大家好,我是晴天学长,本次分享,制作不易,本次题解只用于学习用途,如果有考试需要的小伙伴请考完试再来看题解进行学习,需要的小伙伴可以点赞关注评论一波哦!后续会继续更新第三期的。💪💪💪
一 .放像素
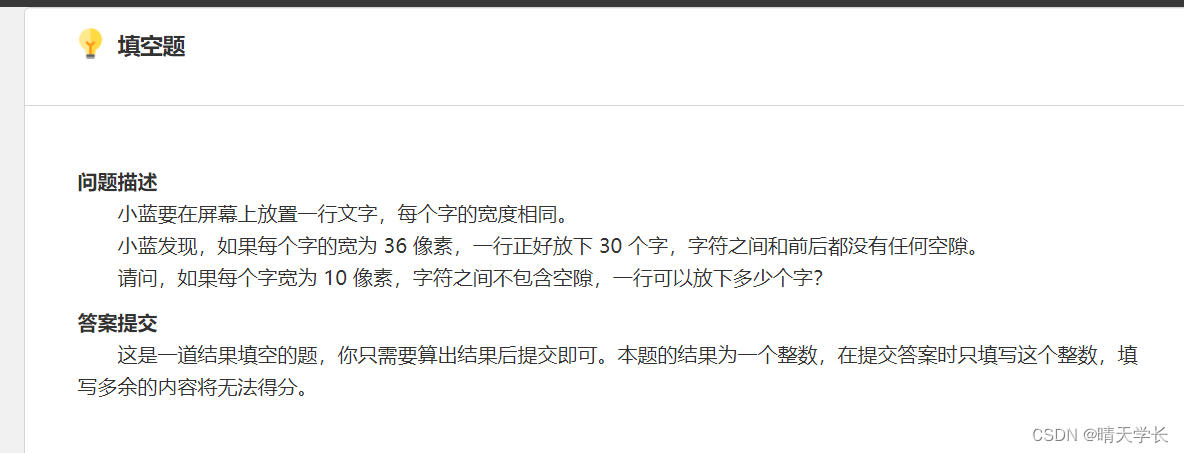
问题描述
小蓝要在屏幕上放置一行文字,每个字的宽度相同。
小蓝发现,如果每个字的宽为 36 像素,一行正好放下 30 个字,字符之间和前后都没有任何空隙。
请问,如果每个字宽为 10 像素,字符之间不包含空隙,一行可以放下多少个字?
答案提交
这是一道结果填空的题,你只需要算出结果后提交即可。本题的结果为一个整数,在提交答案时只填写这个整数,填写多余的内容将无法得分。
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
- 无
4).总结
- 答案:108
二 .求余数

问题描述
求 2**2023%1000,即 2的2023次方除以1000的余数。
答案提交
这是一道结果填空的题,你只需要算出结果后提交即可。本题的结果为一个整数,在提交答案时只填写这个整数,填写多余的内容将无法得分。
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
package LanQiaoTest.枚举;
public class 求余数_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 2;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= 2023; i++) {
num = (num*2)%1000;
sum++;
}
System.out.println(num);
}
}
4).总结
- 答案:608
三 .进制转化

问题描述 如果一个正整数转化成二进制与转换成八进制后所有数位的数字之和相等,则称为数位和相等的数。 前几个数位和相等的正整数为 1, 8, 9, 64, …… 请问第 23 个数位和相等的正整数是多少? 答案提交 这是一道结果填空的题,你只需要算出结果后提交即可。本题的结果为一个整数,在提交答案时只填写这个整数,填写多余的内容将无法得分。
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
package LanQiaoTest.枚举;
public class 进制转换_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 1;
int sum = 0;
while (sum < 23) {
if (two(num) == eight(num)) {
sum++;
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
num++;
}
}
public static int two(int i) {
String two = Integer.toString(i,2);
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < two.length(); j++) {
String temp = String.valueOf(two.charAt(j));
sum += Integer.parseInt(temp);
}
return sum;
}
public static int eight(int i) {
String eight = Integer.toString(i,8);
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < eight.length(); j++) {
String temp = String.valueOf(eight.charAt(j));
sum += Integer.parseInt(temp);
}
return sum;
}
}
4).总结
- 答案:4169
四 .约数个数

