目录
1. Filter & 过滤器
1.1. 过滤器概述
1.2. 过滤器的使用
1.3. 过滤器生命周期
1.4. 过滤器链的使用
1.5. 注解方式配置过滤器
2. Listener & 监听器
2.1. 监听器概述
2.2. Java Web的监听器
2.2.1. 常用监听器
2.2.1.1. ServletContextListener监听器
2.2.1.2. ServletContextAttributeListener监听器
2.2.2. 其他监听器
2.2.2.1. session域监听器
2.2.2.2. HttpSessionListener 监听器
2.2.2.3. HttpSessionAttributeListener 监听器
2.2.2.4. request域监听器
2.2.2.5. ServletRequestListener 监听器
2.2.2.6. ServletRequestAttributeListener 监听器
2.2.3. session域的两个特殊监听器
2.2.3.1. HttpSessionBindingListener 监听器
2.2.3.2. HttpSessionActivationListener 监听器
1. Filter & 过滤器
1.1. 过滤器概述
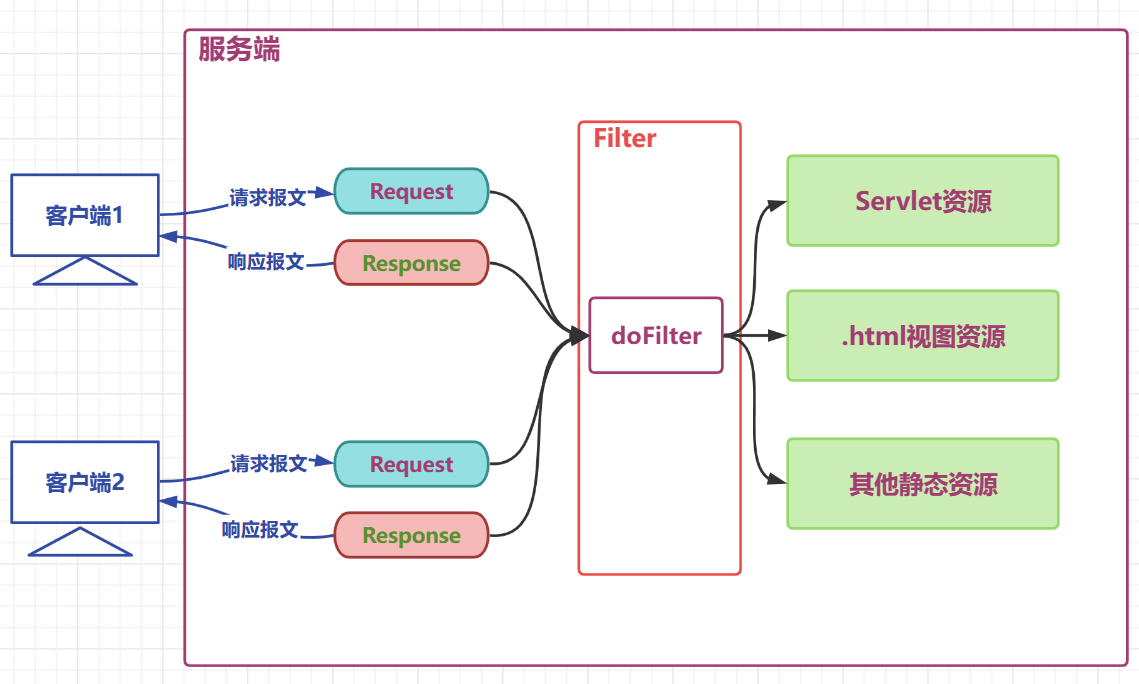
Filter是Java Web开发中的一种技术,它可以对目标资源的请求进行过滤。简单来说,Filter就像是一个前置处理器或者拦截器,它会在目标资源被请求之前执行,对请求进行一定的处理或者拦截。
- Filter接口是Filter的开发规范,所有开发的Filter都需要实现这个接口。当一个请求到达Filter时,容器会先创建一个HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象,然后调用Filter的doFilter方法。
- doFilter方法决定了一个请求是否可以继续执行。如果doFilter方法允许请求继续,那么请求将会被转发到目标资源。如果doFilter方法拒绝了请求,那么请求就会在这个Filter中停止,由Filter自己对请求做出响应。
- 除了对请求进行过滤,Filter也可以在目标资源响应之前对响应进行再次处理。因此,Filter不仅可以用于对请求的过滤,也可以用于对响应的处理。
- Filter是GOF(设计模式)中责任链模式的典型案例。责任链模式是指多个对象形成一个处理请求的链条,每个对象都有机会处理请求,直到有一个对象处理了请求为止。
- Filter的常用应用非常广泛,包括但不限于登录权限检查、解决网站乱码、过滤敏感字符、日志记录、性能分析等。这些应用都是通过Filter技术实现的。
举个例子:
生活举例中,公司前台、停车场安保和地铁验票闸机都是Filter的典型应用。它们都可以对进入的人员或者车辆进行审核和过滤。如果符合条件,就放行;如果不符合条件,就拒绝进入。同时,它们也可以在人员或者车辆离开时进行再次审核和收费。
Filter工作原理图解:
Filter接口API:
从IDEA上面的Filter.java上扒下来的源码,也就三个抽象方法:
- init(FilterConfig filterConfig):这是过滤器初始化时调用的方法。在这个方法中,可以设置过滤器的一些配置信息,如参数等。默认的实现是不执行任何操作。
- doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain):这是过滤器的主要工作方法。每次客户端请求资源时,都会调用此方法。在这个方法中,可以根据需要修改请求和响应对象,并决定是否将请求传递给下一个过滤器或目标资源。这通常涉及检查请求,可能修改请求或响应,然后调用chain.doFilter()来继续过滤器链,最后可能直接在响应上设置头信息。
- destroy():这是过滤器被移除服务时调用的方法。在这个方法中,可以进行一些清理工作,例如释放资源,确保所有持久状态与内存中的当前状态同步。默认的实现同样不执行任何操作。
1.2. 过滤器的使用
目标:开发一个日志记录过滤器
- 用户请求到达目标资源之前,记录用户的请求资源路径
- 响应之前记录本次请求目标资源运算的耗时
- 可以选择将日志记录进入文件,为了方便测试,这里将日志直接在控制台打印
LoggingFilter.java 过滤器
package filter;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class LoggingFilter implements Filter { //实现Filter接口
public void init(FilterConfig config) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("以启用登录过滤器~");
}
private final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat =new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 参数父转子
HttpServletRequest request =(HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response =(HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
// 拼接日志文本
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
String time = dateFormat.format(new Date());
