203.移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
public class Leetcode203 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode head = new ListNode();
head.next = new ListNode(1, new ListNode(2, new ListNode(3)));
ListNode listNode = removeElements(head, 3);
while (listNode != null) {
System.out.print(listNode.val+" -> ");
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
public static ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//虚拟头结点
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead.next = head;
// cur 用于遍历链表
// cur 与 dummyHead 指向堆中同一个对象 cur中删除了 dummyHead中也就删除了
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
// 删除节点
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
// 删除节点之后 不能直接移动链表
// 如果 删除的是最后一个元素 删除之后当前 节点就是 null null没有next 就会报空指针异常
else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {
}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
707.设计链表
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
示例:
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addAtHead(1);
linkedList.addAtTail(3);
linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回2
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回3
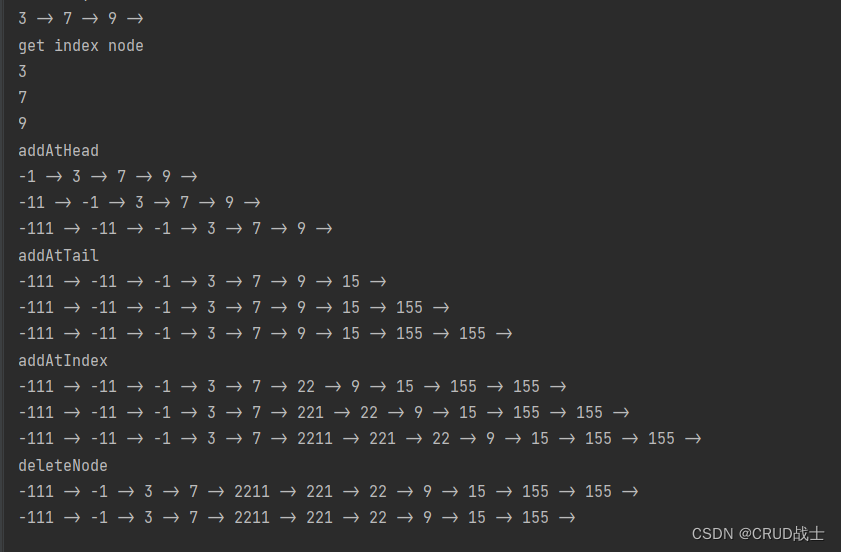
public class Leetcode707 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造链表
Node node = new Node(3, new Node(7, new Node(9)));
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.heard = node;
// 初始链表
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
System.out.println("get index node");
System.out.println(linkedList.get(0));
System.out.println(linkedList.get(1));
System.out.println(linkedList.get(2));
System.out.println("addAtHead");
linkedList.addAtHead(-1);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.addAtHead(-11);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.addAtHead(-111);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
System.out.println("addAtTail");
linkedList.addAtTail(15);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.addAtTail(155);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.addAtTail(155);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
System.out.println("addAtIndex");
linkedList.addAtIndex(5, 22);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.addAtIndex(5, 221);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.addAtIndex(5, 2211);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
System.out.println("deleteNode");
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(10);
linkedList.print(linkedList.heard);
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
Node heard;
public MyLinkedList() {
this.heard = new Node(0);
}
/**
* 获取第 i 个节点 val
*
* @param index index
* @return 第 i 个节点 val
*/
public int get(int index) {
//计数
int i = 0;
// 虚拟头结点
Node dummyHead = new Node();
dummyHead.next = heard;
while (dummyHead.next != null) {
if (i == index) {
return dummyHead.next.val;
}
// 指针右移
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 头插法
*
* @param val val
*/
public void addAtHead(int val) {
// 虚拟头结点
Node dummyHead = new Node();
dummyHead.next = heard;
// 要插入的节点
Node newNode = new Node(val);
// 新节点的next 存放 虚拟头结点的next
newNode.next = dummyHead.next;
// 新节点赋值给 头结点
heard = newNode;
}
/**
* 尾插法
*
* @param val val
*/
public void addAtTail(int val) {
// 虚拟节点
Node dummyHead = new Node();
dummyHead.next = heard;
while (dummyHead.next != null) {
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
// 遍历到最后一个节点了
dummyHead.next = new Node(val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
// 小于0 插入在头部
if (index < 0) {
addAtHead(val);
}
Node dummyHead = new Node();
dummyHead.next = heard;
// 计数
int i = 0;
while (dummyHead.next != null) {
if (i == index) {
Node newNode = new Node(val);
newNode.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = newNode;
return;
}
i++;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
if (index == i) {
addAtTail(val);
}
}
/**
* 删除 第 i 个节点
*
* @param index index
*/
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
Node dummyHead = new Node();
dummyHead.next = heard;
int i = 0;
while (dummyHead.next != null) {
if (i == index) {
dummyHead.next = dummyHead.next.next;
return;
}
i++;
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
}
/**
* 打印 链表
*
* @param list list
*/
public void print(Node list) {
Node dummyHead = new Node();
dummyHead.next = list;
while (dummyHead.next != null) {
System.out.print(dummyHead.next.val + " -> ");
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
public Node(int val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public Node() {
}
}
206.反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
public class Leetcode206 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode head = new ListNode();
head.next = new ListNode(1, new ListNode(2, new ListNode(3)));
ListNode listNode = reverseList(head);
while (listNode != null) {
System.out.print(listNode.val + " -> ");
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
/**
* 头插法实现
*
* @param head head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newList = new ListNode();
while (head != null) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(head.val);
newNode.next = newList.next;
newList.next = newNode;
head = head.next;
}
return newList.next;
}
/**
* 双指针 写法
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseList1(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}

![[思维模式-19]:《复盘》-7- “积”篇 - 操作复盘- 如何做好复盘](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/df070e9ab6544365b887d01c211faee3.png)