前言:
什么是 Linux 下的 platform 设备驱动
Linux下的字符设备驱动一般都比较简单,只是对IO进行简单的读写操作。但是I2C、SPI、LCD、USB等外设的驱动就比较复杂了,需要考虑到驱动的可重用性,以避免内核中存在大量重复代码,为此人们提出了驱动的分离与分层的思路,演化并诞生出了platform设备驱动。
一、驱动的分层分离
1. 驱动的分离
以I2C接口的三轴加速度传感器为例,传统的设备驱动如下图示:每个平台都有一个ADXL345的驱动,因此设备驱动要重复编写三次。
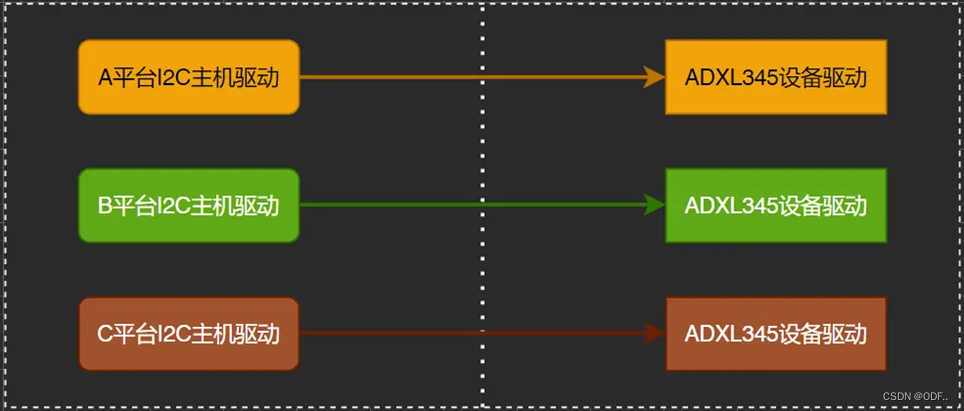
各平台的主机驱动是不同的,但是ADXL345是一样的,因此上图可以精简为一个ADXL345驱动和统一的接口API。
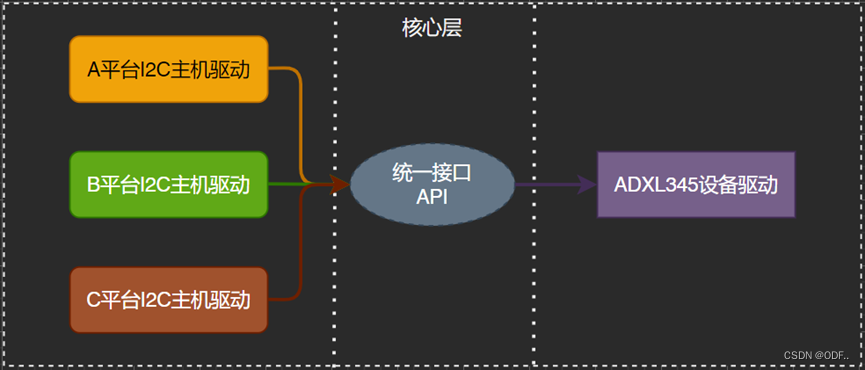 实际上,除了ADXL345还有AT24C02、MPU6050等I2C设备,因此实际的驱动框架图如下示
实际上,除了ADXL345还有AT24C02、MPU6050等I2C设备,因此实际的驱动框架图如下示
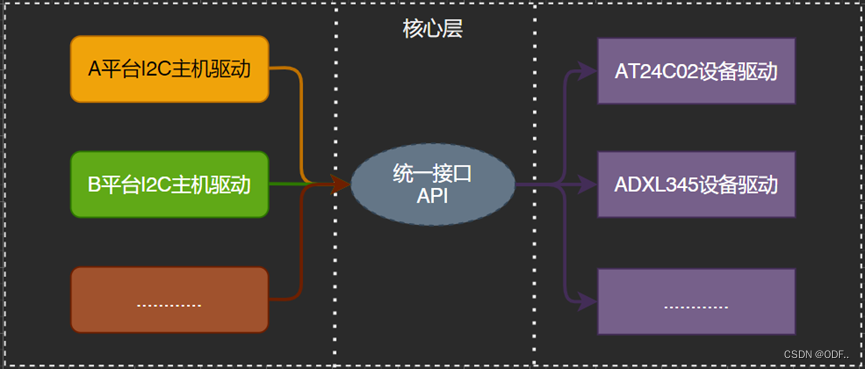
驱动的分离即将主机驱动和设备驱动分隔开来,实际开发中,主机驱动一般由半导体厂家提供,设备驱动也会由器件厂家写好,我们只需要提供设备信息即可。也就是将设备信息从设备驱动中剥离开来,设备驱动使用标准方法获取到设备信息,然后根据获取到的设备信息来初始化设备
因此驱动只负责驱动,设备只负责设备,想办法将两者进行匹配即可。这就是Linux中的总线-驱动-设备模型,也就是常说的驱动分离

如上图示,当向系统注册一个驱动时,总线会在右侧的设备中查找,看看有没有与之匹配的设备,有的话就将两者联系起来;当向系统中注册一个设备时,总线会在左侧的驱动中查找,看有没有与之匹配的驱动,有的话也联系起来。
2. 驱动的分层
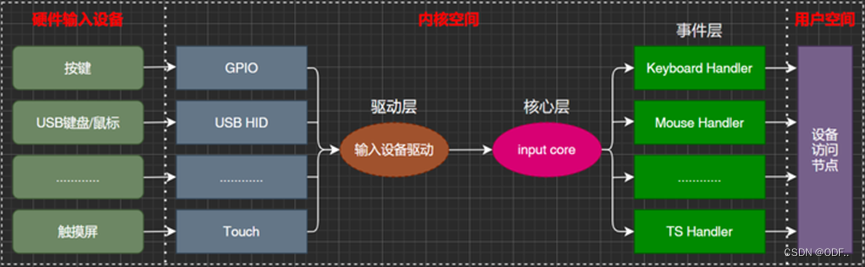
Linux下的驱动也是分层的,分层的目的是为了在不同的层处理不同的内容。以input输入子系统为例,input子系统负责管理所有跟输入有关的驱动,包括键盘、鼠标、触摸等。
- 驱动层:获取输入设备的原始值,获取到的输入事件上报给核心层
- 核心层:处理各种IO模型,并且提供file_operations操作集合
- 事件层:和用户空间进行交互
3. platform平台驱动模型
根据总线-驱动-设备驱动模型,IIC、SPI、USB这样实实在在的总线是完全匹配的,但是要有一些外设是没法归结为具体的总线:比如定时器、RTC、LCD等。为此linux内核创造了一个虚拟的总线:platform总线,以及platform驱动、platform设备模型。
①platform总线:Linux内核使用bus_type结构体表示总线。
其定义在文件include/linux/device.h中
②platform驱动:platform驱动由platform_driver结构体表示。
此结构体定义在文件include/linux/platform_device.h中。
编写platform驱动时,先要定义一个platform_driver结构体变量,然后实现结构体中的各个成员变量,重点是实现匹配方法以及probe函数。当驱动和设备匹配成功以后probe函数就会执行,具体的驱动程序在probe函数里面编写。之后通过以下函数向内核注册platform驱动或卸载platform驱动
