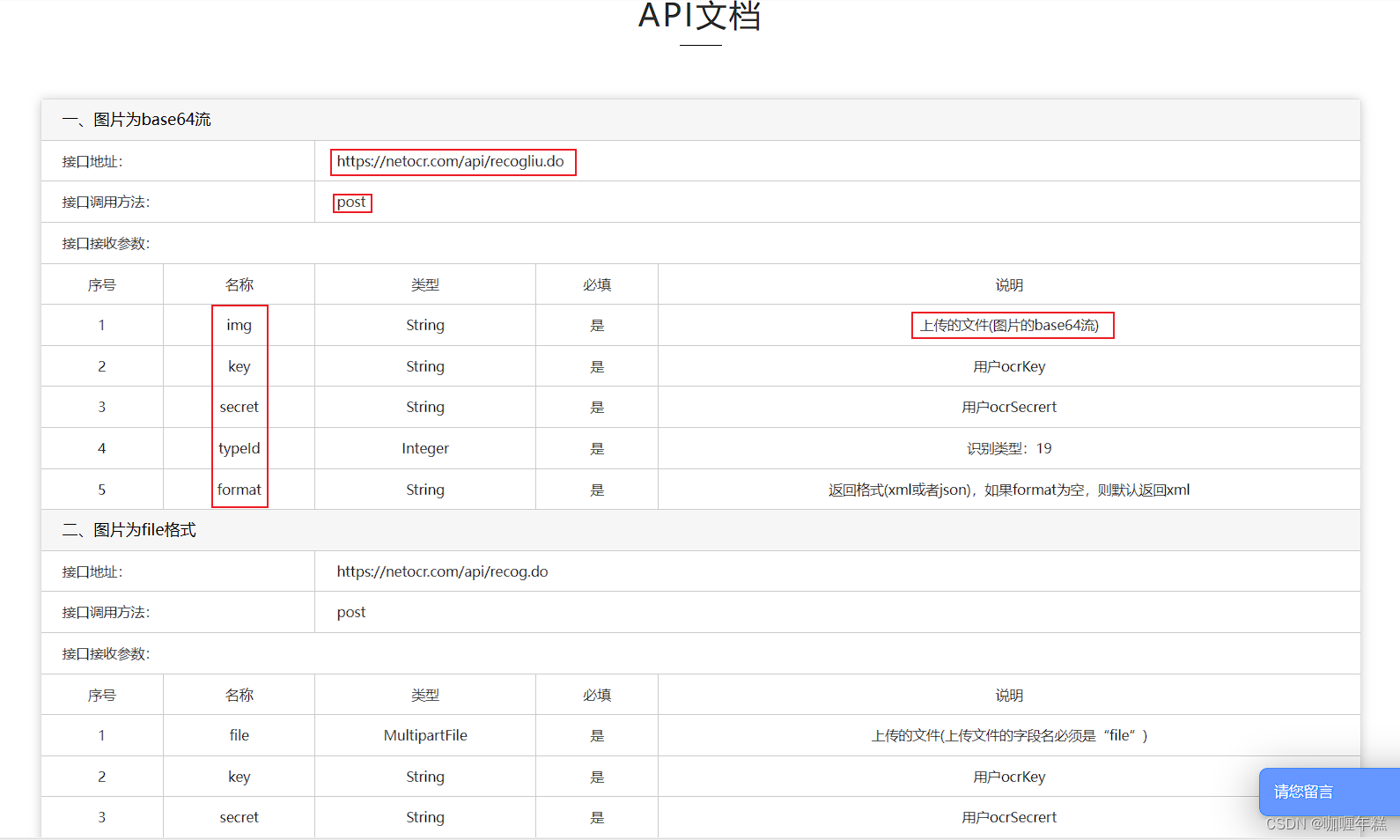
场景再现:
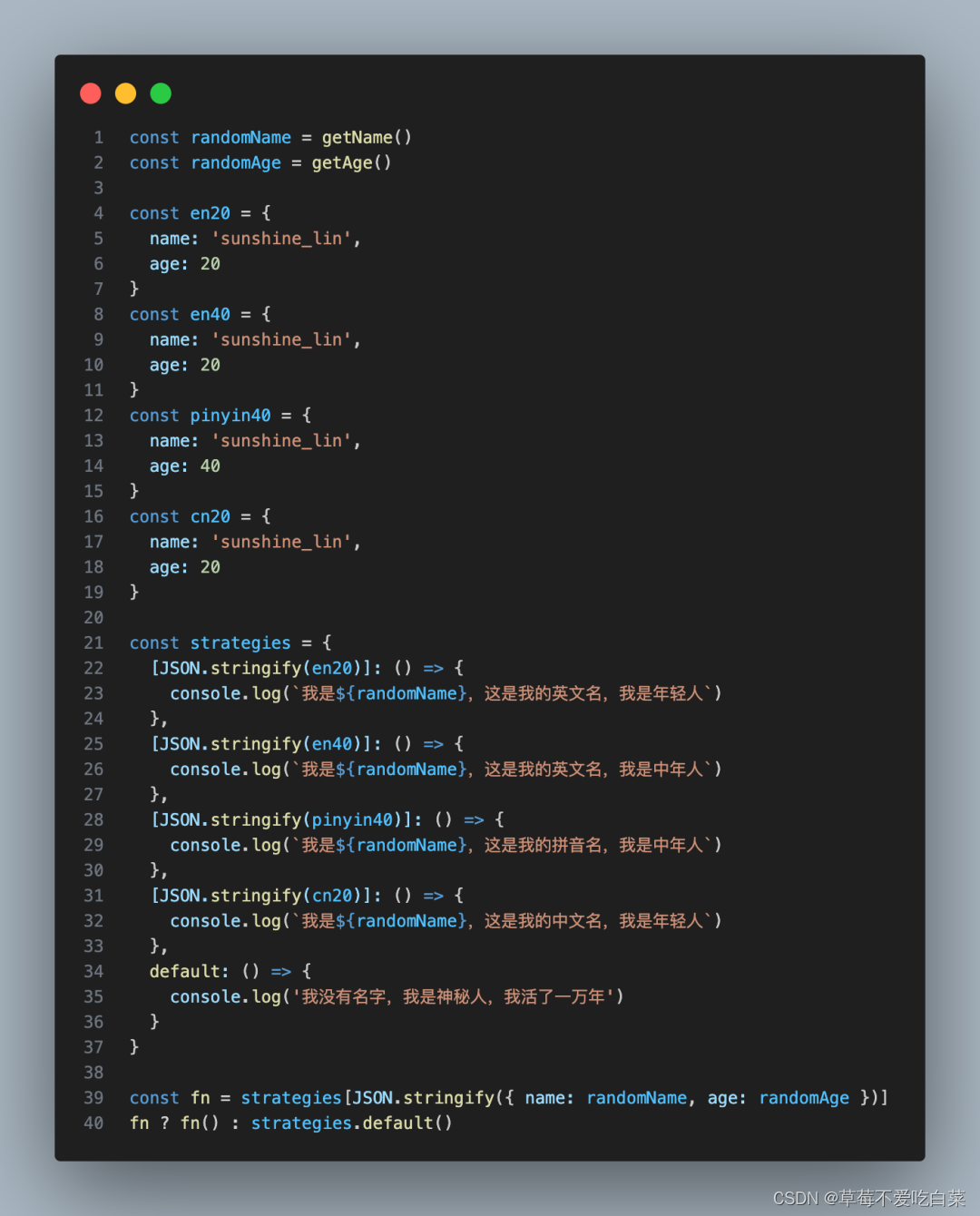
模式正确封装方法:
class Strategy {
map = new Map();
constructor({ defaultCbs, errorCbs }) {
// 默认
this.map.set("default", defaultCbs ?? []);
// 错误
this.map.set("error", errorCbs ?? []);
}
// 获取条件key
getCondition(condition) {
const conditionMap = new Map();
Object.keys(condition)
.sort()
.forEach((key) => {
conditionMap.set(key, condition[key]);
});
return JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(conditionMap));
}
// 增加条件情况
add(condition, conditionCbs) {
const currentCondition = this.getCondition(condition);
let cbs = this.map.get(currentCondition);
if (!cbs) {
this.map.set(currentCondition, []);
cbs = this.map.get(currentCondition);
}
cbs.push(...conditionCbs);
}
// 执行条件情况
do(condition) {
const currentCondition = this.getCondition(condition);
try {
const cbs = this.map.get(currentCondition);
if (cbs) {
cbs.forEach((cb) => cb(JSON.parse(currentCondition)));
} else {