String beforeLogging =requestURI+"在"+time+"被请求了";
// 打印日志
System.out.println(beforeLogging);
// 获取系统时间
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 放行请求
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
// 获取系统时间
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 拼接日志文本
String afterLogging =requestURI+"在"+time+"的请求耗时:"+(t2-t1)+"毫秒";
// 打印日志
System.out.println(afterLogging);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("以销毁登录过滤器~");
}
}
配置web.xml
不配置web.xml就是普通的java类,无法实现filter过滤器的功能
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--配置过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>loggingFilter</filter-name> <!--过滤器名称-->
<filter-class>filter.LoggingFilter</filter-class> <!--过滤器类名-->
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>loggingFilter</filter-name> <!--过滤器名称-->
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <!--过滤器拦截的url,/* 表示对所有资源进行过滤-->
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>说明:
ServletA.java
package servlet;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
// 处理器请求
System.out.println("servletA处理请求的方法,耗时10毫秒");
// 模拟处理请求耗时
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}ServletB.java
package servlet;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
// 处理器请求
System.out.println("servletB处理请求的方法,耗时15毫秒");
// 模拟处理请求耗时
try {
Thread.sleep(15);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}启动服务器

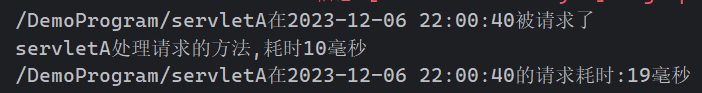

1.3. 过滤器生命周期
Filter在Web项目中是一个重要的组件,其生命周期与Servlet有些类似,但也有一些区别。
- 创建(Creation):Filter对象在系统启动时就会被创建。不像Servlet需要配置load-on-startup参数才能实现系统启动时立即创建,Filter的创建是默认行为,系统启动时就会立即创建Filter对象。
- 初始化(Initialization):在Filter对象创建后,会调用其init方法进行初始化。这个过程通常会接收一个FilterConfig对象作为参数,通过这个对象可以获取到Filter的配置信息。
- 执行(Execution):初始化完成后,Filter就可以开始执行其任务。在Web应用中,Filter通常被用来执行一些通用的操作,如日志记录、数据压缩、认证授权等。Filter的执行顺序是根据其在web.xml中的配置顺序来决定的。
- 销毁(Destroy):当Web应用关闭或重启时,Filter的生命周期结束,会调用其destroy方法进行资源清理。
| 阶段 | 对应方法 | 执行时机 | 执行次数 |
| 创建对象 | 构造器 | web应用启动时 | 1 |
| 初始化方法 | void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) | 构造完毕 | 1 |
| 过滤请求 | void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) | 每次请求 | 多次 |
| 销毁 | default void destroy() | web应用关闭时 | 1次 |
1.4. 过滤器链的使用
过滤器链概述:
在一个Web项目中,可以定义多个过滤器(Filter)。这些过滤器可以同时存在,并且可以对同一个资源进行过滤操作。这些过滤器按照一定的顺序形成一个工作链,这个工作链被称为过滤器链(Filter Chain)。
- 过滤器链中的过滤器的顺序是由filter-mapping的配置顺序决定的。在web.xml文件中,我们可以配置多个filter-mapping,每个filter-mapping定义了一个过滤器及其对应的匹配规则。这些过滤器按照filter-mapping的顺序依次执行。
- 每个过滤器都有其特定的过滤范围。对于同一个资源来说,可能需要经过多个过滤器的过滤。因此,过滤器链中的过滤器个数可能会因为资源的不同而有所差异。