③platform设备:platform_device结构体用来表示platform设备。
注意若内核支持设备树的话,就无需使用该结构体来描述设备,而改用设备树了。该结构体定义在文件include/linux/platform_device.h中,在不支持设备树的Linux版本中,用户需要编写platform_device变量来描述设备信息,然后使用以下函数将设备信息注册到Linux内核中或从内核中注销掉,这里我们使用的linux是新版本的了,也就直接使用设备树就好了。
二、platform框架分析
1.platform总线注册
和字符型驱动一样,我们要使用platform总线之前,也需要告诉一下内核,也就是注册。使用platform_bus_init函数去进行注册,既然要注册,那么我们也得告诉内核我们的一些信息。
注册的内容就是:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
}对于platform平台而言,platform_match函数就是月老,负责驱动和设备的匹配。
2.platform驱动
在注册platform驱动之前要定义一个结构体,为platform_driver,结构体内容为:
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
//-> const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
//-> const char *name;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};然后使用platform_driver_register函数向内核注册platform驱动。向内核注册platform驱动的时候,如果驱动和设备匹配成功,最终会执行platform_driver的probe函数。
3.platform设备
1、无设备树的时候,此时需要驱动开发人员编写设备注册文件,使用platform_device_register函数注册设备。使用platform_device_register函数注册设备也同样需要告诉内核一些注册信息。也就是需要定义个结构体:
结构体platform_device:
struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource;
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};
2,有设备树,修改设备树的设备节点即可。使用兼容性列表,当设备与platform的驱动匹配以后,就会执行platform_driver->probe函数。
三、编写 platform 驱动流程
接下来我们就来学习一下如何在设备树下编写 platform 驱动流程:
1.在设备树中创建设备节点
由于我们使用的linux是支持设备树的,那么毫无疑问,我们肯定要先在设备树中创建设备节点来描述设备信息,重点是要设置好 compatible 属性的值,因为 platform 总线需要通过设备节点的 compatible 属性值来匹配驱动!这点要切记。
2、编写platfrom的驱动兼容表:
1)建立of_device_id 表,也就是驱动的兼容表:
