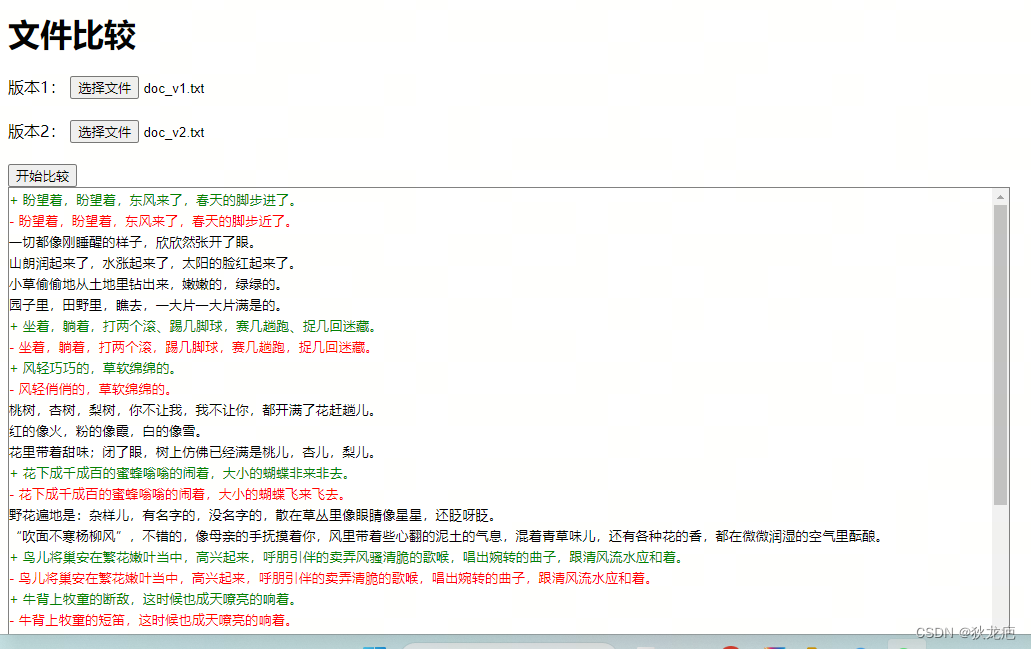
1 文本格式
using System;
namespace Legalsoft.Truffer
{
/// <summary>
/// Computes all eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a real symmetric matrix by
/// reduction to tridiagonal form followed by QL iteration.
/// </summary>
public class Symmeig
{
public int n { get; set; }
public double[,] z;
public double[] d;
public double[] e;
public bool yesvecs { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Computes all eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a real symmetric matrix
/// a[0..n - 1][0..n - 1] by reduction to tridiagonal form followed by QL
/// iteration.On output, d[0..n - 1] contains the eigenvalues of a sorted into
/// descending order, while z[0..n - 1][0..n - 1] is a matrix whose columns contain
/// the corresponding normalized eigenvectors.If yesvecs is input as true (the
/// default), then the eigenvectors are computed.If yesvecs is input as false,
/// only the eigenvalues are computed.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="yesvec"></param>
public Symmeig(double[,] a, bool yesvec = true)
{
this.n = a.GetLength(0);
this.z = a;
this.d = new double[n];
this.e = new double[n];
this.yesvecs = yesvec;
tred2();
tqli();
sort();
}
/// <summary>
/// Computes all eigenvalues and(optionally) eigenvectors of a real,
/// symmetric, tridiagonal matrix by QL iteration.On input, dd[0..n - 1]
/// contains the diagonal elements of the tridi- agonal matrix.The vector
/// ee[0..n-1] inputs the subdiagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix, with
/// ee[0] arbitrary.Output is the same as the constructor above.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="dd"></param>
/// <param name="ee"></param>
/// <param name="yesvec"></param>
public Symmeig(double[] dd, double[] ee, bool yesvec = true)
{
this.n = dd.Length;
this.d = dd;
this.e = ee;
this.z = new double[n, n];
this.yesvecs = yesvec;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
z[i, i] = 1.0;
}
tqli();
sort();
}
public void sort()
{
if (yesvecs)
{
Jacobi.eigsrt( d, z);
}
else
{
Jacobi.eigsrt( d, z);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Householder reduction of a real symmetric matrix z[0..n - 1][0..n-1]. (The
/// input matrix A to Symmeig is stored in z.) On output, z is replaced by the
/// orthogonal matrix Q effecting the transformation.d[0..n - 1] contains the
/// diagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix and e[0..n - 1] the off-diagonal
/// elements, with e[0]=0. If yesvecs is false, so that only eigenvalues will
/// subsequently be determined, several statements are omitted, in which case z
/// contains no useful information on output.
