130道基础OJ编程题之: 47 ~ 57 道
文章目录
- 130道基础OJ编程题之: 47 ~ 57 道
- 0. 昔日OJ编程题:
- 47. BC50 计算单位阶跃函数
- 48. BC51 三角形判断
- 49. BC52 衡量人体胖瘦程度
- 50. BC53 计算一元二次方程
- 51. BC54 获得月份天数
- 52. BC55 简单计算器
- 53. BC56 线段图案
- 54. BC57 正方形图案
- 55. BC58 直角三角形图案
- 56. BC59 翻转直角三角形图案
- 57. BC60 带空格直角三角形图案
- 总结:
- 最后:
OJ技巧
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b;
while (scanf("%d %d", &a, &b) != EOF) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld") to
printf("%d\n", a + b);
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNextInt()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a + b);
}
}
}
0. 昔日OJ编程题:
130道基础OJ编程题之: 1~7道_ChinaRainbowSea的博客-CSDN博客
130道基础OJ编程题之: 8~19 道_ChinaRainbowSea的博客-CSDN博客
130道基础OJ编程题之: 20~28_ChinaRainbowSea的博客-CSDN博客_
130道基础OJ编程题之: 29 ~ 38 道_ChinaRainbowSea的博客-CSDN博客
130道基础OJ编程题之: 39 ~ 46 道_ChinaRainbowSea的博客-CSDN博客_oj编程题
47. BC50 计算单位阶跃函数
计算单位阶跃函数_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
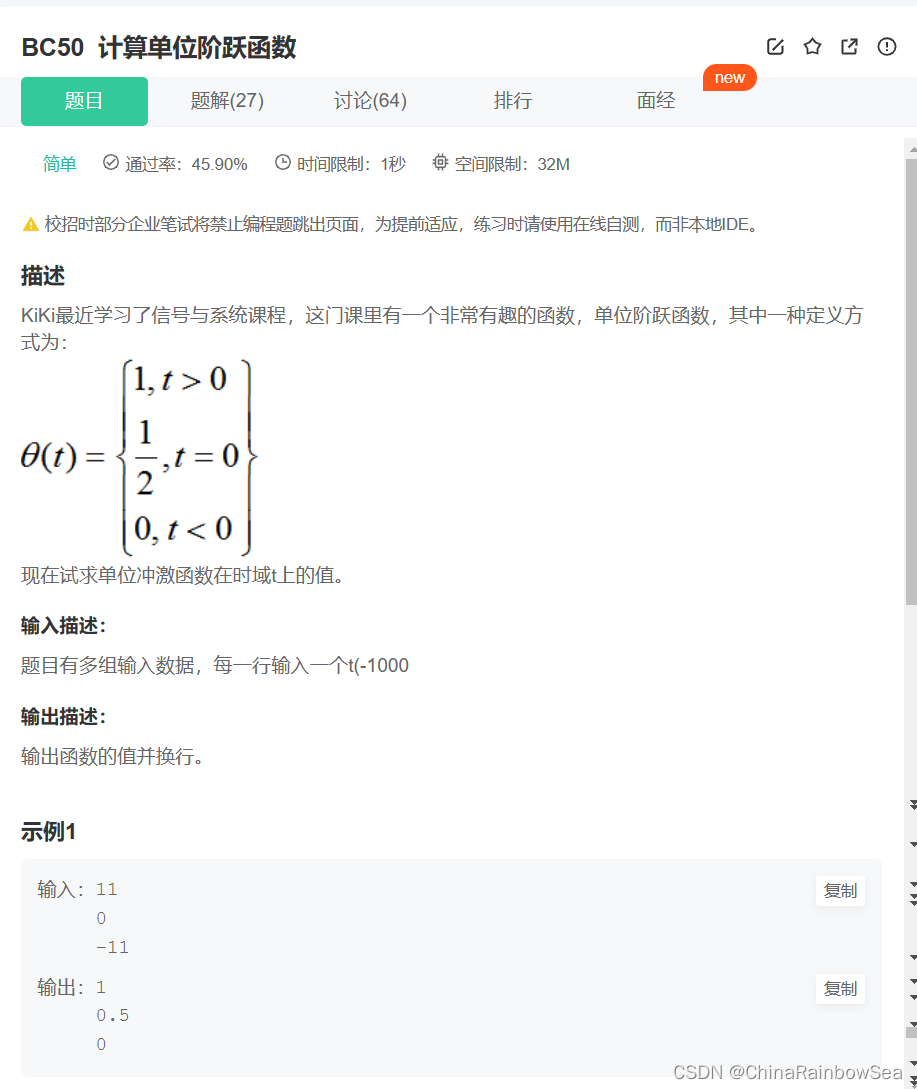
c语言实现:
思路: 注意是多组数据的输入测试,使用 if ~ else 语句,进行一个判断即可。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int t = 0;
while(scanf("%d",&t) != EOF)
{
if( t > 0)
printf("%d\n",1);
else if(t == 0)
printf("%.1f\n",0.5);
else
printf("%d\n",0);
}
return 0;
}
java语言实现:
思路: 注意Java当中的多组数据的输入,使用 if ~ else 语句,进行一个判断即可。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = 0;
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
t = scanner.nextInt();
if(t > 0)
System.out.println(1);
else if(t == 0)
System.out.println(0.5);
else
System.out.println(0);
}
}
}
48. BC51 三角形判断
三角形判断_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
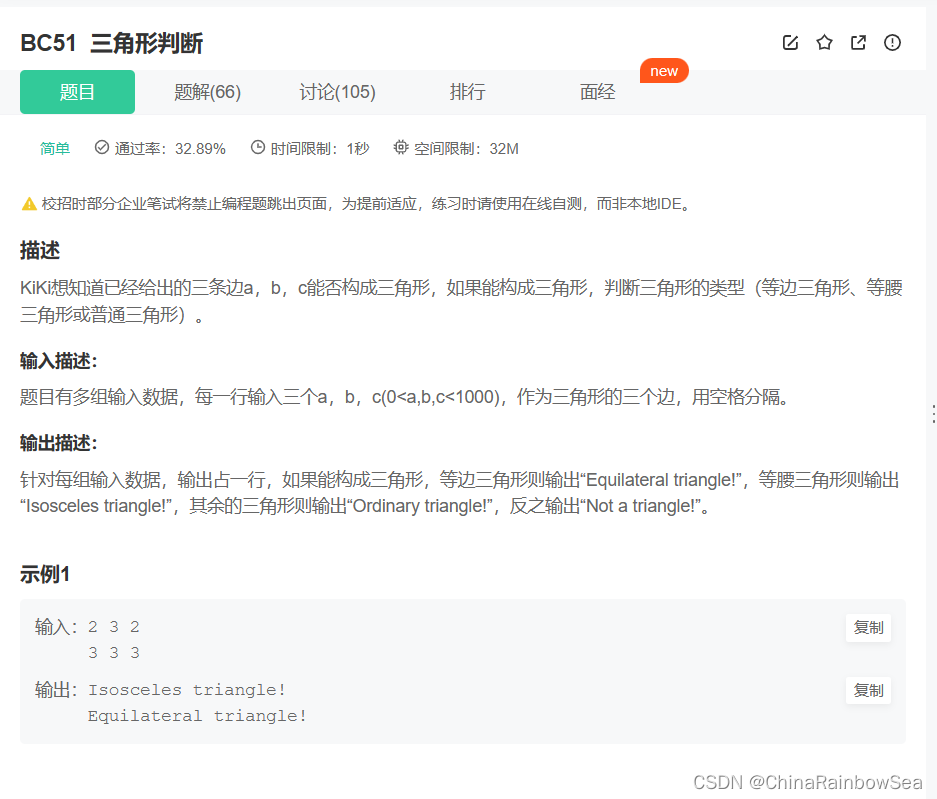
c语言实现:
思路: 多组数据的输入,首先判断是否是三角形(两边之和大于第三边{(a+b > c) && (a+c > b) && (b+c > a)}),如果是三角形:先将比较容易的先判断出来,等边三角形(三边相等: a == c && c == b ),等腰三角形(两边相等: (a == b) || (a == c) || (b == c) )
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
// 多组数据的输入
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c) != EOF)
{
// 判断是否是三角形: 两边之和大于第三边
if((a+b > c) && (a+c > b) && (b+c > a))
{
// 等边三角形
if(a == c && c == b)
{
printf("Equilateral triangle!\n");
} // 等腰三角形
