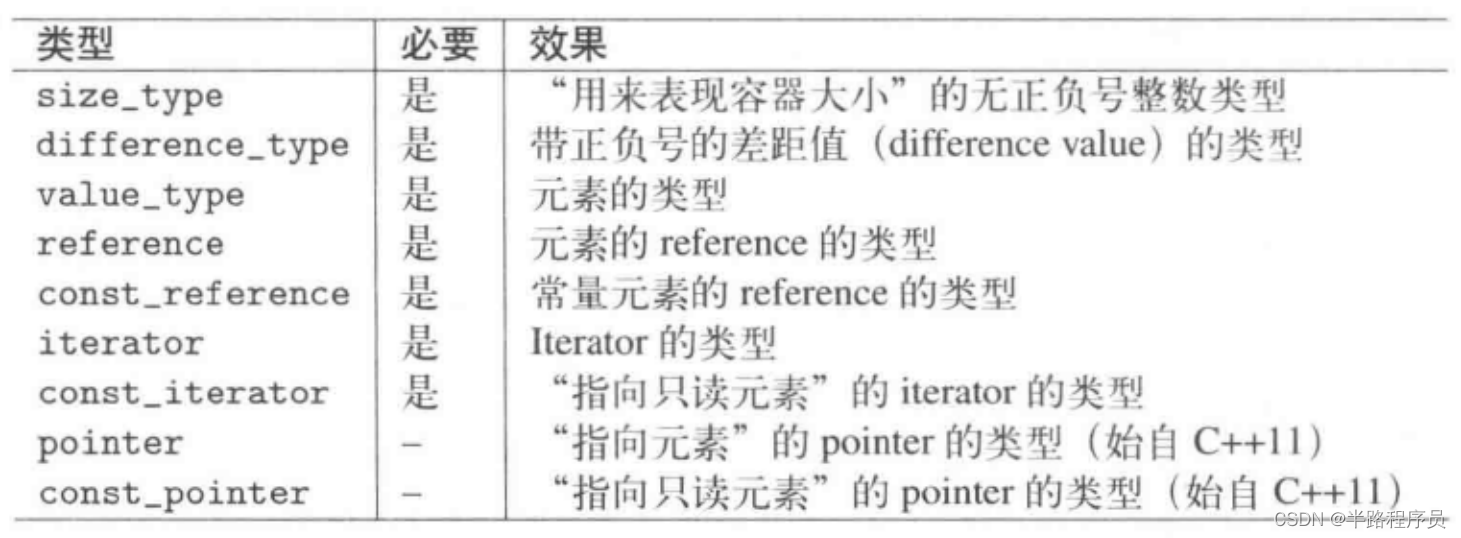
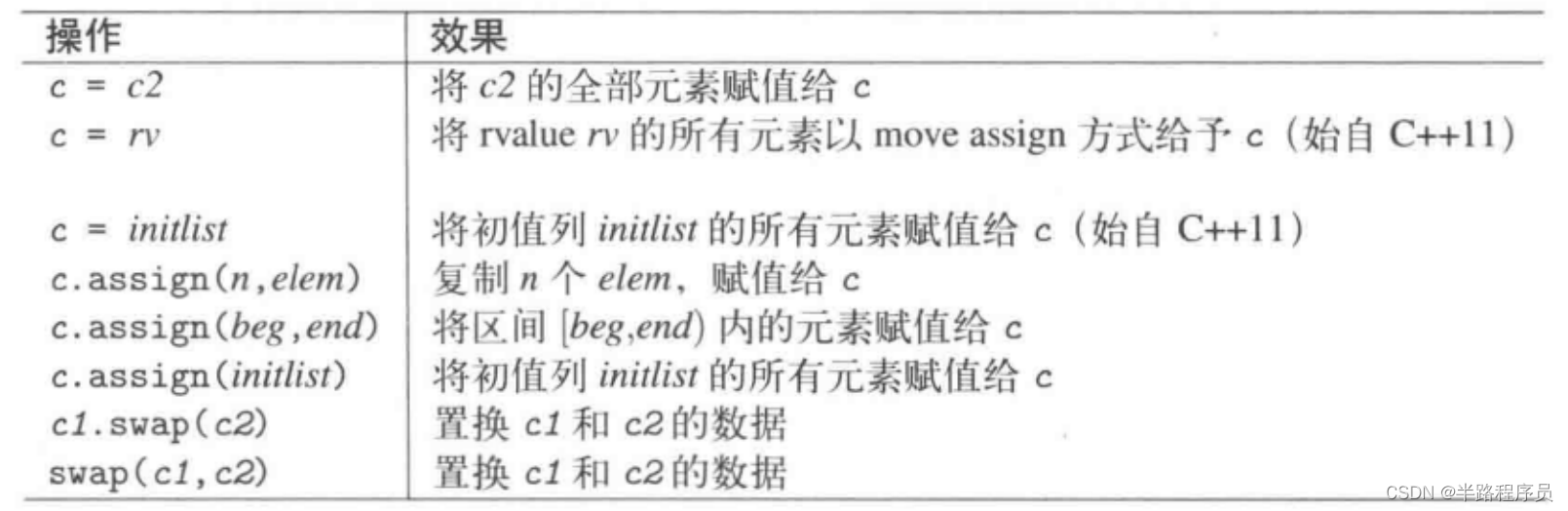
1、容器提供的类型
2、Array
Array大小固定,只允许替换元素的值,不能增加或者移除元素改变大小。Array是一种有序集合,支持随机访问。
std::array<int, 4> x; //elements of x have undefined value
std::array<int, 5> x = {}; // ok,all elements of x have value 0(int())
std::array<iny, 5> x = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::array<int, 5> x = {32} //one element with value 32, followed by 4 elements with value 0由于没有提供针对初值列而写的构造函数或者assignment操作符,因此在array声明期间完成初始化是使用初值列的唯一途径,基于这个原因,无法使用小括号语法指明初值,此不同于其他容器。
std::array<int, 5> a({1, 2, 3, 4, 5}); //error
std::vector<int> v({1, 2, 3, 4, 5}); //ok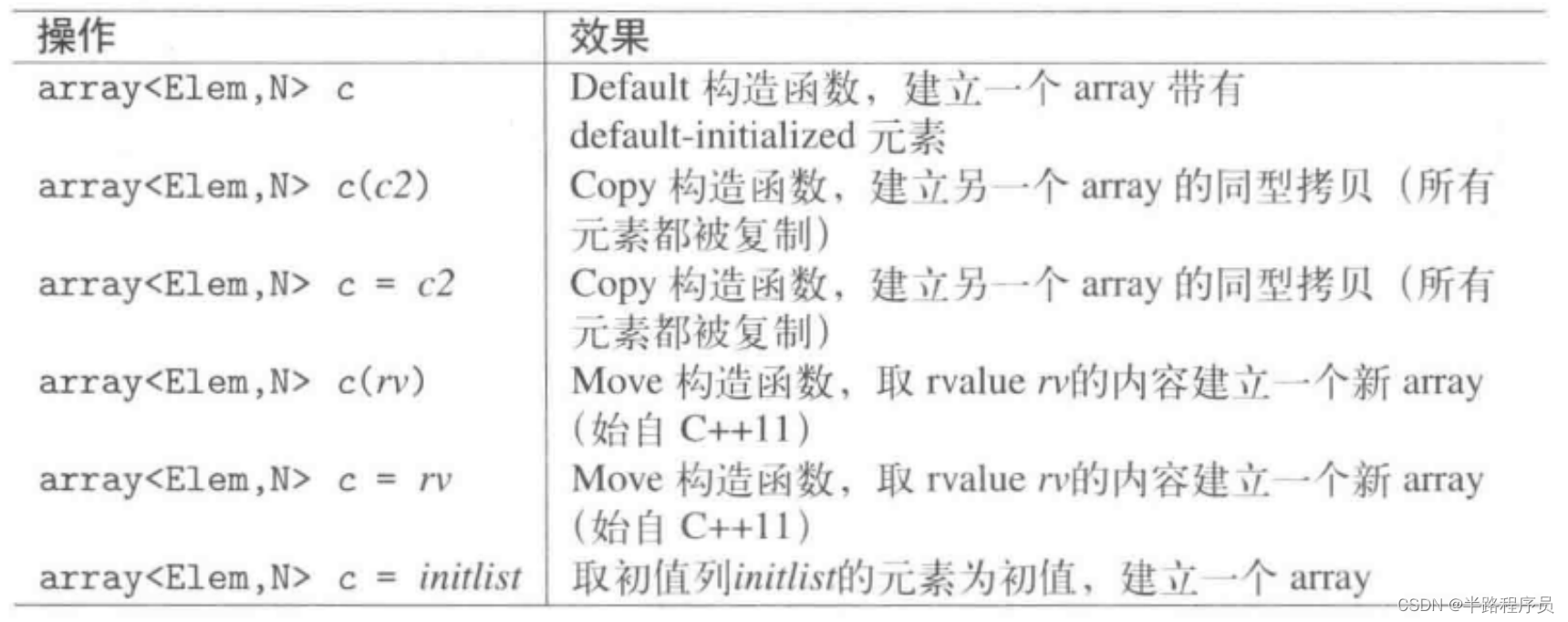
赋值操作:

2、tuple接口
Array提供tuple接口,使用如下:
typedef std::array<std::string, 5> FiveStrings;
FiveStrings a = {"hello", "nico", "how", "are", "you"};
std::tuple_size<FiveStrings>::value; //yield 5
std::tuple_element<1, FiveStrings>::type; //yield std::string
std::get<1>(a); //yield std::string("nico");3、vector
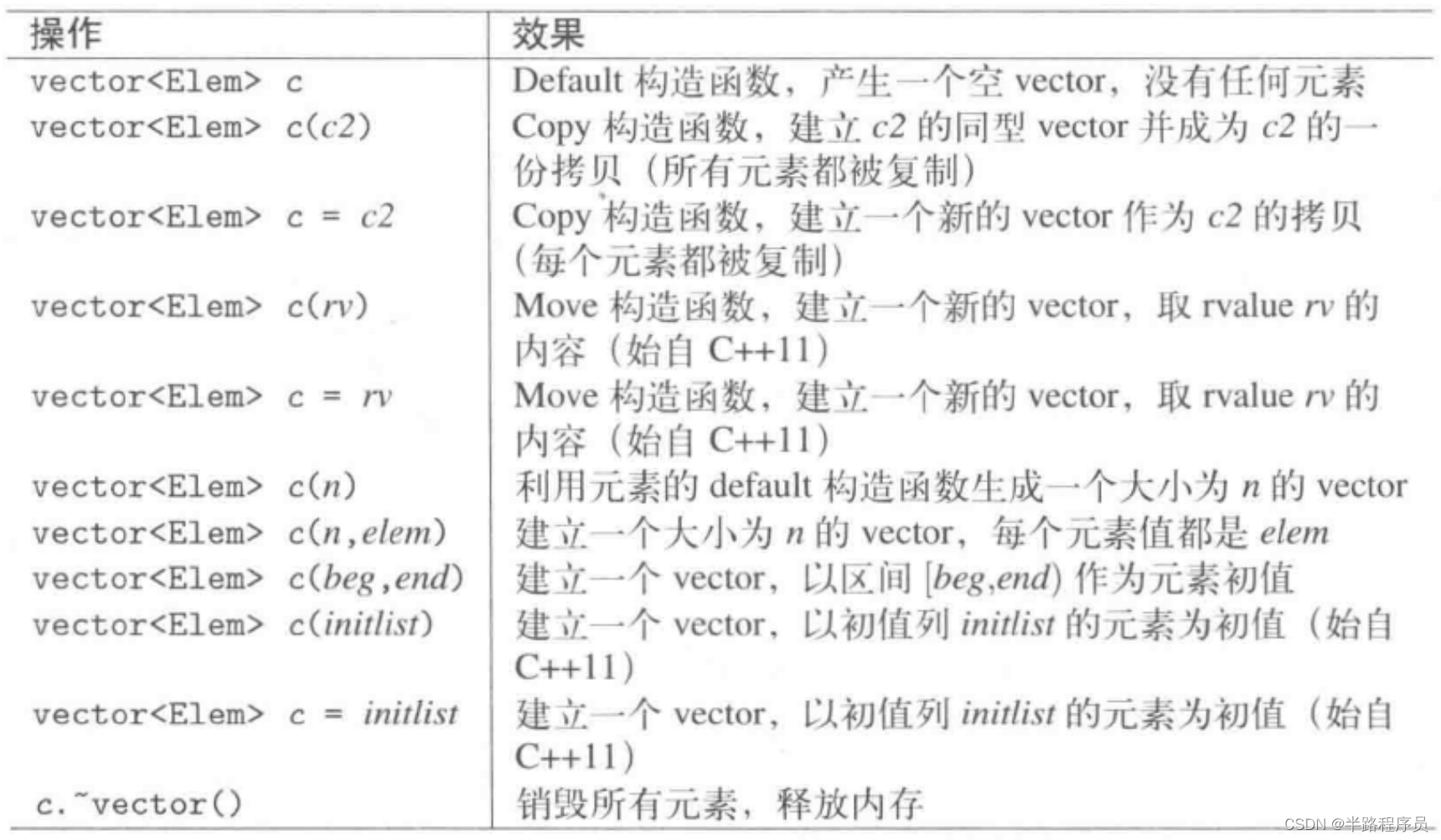
std::vector<int> v(50); //或调用默认构造函数
std::vector<int> v;
v.reserve(5); //不调用默认构造函数
所以上述两种方法,在构造复杂对象时,性能是不一样的vector的reserve不能够缩小容量大小,这一点和String不同。
 赋值操作
赋值操作

插入和删除
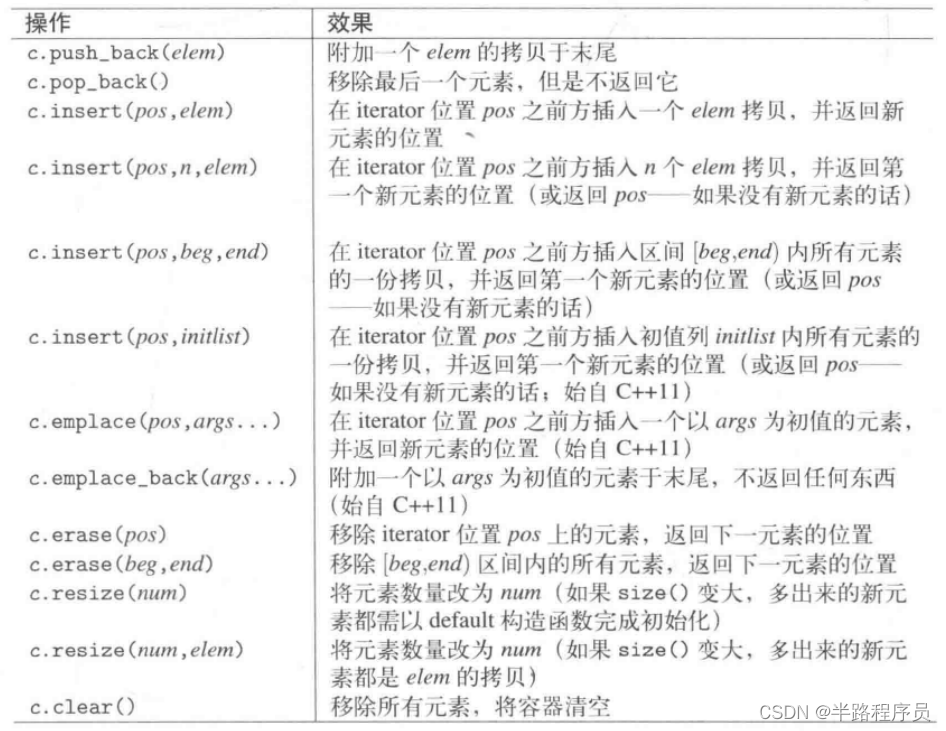
printf("%s\n", v.begin()); //ERROR
printf("%s\n", v.data()); //OK, since C++11
printf("%s\n", &v[0]); //ok, v.data() bettervector<bool>特殊操作:

4、deque
构造和析构函数


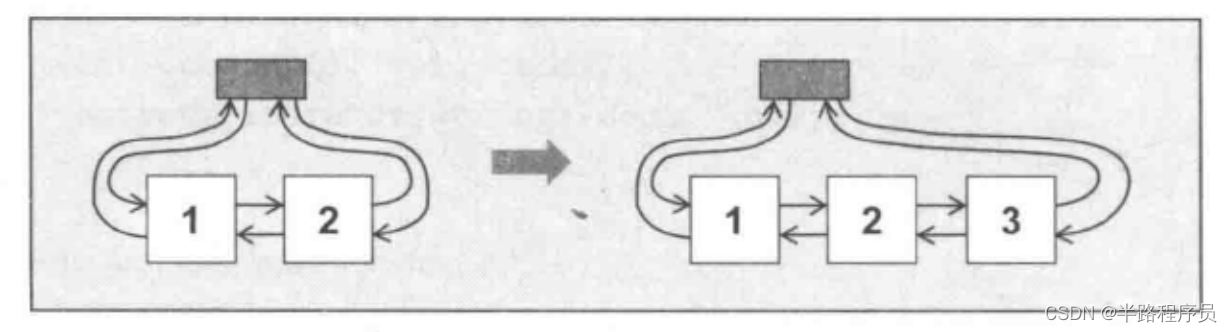
5、List
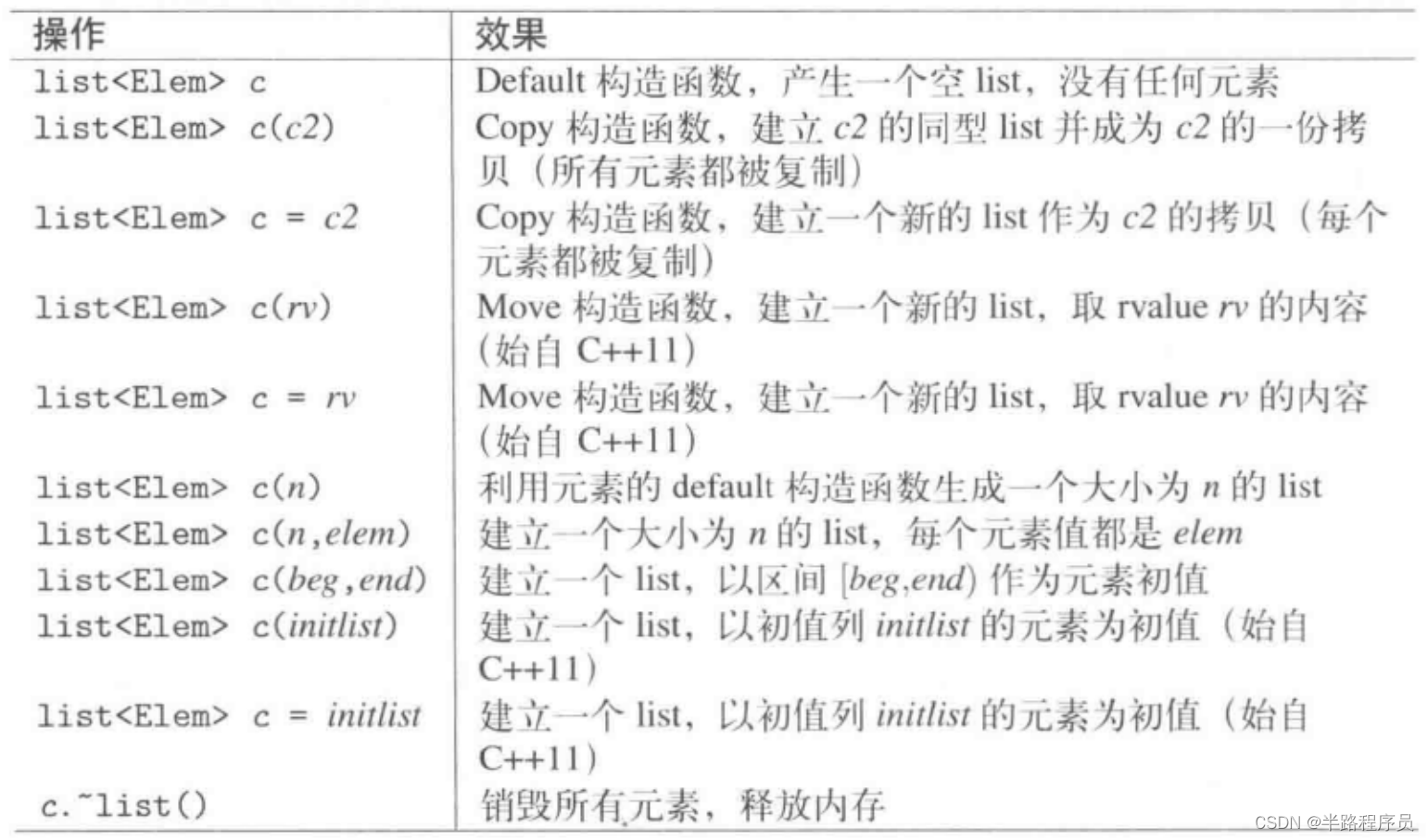
构造和析构函数
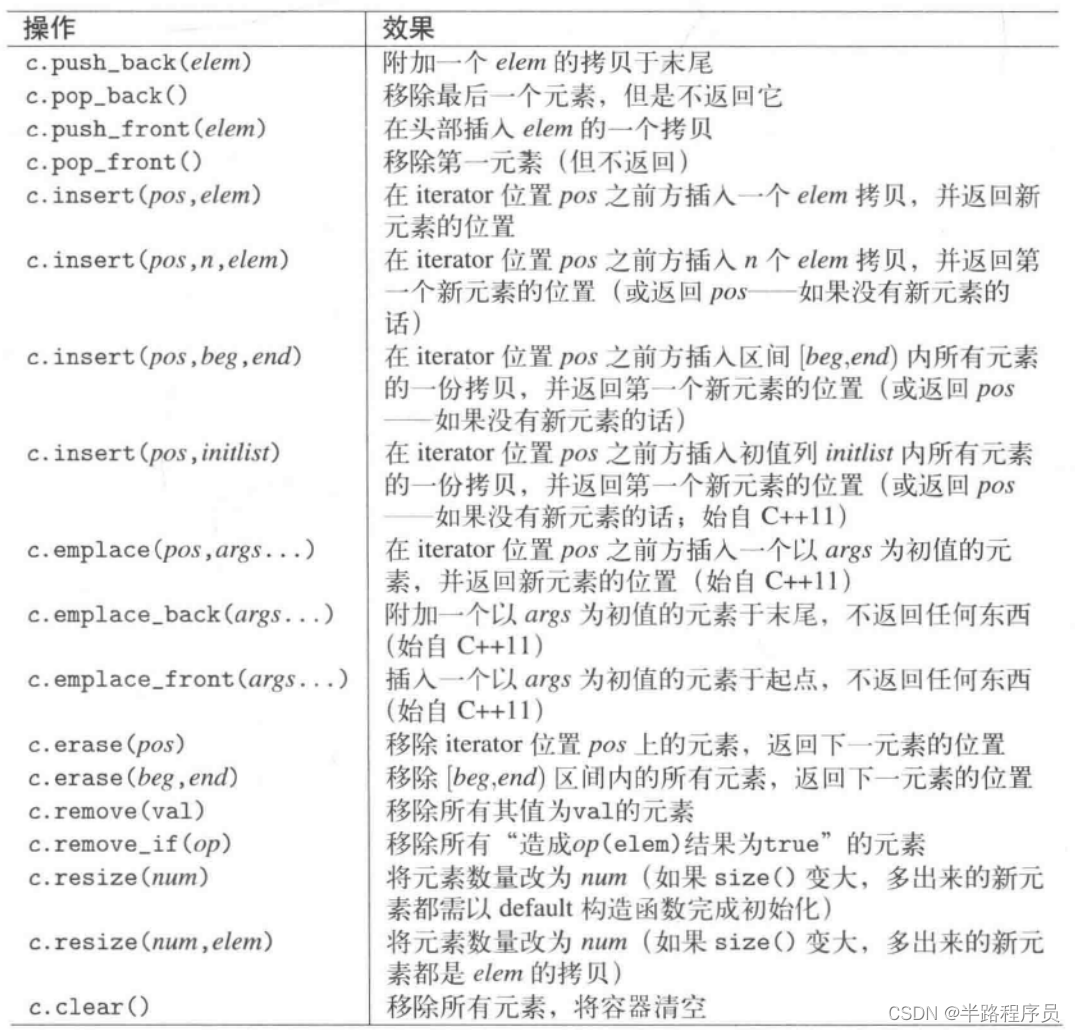
赋值操作:

int main() {
list<int> coll = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 7, 4, 9};
for (auto it = coll.cbegin(); it != coll.cend(); it++) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 下面的remove会移除所有的4
// coll.remove(4);
// 如果只需要移除第一个4
std::list<int>::iterator pos;
pos = find(coll.begin(), coll.end(), 4);
if (pos != coll.end()) {
coll.erase(pos);
}
for (auto it = coll.cbegin(); it != coll.cend(); it++) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
return 0;
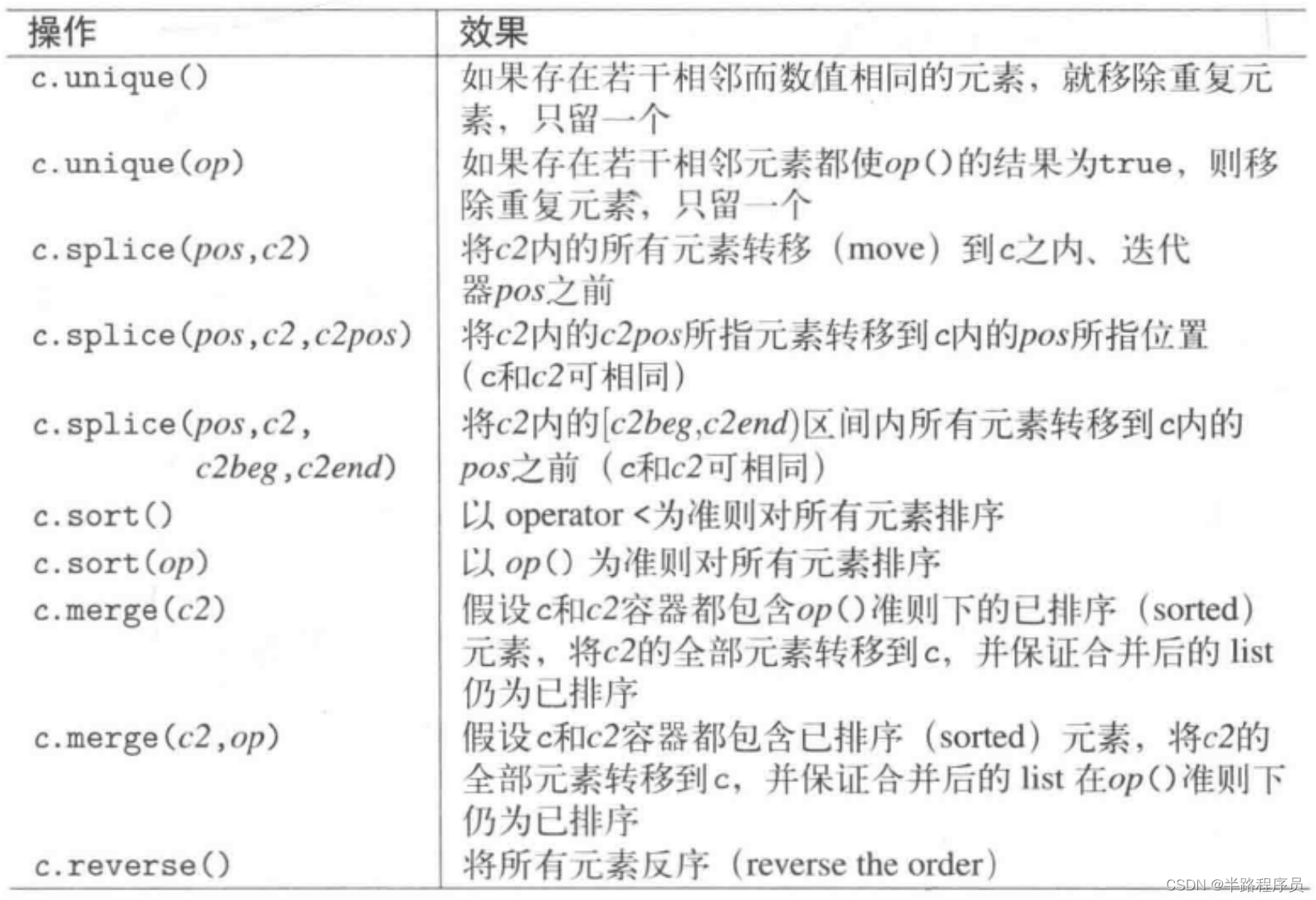
}
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
void printLists (const list<int>& l1, const list<int>& l2)
{
cout << "list1: ";
copy (l1.cbegin(), l1.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
cout << endl << "list2: ";
copy (l2.cbegin(), l2.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
cout << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
// create two empty lists