static const struct of_device_id leds_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "atkalpha-gpioled" }, /* 兼容属性 */
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};3、建立platform_driver结构体:
static struct platform_driver leds_platform_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led",
.of_match_table = leds_of_match,
},
.probe = leds_probe,
.remove = leds_remove,
};1)设置 platform_driver 中的 of_match_table 匹配表为上面创建的 leds_of_match
2)向总线注册驱动的时候,会检查当前总线下的所有设备,有没有与此驱动匹配的设备,如果有的话就执行驱动里面的probe函数。
3)卸载驱动的时候,会执行驱动里面的remove函数。
4、编写probe函数:
函数原型:
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev);5、编写remove函数:
函数原型
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev);四、实验程序编写
1.在设备树中创建设备节点
2.引入字符设备框架
这里直接引入我们之前写过的字符设备框架,在这份驱动的基础上来进行修改,如果没有看过之前那篇也没关系,下面也会贴出完整代码。
3.编写platfrom的驱动兼容表
/* 匹配列表 */
static const struct of_device_id led_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "led-gpio" },
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
4.建立platform_driver结构体
/*platform_driver结构体*/
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led",
.of_match_table = led_of_match,
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};5.编写probe函数:
当设备和驱动兼容表匹配上的时候就会运行peobe函数:
/*当谁列表的设备和驱动匹配上后执行的peobe函数*/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
/* 动态注册字符设备的流程一般如下:
1.调用 alloc_chrdev_region() 函数申请设备编号。
2.使用 cdev_init() 函数初始化设备描述结构体。
3.使用 cdev_add() 函数将设备号与设备描述结构体关联起来,注册字符设备驱动。
4.使用 class_create() 函数创建一个设备类.
