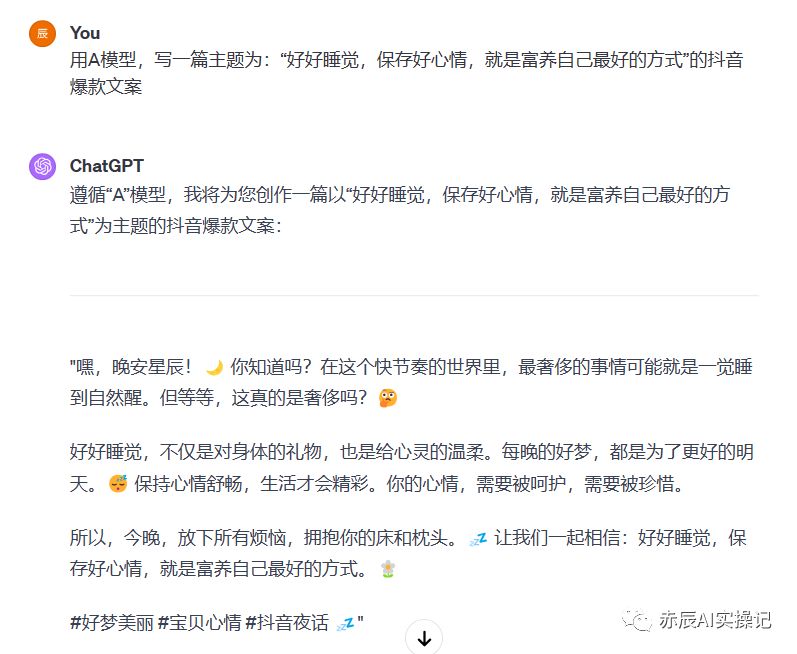
HarmonyOS开发准备(一) TypeScript基本语法
TypsScript官网:https://www.typescriptlang.org/play
可在官网 Playround 在线运行 Typescript

一、变量声明

// 创建 number(数值) 类型变量
let test_number: number = 111
console.log('test_number:', test_number)
console.log(typeof(test_number))
// 创建 string(字符串) 类型变量
let test_string: string = '222'
console.log('test_string:', test_string)
console.log(typeof(test_string))
// 创建 boolean(布尔) 类型变量
let test_bool: boolean = true
console.log('test_bool:', test_bool)
console.log(typeof(test_bool))
// 创建 any(不检查类型,可任意类型,一般适用在函数参数声明) 变量类型
let test_any: any = 34234
console.log('test_any:', test_any)
console.log(typeof(test_any))
// 创建 function(默认类型) 变量类型
let test_function = function () {
console.log('我是function')
}
console.log('test_function :', test_function )
console.log(typeof(test_function))
// 创建 union(联合,指定多个类型中其中一个即可) 变量类型
let test_union: number|string|boolean = true
console.log('test_union:', test_union)
console.log(typeof(test_union))
// 创建 object(对象) 变量类型
let test_object: object = {name: '刘', age: '男'}
console.log('test_object:', test_object)
console.log(typeof(test_object))
// 创建 array(数组) 变量类型
let test_array1: string[] = ['我', '是', '数组']
let test_array2: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3]
console.log('test_array1:', test_array1)
console.log('test_array2:', test_array2)
console.log(typeof(test_array1))
console.log(typeof(test_array2))
二、条件控制

1、if-else 判断
let num: number = 2
if(num % 2 === 0){
console.log('偶数')
}else{
console.log('奇数')
}
if(num > 0){
console.log('正数')
}else if(num < 0){
console.log('负数')
}else{
console.log("为0")
}
2、switch 判断
let word: string = 'A'
switch (word) {
case 'A':
console.log('结果为A')
break
case 'B':
console.log('结果为B')
break
case 'C':
console.log('结果为C')
break
default:
console.log('非法输入')
break
}
三、循环迭代

1、for / while 普通循环
// for 循环
for(let i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
console.log(`点赞${i}次`)
}
// while 循环
let i = 1
while(i <= 10){
console.log(`点赞${i}次`)
i++
}
2、for in / for of 迭代器循环
let nameList1: string[] = ['liu', 'guan', 'zhang']
let nameList2: Array<string> = ['liu', 'guan', 'zhang']
// for in 迭代器循环
for(let i in nameList1){
console.log(`i:${i},${nameList1[i]}`)
}
// for of 迭代器循环
for(let name of nameList2){
console.log(`name:${name}`)
}
四、函数

// 无返回值函数,返回值 void 可以省略
function testHello(name: string): void{
console.log(`您好${name}!`)
}
testHello('liu')
// 有返回值函数
function sum1(x: number, y: number): number {
return x + y
}
let result1 = sum1(5, 5)
console.log(`5 + 5 = ${result1}`)
// 箭头函数:无返回值
let testHi = (name: string): void => {
console.log(`你好${name}!`)
}
testHi('guan')
// 箭头函数:有返回值
let sum2 = (x: number, y: number): number => {
return x + y
}
let result2 = sum1(15, 15)
console.log(`15 + 15 = ${result2}`)
// 可选参数,在参数名后面加 ?,表示是可选的
function fun1(name?: string){
name = name ? name : '陌生人'
console.log(`你好${name}!`)
}
fun1('liu')
fun1()
// 参数默认值,在参数后面赋值,表示参数默认值
// 如果调用没有传参,则使用默认值
function fun2(name: string = '陌生人'){
console.log(`你好${name}!`)
}
fun2('guan')
fun2()
五、类和接口

1、简单使用枚举和类、接口
// 定义枚举
enum Msg {
HI = 'Hi',
HELLO = 'Hello'
}
// 定义接口,抽象方法接收枚举参数
interface A {
say(msg: Msg): void
}
// 实现接口
class B implements A {
say(msg: Msg): void {
console.log(`msg,I am B`)
}
}
// 初始化对象
let a: A = new B()
// 调用方法,传递枚举参数
a.say(Msg.HI)
2、枚举和类、接口全面使用
// 定义矩形类
class Rectangle {
// 成员变量
private width: number
private height: number
// 构造函数
constructor(widht: number, height: number) {
this.width = widht
this.height = height
}
// 成员方法
public area(): number {
return this.width + this.height
}
}
// 定义正方形,继承 Rectangle 类
class Square extends Rectangle {
constructor(side: number) {
// super:调用父类构造
super(side, side)
}
}
// 初始化对象
let s = new Square(10)
// 调用父类方法
console.log(`正方形面积为:${s.area()}`)
模块开发

xtends Rectangle {
constructor(side: number) {
// super:调用父类构造
super(side, side)
}
}
// 初始化对象
let s = new Square(10)
// 调用父类方法
console.log(正方形面积为:${s.area()})
### 模块开发
[外链图片转存中...(img-rThTNF4o-1701334023011)]