list<int> list1, list2;
// fill both lists with elements
for (int i=0; i<6; ++i) {
list1.push_back(i);
list2.push_front(i);
}
printLists(list1, list2);
// insert all elements of list1 before the first element with value 3 of list2
// - find() returns an iterator to the first element with value 3
list2.splice(find(list2.begin(),list2.end(), // destination position
3),
list1); // source list
printLists(list1, list2);
// move first element of list2 to the end
list2.splice(list2.end(), // destination position
list2, // source list
list2.begin()); // source position
printLists(list1, list2);
// sort second list, assign to list1 and remove duplicates
list2.sort();
list1 = list2;
list2.unique();
printLists(list1, list2);
// merge both sorted lists into the first list
list1.merge(list2);
printLists(list1, list2);
}
输出:
list1: 0 1 2 3 4 5
list2: 5 4 3 2 1 0
list1:
list2: 5 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 0
list1:
list2: 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 0 5
list1: 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5
list2: 0 1 2 3 4 5
list1: 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5
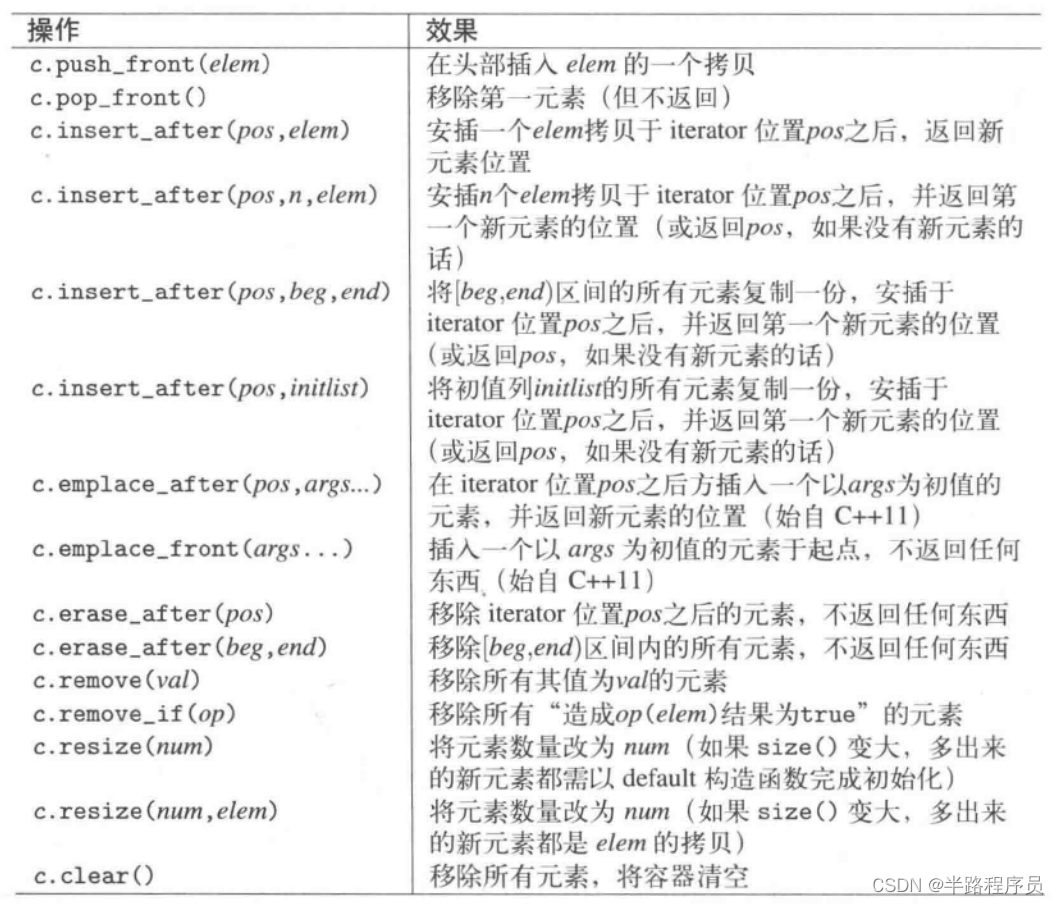
list2:6、forward_list
构造和初始化

赋值
插入和删除
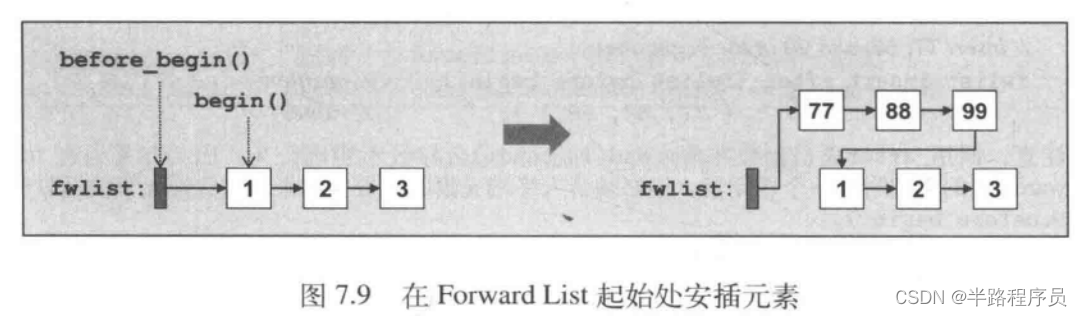
#include <iterator>
auto posBefore = list.before_begin();
for (; next(posBefore) != list.end(); ++posBefore) {
if (*next(posBefore) % 2 == 0) {
break;
}
}
splice_after操作
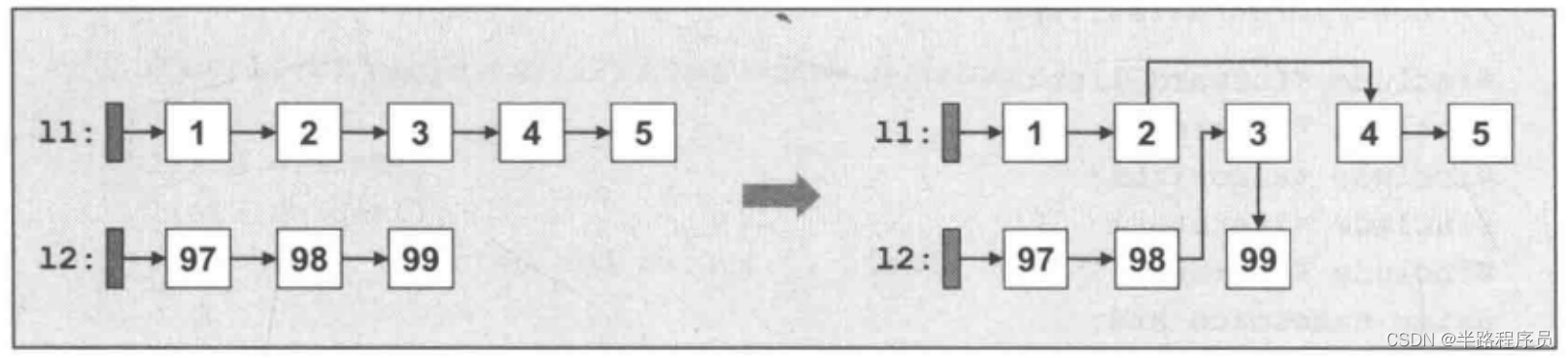
l1.splice_after(l2.find_before(99), l2, //destination
l1.find_before(3)); //source
#include <forward_list>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void printLists (const string& s, const forward_list<int>& l1,
const forward_list<int>& l2)
{
cout << s << endl;
cout << " list1: ";
copy (l1.cbegin(), l1.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
cout << endl << " list2: ";
copy (l2.cbegin(), l2.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
// create two forward lists
forward_list<int> list1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
forward_list<int> list2 = { 77, 88, 99 };
printLists ("initial:", list1, list2);
// insert six new element at the beginning of list2
list2.insert_after(list2.before_begin(),99); // 开头插入99
list2.push_front(10); // 开头插入10
list2.insert_after(list2.before_begin(), {10,11,12,13} ); // 开头插入10 11 12 13
printLists ("6 new elems:", list1, list2);
// insert all elements of list2 at the beginning of list1