5.使用 device_create() 函数创建一个设备
*/
int ret = 0;
/*进入这个函数就表明匹配成功了*/
printk("led driver and device was matched!\r\n");
/*1 创建设备号
根据是否定义了设备号,通过条件判断选择不同的创建方式。
如果定义了设备号,则使用MKDEV宏将主设备号和次设备号合成为设备号,并调用register_chrdev_region()函数注册字符设备号。
如果没有定义设备号,则使用alloc_chrdev_region()函数动态分配设备号,并通过MAJOR和MINOR宏获取分配得到的主设备号和次设备号。*/
if(gpioled.major){
gpioled.devid = MKDEV(gpioled.major,0);
register_chrdev_region(gpioled.devid,DEVICE_CNT,DEVICE_NAME);
}
else{
alloc_chrdev_region(&gpioled.devid,0,DEVICE_CNT,DEVICE_NAME);
gpioled.major = MAJOR(gpioled.devid);
gpioled.minor = MINOR(gpioled.devid);
}
/* 2 初始化cdev
设置cdev结构体的拥有者为当前模块(THIS_MODULE),然后使用 cdev_init() 函数初始化cdev结构体。
参数包括待初始化的cdev结构体和用于操作该设备的file_operations结构体(hello_drv) */
gpioled.cdev.owner= THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&gpioled.cdev,&gpioled_fops);
/* 3、添加一个cdev */
cdev_add(&gpioled.cdev,gpioled.devid,DEVICE_CNT);
/*4 创建设备类
使用 class_create() 函数创建一个设备类,设备类用于在/sys/class目录下创建子目录,以组织同一类设备的相关信息。
该函数的参数包括所属的模块(THIS_MODULE)和设备类的名称(DEVICE_NAME)。
如果创建失败,IS_ERR() 函数将返回true,表示出错,此时使用 PTR_ERR() 函数返回错误码。 */
gpioled.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME);
if(IS_ERR(gpioled.class))
{
printk("newchr fail!\r\n");
return PTR_ERR(gpioled.class);
}
/*5 创建设备
使用 device_create() 函数创建一个设备,并在/dev目录下创建相应的设备节点。
参数包括设备所属的类(newchr.class)、父设备(NULL,如果没有父设备)、设备号(newchr.devid)、设备私有数据(NULL,一般为设备驱动程序提供一个指针)和设备名称(DEVICE_NAME)。
如果创建失败,IS_ERR() 函数将返回true,表示出错,此时使用 PTR_ERR() 函数返回错误码。 */
gpioled.device = device_create(gpioled.class, NULL, gpioled.devid, NULL, DEVICE_NAME);
if(IS_ERR(gpioled.device))
{
printk("newchr fail!\r\n");
return PTR_ERR(gpioled.device);
}
ret = myled_init(&gpioled); //初始化ledgpio
return 0;
}6.编写remove函数:
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
gpio_set_value(gpioled.led_gpio,1);
gpio_free(gpioled.led_gpio);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
/*在模块卸载时,使用 cdev_del() 函数注销字符设备驱动,并使用 unregister_chrdev_region() 函数释放设备号资源。*/
/* 注销字符设备驱动 */
cdev_del(&gpioled.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(gpioled.devid, DEVICE_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(gpioled.class, gpioled.devid);// 销毁设备,删除相应的设备节点
class_destroy(gpioled.class);// 销毁设备类,释放相关资源
printk("gpioled exit!\r\n");
return 0;
}完整代码:
/**************头文件区域*********************************************************/
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_address.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
/**********************************************************************************/
/************************函数定义-begin***********************************************/
static int gpioled_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file);
static ssize_t gpioled_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ptr);
static ssize_t gpioled_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ptr);
static int gpioled_open(struct inode *inode , struct file *file);
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev);
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev);
/************************函数定义-end********************************************/
/************************宏定义-begin***********************************************/
#define DEVICE_NAME "dtsplatled"
#define DEVICE_CNT 1
#define LED_ON 1
#define LED_OFF 0
/************************宏定义-end********************************************/
/************************结构体定义-begin***********************************************/
/* dtsled设备信息结构体 */
struct dtsled_dev
{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
int minor; /* 次设备号 */