/// </summary>
public void tred2()
{
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
int l = i - 1;
double h = 0.0;
double scale = 0.0;
if (l > 0)
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
scale += Math.Abs(z[i, k]);
}
//if (scale == 0.0)
if (Math.Abs(scale) <= float.Epsilon)
{
e[i] = z[i, l];
}
else
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
z[i, k] /= scale;
h += z[i, k] * z[i, k];
}
double f = z[i, l];
double g = (f >= 0.0 ? -Math.Sqrt(h) : Math.Sqrt(h));
e[i] = scale * g;
h -= f * g;
z[i, l] = f - g;
f = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (yesvecs)
{
z[j, i] = z[i, j] / h;
}
g = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < j + 1; k++)
{
g += z[j, k] * z[i, k];
}
for (int k = j + 1; k < i; k++)
{
g += z[k, j] * z[i, k];
}
e[j] = g / h;
f += e[j] * z[i, j];
}
double hh = f / (h + h);
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
f = z[i, j];
e[j] = g = e[j] - hh * f;
for (int k = 0; k < j + 1; k++)
{
z[j, k] -= (f * e[k] + g * z[i, k]);
}
}
}
}
else
{
e[i] = z[i, l];
}
d[i] = h;
}
if (yesvecs)
{
d[0] = 0.0;
}
e[0] = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (yesvecs)
{
if (d[i] != 0.0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
double g = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
g += z[i, k] * z[k, j];
}
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
z[k, j] -= g * z[k, i];
}
}
}
d[i] = z[i, i];
z[i, i] = 1.0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
z[j, i] = z[i, j] = 0.0;
}
}
else
{
d[i] = z[i, i];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// QL algorithm with implicit shifts to determine the eigenvalues and
/// (optionally) the eigenvectors of a real, symmetric, tridiagonal matrix, or
/// of a real symmetric matrix previously reduced by tred2. On input,
/// d[0..n-1] contains the diagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix. On
/// output, it returns the eigenvalues. The vector e[0..n - 1] inputs the
/// subdiagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix, with e[0] arbitrary. On
/// output e is destroyed.If the eigenvectors of a tridiagonal matrix are
/// desired, the matrix z[0..n - 1][0..n - 1] is input as the identity matrix.If
/// the eigenvectors of a matrix that has been reduced by tred2 are required,
/// then z is input as the matrix output by tred2.In either case, column k of
/// z returns the normalized eigenvector corresponding to d[k]
/// </summary>
/// <exception cref="Exception"></exception>
public void tqli()
{
const double EPS = float.Epsilon;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
e[i - 1] = e[i];
}
e[n - 1] = 0.0;
for (int l = 0; l < n; l++)
{
int iter = 0;
int m;
do
{
for (m = l; m < n - 1; m++)
{
double dd = Math.Abs(d[m]) + Math.Abs(d[m + 1]);
if (Math.Abs(e[m]) <= EPS * dd)
{
break;
}
}
if (m != l)
{
if (iter++ == 30)
{
throw new Exception("Too many iterations in tqli");
}
double g = (d[l + 1] - d[l]) / (2.0 * e[l]);
double r = pythag(g, 1.0);
g = d[m] - d[l] + e[l] / (g + Globals.SIGN(r, g));
double s = 1.0;
double c = 1.0;
double p = 0.0;
int i = m - 1;
for (; i >= l; i--)
{
double f = s * e[i];
double b = c * e[i];
e[i + 1] = (r = pythag(f, g));
//if (r == 0.0)
if (Math.Abs(r) <= float.Epsilon)
{
d[i + 1] -= p;
e[m] = 0.0;
break;
}
s = f / r;
c = g / r;
g = d[i + 1] - p;
r = (d[i] - g) * s + 2.0 * c * b;
d[i + 1] = g + (p = s * r);
g = c * r - b;
if (yesvecs)
{