else if((a == b) || (a == c) || (b == c))
{
printf("Isosceles triangle!\n");
}
else // 其余三角形
{
printf("Ordinary triangle!\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("Not a triangle!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
java代码实现:
方式一:
思路: Java当在中的多组输入,其中的空格分隔,默认就是多个数据的输入的分隔。首先判断是否是三角形(两边之和大于第三边{(a+b > c) && (a+c > b) && (b+c > a)}),如果是三角形:先将比较容易的先判断出来,等边三角形(三边相等: a == c && c == b ),等腰三角形(两边相等: (a == b) || (a == c) || (b == c) )
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
// 多组输入数据
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
a = scanner.nextInt();
b = scanner.nextInt();
c = scanner.nextInt();
// 判断三角形
if((a + b > c) && ( a + c > b) && ( b + c > a)) {
// 等边三角形
if((a == b) && (b == c)) {
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle!");
// 等腰三角形
} else if((a == b) || (b == c) || ( a == c)) {
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle!");
} else { // 其余三角形
System.out.println("Ordinary triangle!");
}
} else {
System.out.println("Not a triangle!");
}
}
}
}
方式二:
思路: 主要的思路方法是和方式一的思路是一样的,这里主要与方式一不同的是:多组数据的输入以字符串 的方式输入: 先将数据以字符串的形式读取到,再将读取到的字符串以 空格 的格式分割开成单个的字符串,存储到字符串数组 当中,再将字符串数组中的字符串元素转换为对应的 Integer 基本数据类型的包装类数组,再通过包装类自动拆箱转换为 int 类型的数据,进行判断。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意需要读取到“空格”分割
while(scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String str = scanner.nextLine(); // 需要“空格”
String strs[] = str.split(" "); // 以 "空格" 分割,存储到字符串数组当中
int[] arr = new int[3]; // 存放转为 int 类型的数据
// 循环将分割好的字符串,转换为 int 的数据类型
for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]); // 通过包装类将字符串转换为对应的(自动拆箱) int 类型的数据,注意:已经是字符串了,就不要加双引号了
}
// 判断三角形
if((arr[0] + arr[1] > arr[2]) && (arr[0] + arr[2] > arr[1]) && (arr[1] + arr[2] > arr[0])) {
// 等边三角形
if((arr[0] == arr[1]) && (arr[1] == arr[2])) {
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle!");
} else if((arr[0] == arr[1]) || (arr[1] == arr[2]) || (arr[0] == arr[2])) { // 等腰三角形
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle!");
} else { // 其余三角形
System.out.println("Ordinary triangle!");
}
} else {
System.out.println("Not a triangle!");