问题描述
对于以下这些数(6行,每行6个,共36个),请问约数个数最多的是哪个?(如果有多个,请回答出现最早的那个)
393353 901440 123481 850930 423154 240461
373746 232926 396677 486579 744860 468782
941389 777714 992588 343292 385198 876426
483857 241899 544851 647930 772403 109929
882745 372491 877710 340000 659788 658675
296521 491295 609764 718967 842000 670302
答案提交 这是一道结果填空的题,你只需要算出结果后提交即可。本题的结果为一个整数,在提交答案时只填写这个整数,填写多余的内容将无法得分。
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
package LanQiaoTest.枚举;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class 约数个数_4 {
static String[] lines;
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int[][] nums = new int[6][6];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
nums[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(lines[j]);
}
}
//打印出来
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
System.out.print(nums[i][j] + " ");
;
}
System.out.println();
}
//开始计算
int maxnums = 0;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
int temp = yueshu(nums[i][j]);
if (temp>max){
maxnums = nums[i][j];
max = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(maxnums);
}
//算约数个数
public static int yueshu(int nums) {
int sum = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= nums; i++) {
int temp = 0;
while (nums % i == 0) {
temp++;
nums /= i;
}
if (temp != 0) {
sum *= temp+1;
}
}
return sum;
}
}
4).总结
- 答案: 901440
五 .传染性

问题描述
小蓝有一个01矩阵。他打算将第一行第一列的 0 变为 2 。变化过程有传染性,每次 2 的上下左右四个相邻的位置中的 0 都会变成 2 。直到最后每个 2 的周围都是 1 或 2 结束。
请问,最终矩阵中有多少个 2 ?
以下是小蓝的矩阵,共 30 行 40 列。
0000100010000001101010101001001100000011
0101111001111101110111100000101010011111
1000010000011101010110000000001011010100
0110101010110000000101100100000101001001
0000011010100000111111001101100010101001
0110000110000000110100000000010010100011
0100110010000110000000100010000101110000
0010011010100110001111001101100110100010
1111000111101000001110010001001011101101
0011110100011000000001101001101110100001
0000000101011000010011111001010011011100
0000100000011001000100101000111011101100
0010110000001000001010100011000010100011
0110110000100011011010011010001101011011
0000100100000001010000101100000000000010
0011001000001000000010011001100101000110
1110101000011000000100011001001100111010
0000100100111000001101001000001010010001
0100010010000110100001100000110111110101
1000001001100010011001111101011001110001
0000000010100101000000111100110010101101
0010110101001100000100000010000010110011
0000011101001001000111011000100111010100
0010001100100000011000101011000000010101
1001111010010110011010101110000000101110
0110011101000010100001000101001001100010
1101000000010010011001000100110010000101
1001100010100010000100000101111111111100
1001011010101100001000000011000110110000
0011000100011000010111101000101110110001
答案提交 这是一道结果填空的题,你只需要算出结果后提交即可。本题的结果为一个整数,在提交答案时只填写这个整数,填写多余的内容将无法得分。
1) .算法思路
- dfs
2).算法步骤
1.使用循环读取输入的行,并将每个字符解析为整数存储在nmus数组中。
2.打印输出nmus数组。
3.调用dfs方法进行深度优先搜索,初始时传入起始坐标和nmus数组。
4.在dfs方法中,将当前坐标标记为已访问(值设为2),并增加计数器sum。
5.遍历四个方向上的相邻坐标。
6.计算新的坐标newx和newy。
7.检查新坐标是否在合法范围内,并且对应位置的值为0(未访问)。
8.如果满足条件,递归调用dfs方法,传入新的坐标和nmus数组。
9.在dfs方法结束后,返回上一层递归。
10.在主方法中调用dfs方法,传入起始坐标和nmus数组。
11.输出计数器sum的值。
3). 代码实例
package LanQiaoTest.DFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 传染性_5 {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static String[] lines;
static int sum;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int[] dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//接收矩阵
int[][] nmus = new int[31][41];
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
lines = in.readLine().split("");
for (int j = 1; j <= 40; j++) {
nmus[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(lines[j - 1]);
}
}
//打印出来
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 40; j++) {
System.out.print(nmus[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
dfs(1, 1, nmus);
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static void dfs(int x, int y, int[][] nums) {
//出口
nums[x][y] = 2;
sum++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = x + dx[i];
int newy = y + dy[i];
if (newx >= 1 && newx <= 30 && newy >= 1 && newy <= 40 && nums[newx][newy] == 0) {
dfs(newx, newy, nums);
}
}
}
}
4).总结
- 答案:541
六.左移一位