struct device_node *nd; /* 设备节点 */
int led_gpio; /* led 所使用的 GPIO 编号 */
};
struct dtsled_dev gpioled; /* led设备 */
/* 设备操作函数结构体 */
static const struct file_operations gpioled_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = gpioled_open,
.read = gpioled_read,
.write = gpioled_write,
.release = gpioled_release
};
/* 匹配列表 */
static const struct of_device_id led_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "led-gpio" },
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led",
.of_match_table = led_of_match,
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
/************************结构体定义-end***********************************************/
/************************file_operations操作函数-begin***********************************************/
static int gpioled_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t gpioled_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ptr)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t gpioled_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ptr)
{
int ret;
unsigned char databuf[1];
unsigned char ledstate;
struct dtsled_dev *dev = file->private_data;
ret = __copy_from_user(databuf,buf,size);
if(ret < 0)
{
return -EFAULT;
}
ledstate = databuf[0];
if(ledstate == LED_OFF){
gpio_set_value(dev->led_gpio,1);
}
else if(ledstate == LED_ON){
gpio_set_value(dev->led_gpio,0);
}
return 0;
}
static int gpioled_open(struct inode *inode , struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
file->private_data = &gpioled; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
/************************file_operations操作函数-end***********************************************/
/*****************led初始化函数************************/
static int myled_init(struct dtsled_dev *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
/* 1、设置 LED 所使用的 GPIO */
dev->nd = of_find_node_by_path("/gpioled");
if(dev->nd == NULL){
printk("gpioled node cant not found!\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
else{
printk("gpioled node hase been found!\r\n");
}
/* 2、 获取设备树中的 gpio 属性,得到 LED 所使用的 LED 编号 */
dev->led_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(dev->nd,"gpios",0);
if(dev->led_gpio < 0)
{
printk("can't get led-gpio\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
printk("led-gpio num = %d\r\n", dev->led_gpio);
/* 3、设置 GPIO1_IO03 为输出,并且输出高电平,默认关闭 LED 灯 */
ret = gpio_request(dev->led_gpio,"led0");
if(ret < 0){
printk("led-gpio request fail\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
gpio_direction_output(dev->led_gpio,1);
return ret;
}
/************************platfrom操作函数-begin***********************************************/
/*当谁列表的设备和驱动匹配上后执行的peobe函数*/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
/* 动态注册字符设备的流程一般如下:
1.调用 alloc_chrdev_region() 函数申请设备编号。
2.使用 cdev_init() 函数初始化设备描述结构体。
3.使用 cdev_add() 函数将设备号与设备描述结构体关联起来,注册字符设备驱动。
4.使用 class_create() 函数创建一个设备类.
5.使用 device_create() 函数创建一个设备
*/
int ret = 0;
/*进入这个函数就表明匹配成功了*/
printk("led driver and device was matched!\r\n");
/*1 创建设备号
根据是否定义了设备号,通过条件判断选择不同的创建方式。
如果定义了设备号,则使用MKDEV宏将主设备号和次设备号合成为设备号,并调用register_chrdev_region()函数注册字符设备号。
如果没有定义设备号,则使用alloc_chrdev_region()函数动态分配设备号,并通过MAJOR和MINOR宏获取分配得到的主设备号和次设备号。*/
if(gpioled.major){
gpioled.devid = MKDEV(gpioled.major,0);
register_chrdev_region(gpioled.devid,DEVICE_CNT,DEVICE_NAME);
}
else{
alloc_chrdev_region(&gpioled.devid,0,DEVICE_CNT,DEVICE_NAME);
gpioled.major = MAJOR(gpioled.devid);
gpioled.minor = MINOR(gpioled.devid);
}
/* 2 初始化cdev
设置cdev结构体的拥有者为当前模块(THIS_MODULE),然后使用 cdev_init() 函数初始化cdev结构体。
参数包括待初始化的cdev结构体和用于操作该设备的file_operations结构体(hello_drv) */