}
}
}
}
49. BC52 衡量人体胖瘦程度
衡量人体胖瘦程度_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
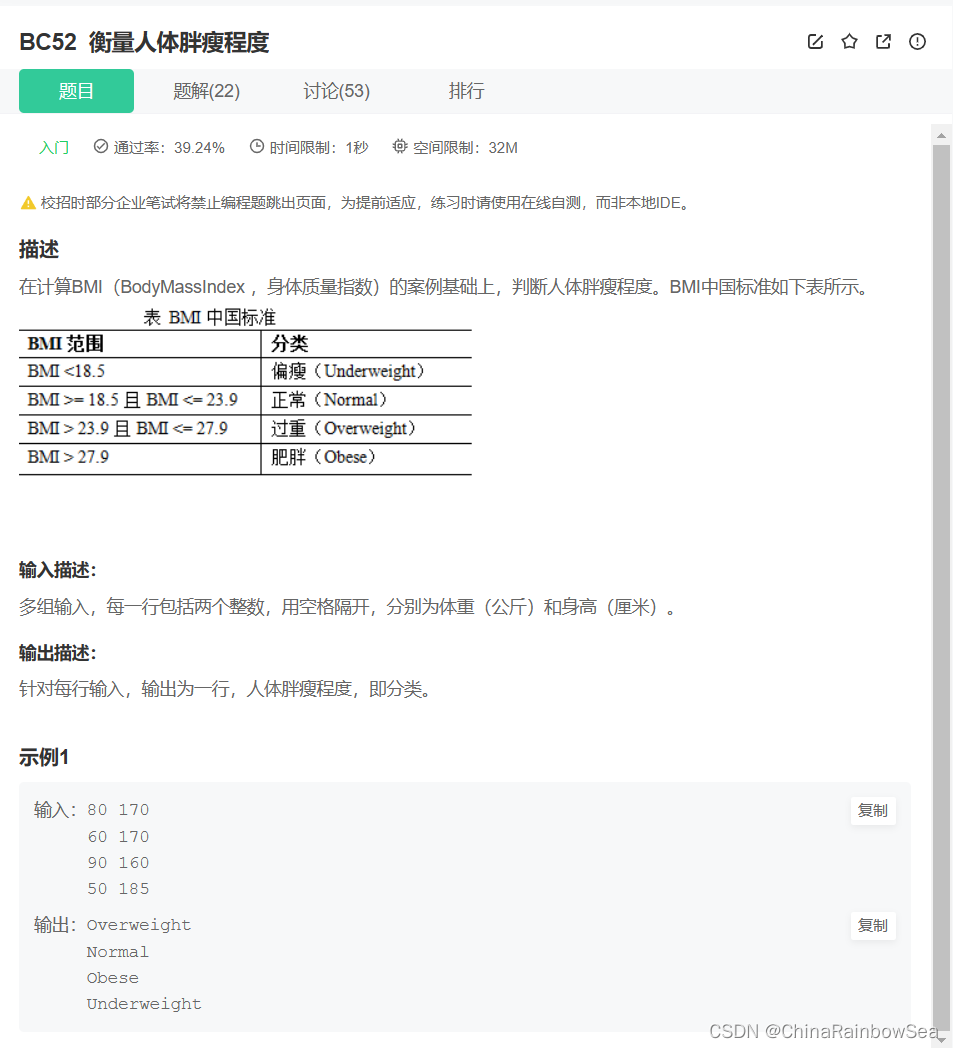
C语言实现:
思路: 多组输入, BMI 的计算方式: 体重 / (身高 * 身高) ; 需要注意的是这里的身高的单位是 cm 厘米,需要转换为 m 米,以及注意最后计算得到的结果是 小数(浮点数)。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int weight = 0;
int height = 0;
while(scanf("%d%d",&weight,&height) != EOF)
{
// 注意结果是 浮点数:
double bmi = weight / ((height/100.0) * (height/100.0));
if(bmi < 18.5)
printf("Underweight\n");
else if(bmi >= 18.5 && bmi <= 23.9)
printf("Normal\n");
else if(bmi > 23.9 && bmi <= 27.9)
printf("Overweight\n");
else if(bmi > 27.9)
printf("Obese\n");
}
return 0;
}
Java实现:
方式一:
思路: 和C语言的思路是一样的,需要注意的是 Java中的多组输入。Math.pow(数值,几次幂)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
double weigth = 0;
double heigth = 0;
while(scanner.hasNextDouble()) {
weigth = scanner.nextDouble();
heigth = scanner.nextDouble();
double bmi = weigth / Math.pow(heigth/100,2.0);
if(bmi < 18.5)
System.out.println("Underweight");
else if(bmi >= 18.5 && bmi <= 23.9)
System.out.println("Normal");
else if(bmi > 23.9 && bmi <= 27.9)
System.out.println("Overweight");
else
System.out.println("Obese");
}
}
}
方式二:
思路: 基本思路和方式一是一样的,不同的是这里将以 字符串 的方式读取其中的数值,再将字符串以 “空格”的方式分割,存储到字符串数组当中,再将字符串数组中的字符串元素转换为对应的包装类 ——> 基本数据类型,再判断
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 多组输入,注意需要“空格”分割
while(scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String str = scanner.nextLine();
String[] strs = str.split(" "); // 将字符串以"空格"分割
int[] arr = new int[strs.length];
for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]); // 将字符串转换为包装类->拆包为基本数据类型 int ,已经是字符串了就不要再加 "双引号"了
}
double bmi = arr[0] / Math.pow(arr[1]/100.0,2);
if(bmi < 18.5)
System.out.println("Underweight");
else if(bmi >= 18.5 && bmi <= 23.9)
System.out.println("Normal");
else if(bmi > 23.9 && bmi <= 27.9)
System.out.println("Overweight");
else
System.out.println("Obese");
}
}
}
50. BC53 计算一元二次方程
计算一元二次方程_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)

C语言实现:
思路: 多组输入数据,根据 △ 值划分情况
- △ = 0,则两个实根相等。其中还需要注意的是当 (-b)/(2*a) = 0.00 的时候,存在正负之分,所以我们需要进一步判断,当 == 0.00 的时候就输入出 0.00 没有正负之分。