list1.insert_after(list1.before_begin(), // 把list2 插入到list1的最前面
list2.begin(),list2.end());
printLists ("list2 into list1:", list1, list2);
// delete second element and elements after element with value 99
list2.erase_after(list2.begin()); // 删除第二个元素
list2.erase_after(find(list2.begin(),list2.end(), // 删除99之后的
99),
list2.end());
printLists ("delete 2nd and after 99:", list1, list2);
// sort list1, assign it to list2, and remove duplicates
list1.sort();
list2 = list1;
list2.unique(); // 排序之后去重
printLists ("sorted and unique:", list1, list2);
// merge both sorted lists into list1
list1.merge(list2);
printLists ("merged:", list1, list2);
}
输出:
initial:
list1: 1 2 3 4
list2: 77 88 99
6 new elems:
list1: 1 2 3 4
list2: 10 11 12 13 10 99 77 88 99
list2 into list1:
list1: 10 11 12 13 10 99 77 88 99 1 2 3 4
list2: 10 11 12 13 10 99 77 88 99
delete 2nd and after 99:
list1: 10 11 12 13 10 99 77 88 99 1 2 3 4
list2: 10 12 13 10 99
sorted and unique:
list1: 1 2 3 4 10 10 11 12 13 77 88 99 99
list2: 1 2 3 4 10 11 12 13 77 88 99
merged:
list1: 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 10 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 77 77 88 88 99 99 99
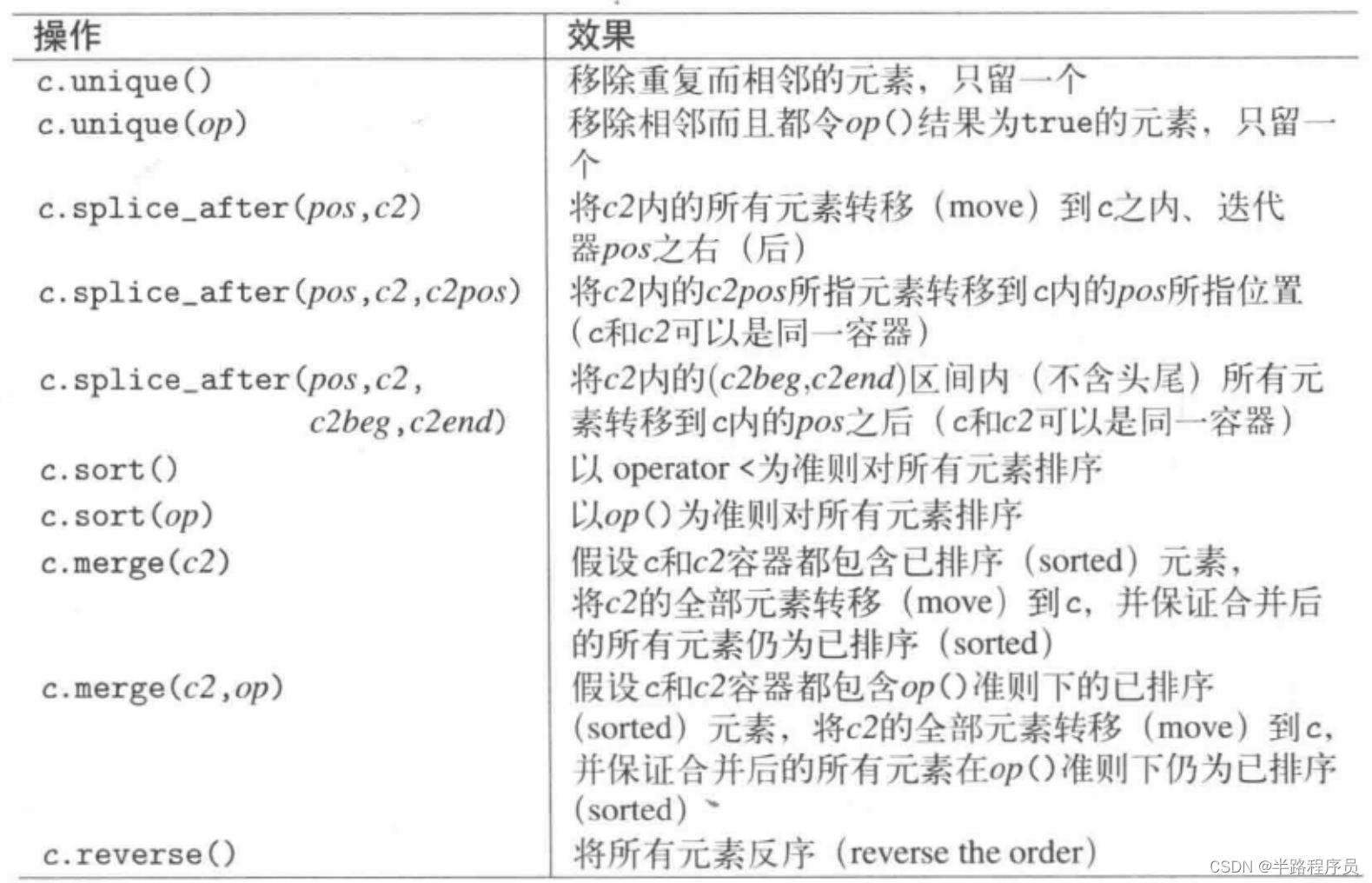
list2:7、set和multiset
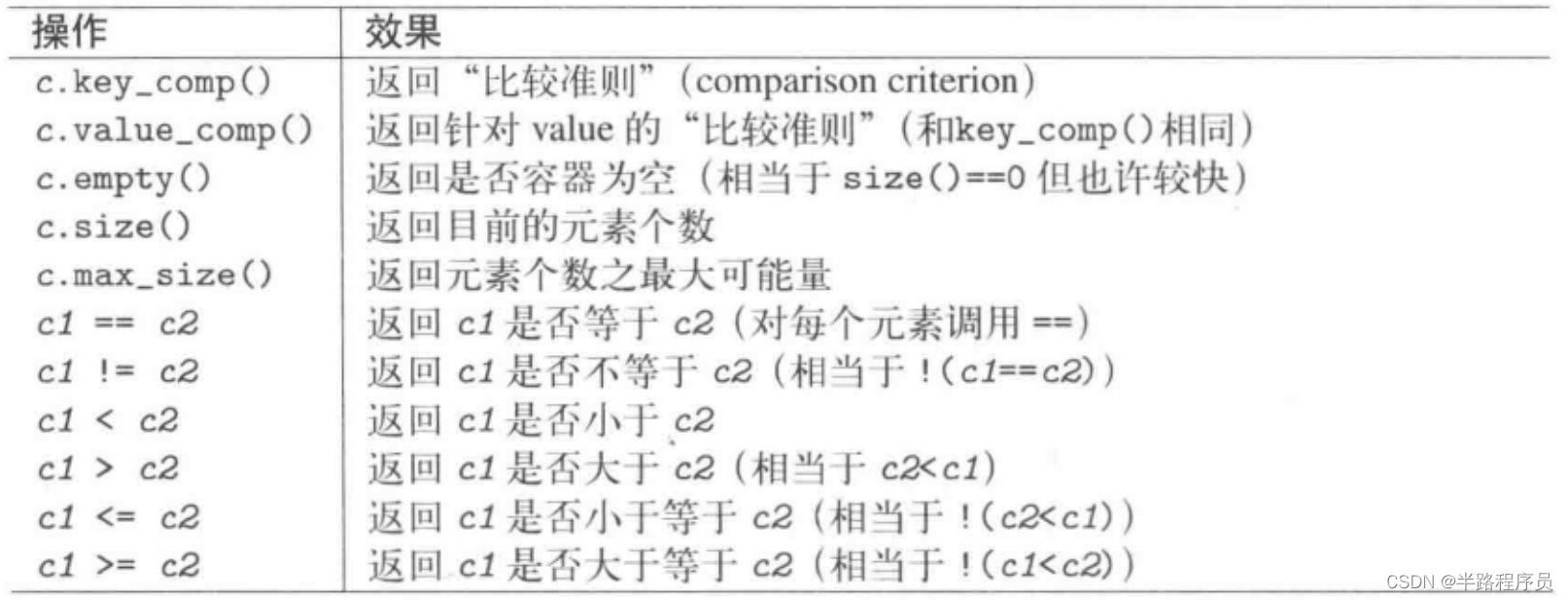

插入和删除
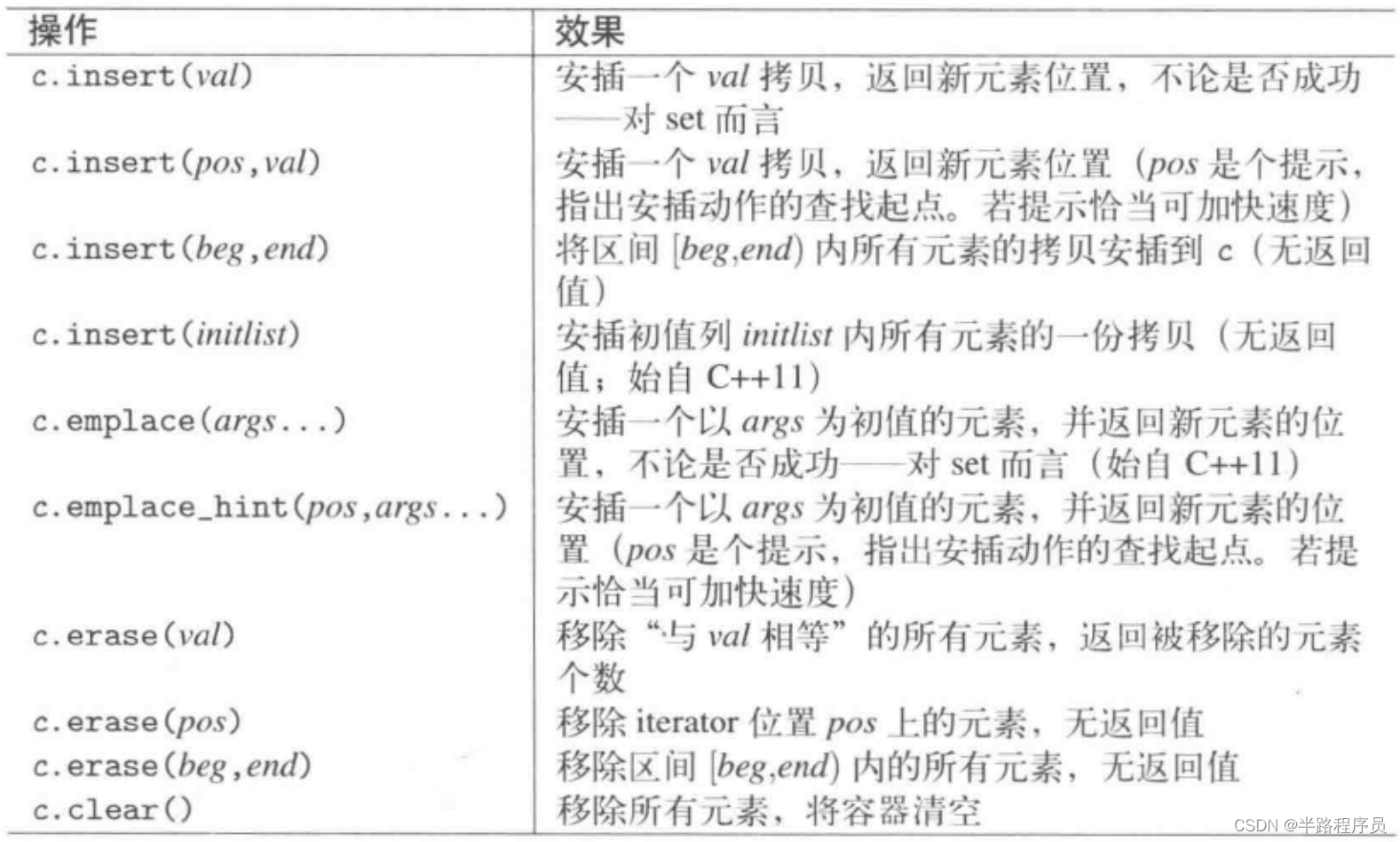
set提供接口如下
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& val);
iterator insert(const_iterator posHint, const value_type &val);
template<typename ... Args>
pair<iterator, bool> emplace(Args&& ... args);
template <typename ...Args>
iterator emplace_hint(const_iterator posHint, Args&&... args);multiset接口
iterator insert(const value_type& val);
iterator insert(const_iterator posHint, const value_type& val);
template <typename... Args>
iterator emplace(Args&&... args);
template <typename... Args>
iterator emplace_hint(const_iterator posHint, Args&& ... args);返回类型不同是因为multiset允许元素重复,而set不允许,将元素插入set内,如果已经有该元素,插入将失败,返回类型是pair
pair中的second成员表示是否安插成功,first成员表示新元素的位置,或者现存的同值元素的位置。
std::set<double> s;
if (s.insert(3.3).second) {
std::cout << "3.3 inserted" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "3.3 already exists" << std::endl;
}#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include "print.hpp"
using namespace std;
class RuntimeCmp {
public:
enum cmp_mode {normal , reverse};
private:
cmp_mode mode;
public:
RuntimeCmp(cmp_mode m=normal):mode(m) {}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T& t1, const T& t2) const {