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
f = z[k, i + 1];
z[k, i + 1] = s * z[k, i] + c * f;
z[k, i] = c * z[k, i] - s * f;
}
}
}
//if (r == 0.0 && i >= l)
if (Math.Abs(r) <= float.Epsilon && i >= l)
{
continue;
}
d[l] -= p;
e[l] = g;
e[m] = 0.0;
}
} while (m != l);
}
}
public double pythag(double a, double b)
{
double absa = Math.Abs(a);
double absb = Math.Abs(b);
//return (absa > absb ? absa * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absb / absa)) : (absb == 0.0 ? 0.0 : absb * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absa / absb))));
return (absa > absb ? absa * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absb / absa)) : ((absb <= float.Epsilon) ? 0.0 : absb * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absa / absb))));
}
}
}
2 代码格式
using System;
namespace Legalsoft.Truffer
{
/// <summary>
/// Computes all eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a real symmetric matrix by
/// reduction to tridiagonal form followed by QL iteration.
/// </summary>
public class Symmeig
{
public int n { get; set; }
public double[,] z;
public double[] d;
public double[] e;
public bool yesvecs { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Computes all eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a real symmetric matrix
/// a[0..n - 1][0..n - 1] by reduction to tridiagonal form followed by QL
/// iteration.On output, d[0..n - 1] contains the eigenvalues of a sorted into
/// descending order, while z[0..n - 1][0..n - 1] is a matrix whose columns contain
/// the corresponding normalized eigenvectors.If yesvecs is input as true (the
/// default), then the eigenvectors are computed.If yesvecs is input as false,
/// only the eigenvalues are computed.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="yesvec"></param>
public Symmeig(double[,] a, bool yesvec = true)
{
this.n = a.GetLength(0);
this.z = a;
this.d = new double[n];
this.e = new double[n];
this.yesvecs = yesvec;
tred2();
tqli();
sort();
}
/// <summary>
/// Computes all eigenvalues and(optionally) eigenvectors of a real,
/// symmetric, tridiagonal matrix by QL iteration.On input, dd[0..n - 1]
/// contains the diagonal elements of the tridi- agonal matrix.The vector
/// ee[0..n-1] inputs the subdiagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix, with
/// ee[0] arbitrary.Output is the same as the constructor above.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="dd"></param>
/// <param name="ee"></param>
/// <param name="yesvec"></param>
public Symmeig(double[] dd, double[] ee, bool yesvec = true)
{
this.n = dd.Length;
this.d = dd;
this.e = ee;
this.z = new double[n, n];
this.yesvecs = yesvec;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
z[i, i] = 1.0;
}
tqli();
sort();
}
public void sort()
{
if (yesvecs)
{
Jacobi.eigsrt( d, z);
}
else
{
Jacobi.eigsrt( d, z);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Householder reduction of a real symmetric matrix z[0..n - 1][0..n-1]. (The
/// input matrix A to Symmeig is stored in z.) On output, z is replaced by the
/// orthogonal matrix Q effecting the transformation.d[0..n - 1] contains the
/// diagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix and e[0..n - 1] the off-diagonal
/// elements, with e[0]=0. If yesvecs is false, so that only eigenvalues will
/// subsequently be determined, several statements are omitted, in which case z
/// contains no useful information on output.