- 另外,如果某个过滤器是使用ServletName进行匹配规则的配置,那么这个过滤器的执行优先级相对较低。这意味着,当一个请求到达时,过滤器链会先执行那些使用ServletName进行匹配规则配置的过滤器,然后再执行其他过滤器。

示例:
如果定义了三个过滤器Filter1、Filter2、Filter3,执行顺序也是1、2、3
这里Filter的代码就不举例了,关键在于web.xml的写法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<filter>
<filter-name>filter1</filter-name>
<filter-class>filters.Filter1</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter>
<filter-name>filter2</filter-name>
<filter-class>filters.Filter2</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter>
<filter-name>filter3</filter-name>
<filter-class>filters.Filter3</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--filter-mapping的顺序决定了过滤器的工作顺序-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>filter1</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servletC</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>filter2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servletC</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>filter3</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/servletC</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
1.5. 注解方式配置过滤器
注解方式配置过滤器是指在Java Web应用程序中使用注解来定义和配置过滤器。
和servlet注解类似,通过注解,可以省略web.xml配置文件,直接在Java类中声明过滤器。
Filter注解源码(还是从IDEA上面复制下来的):
package javax.servlet.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import javax.servlet.DispatcherType;
/**
* Annotation used to declare a servlet filter.
*
* <p>This annotation is processed by the container at deployment time,
* and the corresponding filter applied to the specified URL patterns,
* servlets, and dispatcher types.
*
* @see javax.servlet.Filter
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface WebFilter {
/**
* The description of the filter
*
* @return the description of the filter
*/
String description() default "";
/**
* The display name of the filter
*
* @return the display name of the filter
*/
String displayName() default "";
/**
* The init parameters of the filter
*
* @return the init parameters of the filter
*/
WebInitParam[] initParams() default {};
/**
* The name of the filter
*
* @return the name of the filter
*/
String filterName() default "";
/**
* The small-icon of the filter
*
* @return the small-icon of the filter
*/
String smallIcon() default "";
/**
* The large-icon of the filter
*
* @return the large-icon of the filter
*/
String largeIcon() default "";
/**
* The names of the servlets to which the filter applies.
*
* @return the names of the servlets to which the filter applies
*/
String[] servletNames() default {};
/**
* The URL patterns to which the filter applies
* The default value is an empty array.