return mode == normal ? t1 < t2 : t2 < t1;
}
bool operator ==(const RuntimeCmp& rc) const {
return mode == rc.mode;
}
};
typedef set<int, RuntimeCmp> IntSet;
int main() {
IntSet coll1 = {4, 7, 5, 1, 6, 2};
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll1, "coll1: ");
// 创建一个反向迭代器
RuntimeCmp reverse_order(RuntimeCmp::reverse);
IntSet coll2(reverse_order);
coll2 = {4, 7, 5, 1, 6, 2};
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll2, "coll2: ");
coll1 = coll2;
coll1.insert(3);
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll1, "coll1: ");
if (coll1.value_comp() == coll2.value_comp()) {
std::cout << "coll1 and coll2 have the same sorting criterion" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "coll1 and coll2 have a different sorting criterion" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
coll1: 1 2 4 5 6 7
coll2: 7 6 5 4 2 1
coll1: 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
coll1 and coll2 have the same sorting criterion8、Map和Multimap
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
// function object to compare strings
// - allows you to set the comparison criterion at runtime
// - allows you to compare case insensitive
class RuntimeStringCmp {
public:
// constants for the comparison criterion
enum cmp_mode {normal, nocase};
private:
// actual comparison mode
const cmp_mode mode;
// auxiliary function to compare case insensitive
static bool nocase_compare (char c1, char c2) {
return toupper(c1) < toupper(c2);
}
public:
// constructor: initializes the comparison criterion
RuntimeStringCmp (cmp_mode m=normal) : mode(m) {
}
// the comparison
bool operator() (const string& s1, const string& s2) const {
if (mode == normal) {
return s1<s2;
}
else {
return lexicographical_compare (s1.begin(), s1.end(),
s2.begin(), s2.end(),
nocase_compare);
}
}
};
// container type:
// - map with
// - string keys
// - string values
// - the special comparison object type
typedef map<string,string,RuntimeStringCmp> StringStringMap;
// function that fills and prints such containers
void fillAndPrint(StringStringMap& coll);
int main()
{
// create a container with the default comparison criterion
StringStringMap coll1;
fillAndPrint(coll1);
// create an object for case-insensitive comparisons
RuntimeStringCmp ignorecase(RuntimeStringCmp::nocase);
// create a container with the case-insensitive comparisons criterion
StringStringMap coll2(ignorecase);