- △ > 0,则两个实根不等。求各个 x1,x2 的值,使用公式: x1 = (-b+sqrt(disc)) / (2*a) ; x2 = (-b+sqrt(disc)) / (2*a)
- △ < 0,则有两个虚根,则输出:x1=实部-虚部i;x2=实部+虚部i,即x1的虚部系数小于等于x2的虚部系数,实部为0时不可省略。实部= -b / (2*a),虚部= sqrt(-△ ) / (2*a)
- 所有实数部分要求精确到小数点后2位,数字、符号之间没有空格。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double a = 0.0;
double b = 0.0;
double c = 0.0;
while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c) != EOF)
{
if(a != 0)
{
double disc = b*b - 4*a*c;
if(disc == 0)
{
double temp = (-b)/(2*a);
if(temp == 0)
printf("x1=x2=%.2lf\n",0.00);
else
printf("x1=x2=%.2lf\n",temp);
}
else if(disc > 0)
{
double num1 = (-b-sqrt(disc)) / (2*a);
double num2 = (-b+sqrt(disc)) / (2*a);
printf("x1=%.2lf;x2=%.2lf\n",num1,num2);
}
else
{
double num3 = (-b)/(2*a); // 实部
double num4 = sqrt(-disc)/(2*a); // 虚部
printf("x1=%.2lf-%.2lfi;x2=%.2lf+%.2lfi\n",num3,num4,num3,num4);
}
}
else
{
printf("Not quadratic equation\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Java实现:
思路: 基本思路和C语言实现一样。需要注意的是:Java当中的 System.out.printf(“%f”) 的格式输出,中的浮点数类型没有 %lf ,有的是 %f 。这一点需要注意。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 多组输入
while(scanner.hasNextDouble()) {
double a = scanner.nextDouble();
double b = scanner.nextDouble();
double c = scanner.nextDouble();
if(a != 0) {
double disc = b*b - 4*a*c;
if(disc == 0) {
double temp = (-b)/(2*a);
if(temp == 0)
System.out.printf("x1=x2=%.2f\n",0.00);
else
System.out.printf("x1=x2=%.2f\n",temp);
}
else if(disc > 0) {
double num1 = (-b-Math.sqrt(disc)) / (2*a);
double num2 = (-b+Math.sqrt(disc)) / (2*a);
System.out.printf("x1=%.2f;x2=%.2f\n",num1,num2);
}
else {
double num3 = (-b)/(2*a); // 实部
double num4 = Math.sqrt(-disc)/(2*a); // 虚部
System.out.printf("x1=%.2f-%.2fi;x2=%.2f+%.2fi\n",num3,num4,num3,num4);
}
} else {
System.out.printf("Not quadratic equation\n");
}
}
}
}
51. BC54 获得月份天数
获得月份天数_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
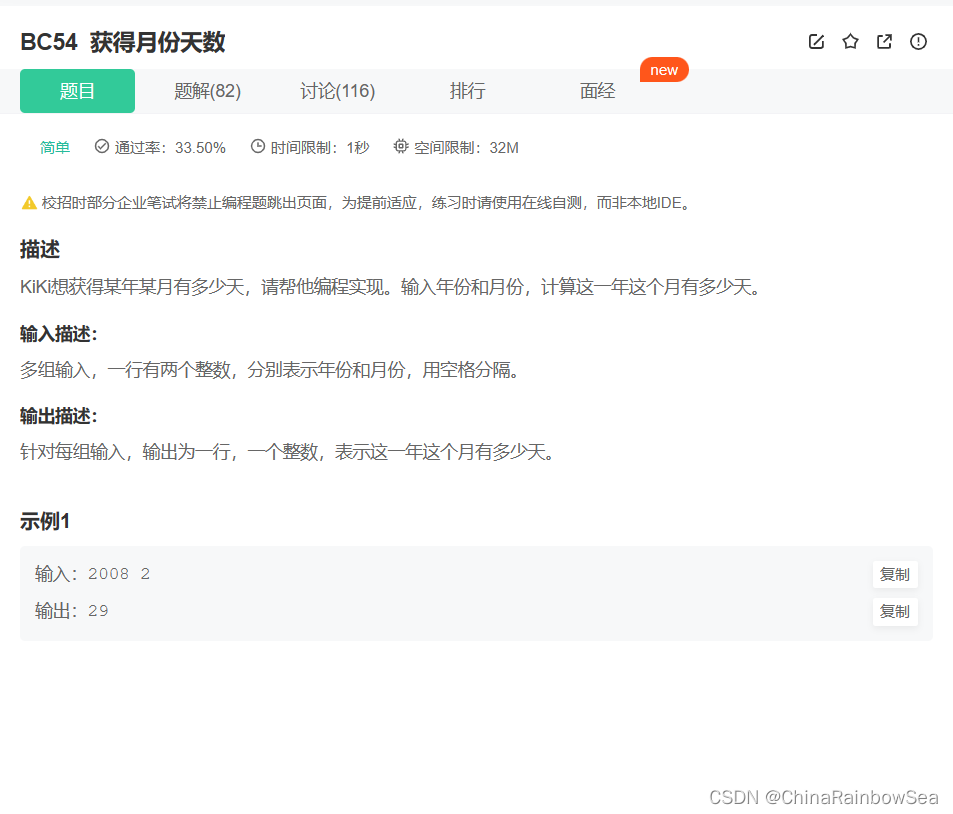
C语言实现:
思路: 多组输入。将各个不是月份的天数存储到数组当中去。再判断输入的是否是 2 月,是 2月,进行一个闰年的判断,是闰年 + 1 天。需要注意的是我们数组实际是从下标 为 0 的位置开始的,所以我们从数组中实际的取值是 需要 - 1 .