// 匹配不到则执行默认函数
const defaultCbs = this.map.get("default");
defaultCbs.forEach((cb) => cb(JSON.parse(currentCondition)));
}
} catch (e) {
// 报错执行报错函数
const errorCbs = this.map.get("error");
errorCbs.forEach((cb) => cb(e));
}
}
}
const strategy = new Strategy({
defaultCbs: [
(v) => {
console.log("这是默认情况", v);
},
],
errorCbs: [
(e) => {
console.log("这是错误情况", e);
},
],
});
const condition = {
name: "sunshine_lin",
weight: 160,
};
// 此时还没有注册条件事件,所以输出默认事件
strategy.do(condition);
// 添加条件函数
strategy.add(condition, [
(v) => {
console.log("事件1", v);
},
(v) => {
console.log("事件2", v);
},
]);
// 此时有条件事件了,输入:事件1 事件2
strategy.do(condition);
const condition2 = {
name: "error_lin",
weight: 1000000,
};
// 可以增加报错条件
strategy.add(condition2, [
(v) => {
throw new Error("我超重啦!!!!");
},
]);
// 报错,输出:我超重啦!!!!
strategy.do(condition2)
要点注释:
1. 使用Map 这个数据结构而非对象,是因为Map 的 key 是有顺序
2. 策略模式=》发布订阅模式的转变
·······················本文原链接 前端之神-林三心 微信公众号文章,如有侵权,可以随时联系删除······················