*
* @return the URL patterns to which the filter applies
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* The URL patterns to which the filter applies
*
* @return the URL patterns to which the filter applies
*/
String[] urlPatterns() default {};
/**
* The dispatcher types to which the filter applies
*
* @return the dispatcher types to which the filter applies
*/
DispatcherType[] dispatcherTypes() default {DispatcherType.REQUEST};
/**
* Declares whether the filter supports asynchronous operation mode.
*
* @return {@code true} if the filter supports asynchronous operation mode
* @see javax.servlet.ServletRequest#startAsync
* @see javax.servlet.ServletRequest#startAsync(ServletRequest,
* ServletResponse)
*/
boolean asyncSupported() default false;
}
对源码进行分析:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}): 这个注解只能应用于类级别。@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME): 这个注解将在运行时保留,在运行时可以被反射API读取。@Documented: 这个注解会被包含在用户的JavaDoc中。String description() default "";: 返回过滤器的描述,默认为空字符串。String displayName() default "";: 返回过滤器的显示名称,默认为空字符串。WebInitParam[] initParams() default {};: 返回过滤器的初始化参数,默认为一个空数组。String filterName() default "";: 返回过滤器的名字,默认为空字符串。String smallIcon() default "";: 返回过滤器的小图标,默认为空字符串。String largeIcon() default "";: 返回过滤器的大图标,默认为空字符串。String[] servletNames() default {};: 返回过滤器应用到的Servlet名字,默认为一个空数组。String[] value() default {};: 和urlPatterns()方法相同,返回过滤器应用到的URL模式,默认为一个空数组。String[] urlPatterns() default {};: 返回过滤器应用到的URL模式,默认为一个空数组。DispatcherType[] dispatcherTypes() default {DispatcherType.REQUEST};: 返回过滤器应用到的调度类型,默认为REQUEST。boolean asyncSupported() default false;: 声明过滤器是否支持异步操作模式,默认为false。
代码示例:
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebFilter(filterName = "MyFilter", urlPatterns = {"/welcome"})
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
// 初始化操作,如读取配置参数等
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("Before processing request");
// 调用下一个过滤器或servlet
chain.doFilter(request, response);
System.out.println("After processing request");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// 清理资源等
}
}2. Listener & 监听器
2.1. 监听器概述
Listener 监听器是 JavaWeb 应用程序中的一种组件,它是 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener 这三个组件之一。Listener 是 Java EE 规范中的一部分,它是一个接口,用于监听特定事件或变化,并在触发时执行相应的任务。
监听器的作用是监听特定的对象或事件,例如对象的创建/销毁或属性变化等,当这些事件发生时,监听器会触发对应的方法来完成相应的任务。
有八个常用的监听器
其中最常用的是 ServletContextListener和ServletContextAttributeListener
举个例子:
监听器可以比喻为“报警器”。比如我们在家里安装的烟雾报警器,当烟雾达到一定浓度时,报警器就会发出警报,提醒我们可能有火灾隐患。这个报警器就是“监听器”,它监听的是烟雾浓度这个事件。当烟雾浓度达到设定阈值时,它就会触发警报。
在JavaWeb应用程序中,监听器也是类似的原理。比如ServletContextListener,它监听的是ServletContext对象的变化。当ServletContext对象创建或销毁时,ServletContextListener就会触发对应的方法来完成相应的任务。
监听器分类:
根据所监听的对象和事件的不同,可以将监听器大致分为以下几类:
- 按监听的对象划分:
- Application域监听器:这类监听器监听的是ServletContext对象,其中包括ServletContextListener和ServletContextAttributeListener。ServletContextListener用于监听ServletContext对象的创建和销毁事件,而ServletContextAttributeListener则用于监听ServletContext对象属性的变化。
- Session域监听器:这类监听器监听的是HttpSession对象,其中包括HttpSessionListener、HttpSessionAttributeListener和HttpSessionBindingListener。HttpSessionListener用于监听HttpSession对象的创建和销毁事件,HttpSessionAttributeListener用于监听HttpSession对象属性的变化,而HttpSessionBindingListener则用于监听HttpSession对象绑定和解绑事件。
- Request域监听器:这类监听器监听的是ServletRequest对象,其中包括ServletRequestListener和ServletRequestAttributeListener。ServletRequestListener用于监听ServletRequest对象的创建和销毁事件,ServletRequestAttributeListener用于监听ServletRequest对象属性的变化。
- 按监听的事件划分:
- 域对象的创建和销毁监听器:这类监听器包括ServletContextListener、HttpSessionListener和ServletRequestListener,它们分别用于监听ServletContext、HttpSession和ServletRequest对象的创建和销毁事件。
- 域对象数据增删改事件监听器:这类监听器包括ServletContextAttributeListener、HttpSessionAttributeListener和ServletRequestAttributeListener,它们分别用于监听ServletContext、HttpSession和ServletRequest对象属性的变化事件。
- 其他监听器:这类监听器包括HttpSessionBindingListener和HttpSessionActivationListener等,它们分别用于监听HttpSession对象绑定和解绑事件以及激活事件等。
2.2. Java Web的监听器
2.2.1. 常用监听器
在Java Web监听器中,常用的监听器是
ServletContextListener 和 ServletContextAttributeListener
ServletContextListener: 这个接口提供了一个监听器,可以监听ServletContext对象的创建和销毁事件。当Web应用程序启动时,会创建一个ServletContext对象,而在应用程序关闭时,该对象将被销毁。通过实现ServletContextListener接口,可以在这两个关键时刻执行特定的操作。例如,可以在ServletContext对象创建时初始化一些全局变量或执行其他必要的设置,或在对象销毁时进行资源清理。
ServletContextAttributeListener: 这个接口提供了一个监听器,可以监听ServletContext属性(即在ServletContext对象中存储的属性)的添加和移除事件。可以通过实现这个接口来监听特定属性的添加或移除操作,并在这些操作发生时执行特定的操作。例如,当某个属性被添加到ServletContext时,可以进行一些初始化操作;当某个属性被移除时,可以执行一些清理操作。
2.2.1.1. ServletContextListener监听器

ServletContextListener监听器:监听ServletContext对象的创建与销毁
ServletContextListener本身就是一个接口,继承EventListener接口
相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) | ServletContext创建时调用 |
| contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) | ServletContext销毁时调用 |
ServletContextListener的源码,一个继承与EventListener的接口
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that the web application initialization
* process is starting.
*
* <p>All ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* initialization before any filters or servlets in the web
* application are initialized.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being initialized
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {}
/**
* Receives notification that the ServletContext is about to be
* shut down.
*
* <p>All servlets and filters will have been destroyed before any
* ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* destruction.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being destroyed