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int days[12] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; // 记录每月的天数信息
while(~scanf("%d%d",&year,&month))
{
// 判断闰年
if( month == 2)
{
month --;
if( (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) )
{
printf("%d\n",days[month]+1);
}
else
printf("%d\n",days[month]);
}
else
printf("%d\n",days[--month]);
}
return 0;
}
方式二:
思路: 输出的天数存储到一个变量当中,最后进行一个输出。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int days[12] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; // 记录每月的天数信息
while(~scanf("%d%d",&year,&month))
{
int day = days[month -1]; // 实际数组是从 0 开始的
// 判断闰年
if( month == 2)
{
if( (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) )
++day; // 闰年的 2月 加 一天
}
printf("%d\n",day);
}
return 0;
}
java实现:
方式一:
思路: C语言实现的方式二的基本思路一致。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] days = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
Integer year = 0;
Integer month = 0;
// 多组输入
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
year = scanner.nextInt();
month = scanner.nextInt();
Integer day = days[month -1];
if(2 == month)
// 闰年判断
if((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 ) || (year % 400 == 0) )
++day;
System.out.println(day);
}
}
}
方式二:
思路: 要的思路方法是和方式一的思路是一样的,这里主要与方式一不同的是:多组数据的输入以字符串 的方式输入: 先将数据以字符串的形式读取到,再将读取到的字符串以 空格 的格式分割开成单个的字符串,存储到字符串数组 当中,再将字符串数组中的字符串元素转换为对应的 Integer 基本数据类型的包装类数组,再通过包装类自动拆箱转换为 int 类型的数据,进行判断。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] days = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; // 记录每月的天数信息
// 多组数据的读取,需要“空格”
while(scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String str = scanner.nextLine(); // 读取空格的字符串
String[] strs = str.split(" "); // 将字符串以 "空格"分割
int[] arr = new int[strs.length]; // 存放将字符串转换为基本数据类型的数据
for(int i = 0; i < strs.length;i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(strs[i]); // 通过包装类将字符串转换为 int的基本数据类型