fillAndPrint(coll2);
}
void fillAndPrint(StringStringMap& coll)
{
// insert elements in random order
coll["Deutschland"] = "Germany";
coll["deutsch"] = "German";
coll["Haken"] = "snag";
coll["arbeiten"] = "work";
coll["Hund"] = "dog";
coll["gehen"] = "go";
coll["Unternehmen"] = "enterprise";
coll["unternehmen"] = "undertake";
coll["gehen"] = "walk";
coll["Bestatter"] = "undertaker";
// print elements
cout.setf(ios::left, ios::adjustfield);
for (const auto& elem : coll) {
cout << setw(15) << elem.first << " "
<< elem.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
输出:
Bestatter undertaker
Deutschland Germany
Haken snag
Hund dog
Unternehmen enterprise
arbeiten work
deutsch German
gehen walk
unternehmen undertake
arbeiten work
Bestatter undertaker
deutsch German
Deutschland Germany
gehen walk
Haken snag
Hund dog
Unternehmen undertake9、无序容器

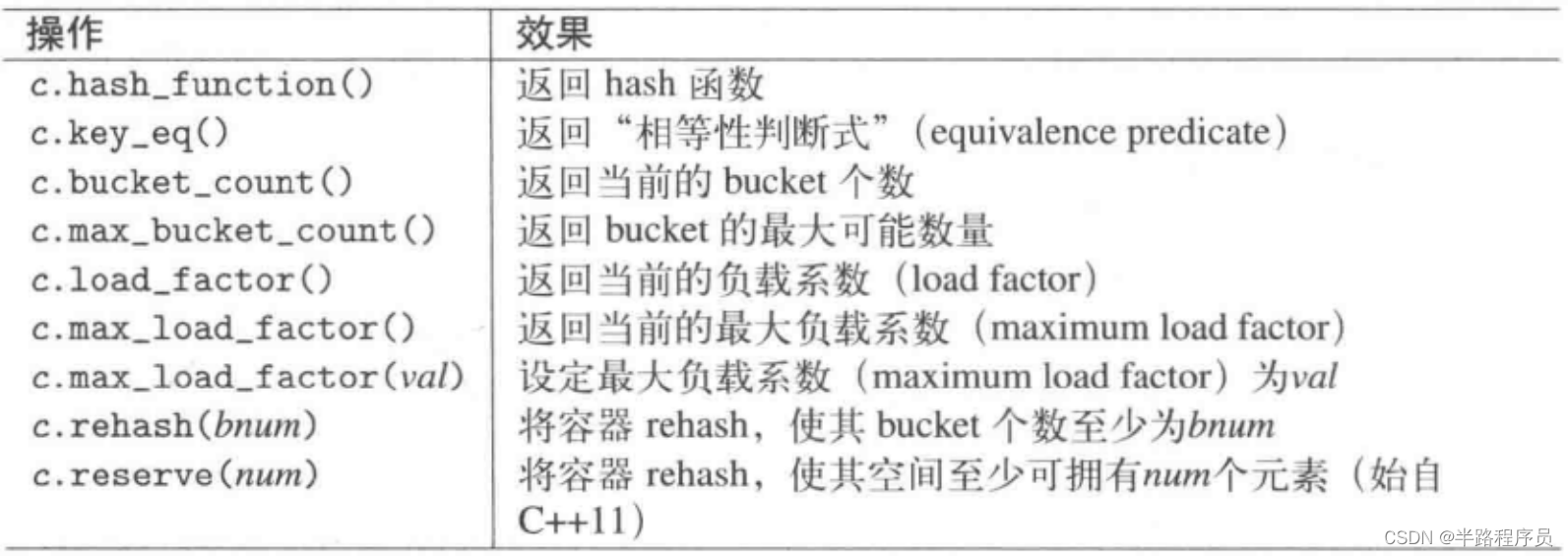
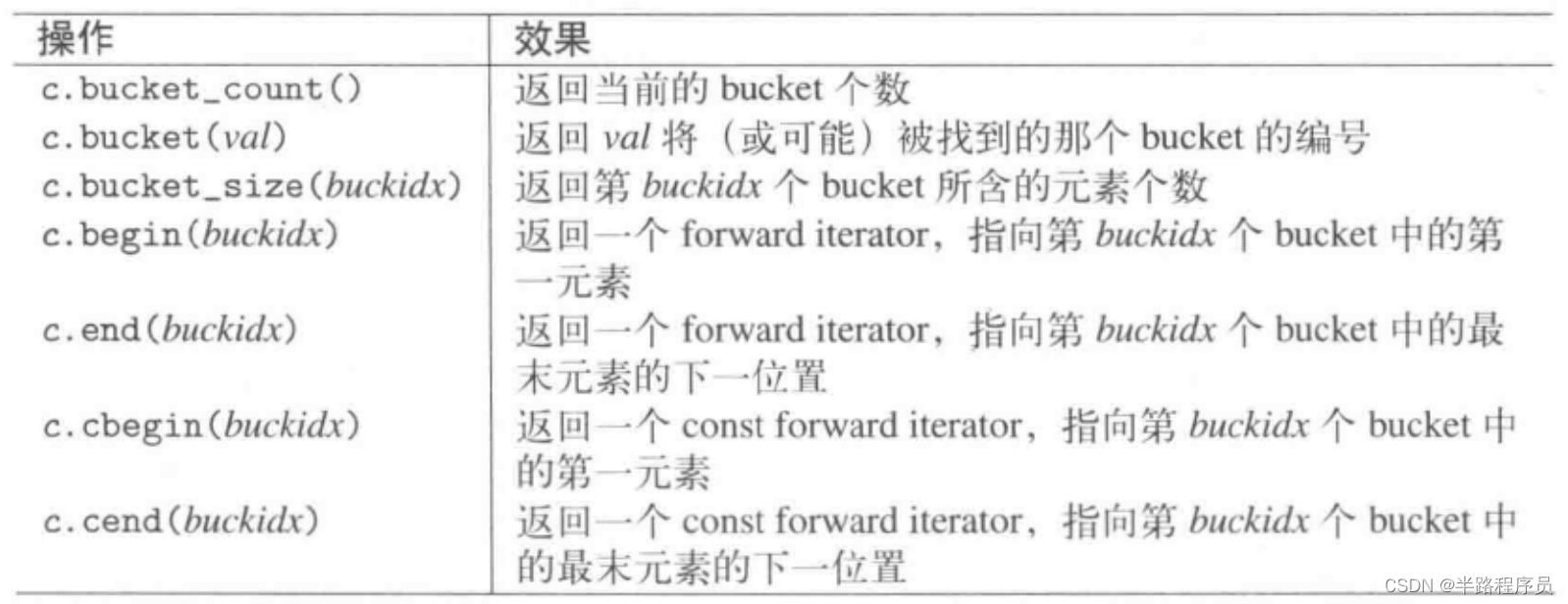
10、Bucket接口
#include <unordered_set>
#include <numeric>
#include "print.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// create and initialize unordered set
unordered_set<int> coll = { 1,2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,77 };
// print elements
// - elements are in arbitrary order
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
// insert some additional elements
// - might cause rehashing and create different order
coll.insert({-7,17,33,-11,17,19,1,13});
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
// remove element with specific value
coll.erase(33);
// insert sum of all existing values
coll.insert(accumulate(coll.begin(),coll.end(),0));
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
// check if value 19 is in the set
if (coll.find(19) != coll.end()) {
cout << "19 is available" << endl;
}
// remove all negative values
unordered_set<int>::iterator pos;
for (pos=coll.begin(); pos!= coll.end(); ) {
if (*pos < 0) {
pos = coll.erase(pos);
}
else {
++pos;
}
}
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
}
输出:
77 19 17 13 11 7 5 3 2 1
-7 77 19 17 13 11 33 7 -11 5 3 2 1
-7 77 19 17 13 11 137 7 -11 5 3 2 1
19 is available
77 19 17 13 11 137 7 5 3 2 111、提供自己的hash函数和等价准则
//hashval.hpp
#include <functional>
// from boost (functional/hash):
// see http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_35_0/doc/html/hash/combine.html
template <typename T>
inline void hash_combine (std::size_t& seed, const T& val)
{
