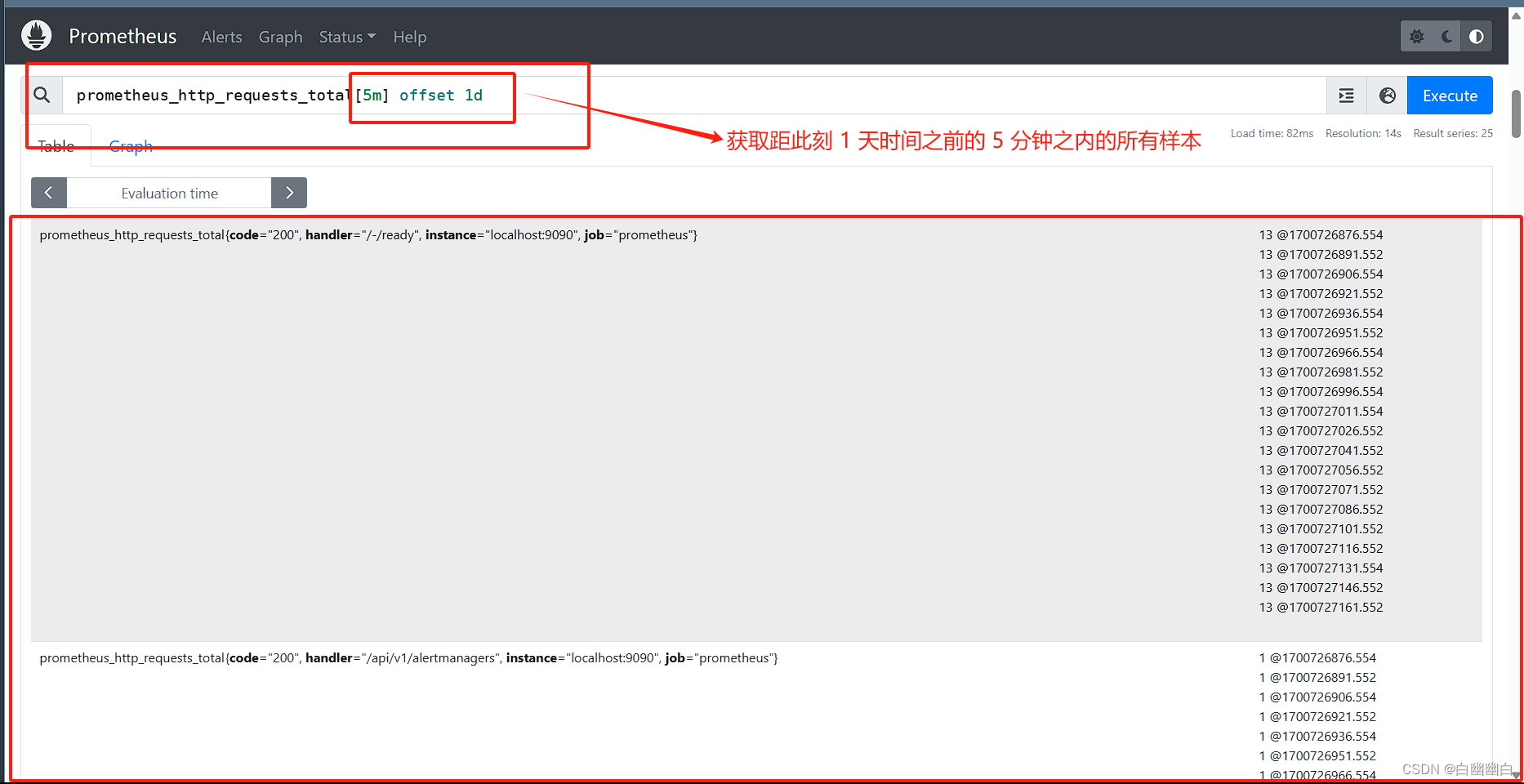
(第一阶段)问题 5a(3 分)
实现该函数,该函数模拟了完整的 Hog 游戏。球员 交替轮流掷骰子,直到其中一名玩家达到分数。playgoal
您现在可以忽略 Feral Hogs 规则和论点; 您将在问题 5b 中实现它。feral_hogs
为了确定每回合掷出多少骰子,每个玩家使用他们的 各自的策略(玩家 0 使用,玩家 1 使用)。 策略是一种函数,给定玩家的分数和对手的分数 score,返回当前玩家想要掷的骰子数量 转。每个策略函数每回合只能调用一次。不用担心 关于实施策略的细节。您将在以下方面开发它们 第 3 阶段。strategy0strategy1
游戏结束后,返回双方玩家的最终总分,其中 玩家 0 得分第一,玩家 1 得分第二。play
以下是一些提示:
- 你应该使用你已经写好的函数!您将需要使用所有三个参数进行调用。
take_turn - 每回合只能呼叫一次。
take_turn - 执行除野猪以外的所有特殊规则。
- 您可以通过调用来获取其他玩家的号码(0 或 1) 提供的功能。
other - 您可以暂时忽略该函数的参数。您将使用 它在项目的第 2 阶段。
sayplay
在编写任何代码之前,请解锁测试以验证您对问题的理解。
python3 ok -q 05a -u完成解锁后,开始实施解决方案。您可以通过以下方式检查您的正确性:
python3 ok -q 05a
def play(strategy0, strategy1, score0=0, score1=0, dice=six_sided,
goal=GOAL_SCORE, say=silence, feral_hogs=True):
"""Simulate a game and return the final scores of both players, with Player
0's score first, and Player 1's score second.