}
int day = days[arr[1] - 1]; // 存放天数
if(arr[1] == 2) {
// 判断闰年
if((arr[0] % 4 == 0 && arr[0] % 100 != 0) || (arr[0] % 400 == 0)) {
++day; // 闰年 2月加 一天 +1
}
}
System.out.println(day);
}
}
}
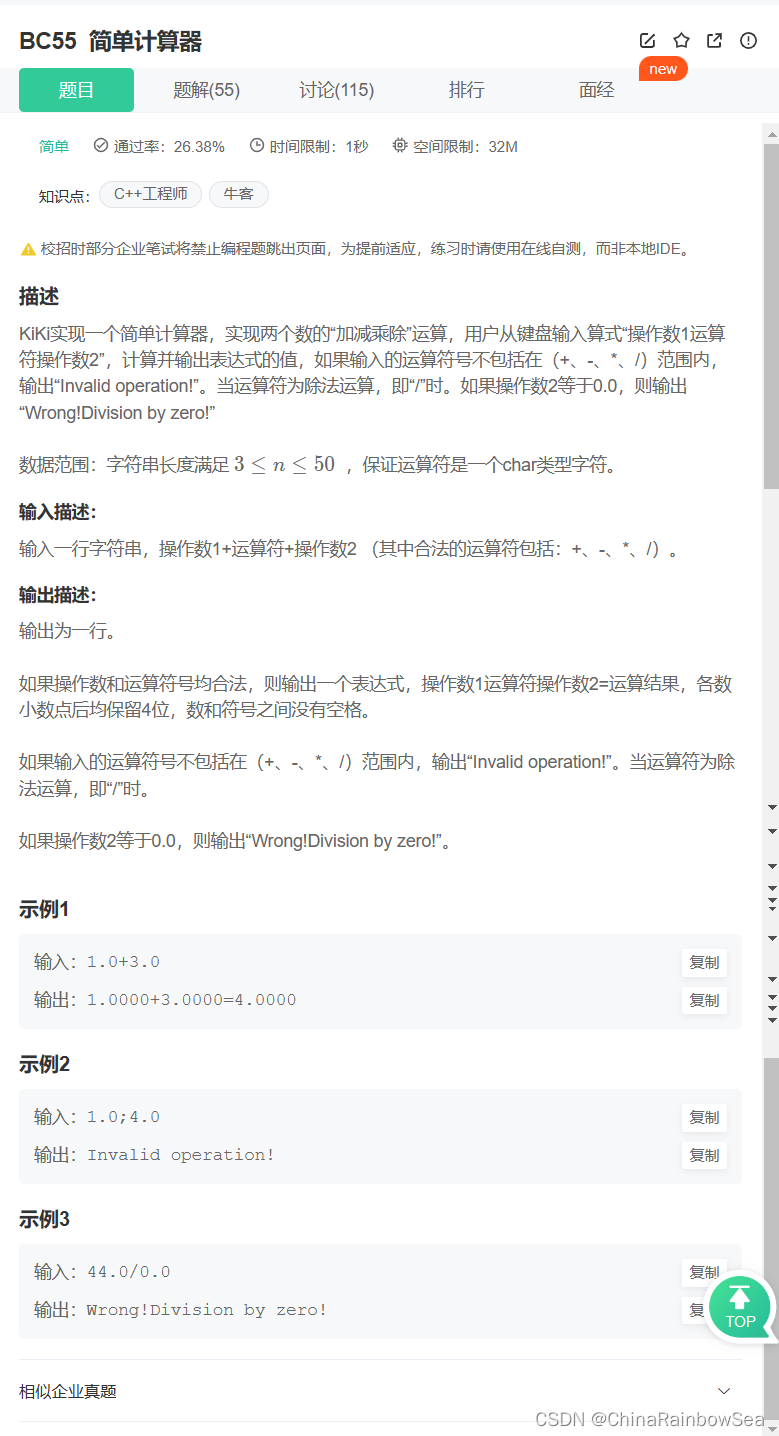
52. BC55 简单计算器
简单计算器_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
C语言实现:
思路: 多组数据的输入,根据题意:使用 switch()多分支语句
- +,-,*,/ ; 除法需要进一步的判断,除数不可以为 0 ,从而导致出错,特殊处理,
- 如果输入的符号不对,特殊处理
- 需要注意的是 所有数值保留 4 位有效数值
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double num1 = 0;
double num2 = 0;
char symbol = 0;
while(~scanf("%lf%c%lf",&num1,&symbol,&num2)) {
switch(symbol) {
case '+':
printf("%.4lf+%.4lf=%.4lf\n",num1,num2,num1 + num2);
break;
case '-':
printf("%.4lf-%.4lf=%.4lf\n",num1,num2,num1-num2);
break;
case '*':
printf("%.4lf*%.4lf=%.4lf\n",num1,num2,num1*num2);
break;
case '/':
if(num2 == 0)
printf("Wrong!Division by zero!\n");
else
printf("%.4lf/%.4lf=%.4lf",num1,num2,num1/num2);
break;
default:
printf("Invalid operation!\n");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
Java实现:
思路: 和C语言实现的思路是一样的,不同的是,这里我们将字符改为字符串的判断。
因为这里Java当没有像C语言的一个格式输入,所以这里我们就将输入的数据以字符串的方式读取到,然后将读取到的字符串根据 str.split(“[+\-*/]”); 加减乘除进行一个分割存储到字符串数组当中,并判断字符串数组当中的元素是否被分成了两部分,如果输入的运算符是不正确的或者无输入,则字符串是无法进行分割成两个部分的。从而就根据题意的要求输出:Invalid operation!。
输出的运算符是正确的再进行一个判断运算,先将字符串通过包装了转换为对应的 double 基本数据类型,进行运算,
运算之前,先将存在到读取到的字符串中的运算符使用 ,String.substing()的方法将其中的运算符截取获取到,再经过 switch()的多分支判断,需要注意的是这里的是字符串,不是字符,同时注意:Java当中的对于浮点数的格式输出是没有 %lf 的只有 %f,整数的格式输出也是一样的没有 %ld 只有 %d。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.next(); // 读取到字符串,这里不需要空格
String[] strs = str.split("[+\\-*/]"); // 通过+-*/进行字符串的分割,存储到字符串数组当中
if(strs.length < 2) {
// 如果没有输入正确的运算符或者无输入,则字符串是无法进行分割成两个部分
System.out.println("Invalid operation!");
} else {
// 输入正确,将字符串通过包装类转换为对应的数值类型 double
double num1 = Double.parseDouble(strs[0]); // 需要注意的是已经是字符串了就不要再加"双引号"了