seed ^= std::hash<T>()(val) + 0x9e3779b9 + (seed<<6) + (seed>>2);
}
// auxiliary generic functions to create a hash value using a seed
template <typename T>
inline void hash_val (std::size_t& seed, const T& val)
{
hash_combine(seed,val);
}
template <typename T, typename... Types>
inline void hash_val (std::size_t& seed,
const T& val, const Types&... args)
{
hash_combine(seed,val);
hash_val(seed,args...);
}
// auxiliary generic function to create a hash value out of a heterogeneous list of arguments
template <typename... Types>
inline std::size_t hash_val (const Types&... args)
{
std::size_t seed = 0;
hash_val (seed, args...);
return seed;
}#include <unordered_set>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include "hashval.hpp"
#include "print.hpp"
using namespace std;
class Customer {
private:
string fname;
string lname;
long no;
public:
Customer (const string& fn, const string& ln, long n)
: fname(fn), lname(ln), no(n) {}
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& strm, const Customer& c) {
return strm << "[" << c.fname << "," << c.lname << ","
<< c.no << "]";
}
friend class CustomerHash;
friend class CustomerEqual;
};
class CustomerHash
{
public:
std::size_t operator() (const Customer& c) const {
return hash_val(c.fname,c.lname,c.no);
}
};
class CustomerEqual
{
public:
bool operator() (const Customer& c1, const Customer& c2) const {
return c1.no == c2.no;
}
};
int main()
{
// unordered set with own hash function and equivalence criterion
unordered_set<Customer,CustomerHash,CustomerEqual> custset;
custset.insert(Customer("nico","josuttis",42));
PRINT_ELEMENTS(custset);
}12、使用Lambda函数作为hash函数和等价准则
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_set>
#include "hashval.hpp"
#include "print.hpp"
using namespace std;
class Customer {
private:
string fname;
string lname;
long no;
public:
Customer(const string& fn, const string& ln, long n):fname(fn),lname(ln), no(n) {}
string firstname() const {
return fname;
}
string lastname() const {
return lname;
}
long number() const {
return no;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& strm, const Customer&c) {
return strm << "[" << c.fname << "," << c.lname << "," << c.no << "]";
}
};
int main() {
auto hash = [](const Customer& c) {
return hash_val(c.firstname(), c.lastname(), c.number());
};
auto eq = [](const Customer& c1, const Customer& c2) {
return c1.number() == c2.number();
};
unordered_set<Customer, decltype(hash), decltype(eq)> custset(10, hash, eq);