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {}
}
代码举例:
ServletContextListenerA.java
package listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
public class ServletContextListenerA implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent sce) {
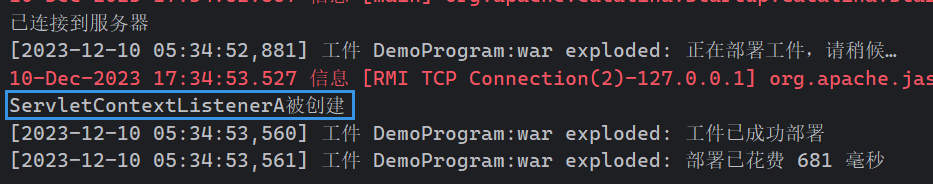
System.out.println("ServletContextListenerA被创建");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent sce) {
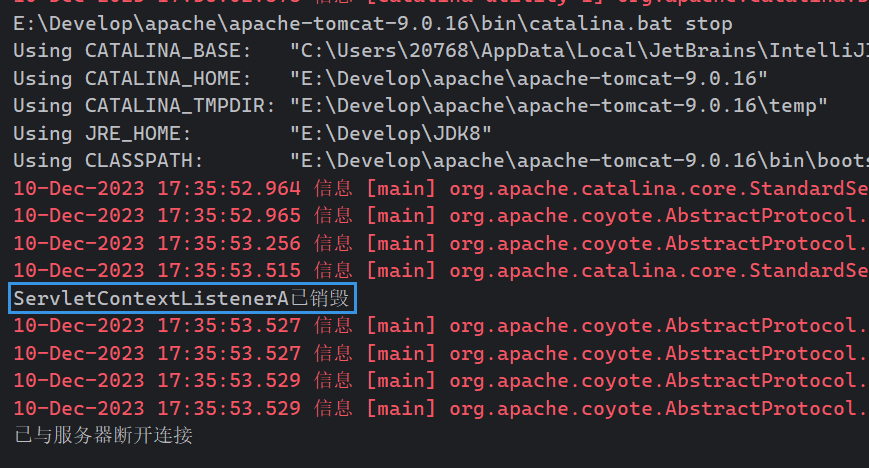
System.out.println("ServletContextListenerA已销毁");
}
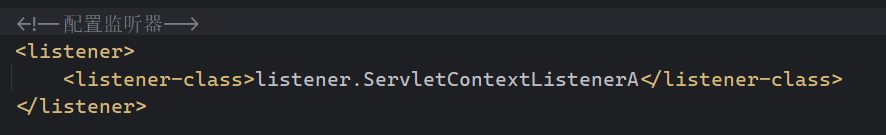
}配置 web.xml
启动服务器:
停止服务器:
小总结:
- 当一个类实现了ServletContextListener接口,它就变成了一个监听器。ServletContextListener是Java Servlet API的一部分,它能够监听ServletContext的创建和销毁事件。
- 这个类可以监听的事件由它实现的监听接口决定。如果一个类实现了ServletContextListener,那么这个类就可以监听ServletContext的创建和销毁事件。也就是说,当web应用启动时,ServletContext对象被创建,以及当web应用关闭时,ServletContext对象被销毁,这些事件都可以被监听。
- ServletContextListenerA是一个实现了ServletContextListener接口的类,因此它也是一个监听器。当web应用启动时,会产生一个ServletContextEvent事件,这个事件会调用监听器的对应事件处理方法contextInitialized。同时,会传递一个事件对象给这个方法。
- 程序员可以通过这个事件对象,来获取需要的信息,然后再进行业务处理。例如,他们可以通过这个对象获取关于ServletContext的信息,以及关于事件类型和其他相关属性的信息。
- Tomcat知道这个监听器存在是因为我们需要在web.xml中配置它。在web.xml文件中,我们可以定义ServletContextListener,当Tomcat加载web应用时,它会读取这个文件并加载所有的ServletContextListener。这样,当web应用启动或关闭时,Tomcat就会调用这些监听器的事件处理方法。
总的来说,ServletContextListener是Java Servlet API的一部分,它允许我们监听web应用的生命周期事件。我们可以通过实现这个接口来创建自己的监听器,并在web.xml中配置它,以便Tomcat知道它的存在。
2.2.1.2. ServletContextAttributeListener监听器
ServletContextAttributeListener监听器:监听ServletContext中属性的添加、移除和修改
ServletContextAttributeListener本身也是一个接口,继承EventListener接口
相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) | 向ServletContext中添加属性时调用 |
| attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) | 从ServletContext中移除属性时调用 |
| attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) | 当ServletContext中的属性被修改时调用 |
ServletContextAttributeListener的源码:
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface ServletContextAttributeListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been added to the
* ServletContext.
*
* @param event the ServletContextAttributeEvent containing the
* ServletContext to which the attribute was added, along with the
* attribute name and value
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent event) {}
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been removed
* from the ServletContext.
*
* @param event the ServletContextAttributeEvent containing the
* ServletContext from which the attribute was removed, along with
* the attribute name and value
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent event) {}
/*
* Receives notification that an attribute has been replaced
* in the ServletContext.