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(strs[1]);
// 通过 字符串.substring()的方法截取其中的符号,进行一个+-*/
// 就是第一个字符串的后面的一个符号大小
String symbol = str.substring(strs[0].length(),strs[0].length()+1);
switch(symbol) { // 注意是字符串,不是字符
case "+":
System.out.printf("%.4f+%.4f=%.4f\n", num1, num2, num1 + num2);
break;
case "-":
System.out.printf("%.4f-%.4f=%.4f\n", num1, num2, num1 - num2);
break;
case "*":
System.out.printf("%.4f*%.4f=%.4f\n", num1, num2, num1 * num2);
break;
case "/":
if (num2 == 0)
System.out.printf("Wrong!Division by zero!\n");
else
System.out.printf("%.4f/%.4f=%.4f", num1, num2, num1 / num2);
break;
default:
System.out.printf("Invalid operation!\n");
break;
}
}
}
}
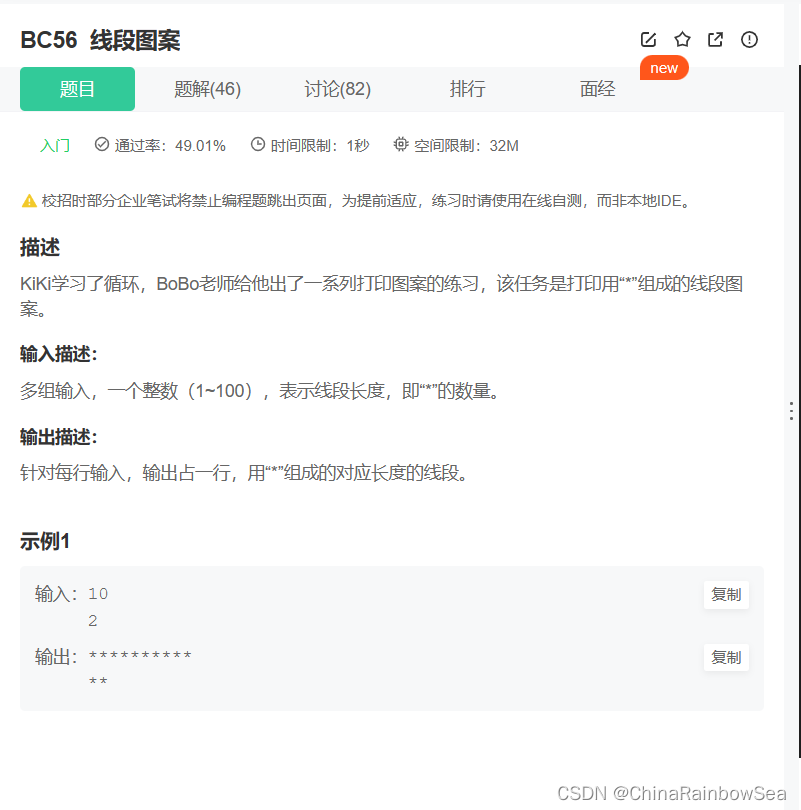
53. BC56 线段图案
线段图案_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
C语言实现:
思路: 注意多组输入的数据
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("*");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Java实现
思路: 注意Java的多组输入数据
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
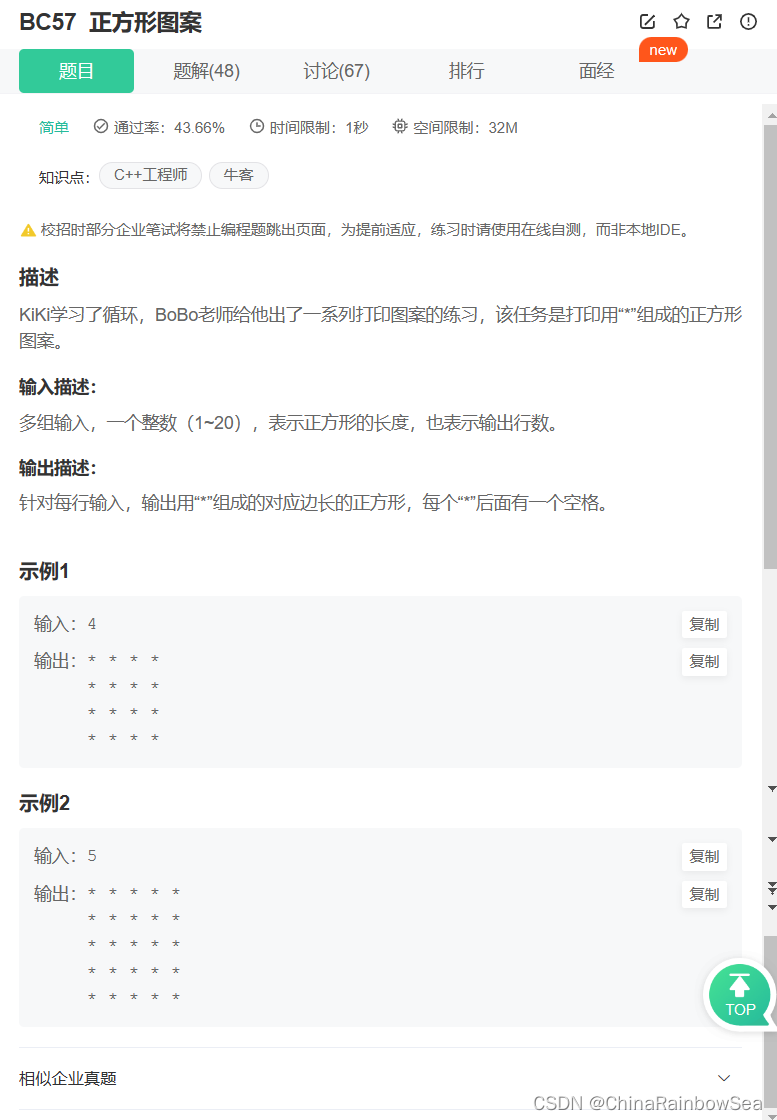
54. BC57 正方形图案
正方形图案_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
C语言实现:
思路: 多组输入,使用两个 for 循环,行,列
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Java实现
思路: 多组输入,使用 两个 for循环,行,列
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
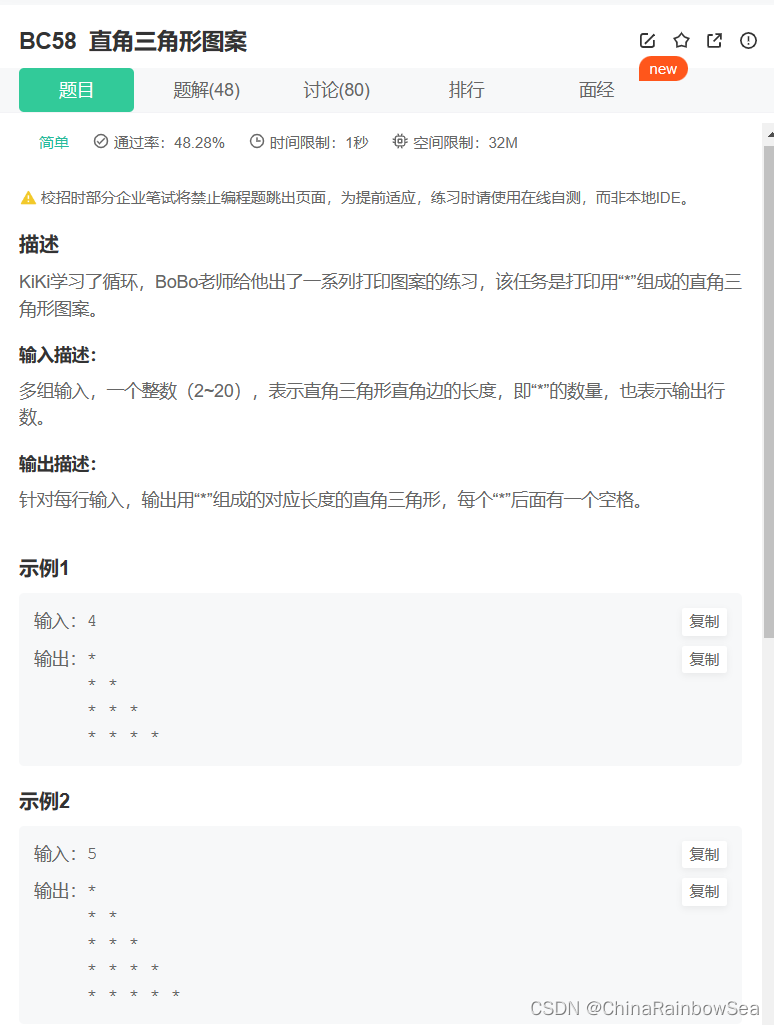
55. BC58 直角三角形图案
直角三角形图案_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
C语言实现
思路: 多组输入,找规律,两个 for 循环
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Java实现:
思路: 多组输入,找规律,两个 for 循环
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
56. BC59 翻转直角三角形图案
翻转直角三角形图案_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)

C语言实现:
思路: 多组输入,找规律,两个 for 循环,行,列
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n-i; j++) {
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Java实现:
思路 多组输入,找规律,两个 for 循环,行,列
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n - i; j++) {