/// </summary>
public void tred2()
{
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
int l = i - 1;
double h = 0.0;
double scale = 0.0;
if (l > 0)
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
scale += Math.Abs(z[i, k]);
}
//if (scale == 0.0)
if (Math.Abs(scale) <= float.Epsilon)
{
e[i] = z[i, l];
}
else
{
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
z[i, k] /= scale;
h += z[i, k] * z[i, k];
}
double f = z[i, l];
double g = (f >= 0.0 ? -Math.Sqrt(h) : Math.Sqrt(h));
e[i] = scale * g;
h -= f * g;
z[i, l] = f - g;
f = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (yesvecs)
{
z[j, i] = z[i, j] / h;
}
g = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < j + 1; k++)
{
g += z[j, k] * z[i, k];
}
for (int k = j + 1; k < i; k++)
{
g += z[k, j] * z[i, k];
}
e[j] = g / h;
f += e[j] * z[i, j];
}
double hh = f / (h + h);
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
f = z[i, j];
e[j] = g = e[j] - hh * f;
for (int k = 0; k < j + 1; k++)
{
z[j, k] -= (f * e[k] + g * z[i, k]);
}
}
}
}
else
{
e[i] = z[i, l];
}
d[i] = h;
}
if (yesvecs)
{
d[0] = 0.0;
}
e[0] = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (yesvecs)
{
if (d[i] != 0.0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
double g = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
g += z[i, k] * z[k, j];
}
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
z[k, j] -= g * z[k, i];
}
}
}
d[i] = z[i, i];
z[i, i] = 1.0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
z[j, i] = z[i, j] = 0.0;
}
}
else
{
d[i] = z[i, i];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// QL algorithm with implicit shifts to determine the eigenvalues and
/// (optionally) the eigenvectors of a real, symmetric, tridiagonal matrix, or
/// of a real symmetric matrix previously reduced by tred2. On input,
/// d[0..n-1] contains the diagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix. On
/// output, it returns the eigenvalues. The vector e[0..n - 1] inputs the
/// subdiagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix, with e[0] arbitrary. On
/// output e is destroyed.If the eigenvectors of a tridiagonal matrix are
/// desired, the matrix z[0..n - 1][0..n - 1] is input as the identity matrix.If
/// the eigenvectors of a matrix that has been reduced by tred2 are required,
/// then z is input as the matrix output by tred2.In either case, column k of
/// z returns the normalized eigenvector corresponding to d[k]
/// </summary>
/// <exception cref="Exception"></exception>
public void tqli()
{
const double EPS = float.Epsilon;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
e[i - 1] = e[i];
}
e[n - 1] = 0.0;
for (int l = 0; l < n; l++)
{
int iter = 0;
int m;
do
{
for (m = l; m < n - 1; m++)
{
double dd = Math.Abs(d[m]) + Math.Abs(d[m + 1]);
if (Math.Abs(e[m]) <= EPS * dd)
{
break;
}
}
if (m != l)
{
if (iter++ == 30)
{
throw new Exception("Too many iterations in tqli");
}
double g = (d[l + 1] - d[l]) / (2.0 * e[l]);
double r = pythag(g, 1.0);
g = d[m] - d[l] + e[l] / (g + Globals.SIGN(r, g));
double s = 1.0;
double c = 1.0;
double p = 0.0;
int i = m - 1;
for (; i >= l; i--)
{
double f = s * e[i];
double b = c * e[i];
e[i + 1] = (r = pythag(f, g));
//if (r == 0.0)
if (Math.Abs(r) <= float.Epsilon)
{
d[i + 1] -= p;
e[m] = 0.0;
break;
}
s = f / r;
c = g / r;
g = d[i + 1] - p;
r = (d[i] - g) * s + 2.0 * c * b;
d[i + 1] = g + (p = s * r);
g = c * r - b;
if (yesvecs)
{
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
f = z[k, i + 1];
z[k, i + 1] = s * z[k, i] + c * f;
z[k, i] = c * z[k, i] - s * f;
}
}
}
//if (r == 0.0 && i >= l)
if (Math.Abs(r) <= float.Epsilon && i >= l)
{
continue;
}
d[l] -= p;
e[l] = g;
e[m] = 0.0;
}
} while (m != l);
}
}
public double pythag(double a, double b)
{
double absa = Math.Abs(a);
double absb = Math.Abs(b);
//return (absa > absb ? absa * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absb / absa)) : (absb == 0.0 ? 0.0 : absb * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absa / absb))));
return (absa > absb ? absa * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absb / absa)) : ((absb <= float.Epsilon) ? 0.0 : absb * Math.Sqrt(1.0 + Globals.SQR(absa / absb))));
}
}
}