custset.insert(Customer("noco", "osuttis", 32));
PRINT_ELEMENTS(custset);
}注意需要使用decltype产生Lambda类型,作为模板参数,因为Lambda并不存在default构造函数和assignment操作符,因此也必须将Lambda传递给构造函数,而由于这两个是占用第二和第三实参,所以指明第一实参bucket的大小。
13、Bucket接口使用
查阅一个unordered容器内部状态。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <utility>
#include <iterator>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <unordered_set>
template <typename T1, typename T2>
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& strm, const std::pair<T1,T2>& p) {
return strm << "[" << p.first << "," << p.second << "]";
}
template <typename T>
void printHashTableState(const T& cont) {
std::cout << "size: " << cont.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "buckets: " << cont.bucket_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "load factor: " << cont.load_factor() << std::endl;
std::cout << "max load factor: " << cont.max_load_factor() << std::endl;
//迭代器类型
if (typeid(typename std::iterator_traits<typename T::iterator>::iterator_category) ==
typeid(std::bidirectional_iterator_tag)) {
std::cout << "chaining style: doubly-linked" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "chaining style: singly-linked" << std::endl;
}
// elements per bucket
std::cout << "data: " << std::endl;
for (auto idx = 0; idx != cont.bucket_count(); ++idx) {
std::cout << " b[" << std::setw(2) << idx << "]: ";
for (auto pos = cont.begin(idx); pos != cont.end(idx); ++pos) {
std::cout << *pos << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
int main() {
std::unordered_set<int> intset = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 18};
printHashTableState(intset);
intset.insert({-7, 17, 33, 4});
printHashTableState(intset);
return 0;
}
输出:
size: 10
buckets: 13
load factor: 0.769231
max load factor: 1
chaining style: singly-linked
data:
b[ 0]: 13
b[ 1]: 1
b[ 2]: 2
b[ 3]: 3
b[ 4]: 17 4
b[ 5]: 18 5
b[ 6]:
b[ 7]: 7
b[ 8]:
b[ 9]:
b[10]:
b[11]: 11
b[12]:
size: 12
buckets: 13
load factor: 0.923077
max load factor: 1
chaining style: singly-linked
data:
b[ 0]: 13
b[ 1]: 1
b[ 2]: 2
b[ 3]: 3
b[ 4]: 17 4
b[ 5]: 18 5
b[ 6]:
b[ 7]: 33 7
b[ 8]:
b[ 9]: -7
b[10]:
b[11]: 11
b[12]:#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <utility>
#include <iterator>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
template <typename T1, typename T2>
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& strm, const std::pair<T1,T2>& p) {