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
57. BC60 带空格直角三角形图案
带空格直角三角形图案_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
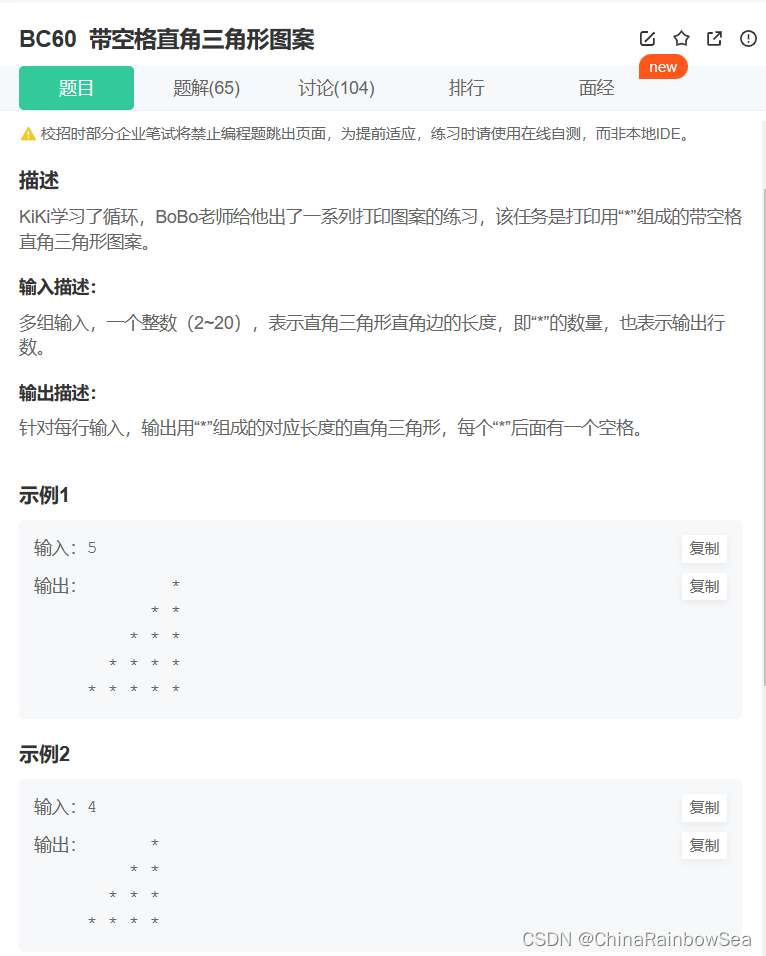
C语言实现:
方式一:
思路: 多组输入,找规律:注意是两个“空格”
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++)
{
printf(" "); // 注意是两个“空格”
}
for(int j = 0; j <= i;j++)
{
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
方式二:
思路:
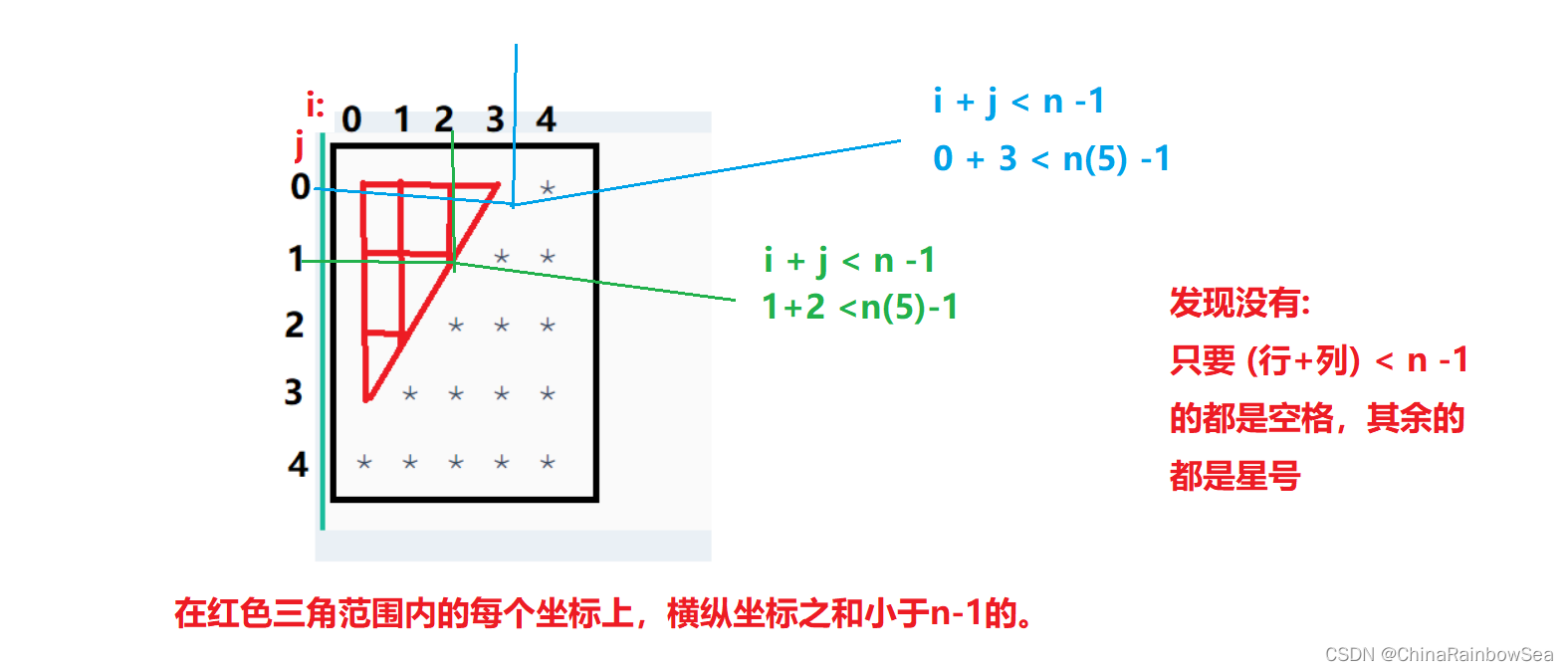
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 0;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 打印“空格”
if( i + j < n - 1)
{
printf(" "); // 两个空格
}
else // 打印“星号”
{
printf("* ");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Java实现
方式一:
思路: 多组输入,找规律,注意是两个空格
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 多组输入
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// 两个空格
for(int j = 0 ; j < n-i-1; j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
// 星号
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("* "); // 加空格
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
方式二:
思路: 和C语言实现的方式二是一样的
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 打印空格
if( (i + j) < n-1) {
System.out.print(" "); // 两个空格
} else {
System.out.print("* ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
总结:
- 注意C语言的多组输入,和Java的多组输入
- Java以字符串读取的处理: 多组数据的输入以字符串 的方式输入: 先将数据以字符串的形式读取到
scanner.hasNextLine()需要读取到空格,再将读取到的字符串以 空格String.split(" ")的格式分割开成单个的字符串,存储到字符串数组 当中,再将字符串数组中的字符串元素转换为对应的 包装类.parseXXX基本数据类型的包装类数组,再通过包装类自动拆箱转换为 基本数据类型的数据。 - Java当中求平方的方法:
Math.pow(double d,double b)其中第一个参数表示:要平方的数,第二个参数表示:几次方 - Java当中的
System.out.print("%d,%f")的格式输出,整数只有 %d 没有 %ld, 浮点数只有 %f,没有 %lf - java当中的
String[] strs = str.split("[+\\-*/]");可以使用 String.split() 进行多个标志进行分割。 - Java当中的
String symbol = str.substring(strs[0].length(),strs[0].length()+1);中的 String.substring()方法进行字符串的截断。 - 两个 for 循环控制,行,列。
最后:
限于自身水平,其中存在的错误,希望大家给予指教,韩信点兵——多多益善,谢谢大家,江湖再见,后会有期!!!