A strategy is a function that takes two total scores as arguments (the
current player's score, and the opponent's score), and returns a number of
dice that the current player will roll this turn.
strategy0: The strategy function for Player 0, who plays first.
strategy1: The strategy function for Player 1, who plays second.
score0: Starting score for Player 0
score1: Starting score for Player 1
dice: A function of zero arguments that simulates a dice roll.
goal: The game ends and someone wins when this score is reached.
say: The commentary function to call at the end of the first turn.
feral_hogs: A boolean indicating whether the feral hogs rule should be active.
"""
who = 0 # Who is about to take a turn, 0 (first) or 1 (second)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 5
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
实现逻辑:
1.循坏条件满足:两人分数均小于规定分数
2.两人逻辑分别写
3.以其中一人0为例:首先计算当前回合抛骰子的次数(strategy0)
计算当前得分(take_turn)
如果满足交换规律,就交换(is_swap)
4.当前回合结束,更换下一个(直至结束)
AC代码:
while score0 <goal and score1 < goal:
if who==0:
get=strategy0(score0,score1)
score0+=take_turn(get,score1,dice)
if is_swap(score0,score1):
score0,score1=score1,score0
else:
get = strategy1(score1, score0)
score1+=take_turn(get,score0,dice)
if is_swap(score1,score0):
score0,score1=score1,score0
who=other(who)
# END PROBLEM 5
# (note that the indentation for the problem 6 prompt (***YOUR CODE HERE***) might be misleading)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 6
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
# END PROBLEM 6
return score0, score1
AC情况(注意要解锁之后,才能测试):
Test summary
3 test cases passed before encountering first failed test case
Backup... 100% complete
Backup past deadline by 1241 days, 23 hours, 51 minutes, and 24 seconds
Backup successful for user: mxylms1210@163.com
OK is up to date
PS D:\python文件\hog> python3 ok -q 05a
=====================================================================
Assignment: Project 1: Hog
OK, version v1.18.1
=====================================================================
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Running tests
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Test summary
11 test cases passed! No cases failed.
Backup... 100% complete
Backup past deadline by 1241 days, 23 hours, 52 minutes, and 25 seconds
Backup successful for user: mxylms1210@163.com