*
* @param event the ServletContextAttributeEvent containing the
* ServletContext in which the attribute was replaced, along with
* the attribute name and its old value
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent event) {}
}代码举例:
ServletContextAttributeListener01.java
package listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeListener;
public class ServletContextAttributeListener01 implements ServletContextAttributeListener {
@Override // 监听ServletContext添加属性
public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent sce) {
System.out.println("ServletContextAttributeListener01监听到了添加属性" +
sce.getName() + "的值");
}
@Override // 监听ServletContext移除属性
public void attributeRemoved(javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeEvent sce) {
System.out.println("ServletContextAttributeListener01监听到了移除属性" +
sce.getName() + "的值");
}
@Override // 监听ServletContext替换属性
public void attributeReplaced(javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeEvent sce) {
System.out.println("ServletContextAttributeListener01监听到了替换属性" +
sce.getName() + "的值");
}
}ServletA.java
package servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/servletA") //这里servlet用的注解,不用在web.xml配置
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
//给ServletContext添加属性
ServletContext servletContext = req.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("name", "Tom");
servletContext.setAttribute("name", "Jerry");
servletContext.removeAttribute("name");
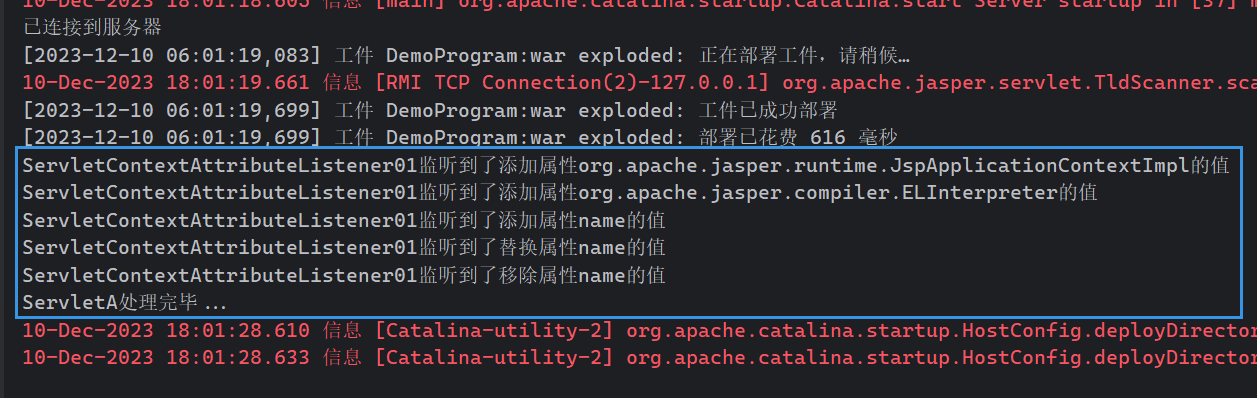
System.out.println("ServletA处理完毕...");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
doPost(req, resp);
}
}配置web.xml

启动服务器

2.2.2. 其他监听器
除了ServletContextListener和ServletContextAttributeListener,其他的监听器用的比较少
2.2.2.1. session域监听器
2.2.2.2. HttpSessionListener 监听器
作用:HttpSessionListener 是一个监听器,用来监听 HTTP 会话的创建和销毁。
当一个 HTTP 会话被创建或销毁时,它就会触发相应的事件,我们可以编写代码来响应这些事件。
例如,在会话创建时,我们可以进行一些初始化操作;在会话销毁时,我们可以释放一些资源。这样,我们就可以在用户的状态变化时,做出相应的处理。
HttpSessionListener的源码:
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface HttpSessionListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that a session has been created.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*
* @param se the HttpSessionEvent containing the session
*/
default public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {}
/**
* Receives notification that a session is about to be invalidated.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*
* @param se the HttpSessionEvent containing the session
*/
default public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {}
}
相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) | 创建session时调用 |
| sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) | 销毁session时调用 |
2.2.2.3. HttpSessionAttributeListener 监听器

作用:HttpSessionAttributeListener 是一个用于监听 HTTP 会话属性变化的监听器。
这意味着,当会话中的属性发生添加、删除或修改时,这个监听器会接收到通知。
HttpSessionAttributeListener源码:
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface HttpSessionAttributeListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been added to a
* session.
*
* @param event the HttpSessionBindingEvent containing the session
* and the name and value of the attribute that was added
*/
default public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been removed from a
* session.
*
* @param event the HttpSessionBindingEvent containing the session
* and the name and value of the attribute that was removed
*/
default public void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been replaced in a
* session.