问题描述
给定一个正好六位的正整数 x,请将 x 循环左移一位后输出。
所谓循环左移一位,是指将原来的十万位变为个位,原来的万位到个位向左移动依次变为十万位到十位。
例如:194910 左移一位变为 949101 。
又如:987123 左移一位变为 871239 。
输入格式
输入一行包含一个整数 x 。保证输入的 x 正好包含 6 个十进制数位,而且十万位和万位上的数字均不为 0 。
输出格式
输出一行包含一个整数,表示答案。
样例输入
194910
样例输出
949101
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new PrintWriter(System.out));
static String[] lines;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(lines[0]);
String s = Integer.toString(n);
String ans = s.substring(1) + s.charAt(0);
int result = Integer.parseInt(ans);
out.print(result);
out.flush();
}
}
4).总结
七.最后元音

问题描述
输入一个仅包含小写英文字母的字符串,请问这个字符串中的最后一元音是什么。
在英文中,a, e, i, o, u 共 5 个字母是元音字母,其它字母不是元音字母。
输入格式
输入一行包含一个字符串,仅由小写英文字符组成,字符串中至少包含一个元音字母。
输出格式
输出一行包含一个字符,表示答案。
样例输入
lanqiao
样例输出
o
样例输入
cup
样例输出
u
评测用例规模与约定
对于所有评测用例,1 <= 字符数量 <= 10000 。
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new PrintWriter(System.out));
static String[] lines;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
String s = lines[0];
set.add("a");
set.add("e");
set.add("i");
set.add("o");
set.add("u");
for (int i = s.length()-1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
String c = String.valueOf(s.charAt(i));
if (set.contains(c)) {
out.println(c);
out.flush();
return;
}
}
}
}
4).总结
- 答案:
八. 整数转化

问题描述
给定一个整数,对这个整数的一次转换是指将这个整数变为这个整数的所有数位上的非零数字的乘积。
例如,对 123456789 进行一次转换变为 1*2*3*4*5*6*7*8*9=362880,再进行一次转换变为 3*6*2*8*8=2304,再进行一次转换变为 2*3*4=24,再进行一次转换变为 8。
给定一个整数,请依次将转换过程中经历的每个整数输出,直到小于 10 。
输入格式
输入一行包含一个整数 n 。
输出格式
输出多行,每行包含一个整数。
样例输入
123456789
样例输出
362880
2304
24
8
评测用例规模与约定
对于 50% 的评测用例,1 <= n <= 10**9 (10的9次方)。
对于所有评测用例,1 <= n <= 10**18 (10的18次方)。
1) .算法思路
- 无
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new PrintWriter(System.out));
static String[] lines;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
long sum = Long.parseLong(lines[0]);
while (sum > 10) {
long temp = sum;
long ans = 1;
while (temp > 0) {
if (temp % 10 != 0) {
ans *= temp % 10;
temp /= 10;
} else temp /= 10;
}
out.println(ans);
sum = ans;
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
4).总结
九. 最大移动方格