OK is up to date
问题 5b (1 pt)
现在,实施野猪规则。当被调用并且它的参数是 时,则应该强加此规则。如果是,则应忽略此规则。 (这样,在解决 5b 后,5a 的测试用例仍将通过。playferal_hogsTrueferal_hogsFalse
野猪规则转载如下:
-
野猪。如果您掷出的骰子数量与您在上一回合获得的分数正好相差 2 分(绝对差异),则该回合将获得 3 分的额外积分。将第一回合前的回合视为得分 0。在计算上一回合的得分数时,不要考虑任何先前的野猪奖金或猪交换(下一个规则)。
例子-
示例 1:
- 两位球员都从 0 开始。(0, 0)
- 玩家 0 掷 3 个骰子并获得 7 分。(7, 0)
- 玩家 1 掷 1 个骰子并获得 4 分。(7, 4)
- 玩家 0 掷 5 个骰子并获得 10 分。5 与 7 相差 2,因此玩家 0 获得 3 的加成。(20, 4)
- 玩家 1 掷 2 个骰子并获得 8 分。2 是 2 与 4 相差 2,因此玩家 1 获得 3 的奖金。(20, 15)
- 玩家 0 掷 8 个骰子并获得 20 分。8 是 2 与 10 相差 10,因此玩家 0 获得 3 的奖励。(43, 15)
- 玩家 1 掷 6 个骰子并获得 1 分。6 与 8 相差 2,因此玩家 1 获得 3 的奖金。(43, 19)
-
示例 2:
- 两位球员都从 0 开始。(0, 0)
- 玩家 0 掷 2 个骰子并获得 3 分。2 是 2 与 0 相差 2,因此玩家 0 获得 3 的奖励。(6, 0)
-
解锁时,注意这里坑爹的strat1:
s0->仍然指向s1(s0只是形参)
(之前我总把s0代入s0,难受)
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 5b > Suite 1 > Case 1
(cases remaining: 103)
>>> import hog
>>> always_one = hog.make_test_dice(1)
>>> always_two = hog.make_test_dice(2)
>>> always_three = hog.make_test_dice(3)
>>> always = hog.always_roll
>>> # example 1
>>> def strat0(s0, s1):
... if s0 == 0: return 3
... if s0 == 7: return 5
... return 8
>>> def strat1(s0, s1):
... if s0 == 0: return 1
... if s0 == 4: return 2
... return 6
>>> s0, s1 = hog.play(
... strat0, strat1, score0=0, score1=0, goal=21,
... dice=hog.make_test_dice(2, 2, 3, 4, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 5, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 6, 1))
>>> s0
1. s0=43(野猪*2)
(计算注意野猪的加分算额外加分,不算计算野猪加分的上回合加分)
s1=15(野猪*1)
2.dice()每次调用后,下一次初始值为上一次调用结尾的后一位
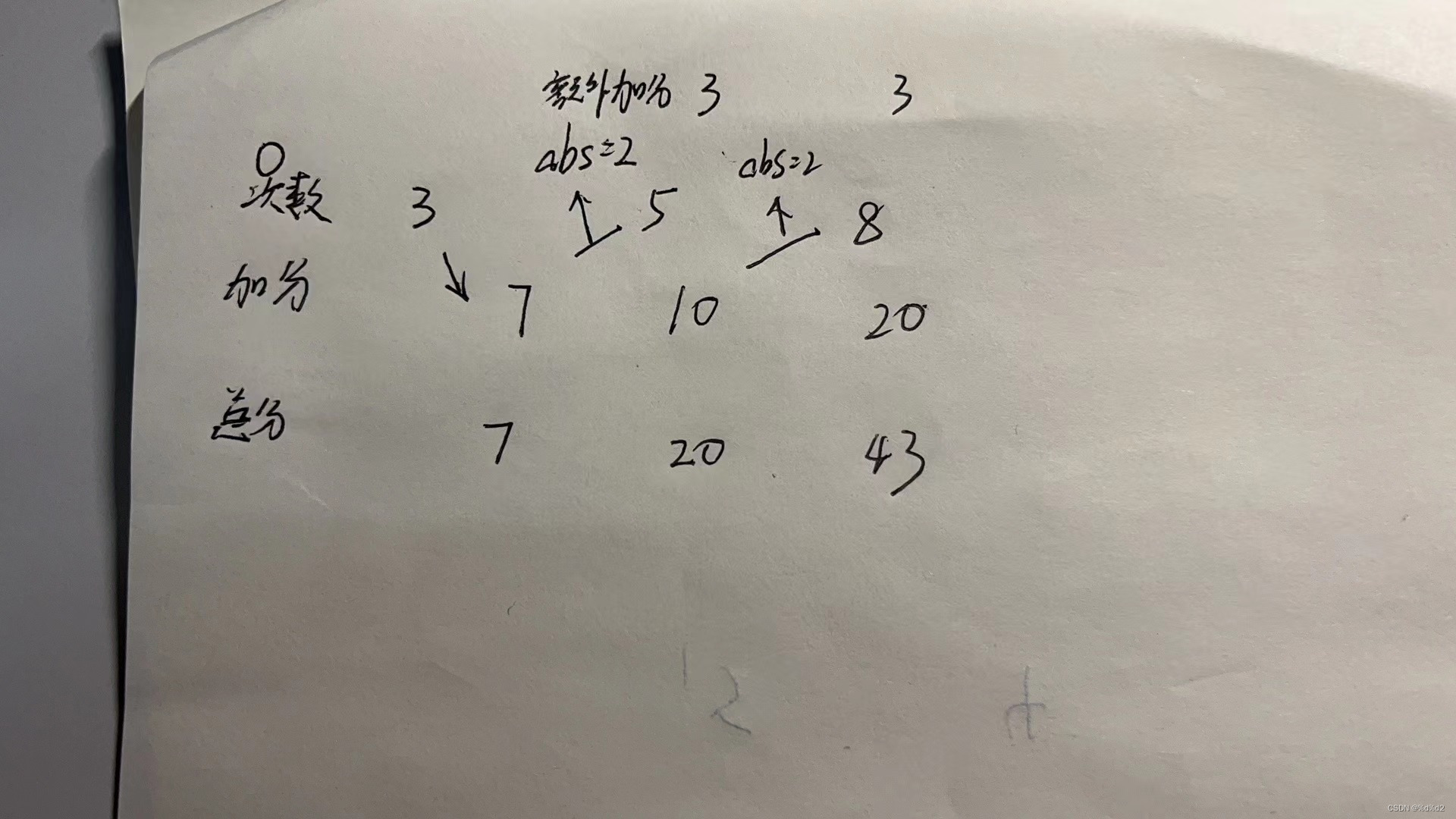
代码:
add0=0
add1=0
while score0 <goal and score1 < goal:
if who==0:
get0=strategy0(score0,score1) # 当前回合的次数
if feral_hogs:
if abs(get0-add0)==2:
score0+=3
add0=take_turn(get0,score1,dice) # 当前回合的加分
score0+=add0
if is_swap(score0,score1):
score0,score1=score1,score0
else:
get1 = strategy1(score1, score0) # 当前回合的次数
if feral_hogs:
if abs(get1-add1)==2:
score1+=3
add1= take_turn(get1,score0,dice) # 当前回合的加分
score1+= add1
if is_swap(score1,score0):
score0,score1=score1,score0
who=other(who)
# END PROBLEM 5
# (note that the indentation for the problem 6 prompt (***YOUR CODE HERE***) might be misleading)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 6
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
# END PROBLEM 6
return score0, score1pass情况:
OK! All cases for Question 5b unlocked.