*
* @param event the HttpSessionBindingEvent containing the session
* and the name and (old) value of the attribute that was replaced
*/
default public void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}
}相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 向HttpSession添加属性时调用 |
| attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 向HttpSession移除属性时调用 |
| attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 向HttpSession替换属性时调用 |
2.2.2.4. request域监听器
2.2.2.5. ServletRequestListener 监听器
作用:监听 Request 创建或销毁,即Request生命周期监听。
ServletRequestListener的源码:
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface ServletRequestListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that a ServletRequest is about to go out
* of scope of the web application.
*
* @param sre the ServletRequestEvent containing the ServletRequest
* and the ServletContext representing the web application
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {}
/**
* Receives notification that a ServletRequest is about to come
* into scope of the web application.
*
* @param sre the ServletRequestEvent containing the ServletRequest
* and the ServletContext representing the web application
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {}
}相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) | 创建request时调用 |
| requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) | 销毁request时调用 |
2.2.2.6. ServletRequestAttributeListener 监听器

作用:ServletRequestAttributeListener 监听器可以监听 ServletRequest 对象中的属性变化。当属性被添加、移除或替换时,这个监听器会收到通知并执行相应的操作。
ServletRequestAttributeListener 源码:
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface ServletRequestAttributeListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been added to the
* ServletRequest.
*
* @param srae the ServletRequestAttributeEvent containing the
* ServletRequest and the name and value of the attribute that was
* added
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void attributeAdded(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) {}
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been removed from the
* ServletRequest.
*
* @param srae the ServletRequestAttributeEvent containing the
* ServletRequest and the name and value of the attribute that was
* removed
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void attributeRemoved(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) {}
/**
* Receives notification that an attribute has been replaced on the
* ServletRequest.
*
* @param srae the ServletRequestAttributeEvent containing the
* ServletRequest and the name and (old) value of the attribute
* that was replaced
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void attributeReplaced(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) {}
}相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| attributeAdded(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) | 向Request添加属性时调用 |
| attributeRemoved(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) | 向Request移除属性时调用 |
| attributeReplaced(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) | 向Request替换属性时调用 |
2.2.3. session域的两个特殊监听器
2.2.3.1. HttpSessionBindingListener 监听器
HttpSessionBindingListener 监听器也叫session绑定监听器
作用:HttpSessionBindingListener 监听 HttpSession 中对象的添加和移除,以确保数据的准确性和一致性。它可以帮助我们跟踪数据变化并触发相应操作。
HttpSessionBindingListener 监听器用于监听某个对象在 HttpSession 中的添加和移除操作。当该对象被添加到 HttpSession 中或从 HttpSession 中移除时,监听器会自动执行相应的操作。这个监听器通常用于管理在 HttpSession 中存储的数据,确保数据的一致性和准确性。
简单来说,它可以帮助我们跟踪 HttpSession 中数据的变化,并触发相应的操作。
HttpSessionBindingListener源码:
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface HttpSessionBindingListener extends EventListener {
/**
*
* Notifies the object that it is being bound to
* a session and identifies the session.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*
* @param event the event that identifies the
* session
*
* @see #valueUnbound
*
*/
default public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}
/**
*
* Notifies the object that it is being unbound
* from a session and identifies the session.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*
* @param event the event that identifies
* the session
*
* @see #valueBound
*
*/
default public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}
}
相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 该类的实例被放到Session域中时调用 |
| void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) | 该类的实例从Session中移除时调用 |
2.2.3.2. HttpSessionActivationListener 监听器
HttpSessionActivationListener 监听器也叫钝化活化监听器
作用:HttpSessionActivationListener 监听 HttpSession 中对象的序列化和反序列化。在分布式系统中,它帮助处理对象的存储和恢复,允许在序列化和反序列化时执行特定操作。
HttpSessionActivationListener 的源码:
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface HttpSessionActivationListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Notification that the session is about to be passivated.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*
* @param se the {@link HttpSessionEvent} indicating the passivation
* of the session
*/
default public void sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent se) {}
/**
* Notification that the session has just been activated.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*
* @param se the {@link HttpSessionEvent} indicating the activation
* of the session
*/
default public void sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent se) {}
} 相关方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
| sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent se) | 该类实例和Session一起钝化到硬盘时调用 |
| sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent se) | 该类实例和Session一起活化到内存时调用 |