gpioled.cdev.owner= THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&gpioled.cdev,&gpioled_fops);
/* 3、添加一个cdev */
cdev_add(&gpioled.cdev,gpioled.devid,DEVICE_CNT);
/*4 创建设备类
使用 class_create() 函数创建一个设备类,设备类用于在/sys/class目录下创建子目录,以组织同一类设备的相关信息。
该函数的参数包括所属的模块(THIS_MODULE)和设备类的名称(DEVICE_NAME)。
如果创建失败,IS_ERR() 函数将返回true,表示出错,此时使用 PTR_ERR() 函数返回错误码。 */
gpioled.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME);
if(IS_ERR(gpioled.class))
{
printk("newchr fail!\r\n");
return PTR_ERR(gpioled.class);
}
/*5 创建设备
使用 device_create() 函数创建一个设备,并在/dev目录下创建相应的设备节点。
参数包括设备所属的类(newchr.class)、父设备(NULL,如果没有父设备)、设备号(newchr.devid)、设备私有数据(NULL,一般为设备驱动程序提供一个指针)和设备名称(DEVICE_NAME)。
如果创建失败,IS_ERR() 函数将返回true,表示出错,此时使用 PTR_ERR() 函数返回错误码。 */
gpioled.device = device_create(gpioled.class, NULL, gpioled.devid, NULL, DEVICE_NAME);
if(IS_ERR(gpioled.device))
{
printk("newchr fail!\r\n");
return PTR_ERR(gpioled.device);
}
ret = myled_init(&gpioled);
#if 0
/* 5、设置 LED 所使用的 GPIO */
gpioled.nd = of_find_node_by_path("/gpioled");
if(gpioled.nd == NULL){
printk("gpioled node cant not found!\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
else{
printk("gpioled node hase been found!\r\n");
}
/* 2、 获取设备树中的 gpio 属性,得到 LED 所使用的 LED 编号 */
gpioled.led_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(gpioled.nd,"gpios",0);
if(gpioled.led_gpio < 0)
{
printk("can't get led-gpio\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
printk("led-gpio num = %d\r\n", gpioled.led_gpio);
/* 3、设置 GPIO1_IO03 为输出,并且输出高电平,默认关闭 LED 灯 */
gpio_request(gpioled.led_gpio,"led0");
gpio_direction_output(gpioled.led_gpio,1);
#endif
return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
gpio_set_value(gpioled.led_gpio,1);
gpio_free(gpioled.led_gpio);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
/*在模块卸载时,使用 cdev_del() 函数注销字符设备驱动,并使用 unregister_chrdev_region() 函数释放设备号资源。*/
/* 注销字符设备驱动 */
cdev_del(&gpioled.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(gpioled.devid, DEVICE_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(gpioled.class, gpioled.devid);// 销毁设备,删除相应的设备节点
class_destroy(gpioled.class);// 销毁设备类,释放相关资源
printk("gpioled exit!\r\n");
return 0;
}
/************************platfrom操作函数-endn***********************************************/
static int __init gpioled_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&led_driver);
}
static void __exit gpioled_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);
}
module_init(gpioled_init);
module_exit(gpioled_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("oudafa");
五 、运行测试
1.编写 Makefile 文件
编写完使用make命令编译驱动程序。
KERN_DIR = /home/odf/linux-imx/linux-imx
all:
clear
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o dtsplatledApp dtsplatledApp.c
clean:
clear
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
rm -f dtsplatledApp
obj-m += dtsplatled.o
2.使用nfs挂载到开发板上。
将编译出来 dtsplatled.ko 和dtsplatledApp 拷贝到 rootfs/lib/modules/4.1.15 目录中,
sudo cp dtsplatled.ko dtsplatledApp /home/odf/nfs_rootfs/rootfs/lib/modules/4.1.15/ 驱动模块加载完成以后到/sys/bus/platform/drivers/目录下查看驱动是否存在,我们在
dtsplatled.c 中设置 led_driver (platform_driver 类型)的 name 字段为“imx6ul-led”,因此会在
/sys/bus/platform/drivers/目录下存在名为“imx6ul-led”这个文件
重启开发板,进 入到目录 lib/modules/4.1.15 中,输入如下命令加载 dtsplatled.ko 这个驱动模块。
insmod dtsplatled.ko驱动和模块都存在,当驱动和设备匹配成功以后就会输出如图一行语句:

3.测试:
驱动和设备匹配成功以后就可以测试 LED 灯驱动了,输入如下命令打开 LED 灯:
./ledApp /dev/dtsplatled 1 输入如下命令关闭 LED 灯:
./ledApp /dev/dtsplatled 0
![[FPGA 学习记录] 快速开发的法宝——IP核](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/876da6e34baea8cb3afca8adf9d99e16.png#pic_center)