Backup... 100% complete
Backup past deadline by 1242 days, 56 minutes, and 10 seconds
Backup successful for user: mxylms1210@163.com
OK is up to date
PS D:\python文件\hog> python3 ok -q 05b
=====================================================================
Assignment: Project 1: Hog
OK, version v1.18.1
=====================================================================
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Running tests
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Test summary
103 test cases passed! No cases failed.
Backup... 100% complete
Backup past deadline by 1242 days, 56 minutes, and 26 seconds
Backup successful for user: mxylms1210@163.com
第一阶段,总算是完结啦:
Assignment: Project 1: Hog
OK, version v1.18.1
=====================================================================
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Scoring tests
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 0
Passed: 0
Failed: 1
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 1
Passed: 3
Failed: 0
[ooooooooook] 100.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 2
Passed: 1
Failed: 0
[ooooooooook] 100.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 3
Passed: 2
Failed: 0
[ooooooooook] 100.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 4
Passed: 1
Failed: 0
[ooooooooook] 100.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 5a
Passed: 3
Failed: 0
[ooooooooook] 100.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 5b
Passed: 2
Failed: 0
[ooooooooook] 100.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 6
Passed: 0
Failed: 2
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 7 > Suite 2 > Case 1
>>> from hog import play, always_roll, announce_highest, both
>>> from dice import make_test_dice
>>> # this might not technically be a possible game for the current rules, this shouldn't be relevant
>>> f0 = announce_highest(1) # Only announce Player 1 score gains
>>> f1 = f0(12, 0)
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
# Error: expected
# but got
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# ...
# TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Run only this test case with "python3 ok -q 07 --suite 2 --case 1"
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 7
Passed: 0
Failed: 1
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 8 > Suite 3 > Case 1
>>> from hog import *
>>> hundred_range = range(1, 100)
>>> hundred_dice = make_test_dice(*hundred_range)
>>> averaged_hundred_dice = make_averaged(hundred_dice, 5*len(hundred_range))
>>> correct_average = sum(range(1, 100)) / len(hundred_range)
>>> averaged_hundred_dice()
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
# Error: expected
# 50.0
# but got
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# ...
# TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Run only this test case with "python3 ok -q 08 --suite 3 --case 1"
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 8
Passed: 0
Failed: 2
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 9
Passed: 0
Failed: 2
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 10 > Suite 2 > Case 1
>>> from hog import *
>>> bacon_strategy(44, 47, 0, 4)
6
# Error: expected
# 0
# but got
# 6
Run only this test case with "python3 ok -q 10 --suite 2 --case 1"
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 10
Passed: 0
Failed: 2
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 11 > Suite 2 > Case 1
>>> from hog import *
>>> swap_strategy(47, 64, 3, 4)
6
# Error: expected
# 0
# but got
# 6
Run only this test case with "python3 ok -q 11 --suite 2 --case 1"
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 11
Passed: 0
Failed: 2
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 12
Passed: 0
Failed: 0
[k..........] 0.0% passed
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Point breakdown
Question 0: 0.0/0
Question 1: 2.0/2
Question 2: 1.0/1
Question 3: 2.0/2
Question 4: 2.0/2
Question 5a: 3.0/3
Question 5b: 1.0/1
Question 6: 0.0/2
Question 7: 0.0/3
Question 8: 0.0/2
Question 9: 0.0/2
Question 10: 0.0/1
Question 11: 0.0/2
Question 12: 0.0/0
Score:
Total: 11.0
Backup... 100% complete
Backup past deadline by 1242 days, 1 hour, 23 minutes, and 40 seconds
Backup successful for user: mxylms1210@163.com
OK is up to date
(第二阶段)问题6(2分)
更新您的play函数,以便在最后调用注释函数 每一个转身。调用注释函数的返回值为您提供 评论功能,以调用下一轮。
例如,say(score0, score1)应该在第一个 依次它的返回值(另一个注释函数)应该在最后调用 的第二个转折点。每一个连续的回合,调用返回的函数 通过调用前一回合的评论功能
解锁遇到的坑点:(line3)
轮到参数者第二加分时,得到13,此时对手为12(两者交换)
line3:12 13
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 6 > Suite 2 > Case 3
(cases remaining: 4)
>>> from hog import play, always_roll
>>> from dice import make_test_dice
>>> #
>>> def echo(s0, s1):
... print(s0, s1)
... return echo
>>> strat0 = lambda score, opponent: 1 - opponent // 10
>>> strat1 = always_roll(3)
>>> s0, s1 = play(strat0, strat1, dice=make_test_dice(4, 2, 6), goal=15, say=echo)
问题7(3分)
实现announce_highest函数,这是一个高阶函数, 返回一个注释函数。每当出现 某个玩家在一个回合中获得的点数比以往任何时候都多。例如,在一个示例中, announce_highest(1)及其返回值完全忽略参与人0, 打印有关参与人1的信息。为了计算增益,它必须比较 从最后一轮到这轮的得分,这是 由who参数指定。此函数还必须跟踪 这是迄今为止玩家获得的最高收益。
announce_highest宣布的方式是非常具体的,你的 实现应该匹配所提供的doctests。不要担心单数 而不是复数时宣布点收益;你应该简单地使用“点(s)”为 两个案子
Hint.提供给您的
announce_lead_changes函数是一个示例, 如何使用评论功能跟踪信息。如果你被卡住了, 首先,请确保您了解announce_lead_changes如何工作。
注意:hog.py中
both/announce_highest的文档测试可能描述 一个不可能按照规则发生的游戏这不应该是一个问题, 评论功能,因为它们不执行任何游戏规则。
Hint.如果你得到一个
local variable [var] reference before assignment错误:这是因为在Python中,通常不允许修改 父框架中定义的变量。而不是重新分配
[var], 解释器认为你试图在当前的 frame.我们将在以后的讲座中学习如何解决这个问题, 这个问题不需要。要解决这个问题,你有两个选择:
1)与其将
[var]重新分配给它的新值,不如创建一个新变量, 保留新值。在以后的计算中使用这个新变量。2)对于此问题,请通过不使用 所有的赋值语句而是将新值作为参数传递给 打电话给#1。
分析:由于形参无法直接赋值新值,
我们可以采用递归的方法,利用新函数重新赋值新的形参
(anounce_highest()函数)
我们分为两个情况考虑:
一种是:当前分数-之前分数>最高增加数
返回新函数的形参:
之前分数为:当前分数
最高增加数为:当前分数-之前分数
另一种是:当前分数-之前分数<最高增加数
返回新函数的形参:
之前分数为:当前分数
最高增加数为:当前最高增加数
pass代码:
def announce_highest(who, last_score=0, running_high=0):
"""Return a commentary function that announces when WHO's score
increases by more than ever before in the game.
NOTE: the following game is not possible under the rules, it's just
an example for the sake of the doctest
>>> f0 = announce_highest(1) # Only announce Player 1 score gains
>>> f1 = f0(12, 0)
>>> f2 = f1(12, 11)
11 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
>>> f3 = f2(20, 11)
>>> f4 = f3(13, 20)
>>> f5 = f4(20, 35)
15 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
>>> f6 = f5(20, 47) # Player 1 gets 12 points; not enough for a new high
>>> f7 = f6(21, 47)
>>> f8 = f7(21, 77)
30 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
>>> f9 = f8(77, 22) # Swap!
>>> f10 = f9(33, 77) # Swap!
55 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
"""
assert who == 0 or who == 1, 'The who argument should indicate a player.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 7
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def bumble(player1,player2):
if who==1:
current1=player2
else:
current1=player1
if (current1-last_score) > running_high:
print(str(current1-last_score)+" point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player "+str(who))
return announce_highest(who,current1,current1-last_score)
return announce_highest(who,current1,running_high)
return bumble
pass情况:
OK is up to date
PS D:\python文件\hog> python3 ok -q 07
=====================================================================
Assignment: Project 1: Hog
OK, version v1.18.1
=====================================================================
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Running tests
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Test summary
5 test cases passed! No cases failed.
Backup... 100% complete
Backup past deadline by 1242 days, 4 hours, 44 minutes, and 54 seconds
Backup successful for user: mxylms1210@163.com
OK is up to date
问题9(2分)
实现max_scoring_num_rolls函数,该函数运行一个实验, 确定给出最大平均值的卷数(从1到10) 一个转身得分。 您的实现应该使用make_averaged和 roll_dice.
如果两个掷骰数相等,则返回 更低的数字。例如,如果3和6都达到了最高平均分, 返回3.
在编写任何代码之前,解锁测试以验证您对问题的理解。
python3 ok -q 09 -u完成解锁后,开始实施解决方案。您可以通过以下方式检查您的正确性:
python3 ok -q 09要在随机骰子上运行此实验,请使用 run_experiments选项:
python3 hog.py -r运行实验对于本项目的剩余部分,您可以更改 run_experiments1average_win_rate1if False:1if True:1always_roll(8)1always_roll(6)1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1undefined1#1 通过调用 undefined,你可以评估各种猪策略。比如说, 将第一个undefined更改为undefined,以评估 undefined对比undefined的基线策略。
某些实验可能需要一分钟才能运行。你总是可以减少 调用make_averaged中的试验次数以加快实验速度。
分析:此题函数需要返回最小的达到最大平均值的骰子个数
利用roll_dice()实现多个骰子同时使用(但返回的是int)
利用make_average()实现计算平均值
形参:骰子的函数,和抛骰子的次数
(注意:需要把roll_dice利用lambda表达式转换为函数)
pass代码:
def max_scoring_num_rolls(dice=six_sided, trials_count=1000):
"""Return the number of dice (1 to 10) that gives the highest average turn
score by calling roll_dice with the provided DICE over TRIALS_COUNT times.
Assume that the dice always return positive outcomes.
>>> dice = make_test_dice(1, 6)
>>> max_scoring_num_rolls(dice)
1
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 9
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
aver={}
max1=-1.0
for i in range(1,11):
av=make_averaged(lambda :roll_dice(i,dice),trials_count)
aver[i-1]=av()
if max1 < aver[i-1]:
max1=aver[i-1]
for i in range(0,10):
if max1== aver[i]:
return i+1
pass情况:
PS D:\python文件\hog> python3 ok -q 09
=====================================================================
Assignment: Project 1: Hog
OK, version v1.18.1
=====================================================================
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Running tests
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Test summary
8 test cases passed! No cases failed.
Backup... 100% complete
最后的final策略,就之后再实现吧(毕竟没有学分...hahaha)
以下为完整代码:
"""CS 61A Presents The Game of Hog."""
from dice import six_sided, four_sided, make_test_dice
from ucb import main, trace, interact
GOAL_SCORE = 100 # The goal of Hog is to score 100 points.
######################
# Phase 1: Simulator #
######################
def roll_dice(num_rolls, dice=six_sided):
"""Simulate rolling the DICE exactly NUM_ROLLS > 0 times. Return the sum of
the outcomes unless any of the outcomes is 1. In that case, return 1.
num_rolls: The number of dice rolls that will be made.
dice: A function that simulates a single dice roll outcome.
"""
# These assert statements ensure that num_rolls is a positive integer.
assert type(num_rolls) == int, 'num_rolls must be an integer.'
assert num_rolls > 0, 'Must roll at least once.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 1
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
ret = 0
pig_out =False
for _ in range(num_rolls):
score = dice()
if score == 1:
pig_out =True
continue
ret += score
return 1 if pig_out else ret
# END PROBLEM 1
def free_bacon(score):
"""Return the points scored from rolling 0 dice (Free Bacon).
score: The opponent's current score.
"""
assert score < 100, 'The game should be over.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 2
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
return 10 - score%10+ int(score / 10)
# END PROBLEM 2
def take_turn(num_rolls, opponent_score, dice=six_sided):
"""Simulate a turn rolling NUM_ROLLS dice, which may be 0 (Free Bacon).
Return the points scored for the turn by the current player.
num_rolls: The number of dice rolls that will be made.
opponent_score: The total score of the opponent.
dice: A function that simulates a single dice roll outcome.
"""
# Leave these assert statements here; they help check for errors.
assert type(num_rolls) == int, 'num_rolls must be an integer.'
assert num_rolls >= 0, 'Cannot roll a negative number of dice in take_turn.'
assert num_rolls <= 10, 'Cannot roll more than 10 dice.'
assert opponent_score < 100, 'The game should be over.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 3
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if num_rolls>0:
return roll_dice(num_rolls,dice)
else:
return free_bacon(opponent_score)
# END PROBLEM 3
def is_swap(player_score, opponent_score):
"""
Return whether the two scores should be swapped
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 4
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if abs(player_score%10-opponent_score%10)==(opponent_score//10)%10:
return True
else:
return False
# END PROBLEM 4
def other(who):
"""Return the other player, for a player WHO numbered 0 or 1.
>>> other(0)
1
>>> other(1)
0
"""
return 1 - who
def silence(score0, score1):
"""Announce nothing (see Phase 2)."""
return silence
def play(strategy0, strategy1, score0=0, score1=0, dice=six_sided,
goal=GOAL_SCORE, say=silence, feral_hogs=True):
"""Simulate a game and return the final scores of both players, with Player
0's score first, and Player 1's score second.
A strategy is a function that takes two total scores as arguments (the
current player's score, and the opponent's score), and returns a number of
dice that the current player will roll this turn.
strategy0: The strategy function for Player 0, who plays first.
strategy1: The strategy function for Player 1, who plays second.
score0: Starting score for Player 0
score1: Starting score for Player 1
dice: A function of zero arguments that simulates a dice roll.
goal: The game ends and someone wins when this score is reached.
say: The commentary function to call at the end of the first turn.
feral_hogs: A boolean indicating whether the feral hogs rule should be active.
"""
who = 0 # Who is about to take a turn, 0 (first) or 1 (second)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 5
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
add0=0
add1=0
while score0 <goal and score1 < goal:
if who==0:
get0=strategy0(score0,score1) # 当前回合的次数
if feral_hogs:
if abs(get0-add0)==2:
score0+=3
add0=take_turn(get0,score1,dice) # 当前回合的加分
score0+=add0
if is_swap(score0,score1):
score0,score1=score1,score0
say = say(score0, score1)
else:
get1 = strategy1(score1, score0) # 当前回合的次数
if feral_hogs:
if abs(get1-add1)==2:
score1+=3
add1= take_turn(get1,score0,dice) # 当前回合的加分
score1+= add1
if is_swap(score1,score0):
score0,score1=score1,score0
say = say(score0, score1)
who=other(who)
# END PROBLEM 5
# (note that the indentation for the problem 6 prompt (***YOUR CODE HERE***) might be misleading)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 6
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
# END PROBLEM 6
return score0, score1
#######################
# Phase 2: Commentary #
#######################
def say_scores(score0, score1):
"""A commentary function that announces the score for each player."""
print("Player 0 now has", score0, "and Player 1 now has", score1)
return say_scores
def announce_lead_changes(last_leader=None):
"""Return a commentary function that announces lead changes.
>>> f0 = announce_lead_changes()
>>> f1 = f0(5, 0)
Player 0 takes the lead by 5
>>> f2 = f1(5, 12)
Player 1 takes the lead by 7
>>> f3 = f2(8, 12)
>>> f4 = f3(8, 13)
>>> f5 = f4(15, 13)
Player 0 takes the lead by 2
"""
def say(score0, score1):
if score0 > score1:
leader = 0
elif score1 > score0:
leader = 1
else:
leader = None
if leader != None and leader != last_leader:
print('Player', leader, 'takes the lead by', abs(score0 - score1))
return announce_lead_changes(leader)
return say
def both(f, g):
"""Return a commentary function that says what f says, then what g says.
NOTE: the following game is not possible under the rules, it's just
an example for the sake of the doctest
>>> h0 = both(say_scores, announce_lead_changes())
>>> h1 = h0(10, 0)
Player 0 now has 10 and Player 1 now has 0
Player 0 takes the lead by 10
>>> h2 = h1(10, 6)
Player 0 now has 10 and Player 1 now has 6
>>> h3 = h2(6, 17)
Player 0 now has 6 and Player 1 now has 17
Player 1 takes the lead by 11
"""
def say(score0, score1):
return both(f(score0, score1), g(score0, score1))
return say
def announce_highest(who, last_score=0, running_high=0):
"""Return a commentary function that announces when WHO's score
increases by more than ever before in the game.
NOTE: the following game is not possible under the rules, it's just
an example for the sake of the doctest
>>> f0 = announce_highest(1) # Only announce Player 1 score gains
>>> f1 = f0(12, 0)
>>> f2 = f1(12, 11)
11 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
>>> f3 = f2(20, 11)
>>> f4 = f3(13, 20)
>>> f5 = f4(20, 35)
15 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
>>> f6 = f5(20, 47) # Player 1 gets 12 points; not enough for a new high
>>> f7 = f6(21, 47)
>>> f8 = f7(21, 77)
30 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
>>> f9 = f8(77, 22) # Swap!
>>> f10 = f9(33, 77) # Swap!
55 point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player 1
"""
assert who == 0 or who == 1, 'The who argument should indicate a player.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 7
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def bumble(player1,player2):
if who==1:
current1=player2
else:
current1=player1
if (current1-last_score) > running_high:
print(str(current1-last_score)+" point(s)! That's the biggest gain yet for Player "+str(who))
return announce_highest(who,current1,current1-last_score)
return announce_highest(who,current1,running_high)
return bumble
# END PROBLEM 7
#######################
# Phase 3: Strategies #
#######################
def always_roll(n):
"""Return a strategy that always rolls N dice.
A strategy is a function that takes two total scores as arguments (the
current player's score, and the opponent's score), and returns a number of
dice that the current player will roll this turn.
>>> strategy = always_roll(5)
>>> strategy(0, 0)
5
>>> strategy(99, 99)
5
"""
def strategy(score, opponent_score):
return n
return strategy
def make_averaged(original_function, trials_count=1000):
"""Return a function that returns the average value of ORIGINAL_FUNCTION when called.
To implement this function, you will have to use *args syntax, a new Python
feature introduced in this project. See the project description.
>>> dice = make_test_dice(4, 2, 5, 1)
>>> averaged_dice = make_averaged(dice, 1000)
>>> averaged_dice()
3.0
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 8
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def average1():
sum=0.0
for i in range(1,trials_count+1):
sum+=original_function()
return sum/trials_count
return average1
# END PROBLEM 8
def max_scoring_num_rolls(dice=six_sided, trials_count=1000):
"""Return the number of dice (1 to 10) that gives the highest average turn
score by calling roll_dice with the provided DICE over TRIALS_COUNT times.
Assume that the dice always return positive outcomes.
>>> dice = make_test_dice(1, 6)
>>> max_scoring_num_rolls(dice)
1
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 9
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
aver={}
max1=-1.0
for i in range(1,11):
av=make_averaged(lambda :roll_dice(i,dice),trials_count)
aver[i-1]=av()
if max1 < aver[i-1]:
max1=aver[i-1]
for i in range(0,10):
if max1== aver[i]:
return i+1
# END PROBLEM 9
def winner(strategy0, strategy1):
"""Return 0 if strategy0 wins against strategy1, and 1 otherwise."""
score0, score1 = play(strategy0, strategy1)
if score0 > score1:
return 0
else:
return 1
def average_win_rate(strategy, baseline=always_roll(6)):
"""Return the average win rate of STRATEGY against BASELINE. Averages the
winrate when starting the game as player 0 and as player 1.
"""
win_rate_as_player_0 = 1 - make_averaged(winner)(strategy, baseline)
win_rate_as_player_1 = make_averaged(winner)(baseline, strategy)
return (win_rate_as_player_0 + win_rate_as_player_1) / 2
def run_experiments():
"""Run a series of strategy experiments and report results."""
if True: # Change to False when done finding max_scoring_num_rolls
six_sided_max = max_scoring_num_rolls(six_sided)
print('Max scoring num rolls for six-sided dice:', six_sided_max)
if False: # Change to True to test always_roll(8)
print('always_roll(8) win rate:', average_win_rate(always_roll(8)))
if False: # Change to True to test bacon_strategy
print('bacon_strategy win rate:', average_win_rate(bacon_strategy))
if False: # Change to True to test swap_strategy
print('swap_strategy win rate:', average_win_rate(swap_strategy))
if False: # Change to True to test final_strategy
print('final_strategy win rate:', average_win_rate(final_strategy))
"*** You may add additional experiments as you wish ***"
def bacon_strategy(score, opponent_score, cutoff=8, num_rolls=6):
"""This strategy rolls 0 dice if that gives at least CUTOFF points, and
rolls NUM_ROLLS otherwise.
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 10
if free_bacon(opponent_score)>=cutoff:
return 0
else:
return num_rolls
# END PROBLEM 10
def swap_strategy(score, opponent_score, cutoff=8, num_rolls=6):
"""This strategy rolls 0 dice when it triggers a beneficial swap. It also
rolls 0 dice if it gives at least CUTOFF points and does not trigger a
non-beneficial swap. Otherwise, it rolls NUM_ROLLS.
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 11
bacon=free_bacon(opponent_score)
if is_swap(bacon+score,opponent_score):
if bacon+score>opponent_score:
return num_rolls
else:
return 0
if bacon >= cutoff:
return 0
else:
return num_rolls
# END PROBLEM 11
def final_strategy(score, opponent_score):
"""Write a brief description of your final strategy.
*** YOUR DESCRIPTION HERE ***
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 12
return 6 # Replace this statement
# END PROBLEM 12
##########################
# Command Line Interface #
##########################
# NOTE: Functions in this section do not need to be changed. They use features
# of Python not yet covered in the course.
@main
def run(*args):
"""Read in the command-line argument and calls corresponding functions.
This function uses Python syntax/techniques not yet covered in this course.
"""
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Play Hog")
parser.add_argument('--run_experiments', '-r', action='store_true',
help='Runs strategy experiments')
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.run_experiments:
run_experiments()pass情况:
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Point breakdown
Question 0: 0.0/0
Question 1: 2.0/2
Question 2: 1.0/1
Question 3: 2.0/2
Question 4: 2.0/2
Question 5a: 3.0/3
Question 5b: 1.0/1
Question 6: 2.0/2
Question 7: 3.0/3
Question 8: 0.0/2
Question 9: 2.0/2
Question 10: 1.0/1
Question 11: 2.0/2
Question 12: 0.0/0
Score:
Total: 21.0
Backup... 0.0% complete
OK is up to date