问题描述
小蓝站在一个 n 行 m 列的方格图中间,方格图的每一个方格上都标有一个正整数。
如果两个相邻方格(上下左右四个方向相邻)内的数的最大公约数大于 1 ,则可以从其中一个方格移动到另一个方格,当然也可以从另一个方格移回第一个方格。
假设小蓝开始时站在第 r 行第 c 列,请问小蓝可以移动到方格图内的多少个方格?
输入格式
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n, m ,用一个空格分隔,表示方格图的行数和列数。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 m 个正整数,相邻整数间用一个空格分隔,依次表示方格图中从第 1 行到第 n 行,每行从第 1 列到第 m 列中的数。
接下来一行包含两个整数 r, c,用一个空格分隔,表示小蓝所在的行号和列号。
输出格式
输出一行包含一个整数,表示答案。
样例输入
3 4
3 6 5 5
2 4 3 5
7 8 3 8
3 2
样例输出
5
评测用例规模与约定
对于50%的评测用例,1 <= n, m <= 100,方格图中的每个数不超过 10**5 (10的5次方)。
对于所有评测用例,1 <= n, m <= 1000,方格图中的每个数不超过 10**9 (10的9次方)。
1) .算法思路
- dfs
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new PrintWriter(System.out));
static String[] lines;
static long nums[][] = new long[1100][1100];
static boolean[][] st = new boolean[1100][1100];
static long sum = 0;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int[] dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(lines[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(lines[1]);
//接收数据
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
nums[i][j] = Long.parseLong(lines[j - 1]);
}
}
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
int r = Integer.parseInt(lines[0]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(lines[1]);
dfs(r,c,nums,n,m);
out.println(sum);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
private static void dfs(int x, int y, long[][] nums, int n, int m) {
st[x][y] = true;
sum++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = x + dx[i];
int newy = y + dy[i];
if (newx >= 1 && newx <= n && newy >= 1 && newy <= m && gcd(nums[x][y], nums[newx][newy]) > 1&&st[newx][newy]==false) {
dfs(newx, newy, nums, n, m);
}
}
}
//最大公约数
private static long gcd(long a, long b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
}
4).总结
十. 最大区间和

问题描述
给定一个序列 a[1], a[2], …, a[n] 和一个整数 k,请找出一个长度正好为 k 的区间,使得区间中所有数的和最大。
即要找到一个整数 p ,使得 1 <= p 且 p+k-1 <= n ,使得 a[p]+a[p+1]+...+a[p+k-1] 最大。
输入格式
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n , k。
第二行包含 n 个整数,相邻的整数之间使用一个空格分隔,表示给定的序列。
输出格式
输出一行包含一个整数,表示最大的区间和,你只需要输出和就行,不需要输出方案。 样例输入
6 3
2 3 9 1 9 5
样例输出
19
评测用例规模与约定
对于 30% 的评测用例,1 <= k <= n <= 30,1 <= a[i] <= 100。
对于 60% 的评测用例,1 <= k <= n <= 1000,1 <= a[i] <= 10000。
对于所有评测用例,1 <= k <= n <= 100000,1 <= a[i] <= 1000000。
1) .算法思路
- 前缀和+滑动窗口
2).算法步骤
- 无
3). 代码实例
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
//前缀和+滑动窗口
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new PrintWriter(System.out));
static String[] lines;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(lines[0]);
int k = Integer.parseInt(lines[1]);
long[] sum = new long[n];
lines = in.readLine().split(" ");
sum[0] = Integer.parseInt(lines[0]);
//前缀和
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
sum[i] += Long.parseLong(lines[i])+sum[i-1];
}
long max = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//滑动窗口
for (int i = 0; i <= n - k; i++) {
long ans = 0;
if (i==0){
ans = sum[i+k-1];
}
else {
ans = sum[i+k-1]-sum[i-1];
}
max = Math.max(max, ans);
}
out.println(max);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}