return strm << "[" << p.first << "," << p.second << "]";
}
template <typename T>
void printHashTableState(const T& cont) {
std::cout << "size: " << cont.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "buckets: " << cont.bucket_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "load factor: " << cont.load_factor() << std::endl;
std::cout << "max load factor: " << cont.max_load_factor() << std::endl;
//迭代器类型
if (typeid(typename std::iterator_traits<typename T::iterator>::iterator_category) ==
typeid(std::bidirectional_iterator_tag)) {
std::cout << "chaining style: doubly-linked" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "chaining style: singly-linked" << std::endl;
}
// elements per bucket
std::cout << "data: " << std::endl;
for (auto idx = 0; idx != cont.bucket_count(); ++idx) {
std::cout << " b[" << std::setw(2) << idx << "]: ";
for (auto pos = cont.begin(idx); pos != cont.end(idx); ++pos) {
std::cout << *pos << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create and initialize an unordered multimap as dictionary
std::unordered_multimap<string,string> dict = {
{"day","Tag"},
{"strange","fremd"},
{"car","Auto"},
{"smart","elegant"},
{"trait","Merkmal"},
{"strange","seltsam"}
};
printHashTableState(dict);
// insert some additional values (might cause rehashing)
dict.insert({{"smart","raffiniert"},
{"smart","klug"},
{"clever","raffiniert"}
});
printHashTableState(dict);
// modify maximum load factor (might cause rehashing)
dict.max_load_factor(0.7);
printHashTableState(dict);
}
输出:
size: 6
buckets: 7
load factor: 0.857143
max load factor: 1
chaining style: singly-linked
data:
b[ 0]: [trait,Merkmal]
b[ 1]: [strange,fremd] [strange,seltsam]
b[ 2]: [day,Tag]
b[ 3]: [smart,elegant]
b[ 4]:
b[ 5]: [car,Auto]
b[ 6]:
size: 9
buckets: 17
load factor: 0.529412
max load factor: 1
chaining style: singly-linked
data:
b[ 0]: [car,Auto]
b[ 1]:
b[ 2]:
b[ 3]:
b[ 4]:
b[ 5]:
b[ 6]: [strange,fremd] [strange,seltsam] [smart,elegant] [smart,klug] [smart,raffiniert]
b[ 7]:
b[ 8]:
b[ 9]:
b[10]: [clever,raffiniert]
b[11]:
b[12]: [trait,Merkmal]
b[13]:
b[14]:
b[15]: [day,Tag]
b[16]:
size: 9
buckets: 17
load factor: 0.529412
max load factor: 0.7
chaining style: singly-linked
data:
b[ 0]: [car,Auto]
b[ 1]:
b[ 2]:
b[ 3]:
b[ 4]:
b[ 5]:
b[ 6]: [strange,fremd] [strange,seltsam] [smart,elegant] [smart,klug] [smart,raffiniert]
b[ 7]:
b[ 8]:
b[ 9]:
b[10]: [clever,raffiniert]
b[11]:
b[12]: [trait,Merkmal]
b[13]:
b[14]:
b[15]: [day,Tag]
b[16]: